实验6 文件I/O与异常处理
实验任务一:
源码:

#pragma once #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <string> struct Contestant { long id; // 学号 std::string name; // 姓名 std::string major; // 专业 int solved; // 解题数 int penalty; // 总罚时 }; // 重载<< // 要求:姓名/专业里不含空白符 inline std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Contestant& c) { out << std::left; out << std::setw(15) << c.id << std::setw(15) << c.name << std::setw(15) << c.major << std::setw(10) << c.solved << std::setw(10) << c.penalty; return out; } // 重载>> inline std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, Contestant& c) { in >> c.id >> c.name >> c.major >> c.solved >> c.penalty; return in; }

#pragma once #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "contestant.hpp" // ACM 排序规则:先按解题数降序,再按罚时升序 inline bool cmp_by_solve(const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) { if(a.solved != b.solved) return a.solved > b.solved; return a.penalty < b.penalty; } // 将结果写至任意输出流 inline void write(std::ostream& os, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { for (const auto& x : v) os << x << '\n'; } // 将结果打印到屏幕 inline void print(const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { write(std::cout, v); } // 将结果保存到文件 inline void save(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { std::ofstream os(filename); if (!os) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); write(os, v); } // 从文件读取信息(跳过标题行) inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { std::ifstream is(filename); if (!is) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); std::string line; std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题 std::vector<Contestant> v; Contestant t; int seq; while (is >> seq >> t) v.push_back(t); return v; }
 task1.cpp
task1.cpp运行结果测试截图:
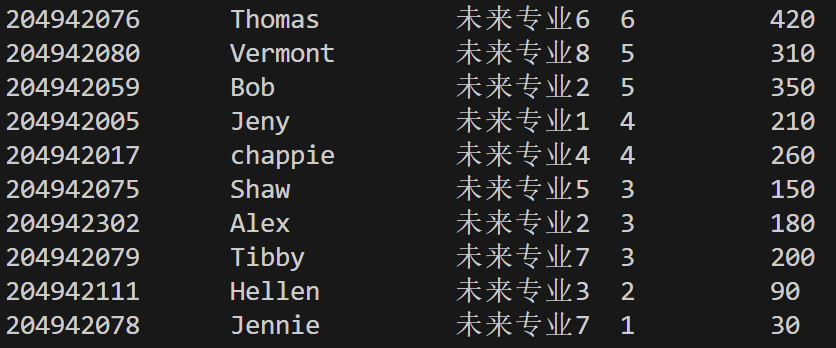
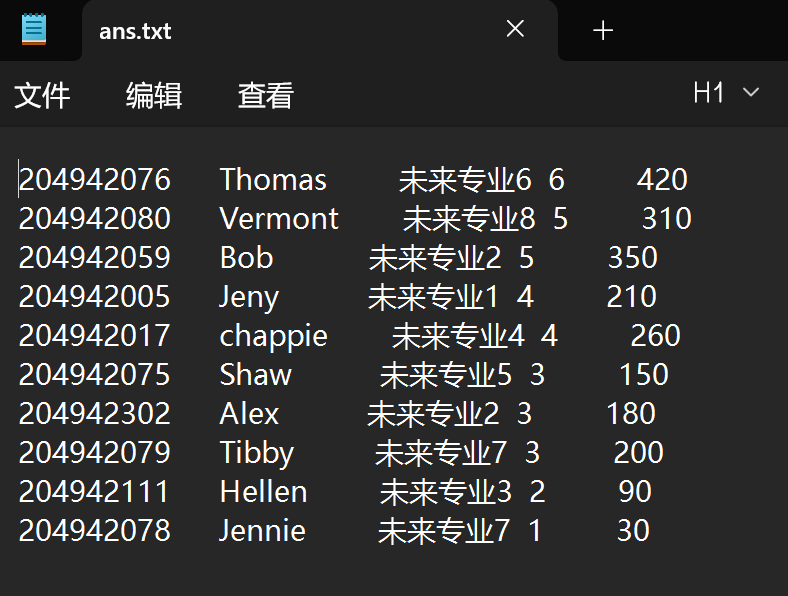
回答问题:
问题1:流操作与代码复用
观察 print() 与 save() 的实现,均在内部调用 write() :
(1) write() 的参数类型是 std::ostream& ,它为什么能同时接受 std::cout 和 std::ofstream 对象作为实参?
答:因为cout是ostream类的对象;ofsream是ostream的派生类,基类引用可以绑定到派生类对象。
(2)如果要把结果写到其他设备,只要该设备也提供std::ostream 接口,还需改动 write() 吗?
答:不需要改动write()。write()只依赖于ostream接口,新设备需要提供输出能力,即能实现ostream接口即可。
问题2:异常处理与捕获
在代码中找到两处 throw 语句,说明:
(1)什么情况下会抛出异常;
答:①打开os文件失败。
1 if (!os) 2 throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename);
②读取is文件失败。
1 if (!is) 2 throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename);
(2)异常被谁捕获、做了哪些处理。
答:异常被app()函数中catch块捕获,并存入exception类型引用e,用cerr无缓冲立刻显示e.what()的错误提示,并立即return防止程序继续执行错误代码。
1 try { 2 contestants = load(in_file); 3 std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve); 4 print(contestants); 5 save(out_file, contestants); 6 } catch (const std::exception& e) { 7 std::cerr << e.what() << '\n'; 8 return; 9 }
问题3:替代写法
函数app中 std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve);参数 cmp_by_solve 换成下面的lambda表达式是否可以?功能、性能、结果是否一致?
1 [](const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) { 2 return a.solved != b.solved ? a.solved > b.solved 3 : a.penalty < b.penalty;}
答:可以,两者功能、性能、结果基本一致。用lambda表达式使代码更易理解、简洁,但是可读性、复用性较差。
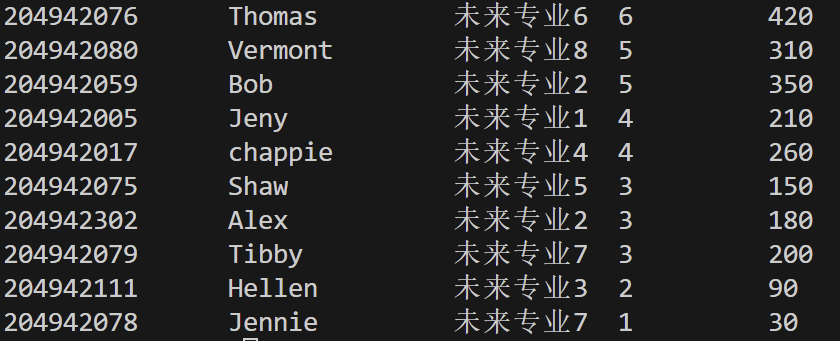
问题4:数据完整性与代码健壮性
把 in_file 改成 "./data_bad.txt" (内含空白行或字段缺失),重新编译运行:
(1)观察运行结果有什么问题?给出测试截图并分析原因。
答:问题是Thomas的解题数和总罚时数据错误、缺失了Vermont的全部信息。原因是txt中没有提供Thomas的解题数和总罚时数据,导致错位读取到了下一组的"8"、"204942078"。而空白行被读入并存储,使最后一行Vermont无法被读入。

