Bash基本语法
Bash语法非常的简单,Bash是一个命令解释程序,单使用Bash做不了什么,但是Bash结合Linux命令就很强大了,几乎可以完成Linux所有的事情,早年第一个接触Bash的时候,可以追溯到2010年了,当时在一家互联网虚产品的公司,那是个时候WEB虚机还很流行的,底层WEB虚机的创建,开户都用Shell脚本实现。当时我作为Java开发人员,但有幸参与到shell脚本开发中,当时对Shell并不是很熟,从那个时候算是对Shell第一次试水,并没有进行深入的学习,之后工作重点后来又转向Java开发,但从那个时候就起就感觉shell这个东西很好玩,最近想重新把这块东西捡起来,一点一滴的记录下来,学习shell一定要把学习Linux命令分开,要不然一开始学可能会一头雾水,这是我的一点建议,随着对Linux命令的掌握,再加上shell脚本的威力,就可以在Linux的高手。
1 标准输入、输出与标准错误输出
系统为这三个文件分配了文件标识符fd(file descripter),在Linux系统下,一切皆是文件,对文件的操作,一般要用到文件标识符。它们的文件标识符,分别为0,1,2,关系如下表:
| 文件描述符 | 名称 | 通用缩写 | 默认值 |
| 0 | 标准输入 | stdin | 键盘 |
| 1 | 标准输出 | stdout | 屏幕 |
| 2 | 标准错误 | stderr | 屏幕 |
1.1 输出重定向
| 语法 | 说明 |
| > | 把标准输出重定向到一个新文件,”>” 会覆盖原有的内容。 |
| >> | 把标准输出重定向到一个文件中,不覆盖原有的内容(追加)。 |
| 2 > | 把标准错误重定向到一个文件中 |
| 2 >> | 把标准错误重定向到一个文件中(追加) |
| 2 > &1 | 把标准输出和错误重定向到一个文件(追加) |
1.2 输入重定向
| 语法 | 说明 |
| < | filename文件作为标准输入 |
| << delimiter | 从标准输入中读入,知道遇到delimiter分界符 |
1.3 绑定重定向
| 语法 | 说明 |
| > &m | 把标准输出重定向到文件描述符m中 |
| < &- | 关闭标准输入 |
| > &- | 关闭标准输出 |
2 变量
2.1 环境变量
通过使用printenv可以显示当前的环境变量
|
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
[root@IDC-D-1699 ~]# printenvHOSTNAME=IDC-D-1699TERM=xtermSHELL=/bin/bashHISTSIZE=1000SSH_CLIENT=111.200.23.36 31752 22QTDIR=/usr/lib64/qt-3.3QTINC=/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/includeSSH_TTY=/dev/pts/3USER=rootMAIL=/var/spool/mail/rootPATH=/usr/local/java/jdk1.8.0_101/bin:/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/binPWD=/rootJAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java/jdk1.8.0_101LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8HISTCONTROL=ignoredupsSHLVL=1HOME=/rootLOGNAME=root |
2.2 本地变量
Shell不需要明确定义类型,事实上Shell变量的值都是字符串,比如我们定义var=45,其实var的值是字符串而非整数,shell变量不需要事先定义就可以使用,如果使用没有定义的变量,这字符串取值为空字符串。
变量名称=”变量Value”,“=”的两边不能有空格,否则shell解释成名称和命令参数。
获取变量使用 $变量名称
|
2
3
|
a="ywq"echo $a |
2.2.1 文件名代换
可以使用*、?、[]对文件名代换
| 匹配符 | 说明 |
| * | 匹配0个多个任意字符 |
| ? | 匹配一个任意字符 |
| [] | 匹配方括号中任意一个字符的一次出现 |
2.2.2 命令代换
将命令替换为命令输出,所有的shell支持使用反引号的方式进行命令替换,命令替换可以嵌套,需要注意的是如果使用反引号的形式,在内部反引用前必须使用反斜杠转移
| 匹配符 | 说明 |
| `` | 例如 echo ${pwd} |
| $() | 例如 echo `pwd` |
2.2.3 算术代换
| 匹配符 | 说明 |
| $(()) | 例如 echo $((4 + 6)) |
3 符号
3.1 转义字符
‘\’用作转义字符。
3.2 单引号
单引号内的所有字符都保持它本身字符的意思,而不会被bash进行解释。
3.3 双引号
除了$、``、/外,双引号内所有的字符保持字符本身的含义。
4 逻辑判断
4.1 if
在shell中用if,then,elif,else,fi这几条命令实现分支控制,这种流程控制语句本质上也是由若干个逻辑判断组成,需要注意的是。
- if/then结束都离不开fi
- if和[]注意用空格隔开,]后面紧跟;
- []内的条件与都有一个空格隔开
例如:
|
2
3
4
|
if [ -f $a ];then echo "hello world!" fi |
4.2 case
case结构用于多种情况的条件判断,类似于其它语言的switch/case,但从语法结构上有很大的不同,常用格式。
|
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
case 字符串 in 模式) 语句 ;; 模式2 | 模式3) 语句 ;; *) 默认执行的 语句 ;;esac |
例如
|
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
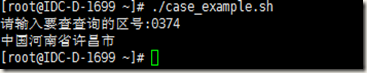
#!/bin/bashread -p "请输入要查查询的区号:" numcase $num in *)echo -n "中国";;& 03*)echo -n "河南省";;& ??71)echo "郑州市";; ??72)echo "安阳市";; ??73)echo "新乡市";; ??73)echo "许昌市";; 07*)echo -n "江西省";;& ??91)echo "南昌市";; ??92)echo "九江市";; ??97)echo "赣州市";;esac |
注意
当程序指定到条件语句;;&时,不会停止,直到执行到;;esac
不管是if还是case,他们的结尾都很有意思,if的结尾是fi,而case的结尾是easc,首位和尾部正好相反。
5. 循环
5.1 for
例如:
打印目录下所有的文件
|
2
3
4
5
|
#!/bin/bashfor i in $( ls ); do echo item: $idone |
打印序列
|
2
3
4
5
6
|
#!/bin/bashfor n in $(seq 1 10);do echo $ndone |
5.2 while
例如:
|
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#!/bin/bashcounter=$1while [ $counter -lt 10 ];do echo the counter is $counter counter=$(($counter+1))done |
5.3 until
例如:
|
