PTA题目集4-6的总结
题目集4:
我们初次知道了继承这种方法,题目也不是很难,就是需要我们在子类里面重写父类的方法,更清楚的知道了private和public在属性和方法设置时候的方法。然后就是正则表达式的运用了,检测时间的时候我们需要特别的判断一下闰年和平年的2月,发现检查这种格式的输出正则表达式其实是一个很好的选择。
题目集5:
在统计关键词的次数这道题中,我们用正则表达式,我们用到了StringBuilde和正则表达式。
题目集6:
我们初次用到了collections.sort这个方法,需要注意的是我们要知道comparable和comparator这两个接口的区别。
7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
心得:
其实刚写这道题的时候会觉得这道题应该很复杂,但你写完年月日这三个类的时候,你就应该发现题目的要求其实很简单,而且老师设置的时间非常的长,长到你可以一天一天的加(减),然后与另一个日期做比较即可
源代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int year=0,month=0,day=0; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int n = in.nextInt(); year = in.nextInt(); month = in.nextInt(); day = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); switch(n) { case 1: int x = in.nextInt(); if(date.checkInputValidity() == false || x < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(x).showDate()); break; case 2: int y = in.nextInt(); if(date.checkInputValidity() == false || y < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(y).showDate()); break; case 3: int ayear = in.nextInt(); int amonth = in.nextInt(); int aday = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(ayear,amonth,aday); if(date.checkInputValidity()==false || date1.checkInputValidity() == false ) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getDaysoDates(date1)); break; default : System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; } } } class DateUtil{ Day day; private int y; private int m; private int d; int []mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; DateUtil(){ } DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ this.y=y; this.m=m; this.d=d; this.day=new Day(y,m,d); } public Day getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(Day day) { this.day = day; } boolean checkInputValidity() { //检验数据的合法性 if(day.vaildate() == true && day.month.vaildate() == true && day.month.year.validate() == true) { return true; } else return false; } boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { //比较两个日期的大小 if(date.day.month.year.getValue() > this.day.month.year.getValue()) { return true; } else if(date.day.month.year.getValue() == this.day.month.year.getValue()){ if(date.day.month.getValue() > this.day.month.getValue()) { return true; } else if(date.day.month.getValue() == this.day.month.getValue()){ if(date.day.getValue() > this.day.getValue()) { return true; } else return false; } } return false; } boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { if(date.day.month.year.getValue() == this.day.month.year.getValue() && date.day.month.getValue() == this.day.month.getValue() &&date.day.getValue() == this.day.getValue()) { return true; } else return false; } String showDate() { return day.month.year.getValue()+"-" +day.month.getValue() + "-" + day.getValue(); } DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { //求下n天 int year = this.y; int month = this.m; int day = this.d; int i=0; DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); while(n > i) { if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else { //该年为闰年 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; } if(date.day.getValue() < date.mon_maxnum[date.day.month.getValue()]) { //天数小于该月最大值 date.day.dayIncrement(); //天数减一 } else { date.day.restMin(); //天数复位为1 date.day.month.monthIncrement(); //月数加一 if(date.day.month.getValue() > 12) { date.day.month.restMin(); //月数复位为1 date.day.month.year.yearIncrement(); //年数加一 } } i++; } return date; } DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { //求前n天 int year = this.y; int month = this.m; int day = this.d; int i=0; DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); while(n > i) { if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //如果该年为平年 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else { //如果该年为闰年 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; } if(date.day.getValue() > 1) { date.day.dayReduction(); //天数减一 } else { date.day.month.monthReduction(); //月数减一 if(date.day.month.getValue() < 1) { date.day.month.restMax(); //月数变为最大值 date.day.month.year.yearReduction(); } date.day.restMax(); //日数变为最大值 } i++; } return date; } int getDaysoDates(DateUtil date) { int d=0; DateUtil date1 = this; //小 DateUtil date2 = date; //大 if(this.compareDates(date) == false) { date1 = date; //小 date2 = this; //大 } while(date1.equalTwoDates(date2) == false) { if(date1.