第二章实验
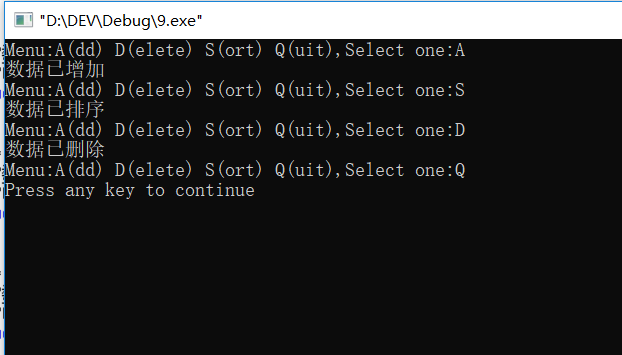
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ char x; int i; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"; for(;i=1;i++){ cin>>x; if(x=='A'){ cout<<"数据已增加"<<endl; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"; continue; } else if(x=='D'){ cout<<"数据已删除"<<endl; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"; continue; } else if(x=='S'){ cout<<"数据已排序"<<endl; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"; continue; } else if (x=='Q') break; } return 0; }
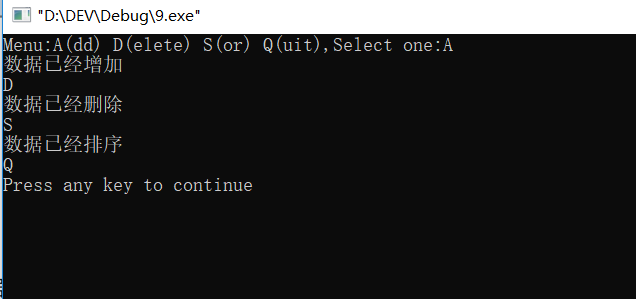
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ char n; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(or) Q(uit),Select one:"; cin>>n; while(n!='Q') { switch(n) { case'A': { cout<<"数据已经增加"<<endl;break; } case 'D': { cout<<"数据已经删除"<<endl;break; } case'S': { cout<<"数据已经排序"<<endl;break; } } cin>>n; } return 0; }
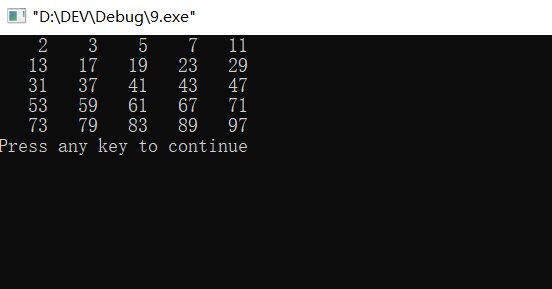
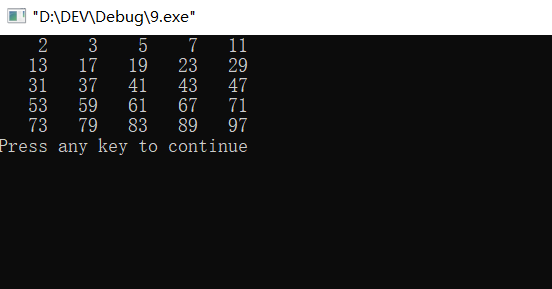
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main(){ int m,j,i,k=1; for(i=2;i<=100;i++){ m=sqrt(i); for(j=2;j<=m;j++){ if(i%j==0)break; } if(j>m){ cout<<setw(5)<<i; k++; if(k>5){ cout<<setw(5)<<endl; k=1; } } } return 0; }
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main(){ int m,j,i=1,k=1; while(i<=100){ m=sqrt(i); for(j=2;j<=m;j++){ if(i%j==0)break; } if(j>m&&i!=1){ cout<<setw(5)<<i; k++; if(k>5){ cout<<setw(5)<<endl; k=1; } } i++; } return 0; }