(2)思考:如何修改函数 std::vector load(const std::string& filename) ,使其提示出错行号并跳过有问题的数据行,同时让程序继续执行?(选答*)
答:因为while中使用getline逐行获得了行信息,所以下面要使用istringstream类型的对象iss,从line创建字符串流,而非文件流is。初始化line_num来追踪行号以提示出错行号。使用if(line.empty())检测有问题的数据行,使用continue跳过。解析失败时用cerr输出错误信息,但不抛出异常以便程序继续执行。
inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { std::ifstream is(filename); if (!is) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); std::string line; std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题 int line_num = 1; std::vector<Contestant> v; while (std::getline(is, line)) { line_num++; // 跳过空行 if (line.empty()) { std::cerr << "警告:第" << line_num << "行为空行,跳过" << std::endl; continue; } Contestant t; int seq; std::istringstream iss(line); if (iss >> seq >> t.id >> t.name >> t.major >> t.solved >> t.penalty) { v.push_back(t); } else { // 读取失败,报告错误但继续 std::cerr << "错误:第" << line_num << "行格式错误: " << line << std::endl; } } return v; }
实验任务二:
源码:

#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <string> class Student { public: Student() = default; ~Student() = default; const std::string get_major() const; int get_grade() const; friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s); friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s); private: int id; std::string name; std::string major; int grade; // 0-100 };