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 date1.mon_maxnum[2]=28; } else { //该年为闰年 date1.mon_maxnum[2]=29; } if(date1.day.getValue() < date1.mon_maxnum[date1.day.month.getValue()]) { //天数小于该月最大值 date1.day.dayIncrement(); //天数减一 } else { date1.day.restMin(); //天数复位为1 date1.day.month.monthIncrement(); //月数加一 if(date1.day.month.getValue() > 12) { date1.day.month.restMin(); //月数复位为1 date1.day.month.year.yearIncrement(); //年数加一 } } d++; } return d; } } class Day{ private int value; Month month; int []mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; Day(){ } Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue){ this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value = dayValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } void restMin() { //日期复位为1 value=1; } void restMax() { //日期改成该月最大值 if(month.getValue()==1 || month.getValue()==3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue()==7 || month.getValue() == 8 ||month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12) { //该月有31天 value = 31; } else if(month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() ==11) { //该月有30天 value = 30; } else { if(month.year.isLeapYear() == true) { //该年为闰年 value = 29; } else //该年为平年 value = 28; } } boolean vaildate() { //检验数据合法性 if(month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } else { mon_maxnum[2]=29; } if(month.vaildate() == false) { return false; } if(value < 1 || value > mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) return false; else return true; } void dayIncrement() { //日期加一 value++; } void dayReduction() { //日期减一 value--; } } class Month{ private int value; //当前月数 Year year; Month(){ } Month(int yearValue, int monthValue){ this.year = new Year(yearValue); this.value= monthValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } void restMin() { //月份复位为1 value=1; } void restMax() { //月份为12 value=12; } boolean vaildate() { //判读数据的合法性 if(value>=1 && value<=12) return true; return false; } void monthIncrement() { //月数加一 value++; } void monthReduction() { //月数减一 value--; } } class Year{ private int value; //当前年数 Year(){ } Year(int value){ this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } boolean isLeapYear() { //判读是否为闰年 if(value%400==0 || (value%4 == 0 && value%100 != 0)) //为闰年 return true; return false; //为平年 } boolean validate() { //判读数据合法性 if(value>=1900 && value<=2050) { return true; } return false; } void yearIncrement() { //年数加一 value++; } void yearReduction() { //年数减一 value--; } }
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
心得:
这道题跟上面的区别不大,主要是设计年月日这三个类,上面的设计方法是声明类感觉是嵌套的,这道题的代码其实跟上面的代码几乎一样没怎么改,但我稍微的优化了一下上面的代码。
就是我上面的代码在改变天数的时候,我每一次加或者减天数的时候,我都判断了一下该年是否是闰年,自己想想发现其实这是没必要的,你只需要在刚进入你的循环的时候判断一下自己的代码,然后在年数改变的时候判断一下年数时候为闰年即可,至少这样我的代码运行时间减少了一半之多,以下是优化的代码。

1 DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { //求下n天 2 int year = this.y; 3 int month = this.m; 4 int day = this.d; 5 int i=0; 6 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); 7 if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 8 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 9 } 10 else { //该年为闰年 11 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 12 } 13 while(n > i) { 14 if(date.day.getValue() < date.mon_maxnum[date.day.month.getValue()]) { //天数小于该月最大值 15 date.day.dayIncrement(); //天数减一 16 17 } 18 else { 19 date.day.restMin(); //天数复位为1 20 date.day.month.monthIncrement(); //月数加一 21 if(date.day.month.getValue() > 12) { 22 date.day.month.restMin(); //月数复位为1 23 date.day.month.year.yearIncrement(); //年数加一 24 if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 25 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 26 } 27 else { //该年为闰年 28 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 i++; 33 } 34 return date; 35 }
