2023南海区赛总结
posted on 2023-12-22 05:17:14 | under 笔记 | source
T1
首先将数列翻转,然后下标 \(1...n\)。不难 \(i\) 询问实质上就是让 \(a_1...a_i=0\) 的最小代价,那么直接模拟这个过程,可以使用指针 \(k\) 指向以 \(i\) 为下标的一段全是 \(1\) 的结尾,有 \(ans+=k-i+1\)。动态维护 \(k\) 即可。
\(i,k\) 单调不减,复杂度 \(O(n)\)。注意细节。
T2
首先“优美棋盘”就两种情况,即左上角是 \(B/W\)。那么在“优美棋盘”上修改 \(d\) 个元素就得到了一个代价为 \(d\) 的普通棋盘。
可以发现 \(ans=2*C_{r*c}^{d}\),逆元、杨辉三角均可解。
注意特判:
- \(r*c=2*d\):此时不需要乘二,原因如下:
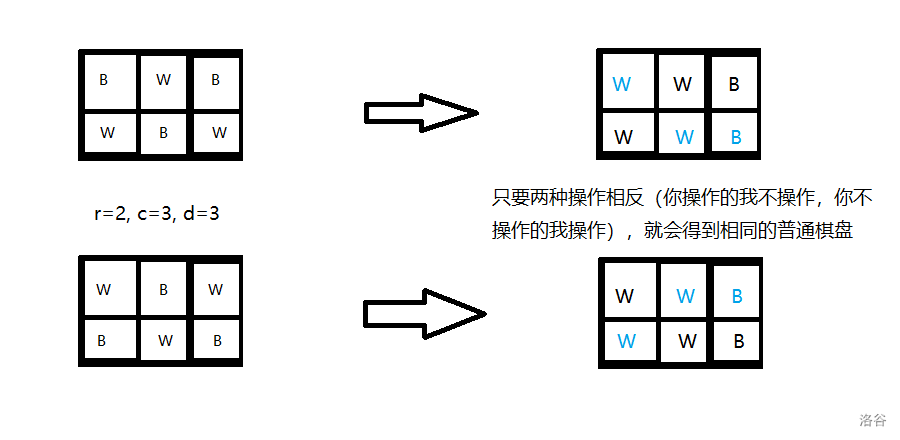
- \(r*c>2*d\):答案是 \(0\)。
注:杨辉三角可解的原因是 \(d\) 较小而 \(r*c\) 较大,于是 \(C\) 数组的第二维不用开太大。
T3
\(\rm bfs\) 硬上即可,应该没有更优解法了。
可以有一个优化:记 \(dis\) 表示最少步数,\((x,y)\) 在向某个方向前进时,若有 \(dis_{x,y} \ge dis_{xx,yy}\),那么可以直接结束该方向的遍历:
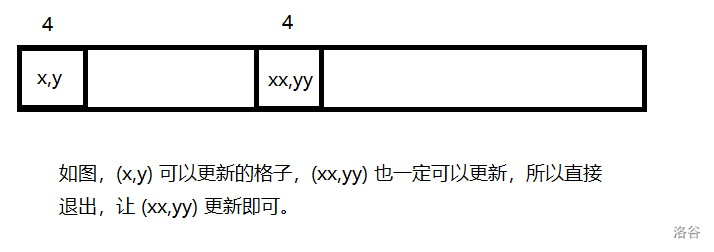
T4
一眼背包。定义 \(f_{i,j}\) 表示总重量为 \(i\),多吃了 \(j\) 个。注意 \(i=S\) 时可表示总重量 \(\ge S\),于是人人为我的做法是不行的,我为人人才可做。
当然也可以贪心加动规,即先取前 \(t\) 个最大的,然后剩下的使用动规。复杂度较优。
注:不用贪心的话,需要先从小到大排序,否则您会被这组数据卡掉:
5 8 1
3 49 49 7 8
答案是 \(105\),没猜错的话您会输出 \(101\)。
T5
是原,二维滑动窗口。
T6
对于每个人,考虑他对答案的影响。
首先处理出 \(c_i\) 表示这个人总分为 \(i\) 时的方案数,很像背包,要用前缀和优化。
然后 \(f_i\) 表示目前为止,最后一个人总分为 \(i\) 时的方案数,有 \(f_i*c_j\to f_j,i>j\),依然可以前缀和优化。
总结
今年第一题远远难于往年,后面难度就降下来了,假如考场 \(T1\) 不想歪耽误时间的话也许可以阿克?
难度大概:黄黄绿绿绿绿。
解题思想上没有太多启示,总结下考场心态相关吧:
- 仔细看题!
