P.31-跨域问题解决、P.32-其他权限校验方法、P.33-自定义权限校验方法
P.31-跨域问题解决
跨域:
浏览器出于安全的考虑,使用 XMLHttpRequest对象发起 HTTP请求时必须遵守同源策略,否则就是跨域的HTTP请求,默认情况下是被禁止的。
同源策略要求源相同才能正常进行通信, 即协议、域名、端口号都完全一致。
前后端分离项目,前端项目和后端项目一般都不是同源的,所以肯定会存在跨域请求的问题。
所以我们就要处理一下,让前端能进行跨域请求。
①先对SpringBoot配置,允许跨域请求
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
// 设置允许跨域的路径
registry.addMapping("/**")
// 设置允许跨域请求的域名
.allowedOriginPatterns("*")
// 是否允许cookie
.allowCredentials(true)
// 设置允许的请求方式
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "DELETE", "PUT")
// 设置允许的header属性
.allowedHeaders("*")
// 跨域允许时间
.maxAge(3600);
}
}
SecurityConfig
P.32-其他权限校验方法
我们前面都是使用@PreAuthorize注解,然后在在其中使用的是hasAuthority方法进行校验。
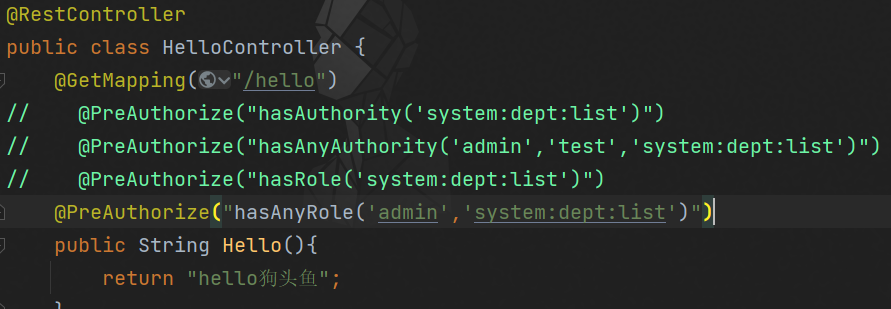
SpringSecurity还为我们提供了其它方法例如:hasAnyAuthority,hasRole,hasAnyRole等。
这里我们先不急着去介绍这些方法,我们先去理解hasAuthority的原理,然后再去学习其他方法你就更容易理解,而不是死记硬背区别。
并且我们也可以选择定义校验方法,实现我们自己的校验逻辑。
hasAuthority方法实际是执行到了SecurityExpressionRoot的hasAuthority,大家只要断点调试既可知道它内部的校验原理。
它内部其实是调用authentication的getAuthorities方法获取用户的权限列表。然后判断我们存入的方法参数数据在权限列表中。
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin','test','system:dept:list')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
hasAnyAuthority方法可以传入多个权限,只有用户有其中任意一个权限都可以访问对应资源。
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('system:dept:list')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin','system:dept:list')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
我们也可以定义自己的权限校验方法,在@PreAuthorize注解中使用我们的方法。
@Component("ex")
public class SGExpressionRoot {
public boolean hasAuthority(String authority){
//获取当前用户的权限
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authentication.getPrincipal();
List<String> permissions = loginUser.getPermissions();
//判断用户权限集合中是否存在authority
return permissions.contains(authority);
}
}
在SPEL表达式中使用 @ex相当于获取容器中bean的名字未ex的对象。然后再调用这个对象的hasAuthority方法
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@PreAuthorize("@ex.hasAuthority('system:dept:list')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号