源代码:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 int year=0,month=0,day=0; 8 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 9 int n = in.nextInt(); 10 year = in.nextInt(); 11 month = in.nextInt(); 12 day = in.nextInt(); 13 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); 14 15 switch(n) { 16 case 1: int x = in.nextInt(); 17 if(date.checkInputValidity() == false || x < 0) { 18 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 19 System.exit(0); 20 } 21 22 System.out.println(date.showDate() + " next " + x + " days is:" + date.getNextNDays(x).showDate()); 23 break; 24 case 2: int y = in.nextInt(); 25 if(date.checkInputValidity() == false || y < 0) { 26 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 27 System.exit(0); 28 } 29 System.out.println(date.showDate() + " previous " + y +" days is:" + date.getPreviousNDays(y).showDate()); 30 break; 31 case 3: 32 int ayear = in.nextInt(); 33 int amonth = in.nextInt(); 34 int aday = in.nextInt(); 35 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(ayear,amonth,aday); 36 if(date.checkInputValidity()==false || date1.checkInputValidity() == false ) { 37 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 38 System.exit(0); 39 } 40 System.out.println("The days between " + date.showDate() +" and " + date1.showDate() +" are:" + date.getDaysoDates(date1)); 41 42 break; 43 default : 44 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 45 break; 46 } 47 } 48 49 } 50 class DateUtil{ 51 Day day; 52 private int y; 53 private int m; 54 private int d; 55 int []mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 56 DateUtil(){ 57 58 } 59 DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ 60 this.y=y; 61 this.m=m; 62 this.d=d; 63 this.day=new Day(y,m,d); 64 } 65 public Day getDay() { 66 return day; 67 } 68 public void setDay(Day day) { 69 this.day = day; 70 } 71 boolean checkInputValidity() { //检验数据的合法性 72 if(day.vaildate() == true && day.month.vaildate() == true && day.month.year.validate() == true) { 73 return true; 74 } 75 else 76 return false; 77 } 78 boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { //比较两个日期的大小 79 if(date.day.month.year.getValue() > this.day.month.year.getValue()) { 80 return true; 81 } 82 else if(date.day.month.year.getValue() == this.day.month.year.getValue()){ 83 if(date.day.month.getValue() > this.day.month.getValue()) { 84 85 return true; 86 } 87 else if(date.day.month.getValue() == this.day.month.getValue()){ 88 if(date.day.getValue() > this.day.getValue()) { 89 return true; 90 } 91 else 92 return false; 93 } 94 } 95 return false; 96 } 97 boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 98 if(date.day.month.year.getValue() == this.day.month.year.getValue() && date.day.month.getValue() == this.day.month.getValue() &&date.day.getValue() == this.day.getValue()) { 99 return true; 100 } 101 else 102 return false; 103 } 104 String showDate() { 105 return day.month.year.getValue()+"-" +day.month.getValue() + "-" + day.getValue(); 106 } 107 DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { //求下n天 108 int year = this.y; 109 int month = this.m; 110 int day = this.d; 111 int i=0; 112 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); 113 if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 114 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 115 } 116 else { //该年为闰年 117 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 118 } 119 while(n > i) { 120 if(date.day.getValue() < date.mon_maxnum[date.day.month.getValue()]) { //天数小于该月最大值 121 date.day.dayIncrement(); //天数减一 122 123 } 124 else { 125 date.day.restMin(); //天数复位为1 126 date.day.month.monthIncrement(); //月数加一 127 if(date.day.month.getValue() > 12) { 128 date.day.month.restMin(); //月数复位为1 129 date.day.month.year.yearIncrement(); //年数加一 130 if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 131 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 132 } 133 else { //该年为闰年 134 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 135 } 136 } 137 } 138 i++; 139 } 140 return date; 141 } 142 DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { //求前n天 143 int year = this.y; 144 int month = this.m; 145 int day = this.d; 146 int i=0; 147 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day); 148 if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //如果该年为平年 149 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 150 } 151 else { //如果该年为闰年 152 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 153 } 154 while(n > i) { 155 156 if(date.day.getValue() > 1) { 157 date.day.dayReduction(); //天数减一 158 } 159 else { 160 date.day.month.monthReduction(); //月数减一 161 if(date.day.month.getValue() < 1) { 162 date.day.month.restMax(); //月数变为最大值 163 date.day.month.year.yearReduction(); 164 if(date.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //如果该年为平年 165 date.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 166 } 167 else { //如果该年为闰年 168 date.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 169 } 170 } 171 date.day.restMax(); //日数变为最大值 172 } 173 i++; 174 } 175 return date; 176 } 177 int getDaysoDates(DateUtil date) { 178 int d=0; 179 DateUtil date1 = this; //小 180 DateUtil date2 = date; //大 181 if(this.compareDates(date) == false) { 182 date1 = date; //小 183 date2 = this; //大 184 } 185 while(date1.equalTwoDates(date2) == false) { 186 if(date1.day.month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { //该年为平年 187 date1.mon_maxnum[2]=28; 188 } 189 else { //该年为闰年 190 date1.mon_maxnum[2]=29; 191 } 192 if(date1.day.getValue() < date1.mon_maxnum[date1.day.month.getValue()]) { //天数小于该月最大值 193 date1.day.dayIncrement(); //天数减一 194 195 } 196 else { 197 date1.day.restMin(); //天数复位为1 198 date1.day.month.monthIncrement(); //月数加一 199 if(date1.day.month.getValue() > 12) { 200 date1.day.month.restMin(); //月数复位为1 201 date1.day.month.year.yearIncrement(); //年数加一 202 } 203 } 204 d++; 205 } 206 return d; 207 } 208 } 209 class Day{ 210 private int value; 211 Month month; 212 int []mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 213 Day(){ 214 215 } 216 Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue){ 217 this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue); 218 this.value = dayValue; 219 } 220 public int getValue() { 221 return value; 222 } 223 public void setValue(int value) { 224 this.value = value; 225 } 226 public Month getMonth() { 227 return month; 228 } 229 public void setMonth(Month month) { 230 this.month = month; 231 } 232 void restMin() { //日期复位为1 233 value=1; 234 } 235 void restMax() { //日期改成该月最大值 236 if(month.getValue()==1 || month.getValue()==3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue()==7 || month.getValue() == 8 ||month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12) { //该月有31天 237 value = 31; 238 } 239 else if(month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() ==11) { //该月有30天 240 value = 30; 241 } 242 else { 243 if(month.year.isLeapYear() == true) { //该年为闰年 244 value = 29; 245 } 246 else //该年为平年 247 value = 28; 248 } 249 } 250 boolean vaildate() { //检验数据合法性 251 if(month.year.isLeapYear() == false) { 252 mon_maxnum[2] = 28; 253 } 254 else { 255 mon_maxnum[2]=29; 256 } 257 if(month.vaildate() == false) { 258 return false; 259 } 260 if(value < 1 || value > mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]) 261 return false; 262 else 263 return true; 264 } 265 void dayIncrement() { //日期加一 266 value++; 267 } 268 void dayReduction() { //日期减一 269 value--; 270 } 271 } 272 273 class Month{ 274 private int value; //当前月数 275 Year year; 276 Month(){ 277 278 } 279 Month(int yearValue, int monthValue){ 280 this.year = new Year(yearValue); 281 this.value= monthValue; 282 } 283 public int getValue() { 284 return value; 285 } 286 public void setValue(int value) { 287 this.value = value; 288 } 289 public Year getYear() { 290 return year; 291 } 292 public void setYear(Year year) { 293 this.year = year; 294 } 295 void restMin() { //月份复位为1 296 value=1; 297 } 298 void restMax() { //月份为12 299 value=12; 300 } 301 boolean vaildate() { //判读数据的合法性 302 if(value>=1 && value<=12) 303 return true; 304 return false; 305 } 306 void