- 不要被某一道题吓倒,以平常心面对考试。
- 想出一道题后,先理清思路再写。
已经初二了,要加把劲啊!!!
程序
T1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n, ans, r;
bool can;
char a[N];
signed main(){
scanf("%lld %s", &n, a + 1);
can = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) if(a[i] == '1') can = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= n >> 1; ++i) swap(a[i], a[n - i + 1]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
r = max(r, i);
while(a[r + 1] == '1' && r < n) ++r;
if(a[i] == '1'){
if(r == n) can = true;
else ans += r - i + 1, a[r + 1] = '1', ++r;
}
if(can) ans = -1;
printf("%lld ", ans);
}
return 0;
}
T2
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e2 + 5, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int r, c, d, C[N * N][N];
signed main(){
for(int i = 0; i < N * N; ++i){
C[i][0] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= min(i, N - 1); ++j)
C[i][j] = (C[i - 1][j] + C[i - 1][j - 1]) % mod;
}
cin >> r >> c >> d;
if(r * c == 2 * d) cout << C[r * c][d];
else if(r * c < 2 * d) cout << 0;
else cout << C[r * c][d] * 2 % mod;
return 0;
}
T3
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, m, k, r1, c1, r2, c2, cnt;
int fx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, fy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
string s[N];
signed main(){
cin >> n >> m >> k;
cin >> r1 >> c1 >> r2 >> c2;
int dis[n + 5][m + 5], vis[n + 5][m + 5];
char c[n + 5][m + 5];
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis), dis[r1][c1] = 0;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
queue<pair<int, int> >q; q.push({r1, c1});
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%s", c[i] + 1);
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front().first, y = q.front().second, xx, yy;
if(++cnt >= 80000000) break; //玄学优化
if(x == r2 && y == c2){
printf("%d", dis[x][y]);
return 0;
}
vis[x][y] = 0;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
for(int j = 1; j <= k; ++j){
xx = x + fx[i] * j, yy = y + fy[i] * j;
if(xx < 1 || xx > n || yy < 1 || yy > m || c[xx][yy] == '@') break;
if(dis[x][y] >= dis[xx][yy]) break;
if(dis[x][y] + 1 < dis[xx][yy]){
dis[xx][yy] = dis[x][y] + 1;
if(!vis[xx][yy]){
vis[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push({xx, yy});
}
}
}
}
printf("-1");
return 0;
}
T4
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e2 + 5, M = 1e4 + 5;
int n, a, b[N], f[M][N][2], s, t, ans, inf, res, f2[M][N];
signed main(){
cin >> n >> s >> t;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%lld", &b[i]);
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + n);
memset(f, -0x3f, sizeof f), inf = ans = f[0][0][0];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
a = b[i];
res += a;
f[0][0][0] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j <= s; ++j)
for(int p = 0; p <= t; ++p)
f2[j][p] = max(f[j][p][0], f[j][p][1]);
//f0/1:ai 是否已经被计算过
for(int j = 0; j <= s; ++j)
for(int p = 0; p <= t; ++p){
if(f2[j][p] == inf) continue;
if(j < s)
f[min(j + a, s)][p][1] = max(f[min(j + a, s)][p][1], f2[j][p] + a);
f[j][p + 1][0] = max(f[j][p + 1][0], f2[j][p] + a);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i <= s; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j <= t; ++j)
ans = max(ans, max(f[i][j][0], f[i][j][1]));
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
T5
T6
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 25, M = 2e5 + 5, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int t, p[5], n, c[M], f[M], qs[M], S, ans;
char sub[5];
signed main(){
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> p[1] >> p[2] >> p[3] >> n;
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
S = p[1] + p[2] + p[3]; ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
scanf("%s", sub + 1);
bool flag = false;
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; ++j)
if(sub[j] == 'Y'){
if(!flag){
flag = true;
for(int k = 1; k <= p[j]; ++k) c[k] = 1;
}
else{
memset(qs, 0, sizeof qs);
for(int k = 1; k <= S; ++k) qs[k] = (qs[k - 1] + c[k]) % mod;
for(int k = 1; k <= S; ++k) c[k] = ((qs[k - 1] - qs[max(0ll, k - 1 - p[j])]) % mod + mod) % mod;
}
}
if(!flag) c[0] = 1;
if(i > 1){
memset(qs, 0, sizeof qs);
for(int j = 0; j <= S; ++j) qs[j] = (qs[j - 1] + f[j]) % mod;
for(int j = 0; j <= S; ++j)
f[j] = ((qs[S] - qs[j]) % mod + mod) % mod * c[j] % mod;
}
else
for(int j = 0; j <= S; ++j) f[j] = c[j];
}
for(int i = 0; i <= S; ++i)
ans = (ans + f[i]) % mod;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号