基于Chains构造大模型流程
目录
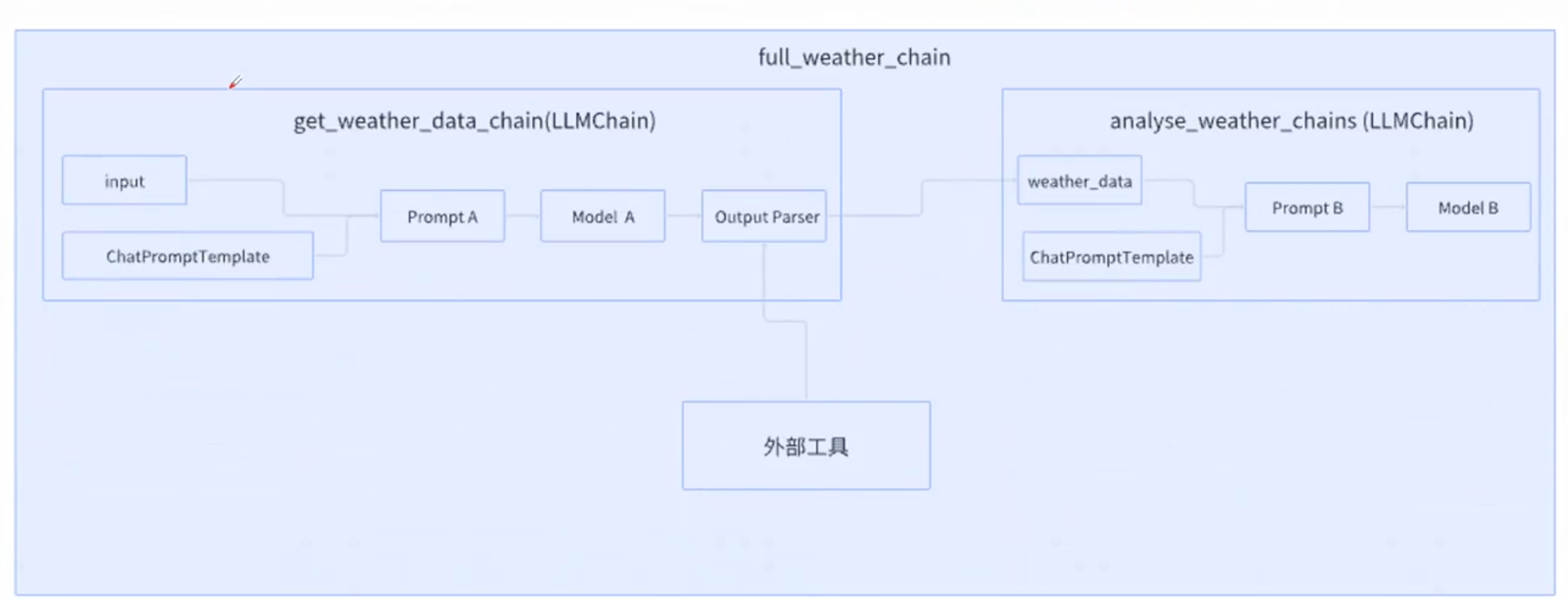
阶段1:实现第一个chain。 获取天气数据
1. 构造提示词模板
1.1 规划
如果模型推理能力弱的大模型,你给他一个复杂的问题,他回答不好,我们需要根据场景准备好一系列回答好的问题(示例)投喂给大模型,让大模型学习。
。所以我们需要通过few show拆解步骤。
大概步骤
1 准备好问题
2 组装成提示词模板+用户的提的问题给到大模型
使用fewshot可以简化问题的拼接。
设计原则:1 静态的提示词示例和动态的用户输入问题分离。2 历史聊天记录和用户输入的消息分类
建议
1. 使用Few-shot示例提示:将固定示例作为Few-shot示例,与动态输入分开,这样模型既能参考示例,又能处理实际用户输入。
2. 消息角色分离:将系统消息、示例对话和实际用户输入明确区分,避免混淆。
3. 维护对话历史:正确处理多轮对话中的消息历史,确保工具调用的结果能够被正确记录和响应。
反模式
chat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "..."),
("human", "{user_input}"),
("human", "我要退货,订单号是: "), # 硬编码用户输入
("ai", "按流程处理退货...") # 硬编码AI回复
])
推荐写法
class ExamplePrompts:
examples = [
{"input": "我要退货,订单号是: ",
"output": "按严格流程处理退货请求 "
"1. 获取订单号并验证有效性,调用函数validate_order ,如果返回结果为 无效订单,告诉用户订单号无效流程结束 。如果订单号有效继续走后续流程 "
"2. 检查订单时间是否符合退货政策,调用函数 get_order_date "
"3. 若超期,拒绝退货但提供替代方案(维修服务),提供维护服务地址 taobao.com/mend/xxx "
"4. 若未超期,引导客户填写退货表单,表单地址 taobao.com/refund/xxx"},
{"input": "食堂总共有23个苹果,如果他们用掉20个苹果,然后又买了6个苹果,请问现在食堂总共有多少个苹果?",
"output": "食堂最初有23个苹果,用掉20个,然后又买了6个,总共有23-20+6=9个苹果,答案是9。"},
]
def get_prompts(self) -> ChatPromptTemplate:
example_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("human", "{input}"),
("ai", "{output}")
])
few_shot_prompt = FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate(
example_prompt=example_prompt,
examples=self.examples
)
# 添加历史占位符
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
few_shot_prompt,
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"), # 动态历史支持
("human", "{input}")
])
return prompt
使用
def invoke_without_tools(self, prompt: ChatPromptTemplate, user_input: str, history: list):
llm = self.create_llm()
chain = prompt | llm
return chain.invoke({
"input": user_input,
"history": history # 传递历史状态
})
1.2 根据用户提的问题精准找到高质量的示例,投喂给大模型,以节约token,降低成本,提升效率
基于向量数据库
langchain 提供 selector的工具支持示例过滤。支持向量化,问题长度等方式。
2 定义外部函数
2.1 定义外部函数
2.2 编写函数工具说明 (可通过@tools注解可以不用编写工具说明)
2.3 构建函数列表
构造chains链 提示词模板 | llm.bind_tools | 输出格式化 | 调用外部函数
def invoke_with_tools(self,prompt:ChatPromptTemplate, user_input:str, history:list):
llm = self.create_llm()
chain = prompt | llm.bind_tools([
self.validate_order,
self.check_order_time_complies_policy
])
return chain.invoke({
"input": user_input,
"history": history # 传递历史状态
})
阶段2:基于外部函数的结果交给大模型组织输出
通过一个simple chain 串联阶段1,2完成调用。
底层 memory 贯穿
性能优化点
1 使用摘要功能简化存储,2
简单memory ConversationBufferMemory
简化多轮对话历史消息传递。
用法 https://www.cnblogs.com/aibi1/p/18804608
【注意】
- 使用ConversationChain 或带记忆的链时 框架会自动记录历史消息,如果直接调用LLM.invoke不会自动记录历史消息】