#include "student.hpp" #include <iomanip> const std::string Student::get_major() const { return major; } int Student::get_grade() const { return grade; } // 格式化输出,列宽与 stumgr.cpp 保持一致 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s) { const int w_id = 6; const int w_name = 12; const int w_major = 12; const int w_grade = 6; auto flags = os.flags(); std::streamsize prec = os.precision(); os << std::left << std::setw(w_id) << s.id << std::setw(w_name) << s.name << std::setw(w_major)<< '\t' << s.major << std::right << std::setw(w_grade) << s.grade; os.flags(flags); os.precision(prec); return os; } std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s) { is >> s.id >> s.name >> s.major >> s.grade; return is; }

#pragma once #include <string> #include <vector> #include "student.hpp" class StuMgr { public: void load(const std::string& file); // 加载数据文件(空格分隔) void sort(); // 排序: 按专业字典序升序、同专业分数降序 void print() const; // 打印到屏幕 void save(const std::string& file) const; // 保存到文件 private: void write(std::ostream &os) const; // 把数据写到任意输出流 private: std::vector<Student> students; };

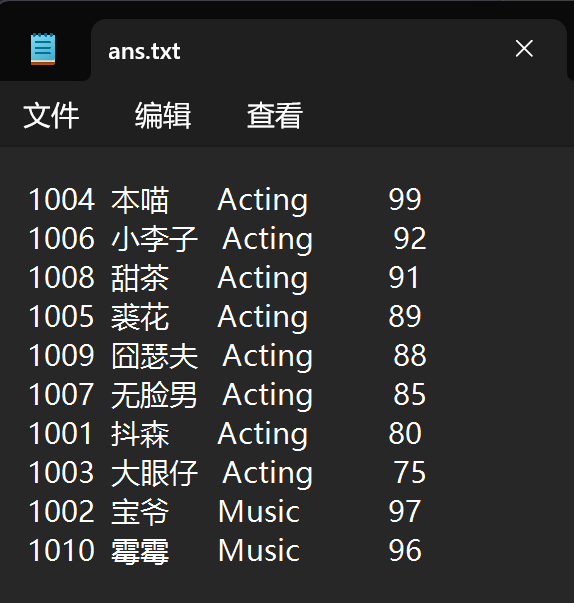
#include "stumgr.hpp" #include "student.hpp" #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <stdexcept> void StuMgr::load(const std::string& file) { students.clear(); std::ifstream ifs(file); if (!ifs) { throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + file); } // 跳过第一行表头 std::string header; std::getline(ifs, header); Student s; while (ifs >> s) { students.push_back(s); } } void StuMgr::sort() { if (students.empty()) { std::cout << "(empty)\n"; std::cout << "排序已完成\n"; return; } std::sort(students.begin(), students.end(), [](const Student& a, const Student& b) { if (a.get_major() != b.get_major()) return a.get_major() < b.get_major(); return a.get_grade() > b.get_grade(); }); std::cout << "排序已完成\n"; } void StuMgr::write(std::ostream &os) const { const int w_id = 6; const int w_name = 12; const int w_major = 12; const int w_grade = 6; for (const auto& s : students) { os << s << '\n'; } } void StuMgr::print() const { write(std::cout); } void StuMgr::save(const std::string& file) const { std::ofstream ofs(file); if (!ofs) { throw std::runtime_error("无法创建/打开文件: " + file); } write(ofs); }