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#!/bin/bashcounter=$1until [ $counter -lt 10 ];do echo the counter:$counter let counter=counter-1done |
6 比较运算
6.1 比较符
| 比较符 | 说明 | 举例 |
| -e filename | 如果filename存在,则为真 | [ -e /var/log/syslog ] |
| -d filename | 如果filename为目录,则为真 | [ -d /tmp/mydir ] |
| -f filename | 如果filename常规文件,则为真 | [ -f /usr/bin/grep ] |
| -L filename | 如果filename为符号链接,则为真 | [ –L /usr/bin/grep ] |
| -r filename | 如果filename可读,则为真 | [ –r /var/log/syslog ] |
| -w filename | 如果filename可写,则为真 | [ –w /varmytmp.txt ] |
| -x filename | 如果filename可执行,则为真 | [ –x /usr/bin/grep ] |
| -s filename | 如果filename不是空白文件,则为真 | |
| -u filename | 如果filename有SUID属性,则为真 | |
| -g filename | 如果filename有SGID属性,则为真 | |
| -k filename | 如果filename有stickybit属性,则为真 | |
| file1 –nt file2 | 如果file1比file2新,则为真 | |
| file1 –ot file2 | 如果file1比file2旧,则为真 |
6.2 字符串比较运算符
| 比较符 | 说明 | 举例 |
| -z string | 如果string长度为零,则为真 | |
| -n string | 如果string长度不为零,则为真 | |
| str1 = str2 | 如果str1与str2相同,则为真 | |
| str1 != str2 | 如果str1与str2不相同,则为真 |
6.3 算数比较符
| 比较符 | 说明 | 举例 |
| -eq | 等于 | |
| -ne | 不等于 | |
| -lt | 小于 | |
| -le | 小于或等于 | |
| -gt | 大于 | |
| -ge | 大于或等于 |
1 #!/bin/sh 2 # 3 # Copyright 2015 Google LLC All rights reserved. 4 # 5 # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 6 # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 7 # You may obtain a copy of the License at: 8 # 9 # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 10 # 11 # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 12 # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 13 # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 14 # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 15 # limitations under the License. 16 # ----------------------------------------- 17 # american fuzzy lop - QEMU build script 18 # -------------------------------------- 19 # 20 # Written by Andrew Griffiths <agriffiths@google.com> and 21 # Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@google.com> 22 # 23 # This script downloads, patches, and builds a version of QEMU with 24 # minor tweaks to allow non-instrumented binaries to be run under 25 # afl-fuzz. 26 # 27 # The modifications reside in patches/*. The standalone QEMU binary 28 # will be written to ../afl-qemu-trace. 29 # 30 31 32 VERSION="2.10.0" 33 QEMU_URL="http://download.qemu-project.org/qemu-${VERSION}.tar.xz" 34 QEMU_SHA384="68216c935487bc8c0596ac309e1e3ee75c2c4ce898aab796faa321db5740609ced365fedda025678d072d09ac8928105" 35 36 echo "=================================================" 37 echo "AFL binary-only instrumentation QEMU build script" 38 echo "=================================================" 39 echo 40 41 echo "[*] Performing basic sanity checks..." 42 43 if [ ! "`uname -s`" = "Linux" ]; then 44 45 echo "[-] Error: QEMU instrumentation is supported only on Linux." 46 exit 1 47 48 fi 49 50 if [ ! -f "patches/afl-qemu-cpu-inl.h" -o ! -f "../config.h" ]; then 51 52 echo "[-] Error: key files not found - wrong working directory?" 53 exit 1 54 55 fi 56 57 if [ ! -f "../afl-showmap" ]; then 58 59 echo "[-] Error: ../afl-showmap not found - compile AFL first!" 60 exit 1 61 62 fi 63 64 65 for i in libtool wget python automake autoconf sha384sum bison iconv; do 66 67 T=`which "$i" 2>/dev/null` 68 69 if [ "$T" = "" ]; then 70 71 echo "[-] Error: '$i' not found, please install first." 72 exit 1 73 74 fi 75 76 done 77 78 if [ ! -d "/usr/include/glib-2.0/" -a ! -d "/usr/local/include/glib-2.0/" ]; then 79 80 echo "[-] Error: devel version of 'glib2' not found, please install first." 