第五周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
- 本章解释了继承的概念,继承是从已有类派生新类的一个过程,是支持软件复用思想的一种方法
- 继承在子类与父类之间建立了"is a"关系,使用保留字extends
- 子类实例不依赖于父类实例
- 继承是单向的
- 不允许多重继承
- 重写(重定义)父类方法
- 子类可以间接引用私有成员
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:抽象类、抽象方法的作用是什么?
- 问题1解决方案:抽象类表示一般的概念,有一些没有声明的方法,以供子类重写。抽象方法提供方法签名,由子类继承它们。
- 问题2:保留字super的作用都有哪些?
- 问题2解决方案:可以用super引用来调用父类的构造方法,也可以进入父类的方法和实例数据(不管是否被隐藏)
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
-
问题1:在java中输入字符遇到吃回车问题
![]()
![]()
-
问题1解决方案:我先试着一共写了两个输入暂时解决了问题。接着上网查询,将nextline改为next也可解决此问题
-
问题2:在学习密码的过程中,运行非对称加密的过程中,运行程序出现了错误
![]()
-
问题2解决方案:要按照顺序依次运行程序,不能贸然改变顺序,否则会出现错误
![]()
-
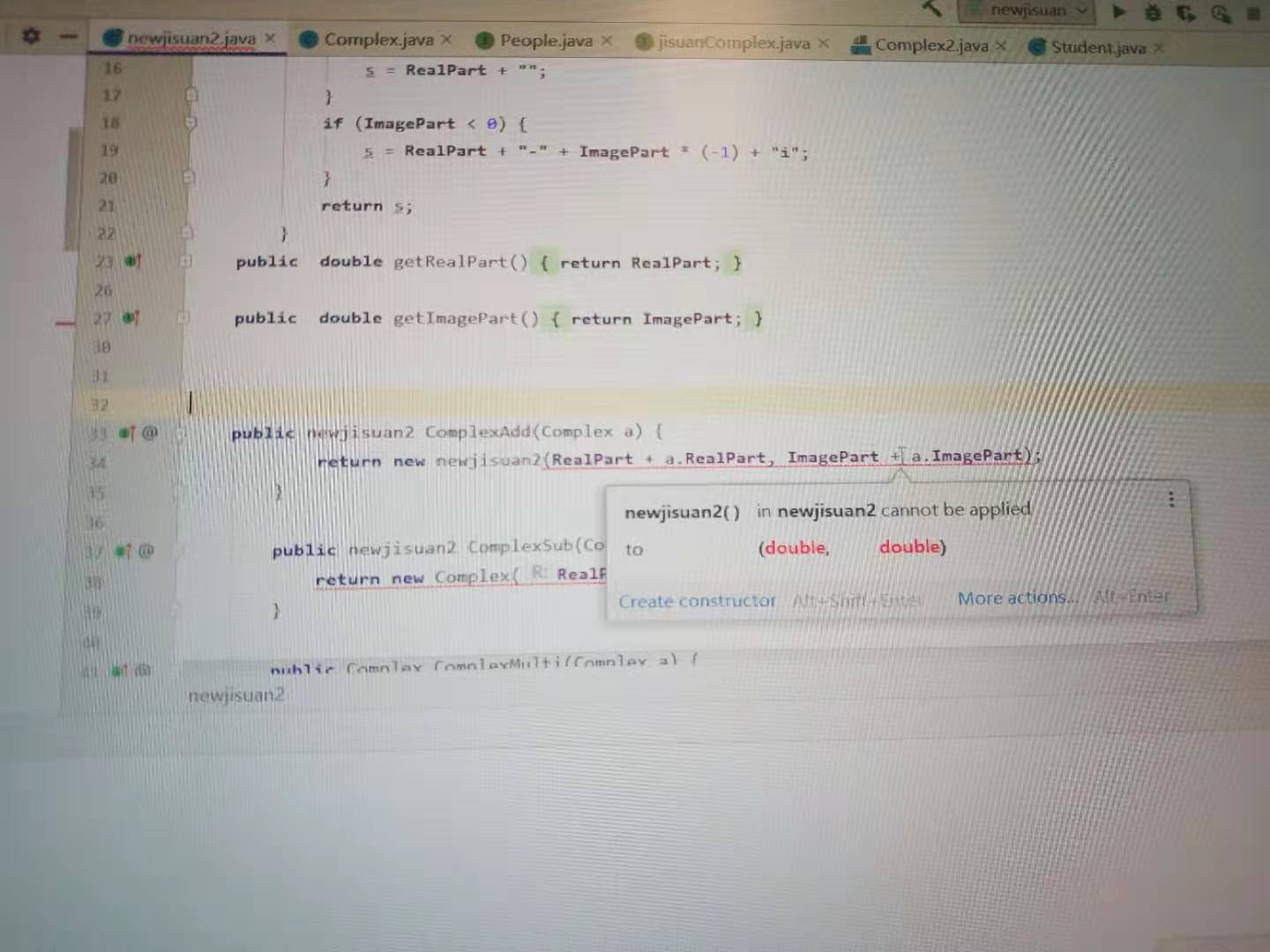
问题3:对接口的理解不到位,不会把计算器改编为接口形式
![]()
-
问题3解决方案:我对接口的理解有误,把接口的方法返回值类型几乎都改为String类型。其实接口只是简化我们的思路,可以把接口方法的返回值类型保持为已编好的Complex类型,这样会简洁高效很多
代码托管
(statistics.sh脚本的运行结果截图)
上周考试错题总结
-
Abstract methods are used when defining
- A .interface classes
- D .arrays
- E .classes that have no methods
- An interface is a class that has defined some of its components, but leaves other components (methods) for you to implement. So, these components (methods) are referred to as abstract and defined in the interface class as abstract.
