1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <typeinfo>
3
4 // definitation of Graph
5 class Graph
6 {
7 public:
8 virtual void draw() { std::cout << "Graph::draw() : just as an interface\n"; }
9 };
10
11
12 // definition of Rectangle, derived from Graph
13 class Rectangle : public Graph
14 {
15 public:
16 void draw() { std::cout << "Rectangle::draw(): programs of draw a rectangle\n"; }
17 };
18
19
20 // definition of Circle, derived from Graph
21 class Circle : public Graph
22 {
23 public:
24 void draw() { std::cout << "Circle::draw(): programs of draw a circle\n"; }
25 };
26
27
28 // definitaion of fun(): as a call interface
29 void fun(Graph* ptr)
30 {
31 std::cout << "pointer type: " << typeid(ptr).name() << "\n";
32 std::cout << "RTTI type: " << typeid(*ptr).name() << "\n";
33 ptr->draw();
34 }
35
36 // test
37 int main()
38 {
39 Graph g1;
40 Rectangle r1;
41 Circle c1;
42
43 // call by object name
44 g1.draw();
45 r1.draw();
46 c1.draw();
47
48 std::cout << "\n";
49
50 // call by object name, and using the scope resolution operator::
51 r1.Graph::draw();
52 c1.Graph::draw();
53
54 std::cout << "\n";
55
56 // call by pointer to Base class
57 fun(&g1);
58 fun(&r1);
59 fun(&c1);
60 return 0;
61 }
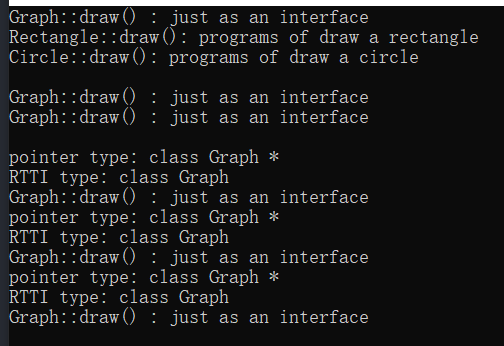
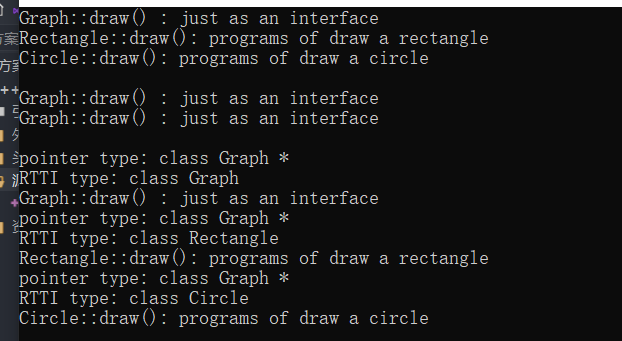
62 //本实验通过加virtual关键字可使基类指针调用派生类成员
63
64 // 总结:1、同名覆盖原则:外有内无外有效 。 内有外有(即使只是函数名相同,重载的也包括其中)内有效。 若几个基类有同名成员,则派生类将绝杀。
65 // 2、二元作用域运算符 通过:: 可以访问被隐藏的父级成员,形式:对象名.基类:: ptr->基类::
66 // 3、类型兼容:子转父,子初父&,子p*隐含转父p* attention:兼容后只能使用从基类继承来的成员
![]()
![]()
#ifndef _BATTERY_HPP
#define _BATTERY_HPP
class Battery {
private:
int capacity;
public:
Battery(int cp=70):capacity(cp){}
int get_capacity()const { return capacity; }
};
#endif
#ifndef _CAR_HPP
#define _CAR_HPP
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
class Car {
private:
string maker,model;
int year, odometers;
public:
Car(string maker,string model,int y,int od=0):maker(maker),model(model),year(y),odometers(od){}
void info()const;
void update_odometers(int od);
};
void Car::info()const {
cout << left << setw(15) << "maker:" << maker << endl
<< setw(15) << "model:" << model << endl
<< setw(15) << "year:" << year << endl
<< setw(15) << "odometers:" << odometers << endl;
}
void Car::update_odometers(int od) {
if (od < 0)cout << "wrong odometers" << endl;
else odometers = od;
}
#endif // !_CAR_HPP
#ifndef _ELECTRICCAR_HPP
#define _ELECTRICCAR_HPP
//#include<string>
#include"Car.hpp"
#include"Battery.hpp"
class ElectricCar :public Car{
private:
Battery battery;
public:
ElectricCar(std::string maker, std::string model, int y, int od=0, int cp=70) :Car(maker, model, y, od), battery(cp) {}
void info()const;
};
void ElectricCar::info()const {
Car::info();
cout << left << setw(15) << "capacity:" << battery.get_capacity() << "-kwh" << endl;
}
#endif // !_ELECTRICCAR_HPP
#include <iostream>
#include "ElectricCar.hpp"
int main()
{
using namespace std;
// test class of Car
Car oldcar("Audi", "q7", 2017);
cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl;
oldcar.update_odometers(13000);
oldcar.info();
cout << endl;
// test class of ElectricCar
ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2015);
newcar.update_odometers(1145);
cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n";
newcar.info();
return 0;
}
![]()
#ifndef _PETS_HPP
#define _PETS_HPP
#include<string>
#include<windows.h>
#include<Mmsystem.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"winmm.lib")
using namespace std;
class MachinePets {
private:
string nickName;
public:
MachinePets(const string name):nickName(name){}
virtual string talk() const { return static_cast<string>("a interface "); }
string get_nickName()const;
};
string MachinePets::get_nickName()const {
return nickName;
}
class PetCats:public MachinePets {
public:
PetCats(const string name):MachinePets(name){}
string talk()const;
};
string PetCats::talk()const {
string s = get_nickName() + " says miao wu~";
PlaySound(TEXT("./cat.wav"), NULL, SND_FILENAME| SND_NODEFAULT);
return s;
}
class PetDogs :public MachinePets {
public:
PetDogs(const string name) :MachinePets(name) {}
string talk()const;
};
string PetDogs::talk()const {
string s = get_nickName() + " says wang wang~";
PlaySound(TEXT("./dog.wav"), NULL, SND_FILENAME);
return s;
}
#endif // !_PETS_HPP
#include<iostream>
#include "pets.hpp"
void play(MachinePets* ptr)
{
std::cout << ptr->talk() << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
PetCats cat("miku");
PetDogs dog("da huang");
play(&cat);
//pause
system("pause");
play(&dog);
return 0;
}
![]()
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include <string>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
void fun01() {
map<char, char > dict{ {'0','a'},{'1','b'} ,{'2','c'} ,{'3','d'} ,{'4','e'} ,{'5','f'} ,{'6','g'} ,{'7','h'} ,{'8','i'} ,{'9','j'}};
string num;
cin >> num;
for (auto& i : num)
cout << dict[i];
cout << endl;
}
void fun02(int x,int n = 2) {
if (n == 8)cout <<showbase<< uppercase << oct << x << endl;
else if (n == 16)cout << showbase << uppercase << hex << x << endl;
else {
stack<int> s;
while (x) {
s.push(x % 2);
x /= 2;
}
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top();
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号