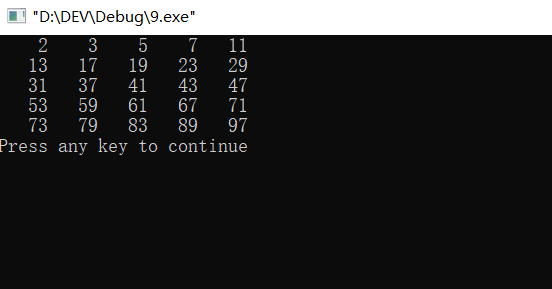
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main(){ int m,j,i=1,k=1; do{ m=sqrt(i); for(j=2;j<=m;j++){ if(i%j==0)break; } if(j>m&&i!=1){ cout<<setw(5)<<i; k++; if(k>5){ cout<<setw(5)<<endl; k=1; } } i++; }while(i<=100); return 0; }
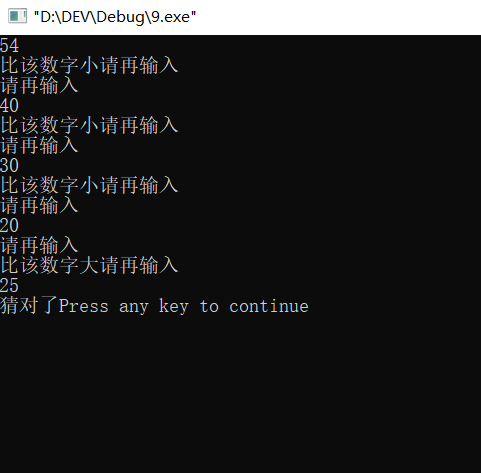
#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<ctime> using namespace std; int main(){ srand((unsigned)time(0)); int m,n; m=rand()%100+1; cin>>n; while(n!=m){ if(n>m) cout<<"比该数字小"; cout<<"请再输入"<<endl; if(n<m) cout<<"比该数字大"; cout<<"请再输入"<<endl; cin>>n; } cout<<"猜对了"; return 0; }
#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<ctime> using namespace std; int main(){ srand((unsigned)time(0)); int m,n; m=rand()%100+1; cin>>n; do{ if(n>m) cout<<"比该数字小"; cout<<"请再输入"<<endl; if(n<m) cout<<"比该数字大"; cout<<"请再输入"<<endl; cin>>n; }while(n!=m); cout<<"猜对了"; return 0; }

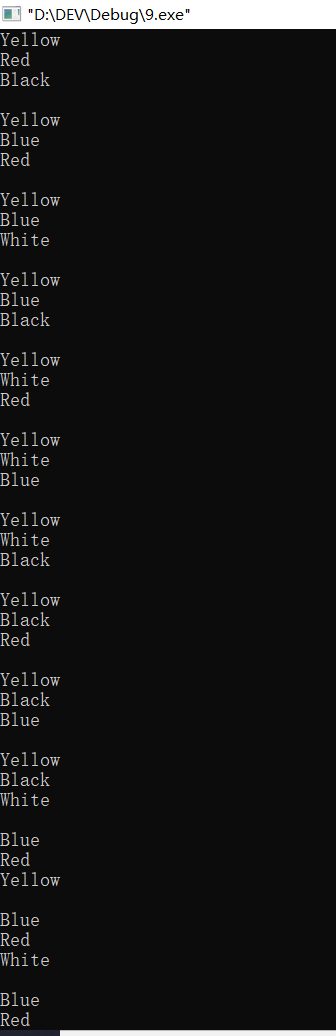
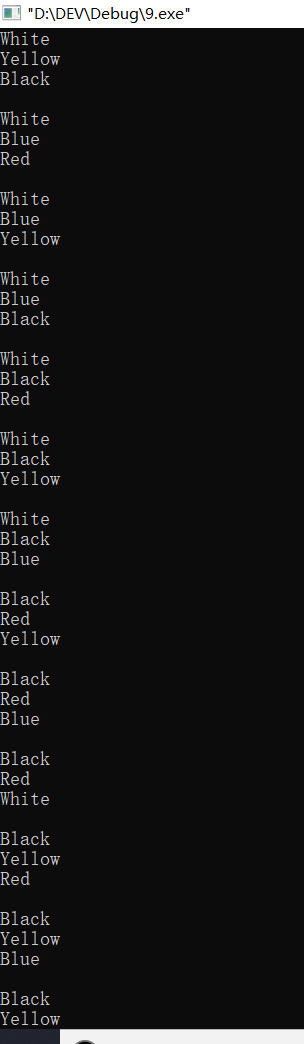
#include<iostream> using namespace std; enum Packet{Red,Yellow,Blue,White,Black}; void change(int n) { switch(n) { case 0:cout<<"Red"<<endl;break; case 1:cout<<"Yellow"<<endl;break; case 2:cout<<"Blue"<<endl;break; case 3:cout<<"White"<<endl;break; case 4:cout<<"Black"<<endl;break; } } int main() { int i,j,k,total=0; cout<<"The type:\n"; for(i=Red;i<=Black;i++) { for(j=Red;j<=Black;j++) { for(k=Red;k<=Black;k++) { if(i!