monthIncrement() { //月数加一 307 value++; 308 } 309 void monthReduction() { //月数减一 310 value--; 311 } 312 } 313 314 class Year{ 315 private int value; //当前年数 316 Year(){ 317 318 } 319 Year(int value){ 320 this.value = value; 321 } 322 public int getValue() { 323 return value; 324 } 325 public void setValue(int value) { 326 this.value = value; 327 } 328 boolean isLeapYear() { //判读是否为闰年 329 if(value%400==0 || (value%4 == 0 && value%100 != 0)) //为闰年 330 return true; 331 return false; //为平年 332 } 333 boolean validate() { //判读数据合法性 334 if(value>=1820 && value<=2020) { 335 return true; 336 } 337 return false; 338 } 339 void yearIncrement() { //年数加一 340 value++; 341 } 342 void yearReduction() { //年数减一 343 value--; 344 } 345 }
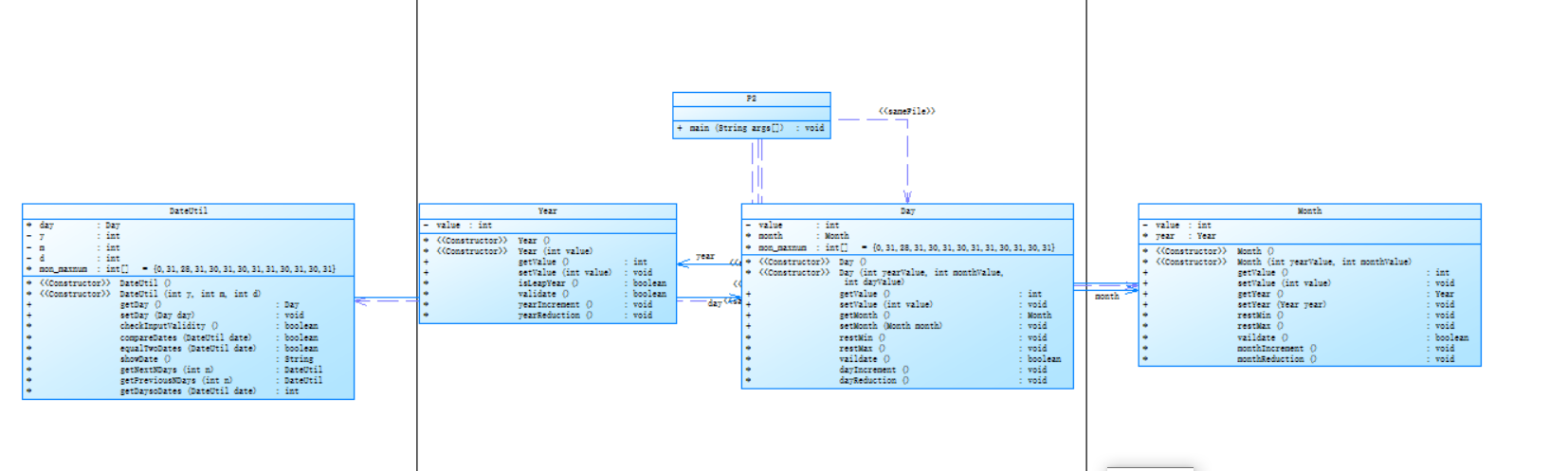
题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
在我看来,题目集5(7-4)设计的类图比较好,因为它里面的类更加符合java的封装,不会让day访问到month,year里面的方法。并且如果是题目集4(7-2)中我们要调用year里面的方法,我们需要调用day,month然后再调用year,这样我们的运行时间大大增加。这就是为什么有些人为什么偷懒把题目集4(7-2)复制下来然后发现自己的代码超时,或者运行时间巨长。** **
7-3 图形继承
心得:
刚开始接触这道题的时候会有点懵,什么是继承呢?重写父类的方法又是什么玩意?后面通过深入的学习,为什么要用继承?就是为了重复的代码不用多次的写,只需要子类继承父类的公共的方法和属性,声明子类之后可以直接调用父类的方法。而重写父类的方法就是因为子类其实是一个个特殊的个体,他们与父类并不完全一致,子类在调用他们的方法中,需要自己改写方法,这其实就是多态的体现。
源代码:

1 import java.math.BigDecimal; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 4 public class Main { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 8 Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); 9 10 int n = in.nextInt(); //选择功能 11 12 Shape a = new Shape(); 13 14 switch(n) { 15 case 1: //求圆的面积 16 double radius = in.nextDouble(); //输入圆的半径 17 checkn1(radius); //判断数据是否合法 18 19 a.shape(); 20 Circle b = new Circle(); 21 b.circle(); 22 23 b.setRadius(radius); 24 System.out.print("Circle's area:" + String.format("%.2f", b.getArea())); //输出圆的面积 25 break; 26 case 2: //求矩形的面积 27 double width = in.nextDouble(); //输入矩形的宽 28 double length = in.nextDouble(); //输入矩形的长 29 checkn1(width); 30 checkn1(length); //判断数据是否合法 31 32 a.shape(); 33 Rectangle c = new Rectangle(); 34 35 c.rectangle(); 36 c.setWidth(width); 37 c.setLength(length); 38 System.out.println("Rectangle's area:" + String.format("%.2f", c.getArea())); 39 break; 40 case 3: //求球的表面积和体积 41 double radius1= in.nextDouble(); //输入球的半径 42 checkn1(radius1); 43 44 a.shape(); 45 Circle f = new Circle(); 46 f.circle(); 47 Ball d =new Ball(); 48 d.ball(); 49 50 d.setRadius(radius1); 51 System.out.println("Ball's surface area:" + String.format("%.2f", d.getArea())); 52 System.out.println("Ball's volume:" + String.format("%.2f", d.getVolume())); 53 break; 54 case 4: //求立方体的宽、长、高 55 double width1 = in.nextDouble(); //输入立方体的宽 56 double length1 = in.nextDouble(); //输入立方体的长 57 double height = in.nextDouble(); //输入立方体的高 58 checkn1(width1); 59 checkn1(length1); 60 checkn1(height); //判断数据是否合法 61 62 a.shape(); 63 Rectangle g = new Rectangle(); 64 g.rectangle(); 65 Box e = new Box(); 66 e.box(); 67 68 69 e.setWidth(width1); 70 e.setLength(length1); 71 e.setHeight(height); 72 73 System.out.println("Box's surface area:" + String.format("%.2f", e.getArea())); 74 System.out.println("Box's volume:" + String.format("%.2f", e.getVolume())); 75 break; 76 default : 77 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 78 break; 79 } 80 } 81 82 public static void checkn1(double n) { 83 if(n<0) { 84 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 85 System.exit(0); 86 } 87 } 88 } 89 class Shape{ 90 void shape() { 91 System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); 92 } 93 public double getArea() { //求图形面积 94 return 0.0; 95 } 96 } 97 class Circle extends Shape { //求圆的面积 98 private double radius; //圆的半径 99 private double area; //圆的面积 100 private double area1; //保留小数点后圆的面积 101 void circle() { 102 System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); 103 } 104 105 public double getRadius() { 106 return radius; 107 } 108 109 public void setRadius(double radius) { 110 this.radius = radius; 111 } 112 113 public double getArea() { //求圆的面积 114 115 area = Math.PI*Math.pow(radius, 2); 116 117 return area; 118 } 119 } 120 class Rectangle extends