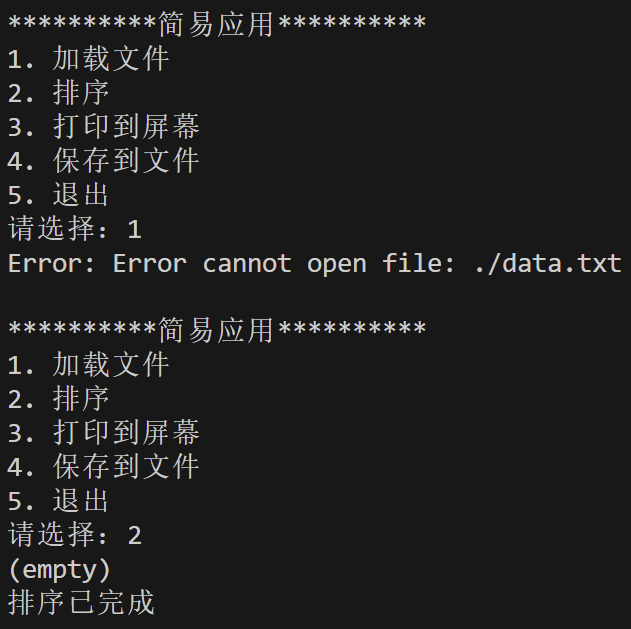
#include <iostream> #include <limits> #include <string> #include "stumgr.hpp" const std::string in_file = "./data.txt"; const std::string out_file = "./ans.txt"; void menu() { std::cout << "\n**********简易应用**********\n" "1. 加载文件\n" "2. 排序\n" "3. 打印到屏幕\n" "4. 保存到文件\n" "5. 退出\n" "请选择:"; } void app() { StuMgr mgr; while(true) { menu(); int choice; std::cin >> choice; try { switch (choice) { case 1: mgr.load(in_file); std::cout << "加载成功\n"; break; case 2: mgr.sort(); break; case 3: mgr.print(); std::cout << "打印已完成\n"; break; case 4: mgr.save(out_file); std::cout << "导出成功\n"; break; case 5: return; default: std::cout << "不合法输入\n"; } } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cout << "Error: " << e.what() << '\n'; } } } int main() { app(); }
运行结果测试截图:
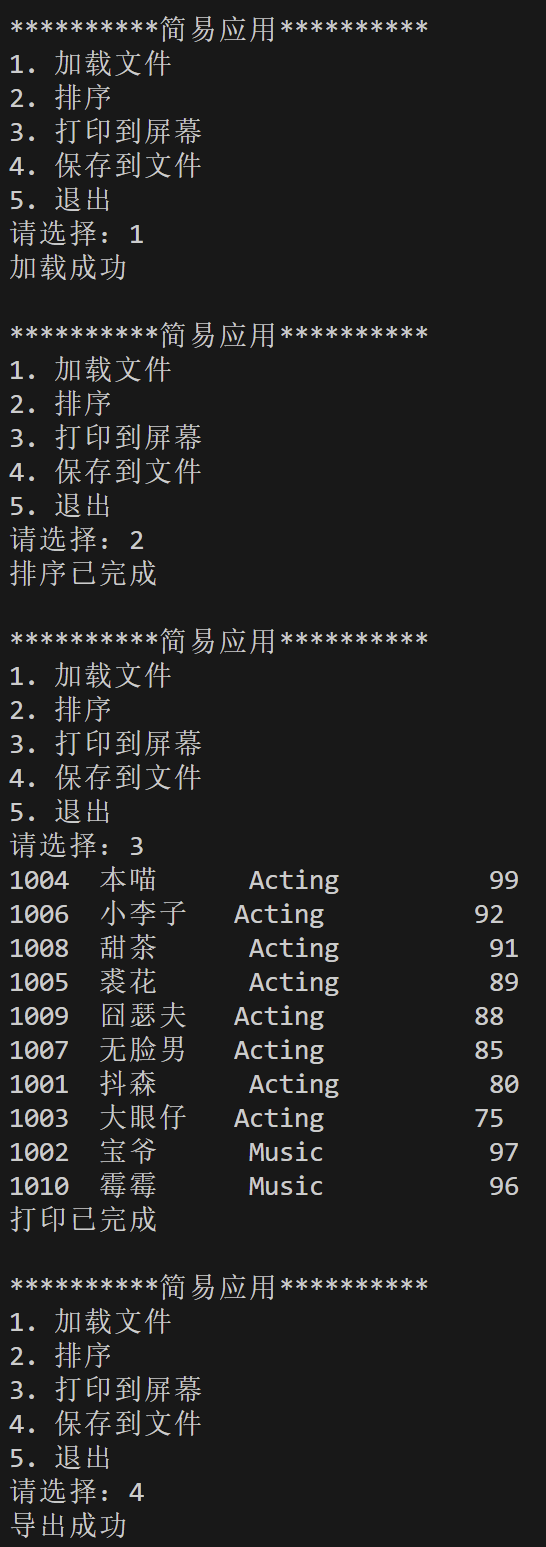




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号