- 即使使用ConversationBufferMemory, 当前命中的工具信息还是要手动传递到历史消息记录。
memory.chat_memory.add_message(
ToolMessage(
content=result,
name=tool_call['name'],
tool_call_id=tool_call['id']
)
)
entity memory
具备摘要功能的memory (减少token占用)
示例
示例1,使用原生的写法,自己构造历史消息,工具调用,工具链传递
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
import os
import json
import os
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage
import json
from langchain.tools import BaseTool, StructuredTool, tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.output_parsers import JsonOutputKeyToolsParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage, ToolMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate,
MessagesPlaceholder
)
class ExamplePrompts:
examples = [
{"input": "我要退货,订单号是: ",
"output": "按严格流程处理退货请求 "
"1. 获取订单号并验证有效性,调用函数validate_order ,如果返回结果为 无效订单,告诉用户订单号无效流程结束 。如果订单号有效继续走后续流程 "
"2. 检查订单时间是否符合退货政策,调用函数 get_order_date "
"3. 若超期,拒绝退货但提供替代方案(维修服务),提供维护服务地址 taobao.com/mend/xxx "
"4. 若未超期,引导客户填写退货表单,表单地址 taobao.com/refund/xxx"},
{"input": "食堂总共有23个苹果,如果他们用掉20个苹果,然后又买了6个苹果,请问现在食堂总共有多少个苹果?",
"output": "食堂最初有23个苹果,用掉20个,然后又买了6个,总共有23-20+6=9个苹果,答案是9。"},
]
def get_prompts(self) -> ChatPromptTemplate:
example_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("human", "{input}"),
("ai", "{output}")
])
few_shot_prompt = FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate(
example_prompt=example_prompt,
examples=self.examples
)
# 添加历史占位符
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
few_shot_prompt,
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"), # 动态历史支持
("human", "{input}")
])
return prompt
class IntelligentCustomerService:
@tool
def validate_order(orderNumber: str) -> str:
"""
订单号是否有效校验函数,该函数定义了订单号是否有效的校验
:param orderNumber: 必要参数,表示订单号,用字符串进行表示
:return:"无效订单" 表示无效订单,"有效订单" 表示有效订单
"""
if orderNumber == "123":
return "无效订单"
else:
return "有效订单"
@tool
def check_order_time_complies_policy(orderNumber: str) -> str:
"""
检查订单时间是否符合退货政策
:param orderNumber: 必要参数,表示订单号,用字符串进行表示
:return:"无效订单" 表示无效订单,"有效订单" 表示有效订单
"""
if orderNumber == "125":
return "符合退货政策"
else:
return "不符合退货政策"
def create_llm(self) -> ChatOpenAI:
"""创建并返回配置好的大模型实例"""
return ChatOpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY") or "your_api_key_here",
base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
model="qwen2.5-72b-instruct"
)
def invoke_with_tools(self,prompt:ChatPromptTemplate, user_input:str, history:list):
llm = self.create_llm()
chain = prompt | llm.bind_tools([