Shape{ //求矩形的面积 121 122 private double width; //矩形的宽 123 private double length; //矩形的长 124 private double area; //矩形的面积 125 private double area1; //保留小数点两位后矩形的面积 126 void rectangle() { 127 System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); 128 } 129 130 public double getWidth() { 131 return width; 132 } 133 134 public void setWidth(double width) { 135 this.width = width; 136 } 137 138 public double getLength() { 139 return length; 140 } 141 142 public void setLength(double length) { 143 this.length = length; 144 } 145 146 public double getArea() { //求矩形的面积 147 148 area = width*length; 149 150 return area; 151 } 152 } 153 class Ball extends Circle{ //求球的表面积和球的体积 154 private double volume1; //球的体积 155 private double volume2; //保留两位小数点后球的体积 156 private double area; 157 158 private double radius; 159 160 public double getRadius() { 161 return radius; 162 } 163 public void setRadius(double radius) { 164 this.radius = radius; 165 } 166 void ball() { 167 System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); 168 } 169 public double getArea() { //求球的表面积 170 area = 4*Math.PI*Math.pow(radius, 2); 171 return area; 172 } 173 public double getVolume() { //求球的体积 174 volume1 = (4.0/3.0)*Math.PI*Math.pow(radius, 3); 175 176 return volume1; 177 } 178 } 179 class Box extends Rectangle{ //求立方体的表面积和立方体的体积 180 private double height; //立方体的高 181 private double width; 182 private double length; 183 private double area; 184 185 private double volume1; //立方体的体积 186 187 188 public double getWidth() { 189 return width; 190 } 191 public void setWidth(double width) { 192 this.width = width; 193 } 194 public double getLength() { 195 return length; 196 } 197 public void setLength(double length) { 198 this.length = length; 199 } 200 public double getHeight() { 201 return height; 202 } 203 public void setHeight(double height) { 204 this.height = height; 205 } 206 207 void box() { 208 System.out.println("Constructing Box"); 209 } 210 public double getArea() { //求立方体的表面积 211 area = width*length*2+width*height*2+2*length*height; 212 213 return area; 214 } 215 public double getVolume() { //求立方体的体积 216 volume1 = width*length*height; 217 218 return volume1; 219 } 220 }
7-5 图形继承与多态
心得:
其实这道题很多人都没按照题目的要求来做,这道题看起来其实是很简单的,但题目要求我们在list里面的对象进行排序而不是把面积算出来然后排序。这时候我们就要用到ArrayList这个类是专门来存储对象的,然后我们要用到collections.sor这个方法,Collections是一个工具类,sort是其中的静态方法,是用来对List类型进行排序的,它有两种参数形式
一种是comparable,另一种是comparator,我用的是comparator这个接口,自己重写一个类然后继承comparator这个接口来制定排序规则。
源代码:

1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collections; 3 import java.util.Comparator; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 6 public class Main { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 11 int i=0; 12 int cnum = in.nextInt(); //圆的个数 13 int rnum = in.nextInt(); //长方形的个数 14 int tnum = in.nextInt(); //三角形的个数 15 if(cnum >=0 && rnum >=0 && tnum>=0) { 16 Circle[] c = new Circle[cnum]; 17 Rectangle[] r = new Rectangle[rnum]; 18 Triangle[] t = new Triangle[tnum]; 19 ArrayList <Shape> list = new ArrayList(); 20 for( i=0;i<cnum;i++) { 21 c[i] = new Circle(in.nextDouble()); 22 if(c[i].validate()==false) { 23 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 24 System.exit(0); 25 } 26 list.add(c[i]); 27 } 28 for( i=0;i<rnum;i++) { 29 r[i] = new Rectangle(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); 30 if(r[i].validate()==false) { 31 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 32 System.exit(0); 33 } 34 list.add(r[i]); 35 } 36 for(i=0;i<tnum;i++) { 37 t[i] = new Triangle(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); 38 if(t[i].validate()==false) { 39 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 40 System.exit(0); 41 } 42 list.add(t[i]); 43 } 44 System.out.println("Original area:"); 45 printArea(list); 46 System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f", sumArea(list))); 47 Collections.sort(list,new MyComparator()); 48 System.out.println("Sorted area:"); 49 printArea(list); 50 System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f", sumArea(list))); 51 } 52 else { 53 