81 exit 1 82 83 fi 84 85 if echo "$CC" | grep -qF /afl-; then 86 87 echo "[-] Error: do not use afl-gcc or afl-clang to compile this tool." 88 exit 1 89 90 fi 91 92 echo "[+] All checks passed!" 93 94 ARCHIVE="`basename -- "$QEMU_URL"`" 95 96 CKSUM=`sha384sum -- "$ARCHIVE" 2>/dev/null | cut -d' ' -f1` 97 98 if [ ! "$CKSUM" = "$QEMU_SHA384" ]; then 99 100 echo "[*] Downloading QEMU ${VERSION} from the web..." 101 rm -f "$ARCHIVE" 102 wget -O "$ARCHIVE" -- "$QEMU_URL" || exit 1 103 104 CKSUM=`sha384sum -- "$ARCHIVE" 2>/dev/null | cut -d' ' -f1` 105 106 fi 107 108 if [ "$CKSUM" = "$QEMU_SHA384" ]; then 109 110 echo "[+] Cryptographic signature on $ARCHIVE checks out." 111 112 else 113 114 echo "[-] Error: signature mismatch on $ARCHIVE (perhaps download error?)." 115 exit 1 116 117 fi 118 119 echo "[*] Uncompressing archive (this will take a while)..." 120 121 rm -rf "qemu-${VERSION}" || exit 1 122 tar xf "$ARCHIVE" || exit 1 123 124 echo "[+] Unpacking successful." 125 126 echo "[*] Configuring QEMU for $CPU_TARGET..." 127 128 ORIG_CPU_TARGET="$CPU_TARGET" 129 130 test "$CPU_TARGET" = "" && CPU_TARGET="`uname -m`" 131 test "$CPU_TARGET" = "i686" && CPU_TARGET="i386" 132 133 cd qemu-$VERSION || exit 1 134 135 echo "[*] Applying patches..." 136 137 patch -p1 <../patches/elfload.diff || exit 1 138 patch -p1 <../patches/cpu-exec.diff || exit 1 139 patch -p1 <../patches/syscall.diff || exit 1 140 patch -p1 <../patches/configure.diff || exit 1 141 patch -p1 <../patches/memfd.diff || exit 1 142 143 echo "[+] Patching done." 144 145 # --enable-pie seems to give a couple of exec's a second performance 146 # improvement, much to my surprise. Not sure how universal this is.. 147 148 CFLAGS="-O3 -ggdb" ./configure --disable-system \ 149 --enable-linux-user --disable-gtk --disable-sdl --disable-vnc \ 150 --target-list="${CPU_TARGET}-linux-user" --enable-pie --enable-kvm || exit 1 151 152 echo "[+] Configuration complete." 153 154 echo "[*] Attempting to build QEMU (fingers crossed!)..." 155 156 make || exit 1 157 158 echo "[+] Build process successful!" 159 160 echo "[*] Copying binary..." 161 162 cp -f "${CPU_TARGET}-linux-user/qemu-${CPU_TARGET}" "../../afl-qemu-trace" || exit 1 163 164 cd .. 165 ls -l ../afl-qemu-trace || exit 1 166 167 echo "[+] Successfully created '../afl-qemu-trace'." 168 169 if [ "$ORIG_CPU_TARGET" = "" ]; then 170 171 echo "[*] Testing the build..." 172 173 cd .. 174 175 make >/dev/null || exit 1 176 177 gcc test-instr.c -o test-instr || exit 1 178 179 unset AFL_INST_RATIO 180 181 # We shouldn't need the /dev/null hack because program isn't compiled with any 182 # optimizations. 183 echo 0 | ./afl-showmap -m none -Q -q -o .test-instr0 ./test-instr || exit 1 184 echo 1 | ./afl-showmap -m none -Q -q -o .test-instr1 ./test-instr || exit 1 185 186 rm -f test-instr 187 188 cmp -s .test-instr0 .test-instr1 189 DR="$?" 190 191 rm -f .test-instr0 .test-instr1 192 193 if [ "$DR" = "0" ]; then 194 195 echo "[-] Error: afl-qemu-trace instrumentation doesn't seem to work!" 196 exit 1 197 198 fi 199 200 echo "[+] Instrumentation tests passed. " 201 echo "[+] All set, you can now use the -Q mode in afl-fuzz!" 202 203 else 204 205 echo "[!] Note: can't test instrumentation when CPU_TARGET set." 206 echo "[+] All set, you can now (hopefully) use the -Q mode in afl-fuzz!" 207 208 fi 209 210 exit 0




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号