第一章 静态方法 Lambda 作为函数传递
容器:List<People> result=new ArrayList<>();
构造参数: List<People> company=Arrays.asList(new People("Bob", 20),
new People("Allen", 25),
new People("Crystal", 30));
容器遍历方法: for (People people:company)
容器添加方法:result.add(people);
传递方法格式:fIlterPeoples(company, FilteringPeoples::isOldPeole);
传递lambda格式:fIlterPeoples(company, (People p)->p.getAge()>25)
方法使用:
接受形式:fIlterPeoples(List<People> company,Predicate<People> p)
使用格式:p.test(people)
固定部分Predicate<Xxxx> xxx
xxx.test(Xxx的实例)
构造三个对象按条件筛选 1.按年龄 2.按名字开头字母
传递方法实现一遍 传递lambda表达式实现一遍
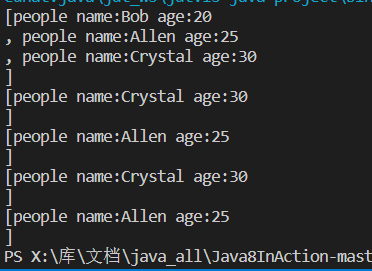
代码输出:
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class FilteringPeoples {
public static void main(String[] args){
// People p= new People("bob", 20);
List<People> company=Arrays.asList(new People("Bob", 20),
new People("Allen", 25),
new People("Crystal", 30));
System.out.println(company);
List<People> oldPeoples=fIlterPeoples(company, FilteringPeoples::isOldPeole);
System.out.println(oldPeoples);
List<People> aPeoples=fIlterPeoples(company, FilteringPeoples::isStartswithA);
System.out.println(aPeoples);
oldPeoples=fIlterPeoples(company, (People p)->p.getAge()>25);
System.out.println(oldPeoples);
aPeoples=fIlterPeoples(company, (People p)->p.getName().startsWith("A"));
System.out.println(aPeoples);
}
public static boolean isOldPeole(People people){
return people.getAge()>25;
}
public static boolean isStartswithA(People people){
return people.getName().startsWith("A");
}
public static List<People> fIlterPeoples(List<People> company,Predicate<People> p){
List<People> result=new ArrayList<>();
for (People people:company){
if(p.test(people)){
result.add(people);
}
}
return result;
}
}
class People{
String name;
Integer age;
public People(String name,Integer age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public Integer getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age){
this.age=age;
}
public String toString(){
return MessageFormat.format("people name:{0} age:{1}\n", name,age);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号