C++ std::vector emplace_back 优于 push_back 的理由
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;
// 要考虑 copy ctor 和 copy opt=
class Item
{
public:
Item() = delete;
Item(const Item & ths);
Item(std::string str);
Item & operator = (const Item & ths);
~Item();
private:
};
Item::Item(const Item & ths)
{
//cout << "copy ctor" << endl;
Sleep(2);
}
Item::Item(std::string str)
{
//cout << str.c_str() << endl;
Sleep(2);
}
Item & Item::operator=(const Item & ths)
{
//cout << "copy opt=" << endl;
Sleep(2);
}
Item::~Item()
{
}
int main()
{
{
auto tbegin = steady_clock::now();
std::vector<Item> vec8;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 2000; ++i)
vec8.push_back(Item("111"));
auto used = duration_cast<milliseconds>(steady_clock::now() - tbegin);
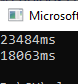
std::cout << used.count() << "ms" << std::endl;
}
{
auto tbegin = steady_clock::now();
std::vector<Item> vec8;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 2000; ++i)
vec8.emplace_back("222"); // 少一次 copy ctor 的调用
auto used = duration_cast<milliseconds>(steady_clock::now() - tbegin);
std::cout << used.count() << "ms" << std::endl;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号