爬取百度热搜和数据处理
一、主题式网络爬虫设计方案
1.主题式网络爬虫名称:爬取百度热榜与数据处理
2.爬取内容:百度前十,搜索指数
3.难点:如何爬取和函数的应用
二、主题页面的结构特征分析
分析网页
得到url为http://top.baidu.com/buzz?b=341&fr=topindex
3.节点查找方法
js = json.loads(html) # 定位到albumTime和albumCount albumlist = js['data']['album']['list'] for song in albumlist: albumtime = song['publicTime'] albumsongs = song['song_count'] #判断,将符合条件的值加入value中。 if eval(albumtime.split('-')[0]) in all_albumcount: temp = eval(albumtime.split('-')[0]) all_albumcount[temp] += eval(str(albumsongs))
三、网络爬虫程序设计
import requests from lxml import etree head = {} url = "http://top.baidu.com/buzz?b=341&fr=topindex" head["User-Agent"] = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0" head["Accept"]= "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8" head["Accept-Language"]= "zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2" head["Connection"] = "keep-alive" def main(): print("百度热搜top10: ") res = requests.get(url , headers = head) with open("html.txt", "wb") as f: f.write(res.content) html = etree.parse('html.txt' , etree.HTMLParser(encoding='gbk')) top_list = html.xpath('//a[@class="list-title"]/text()') num_search = html.xpath('//span[@class="icon-rise"]/text()') for i , j in zip(top_list[:10] , num_search[:10]): print(i ,"搜索指数为:" , j ) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
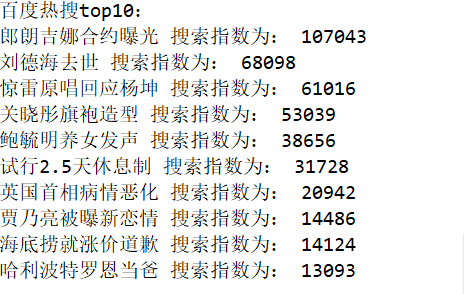

直方图
def ChartBar(xaxis, yaxis): plt.figure() plt.bar(left=xaxis, height=yaxis, color='b', width=0.5) plt.ylabel('top_list')
plt.xlabel('num_search') plt.title('Barplot')
# 保存程序结果,数据持久化 plt.savefig('Bar', dpi=600) print('条形图保存成功') plt.show()
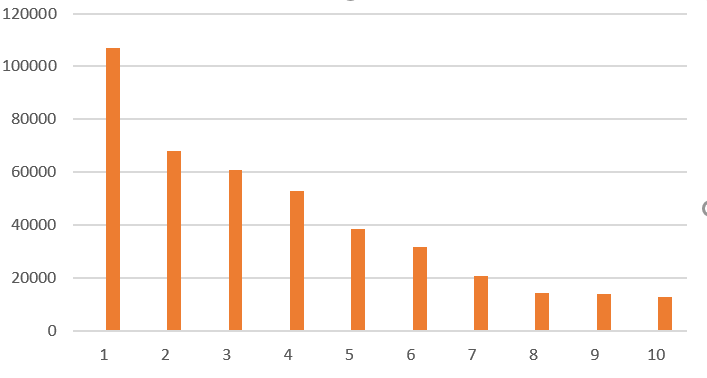
折线图
def ChartBroken(x, y): #图片在额外的窗口显示 plt.figure() plt.plot(x, y) #y轴命名 plt.ylabel('num_search') #x轴命名 plt.xlabel('top_list') plt.axis([0, 120000, 0, 20000]) plt.title('Brokenplot') # 保存程序结果,数据持久化 plt.savefig('Broken', dpi=600) print('折线图保存成功') plt.show()
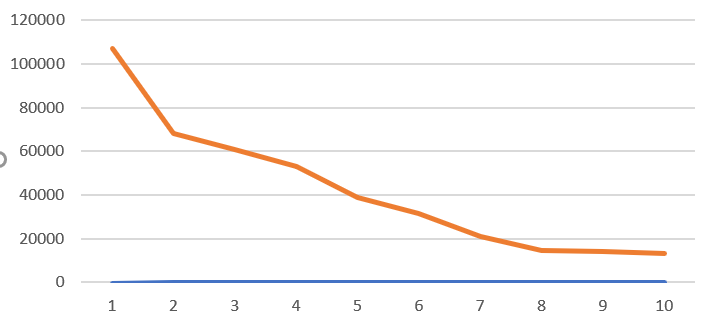
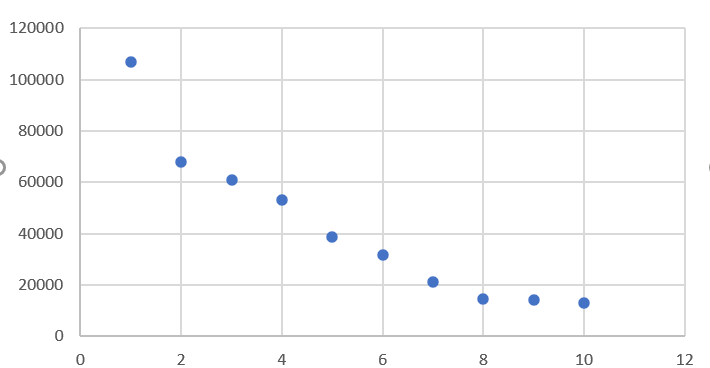
散点图