self.validate_order,
self.check_order_time_complies_policy
])
return chain.invoke({
"input": user_input,
"history": history # 传递历史状态
})
def invoke_without_tools(self, prompt: ChatPromptTemplate, user_input: str, history: list):
llm = self.create_llm()
chain = prompt | llm
return chain.invoke({
"input": user_input,
"history": history # 传递历史状态
})
def process_without_tool_calls(self, prompt_template: ChatPromptTemplate, question: str, history: list) :
response = self.invoke_without_tools(prompt_template, question, history)
history.extend([
response
])
return response
def process_tool_calls(self, prompt_template: ChatPromptTemplate, question: str, history: list) -> bool:
response = self.invoke_with_tools(prompt_template, question, history)
print(response)
if isinstance(response, AIMessage) and hasattr(response, 'tool_calls'):
for tool_call in response.tool_calls:
try:
func_name = tool_call["name"]
args = json.loads(tool_call["args"]["orderNumber"])
# 通过实例调用工具方法
tool_func = getattr(self, func_name)
result = tool_func(str(args))
print(result)
# 更新历史记录
history.extend([
response,
ToolMessage(
content=result,
name=func_name,
tool_call_id=tool_call["id"]
)
])
return True
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print("❌ 工具参数解析失败")
except (AttributeError, ValueError) as e:
print(f"❌ 工具调用错误: {str(e)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 未知工具错误: {str(e)}")
return False
else:
return False
def answer(self, prompt_template: ChatPromptTemplate, question: str, history: list):
i = 4
while (i := i - 1) > 0:
try:
result = self.process_tool_calls(prompt_template, question, history)
if not result: # 如果处理失败,回退到无工具调用
return self.process_without_tool_calls(prompt_template, question, history)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print("❌ 工具参数解析失败")
except (AttributeError, ValueError) as e:
print(f"❌ 工具调用错误: {str(e)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 未知工具错误: {str(e)}") # 英文引号
# 所有尝试失败后的默认返回(可选)
return self.invoke_without_tools(prompt_template, question, history)
def main():
# 1. 获取用户输入
user_input = ""
aiChat = IntelligentCustomerService()
exampleService = ExamplePrompts()
history = []
while (True):
user_input = input("请输入文本:")
if(user_input == "exit"):
print("程序结束")
break
# 2. 处理数据
print(user_input)
aiChat.answer(exampleService.get_prompts(),user_input,history)
## TODO history 要追加到下次的聊天里面
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() # 启动主程序




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号