=j&&i!=k&&j!=k) { change(i); change(j); change(k); cout<<endl; ++total; } } } } cout<<"The count:"<<total<<endl; return 0; }
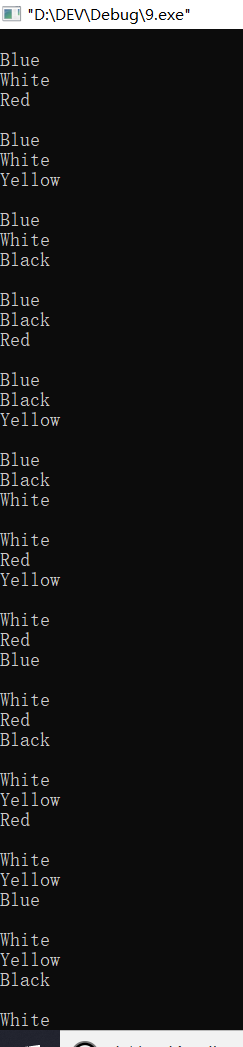
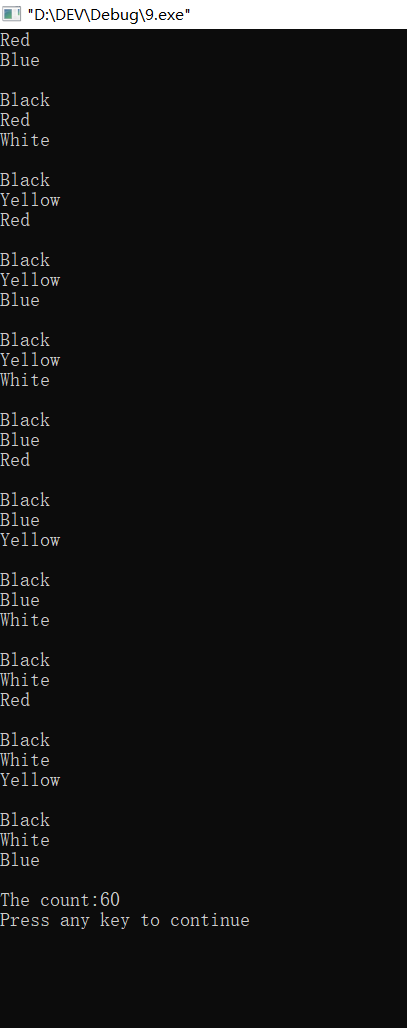
#include<iostream> using namespace std; enum Packet{Red,Yellow,Blue,White,Black}; void change(int n) { switch(n) { case 0:cout<<"Red"<<endl;break; case 1:cout<<"Yellow"<<endl;break; case 2:cout<<"Blue"<<endl;break; case 3:cout<<"White"<<endl;break; case 4:cout<<"Black"<<endl;break; } } int main() { int i,j,k,total=0; cout<<"The type:\n"; for(i=Red;i<=Black;i++) { for(j=Red+i+1;j<=Black;j++) { for(k=Red+j+1;k<=Black;k++) { if(i!=j&&i!=k&&j!=k) { change(i); change(j); change(k); cout<<endl; ++total; } } } } cout<<"The count:"<<total<<endl; return 0; }
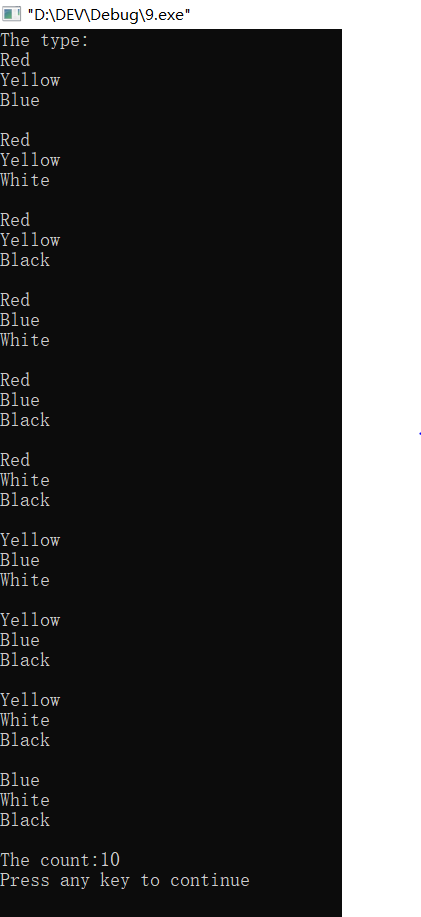
这几个实验中,基本上都要求多种方法编程,对复习上学期C语言的知识有一定的帮助。
其中相较而言比较难的是枚举类型和随机函数,随机类型中rand和srand函数都很重要,在上网查阅和同学帮助下弄懂并完成。
而枚举类型中需要注意对枚举元素按常量处理,不能对它们赋值且枚举元素具有默认值,也可以在声名时另行定义枚举元素的值。枚举值可以进行关系运算,且整数值不能赋给枚举变量。
在编程过程中发现自身存在很多不足,以后会加紧学习。
https://www.cnblogs.com/changtingzao/
https://www.cnblogs.com/jackyayue/
https://www.cnblogs.com/zxz2425405395/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号