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 54 } 55 } 56 public static void printArea(ArrayList <Shape> list) { //输出各个面积 57 int i=0; 58 for(i=0;i<list.size();i++) { 59 System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", list.get(i).getArea())+" "); 60 } 61 System.out.println(); 62 } 63 public static double sumArea(ArrayList <Shape> list) { 64 double sum=0; 65 for(Shape i:list) { //使用 for-each 来迭代元素: 66 sum=sum+i.getArea(); 67 } 68 return sum; 69 } 70 } 71 class MyComparator implements Comparator<Shape>{ 72 73 @Override 74 public int compare(Shape o1, Shape o2) { 75 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 76 if(o1.getArea()>o2.getArea()) 77 return 1; 78 else 79 return -1; 80 } //自定义的排序规则 81 82 } 83 class Shape { 84 public double getArea() { 85 return 0.0; 86 } 87 public boolean validate() { 88 return true; 89 } 90 public String toString() { 91 return null; 92 93 } 94 } 95 class Circle extends Shape{ 96 private double radius; 97 98 Circle(double radius){ 99 this.radius=radius; 100 } 101 public boolean validate() { 102 if(radius<=0) { 103 return false; 104 } 105 return true; 106 } 107 public double getArea() { 108 109 return Math.PI*radius*radius; 110 } 111 public String toString() { 112 113 return String.valueOf(getArea()); 114 } 115 } 116 class Rectangle extends Shape{ 117 private double width; 118 private double length; 119 Rectangle(double width,double length){ 120 this.width=width; 121 this.length=length; 122 } 123 public boolean validate() { 124 if(width <= 0 || length <= 0) { 125 return false; 126 } 127 return true; 128 } 129 public double getArea() { 130 return width*length; 131 } 132 public String toString() { 133 return String.valueOf(getArea()); 134 } 135 } 136 class Triangle extends Shape{ 137 private double side1; 138 private double side2; 139 private double side3; 140 Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){ 141 this.side1=side1; 142 this.side2=side2; 143 this.side3=side3; 144 } 145 public boolean validate() { 146 if(side1 <=0 || side2<=0 || side3 <= 0) 147 return false; 148 if(side1 < side2+side3 && side2<side1+side3 && side3<side2+side1){ 149 return true; 150 } 151 else { 152 return false; 153 } 154 } 155 public double getArea() { 156 double p; 157 p=0.5*(side1+side2+side3); 158 return Math.pow(p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3), 0.5); 159 } 160 public String toString() { 161 return String.valueOf(getArea()); 162 } 163 }
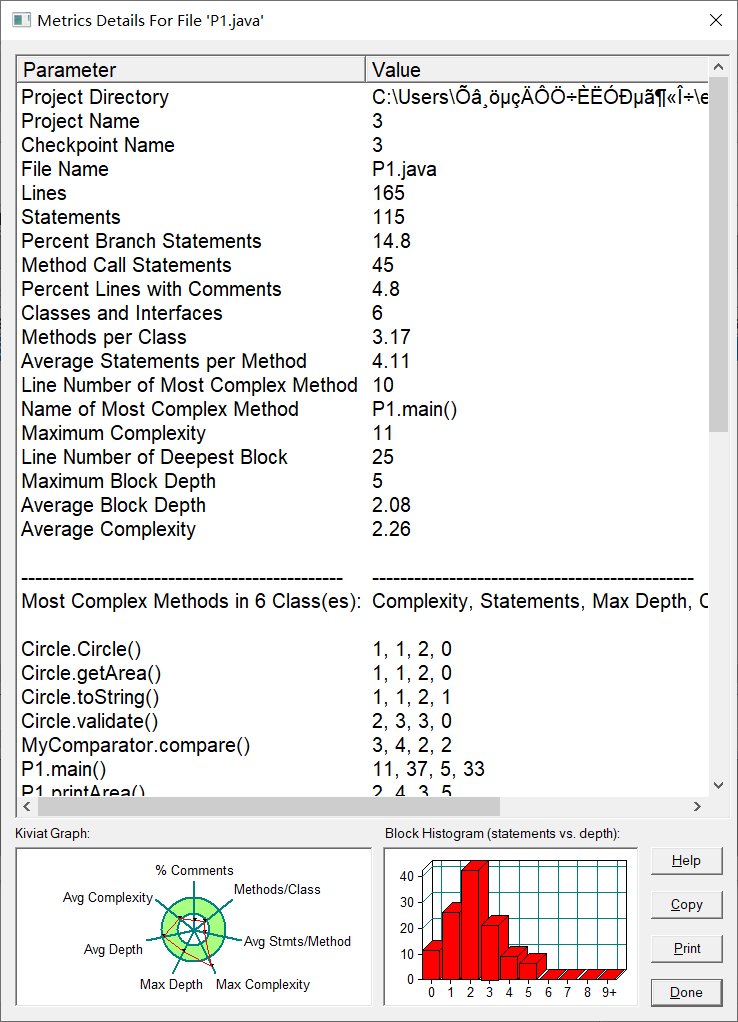
7-6 实现图形接口及多态性
心得:
这道题我们要知道java的抽象类 abstract class ,在这个类里面我们不用在方法里面写任何代码,只需声明方法和属性,然后通过子类的继承,重写父类的方法来完成这道题,而重写父类的方法就是多态的体现,这道题本身并不难,直接上代码吧。
源代码 :

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 8 double radius,width,length; 9 radius=in.nextDouble(); 10 width=in.nextDouble(); 11 length=in.nextDouble(); 12 if(radius <=0 || width <= 0 || length <= 0) { 13 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 14 System.exit(0); 15 } 16 // vailDate(radius,width,length); 17 Circle a = new Circle(radius); 18 Rectangle b = new Rectangle(width,length); 19 System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", a.getArea())); 20 System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", b.getArea())); 21 } 22 /* public static void vailDate(double radius,double width,double length){ 23 24 }*/ 25 } 26 class GetArea{ 27 public double getArea() { 28 return 0.0; 29 } 30 } 31 class Rectangle extends GetArea{ 32 private double width; 33 private double length; 34 Rectangle() { 35 36 } 37 Rectangle(double width,double length) { 38 this.width=width; 39 this.length=length; 40 } 41 public double getWidth() { 42 return width; 43 } 44 public void setWidth(double width) { 45 this.width = width; 46 } 47 public double getLength() { 48 return length; 49 } 50 public void setLength(double length) { 51 this.length = length; 52 } 53 public double getArea() { 54 return width*length; 55 } 56 } 57 class Circle extends GetArea{ 58 private double radius; 59 Circle(){ 60 61 } 62 Circle(double radius){ 63 this.radius=radius; 64 } 65 public double getRadius() { 66 return radius; 67 } 68 public void setRadius(double radius) { 69 this.radius = radius; 70 } 71 public double getArea() { 72 return Math.PI*radius*radius; 73 } 74 }