- 理解:是要重写父类中的所有抽象方法,即接口让我们实现方法,而非没有方法
-
Which of the following is true regarding Java classes?
- A .All classes must have 1 parent but may have any number of children (derived or extended) classes
- E .All classes can have either 0 or 1 parent class and any number of children (derived or extended) classes
- Further, since all Java classes inherit either directly or indirectly from the Object class, all Java classes have exactly 1 parent class.
- 理解:java类与Object类有直接见解的关系,所以每个类都有一个父类,那Object类自己呢?
-
A variable declared to be of one class can later reference an extended class of that class. This variable is known as
- D .polymorphic
- The term polymorphic means that the variable can have many forms. Under ordinary circumstances, Java is strongly defined that is, a variable, once declared to be of a type, can never change to be of a different type. The exception to this is that polymorphic variables can be any type of derived class (although not at the same time, the variable can change from one type to another).
- 理解:第九章
-
In order to determine the type that a polymorphic variable refers to, the decision is made
- by the Java run-time environment at run time
- The polymorphic variable can take on many different types, but it is not know which type it has taken on until the program is executing. At the time the variable is referenced, then the decision must be made. That decision is made by the run-time environment based on the latest assignment of the variable.
- 理解:第九章
-
Using the reserved word, super, one can
- A .access a parent class'constructor(s)
- B . access a parent class'methods and instance data
- E .none of the above
- The super reserved word provides a mechanism for accessing a parent class'methods and instance data (whether or not they are hidden). In addition, a parent class'constructor(s) may be accessed using super. So the correct answer is the combination of A and B which isn't an option so the correct answer is E.
- 理解:其实两者都可以
-
Interface classes cannot be extended but classes that implement interfaces can be extended.
- B .false
- Any class can be extended whether it is an interface, implements an interface, or neither. The only exception to this is if the class is explicitly modified with the word "final" in which case it cannot be extended.
- 理解:前面带final的不行
-
If class AParentClass has a protected instance data x, and AChildClass is a derived class of AParentClass, then AChildClass can access x but can not redefine x to be a different type.
- B .false
- A derived class can redefine any of the instance data or methods of the parent class. The parent class'version is now hidden, but can be accessed through the use of super, as in super.x.
- 理解:可以用super更改x的值
-
You may use the super reserved word to access a parent class'private members.
- 理解:Super will allow access to all non-private members of a parent class but, not to the private ones.
结对及互评
评分标准
-
正确使用Markdown语法(加1分):
- 不使用Markdown不加分
- 有语法错误的不加分(链接打不开,表格不对,列表不正确...)
- 排版混乱的不加分
-
模板中的要素齐全(加1分)
- 缺少“教材学习中的问题和解决过程”的不加分
- 缺少“代码调试中的问题和解决过程”的不加分
- 代码托管不能打开的不加分
- 缺少“结对及互评”的不能打开的不加分
- 缺少“上周考试错题总结”的不能加分
- 缺少“进度条”的不能加分
- 缺少“参考资料”的不能加分
-
教材学习中的问题和解决过程, 一个问题加1分
-
代码调试中的问题和解决过程, 一个问题加1分
-
本周有效代码超过300分行的(加2分)
- 一周提交次数少于20次的不加分
-
其他加分:
- 周五前发博客的加1分
- 感想,体会不假大空的加1分
- 排版精美的加一分
- 进度条中记录学习时间与改进情况的加1分
- 有动手写新代码的加1分
- 课后选择题有验证的加1分
- 代码Commit Message规范的加1分
- 错题学习深入的加1分
- 点评认真,能指出博客和代码中的问题的加1分
- 结对学习情况真实可信的加1分
-
扣分:
- 有抄袭的扣至0分
- 代码作弊的扣至0分
- 迟交作业的扣至0分
点评模板:
-
博客中值得学习的或问题:
- 本周问题总结不够深刻全面
- 对教材内容要点概括性较强
-
代码中值得学习的或问题:
- 本周实践代码量较大
- 本周代码格式有待于进一步优化
-
基于评分标准,我给本博客打分:16分。
点评过的同学博客和代码
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
- 继承这一章难度不大,但测试结果却很糟糕,是因为有很多细节我还理解不到位,研究的不够仔细
- 在实践中,我发现我对接口的运用熟练度很差,有待于进一步提升自己的理解
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第五周 | 1600/2900 | 2/2 | 20/110 | |
| 第二周 | 300/500 | 2/4 | 18/38 | |
| 第三周 | 500/1000 | 3/7 | 22/60 | |
| 第四周 | 300/1300 | 2/9 | 30/90 |
尝试一下记录「计划学习时间」和「实际学习时间」,到期末看看能不能改进自己的计划能力。这个工作学习中很重要,也很有用。
耗时估计的公式:Y=X+X/N ,Y=X-X/N,训练次数多了,X、Y就接近了。
-
计划学习时间:20小时
-
实际学习时间:20小时
-
改进情况:有待进一步提高
(有空多看看现代软件工程 课件
软件工程师能力自我评价表)






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号