def sandian(): x = df['排名'] y = df['热度'] plt.xlabel('排名') plt.ylabel('热度') plt.scatter(x,y,color="red",label=u"热度分布数据",linewidth=2) plt.title("排名与热度散点图") plt.legend() plt.show() sandian()
代码汇总
import requests from lxml import etree head = {} url = "http://top.baidu.com/buzz?b=341&fr=topindex" head["User-Agent"] = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0" head["Accept"]= "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8" head["Accept-Language"]= "zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2" head["Connection"] = "keep-alive" def main(): print("百度热搜top10: ") res = requests.get(url , headers = head) with open("html.txt", "wb") as f: f.write(res.content) html = etree.parse('html.txt' , etree.HTMLParser(encoding='gbk')) top_list = html.xpath('//a[@class="list-title"]/text()') num_search = html.xpath('//span[@class="icon-rise"]/text()') for i , j in zip(top_list[:10] , num_search[:10]): print(i ,"搜索指数为:" , j ) if __name__ == '__main__': main() js = json.loads(html) # 定位到albumTime和albumCount albumlist = js['data']['album']['list'] for song in albumlist: albumtime = song['publicTime'] albumsongs = song['song_count'] #判断,将符合条件的值加入value中。 if eval(albumtime.split('-')[0]) in all_albumcount: temp = eval(albumtime.split('-')[0]) all_albumcount[temp] += eval(str(albumsongs)) def ChartBar(xaxis, yaxis): plt.figure() plt.bar(left=xaxis, height=yaxis, color='b', width=0.5) plt.ylabel('top_list') plt.xlabel('num_search') plt.title('Barplot') # 保存程序结果,数据持久化 plt.savefig('Bar', dpi=600) print('条形图保存成功') plt.show() def ChartBroken(x, y): #图片在额外的窗口显示 plt.figure() plt.plot(x, y) #y轴命名 plt.ylabel('num_search') #x轴命名 plt.xlabel('top_list') plt.axis([0, 120000, 0, 20000]) plt.title('Brokenplot') # 保存程序结果,数据持久化 plt.savefig('Broken', dpi=600) print('折线图保存成功') plt.show() def sandian(): x = df['排名'] y = df['热度'] plt.xlabel('排名') plt.ylabel('热度') plt.scatter(x,y,color="red",label=u"热度分布数据",linewidth=2) plt.title("排名与热度散点图") plt.legend() plt.show() sandian()
四.结论
1.根据图形表明,热度是随着排名的递增而递增的。排名越高,热度越高
2.在这次对百度热榜的分析的过程中,我学习到了很多函数的用法,也碰到了很多难题,但最后都依靠观看视频和请教别人解决。提高了我对Python的兴趣



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号