鸢尾花数据集的分类——SVM算法
Iris 鸢尾花数据集是一个经典数据集,在统计学习和机器学习领域都经常被用作示例。数据集内包含 3 类共 150 条记录,每类各 50 个数据,每条记录都有 4 项特征:花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度,可以通过这4个特征预测鸢尾花卉属于(iris-setosa, iris-versicolour, iris-virginica)三种中的哪一品种。
1、鸢尾花数据集的分类——SVM算法
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np from sklearn import svm from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def iris_type(s): it = {b'Iris-setosa': 0, b'Iris-versicolor': 1, b'Iris-virginica': 2} return it[s] # 'sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width' iris_feature = u'花萼长度', u'花萼宽度', u'花瓣长度', u'花瓣宽度' def show_accuracy(a, b, tip): acc = a.ravel() == b.ravel() print (tip + '正确率:', np.mean(acc)) if __name__ == "__main__": path = 'iris.data' # 数据文件路径) data = np.loadtxt(path, dtype=float, delimiter=',', converters={4: iris_type}) x, y = np.split(data, (4,), axis=1) x = x[:, :2] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=1, train_size=0.6) # 分类器 # clf = svm.SVC(C=0.1, kernel='linear', decision_function_shape='ovr') clf = svm.SVC(C=0.8, kernel='rbf', gamma=20, decision_function_shape='ovr') clf.fit(x_train, y_train.ravel()) # 准确率 print (clf.score(x_train, y_train)) # 精度 y_hat = clf.predict(x_train) show_accuracy(y_hat, y_train, '训练集') print (clf.score(x_test, y_test)) y_hat = clf.predict(x_test) show_accuracy(y_hat, y_test, '测试集') # 画图 x1_min, x1_max = x[:, 0].min(), x[:, 0].max() # 第0列的范围 x2_min, x2_max = x[:, 1].min(), x[:, 1].max() # 第1列的范围 x1, x2 = np.mgrid[x1_min:x1_max:500j, x2_min:x2_max:500j] # 生成网格采样点 grid_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) # 测试点 Z = clf.decision_function(grid_test) # 样本到决策面的距离 print (Z) grid_hat = clf.predict(grid_test) # 预测分类值 print (grid_hat) grid_hat = grid_hat.reshape(x1.shape) # 使之与输入的形状相同 mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [u'SimHei'] # 指定默认字体 mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF']) cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r', 'b']) x1_min, x1_max = x[:, 0].min(), x[:, 0].max() # 第0列的范围 x2_min, x2_max = x[:, 1].min(), x[:, 1].max() # 第1列的范围 x1, x2 = np.mgrid[x1_min:x1_max:500j, x2_min:x2_max:500j] # 生成网格采样点 grid_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) # 测试点 plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, grid_hat, cmap=cm_light) plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=y[:,0], edgecolors='k', s=50, cmap=cm_dark) # 样本 plt.scatter(x_test[:, 0], x_test[:, 1], s=120, facecolors='none', zorder=10) # 圈中测试集样本 plt.xlabel(iris_feature[0], fontsize=13) plt.ylabel(iris_feature[1], fontsize=13) plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max) plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max) plt.title(u'鸢尾花SVM二特征分类', fontsize=15) plt.grid() plt.show()
2、运行结果
0.8666666666666667
训练集正确率: 0.8666666666666667
0.65
测试集正确率: 0.65
[[-0.02248787 2.04243623 0.98005163]
[-0.02092291 2.04165431 0.9792686 ]
[-0.01929329 2.04084007 0.97845322]
...
[-0.04903923 2.05568979 0.99334945]
[-0.04903923 2.05568979 0.99334945]
[-0.04903923 2.05568979 0.99334945]]
[1. 1. 1. ... 1. 1. 1.]
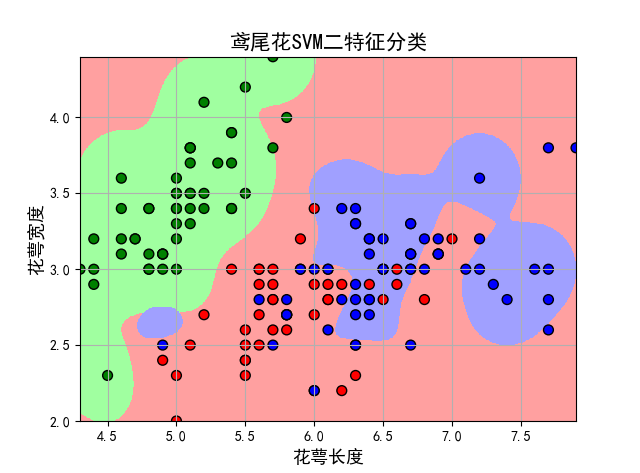
实验结果表明:采用SVM可以大概分类出这三种花卉,测试集精度为0.65。
3、补充说明
1)导入sklearn算法包
Scikit-Learn库已经实现了所有基本机器学习的算法,具体使用详见官方文档说明:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#support-vector-machines。
skleran中集成了许多算法,其导入包的方式如下所示:
支持向量机:from sklearn import svm
逻辑回归:from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
朴素贝叶斯:from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
K-近邻:from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
决策树:from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
2)使用numpy中的loadtxt读入数据文件
loadtxt()的使用方法:np.loadtxt(fpath, dtype, comments, delimiter, converters, skiprows, usecols)
fname:文件路径。eg:C:/Dataset/iris.txt。
dtype:数据类型。eg:float、str等。
delimiter:分隔符。eg:‘,’。
converters:将数据列与转换函数进行映射的字典。eg:{1:fun},含义是将第2列对应转换函数进行转换。
usecols:选取数据的列。
通过loadtxt()函数中的converters参数将第五列通过转换函数iris_type(s)映射成浮点类型的数据。
3) 将Iris分为训练集与测试集
1. split(数据,分割位置,轴=1(水平分割) or 0(垂直分割))。
2. x = x[:, :2]是为方便后期画图更直观,故只取了前两列特征值向量训练。
3. sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split随机划分训练集与测试集。train_test_split(train_data,train_target,test_size=数字, random_state=0)
参数解释:
train_data:所要划分的样本特征集
train_target:所要划分的样本结果
test_size:样本占比,如果是整数的话就是样本的数量
random_state:是随机数的种子。填1: 每次产生随机数组是一样的。但填0或不填,每次都会不一样。
4) 训练svm分类器
clf = svm.SVC(C=0.1, kernel='linear', decision_function_shape='ovr')
clf = svm.SVC(C=0.8, kernel='rbf', gamma=20, decision_function_shape='ovr')
clf.fit(x_train, y_train.ravel())
注:
kernel='linear'时,为线性核,C越大分类效果越好,但有可能会过拟合(defaul C=1)。
kernel='rbf'时(default),为高斯核,gamma值越小,分类界面越连续;gamma值越大,分类界面越“散”,分类效果越好,但有可能会过拟合。
decision_function_shape='ovr'时,为one v rest,即一个类别与其他类别进行划分,可实现多分类。
decision_function_shape='ovo'时,为one v one,即将类别两两之间进行划分,用二分类的方法模拟多分类的结果。
5) 作图
pcolormesh(x,y,z,cmap)这里参数代入x1,x2,grid_hat,cmap=cm_light绘制的是背景。
scatter中edgecolors是指描绘点的边缘色彩,s指描绘点的大小,cmap指点的颜色。
xlim指图的边界。
参考文献
[1] https://www.cnblogs.com/luyaoblog/p/6775342.html
附录
数据集下载:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fYNFUYNIXO8OrUiqlpKYqA
提取码:dfzw





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号