对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
7-1水文数据校验及处理
boolean validateMeasureDateTime(String measureDateTime){ //检验测量时间的合法性
if(measureDateTime.matches("(([1-9]|[1-9][0-9]|[1-9][0-9][0-9]|[1-9][0-9][0-9][0-9])/((([13578]|1[02])/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2/([0-9]|1[0-9]|2[0-8]))) ((([02468]|1[02468]|2[02]):00)))|((((([1-9]|[1-9][0-9])(0[48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26]))|([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])00)/2/29) ((([02468]|1[02468]|2[02]):00)))")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
这是水文数据校验及处理这道题里面检验时间的合法性,我们通过 | 这个符号来表示或,
(([1-9]|[1-9][0-9]|[1-9][0-9][0-9]|[1-9][0-9][0-9][0-9])/((([13578]|1[02])/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)/([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2/([0-9]|1[0-9]|2[0-8]))) ((([02468]|1[02468]|2[02]):00)))
这一段的意思就是不管是闰年或者平年都会有的情况,然后我们在特判一下是闰年的时候,2月是29即可
([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])00)/2/29) ((([02468]|1[02468]|2[02]):00)))
统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数
这道题其实还是比较坑的,就比如注释符有两种表现 // 和 /* */,我们这里的*是不是和正则里面的*一样,所以这样就会出现歧义,所以我们就要用到转义符了也就是 \\
你以为这样就结束了吗?看一下代码
package Main;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a="asd/*dsadkas*/das/*jkadja*/";
a= a.replaceAll("/\\*.*\\*/", " ");
System.out.print(a);
}
}
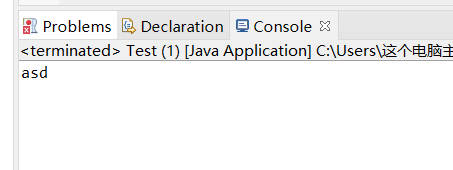
结果应该是asddas中间的das怎么没了?,这就是正则的贪婪行,它并没有检验到第一个/就提下了,它还要往后面检验检验到第二个/它就停下了,所以后面的全都替换成空格了,我们只需在 '.'后面加个 '?' ,这个的意思是0或者1个字符,它会先判断当0个字符的时候后面是不是 */ 如果是则就截取这段为空格,也就是正则的非贪婪
package Main;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String a="asd/*dsadkas*/das/*jkadja*/";
a= a.replaceAll("/\\*.*?\\*/", " ");
System.out.print(a);
}
}

第三次的作业的正则实在是太简单了,如果你是真的把前两次的正则搞懂了第三次就是小菜一碟,所以我就不分析了。
7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数
心得:
其实前面已经说了就是主要字符的冲突,我们需要把它转义成普通字符,然后就是正则表达式的非贪婪
源代码:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 8 String [] list=new String[]{"abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const", 9 "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "false", "final", "finally", 10 "float", "for", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", 11 "native", "new", "null", "package", "private", "protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", 12 "strictfp", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws", "transient", "true", "try", 13 "void", "volatile", "while"}; 14 String[] a = new String [100000]; 15 int[] d = new int [1000]; //关键字出现的次数 16 int i = 0,j=0,k=0; //flag=1,说明是注释里面的词 17 boolean wrong = true; 18 int start=0; 19 int end = 1; 20 int flag=0; 21 int check=0; 22 StringBuilder b= new StringBuilder(); 23 a[i]=in.nextLine(); 24 String c; 25 while(a[i].equals("exit") == false) { 26 27 if(a[i].trim().length()!=0) 28 wrong = false; 29 b.append(a[i].replaceAll("//.*", " ").replaceAll("\".*?\"", " ")+" "); //把//后面的内容和双引号里面的内容替换成空格 30 i++; 31 a[i]=in.nextLine(); 32 33 } 34 if(wrong) { 35 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 36 System.exit(0); 37 } 38 c = b.toString().replaceAll("/\\*.*?\\*/", " "); 39 c=c.replaceAll("_", "a"); 40 c=c.replaceAll("=", "a"); 41 c=c.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", " "); 42 for(i=0;i<c.length();i++) { 43 if(c.charAt(i)==' ') { 44 if(flag == 1) { 45 end = i; 46 flag=0; 47 check=1; 48 } 49 50 if(check == 1) { //check=1说明start和end都赋值了 51 check=0; 52 wrong=false; 53 for(k=0;k<list.length;k++) { 54 if(c.substring(start, end).equals(list[k])) { 55 d[k]++; 56 wrong=true; 57 } 58 if(wrong) 59 break; 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 else { 64 if(flag==0) { //flag等于0说明是这个字符串的开头 65 flag=1; 66 start = i; 67 } 68 69 } 70 71 } 72 for(k=0; k <list.length; k++) { 73 if(d[k]!=0) { 74 System.out.println(d[k] + " " + list[k]); 75 } 76 } 77 78 } 79 }

 老师的任务罢了
老师的任务罢了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号