线程处理
线程分为前台线程和后台线程,一个进程里至少要有一个前台线程若干后台线程,如果前台线程结束了,意味着进程也就退出了;
线程主要有4种状态:Unstarted、Running、WaitSleepJoin(阻塞)、Stopped(停止)


c# Thread.Abort()和Thread.ResetAbort()的使用
Thread类的Abort()方法用于终止正在运行的线程(.net core中Abort()方法虽然存在,但是调用它会引发PlatformNotSupportedException的异常提示)。它可以强行终止线程,而不管线程是否是sleep中。
执行了Abort()后,被终止的线程就会继续运行catch{}finally{}块中代码,因为是强行终止,catch块之后的语句则不再运行。除非在catch语句中执行Thread.ResetAbort()这个静态方法。
先举例没有ResetAbort()的情况:
<span style="font-size:14px;">using System; using System.Threading; namespace AbortAndResetabortExp { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(DoWork); t.Name = "八戒"; t.Start(); Thread.Sleep(10000); Console.WriteLine("悟空:八戒,该起床了"); t.Abort(); } static void DoWork() { try { while (true) { Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":呼呼~~~~~"); Thread.Sleep(1000); } } catch (ThreadAbortException e) { Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":还早呢,我还要再睡会"); Thread.ResetAbort(); } for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ":呼呼~~~~~"); Thread.Sleep(1000); } } } }</span>
实例中,主线程启动“八戒”线程,使其“呼呼”睡觉。10秒钟后,主线程通过调用“八戒”线程的Abort方法中止“八戒”线程,“八戒”线程的Abort方法被调用后会触发ThreadAbortException异常,“八戒”线程捕获到该异常后,使用ResetAbort方法取消中止线程的操作,因为他还没有睡够呢。
整个程序的执行结果如下图所示,从结果中可以看出,调用ResetAbort方法后,线程仍然在执行。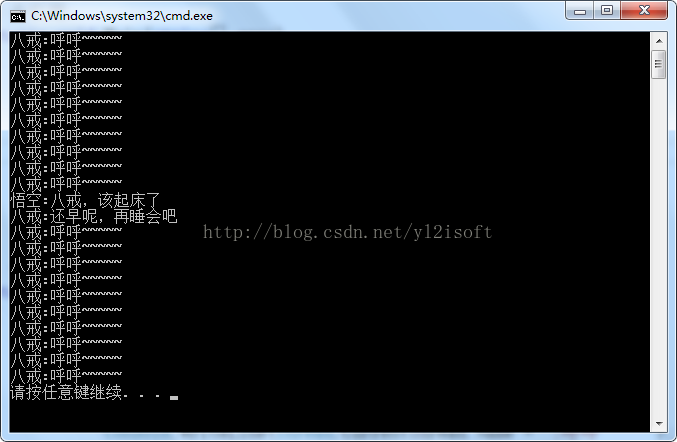
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ThreadDemo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ThreadLocalTest(); Console.ReadKey(); } // 线程局部存储区(TLS),是操作系统为线程提供的一个私密空间,其他线程不能访问; #region 1.使用ThreadStatic特性 static void ThreadStaticTest() { Test.a = 100; Test.b = "hello"; Console.WriteLine($"子线程未运行时,主线程中Test.a={ Test.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程未运行时,主线程中Test.b={ Test.b}"); var worker = new Thread(go); worker.Start(); worker.Join(); //主线程中的Test.a、Test.b不会改变,因为他们是TLS变量 Console.WriteLine($"子线程执行完成,主线程中Test.a={ Test.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程执行完成,主线程中Test.b={ Test.b}"); } static void go() { Test.a = 99; Test.b = "world"; Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改了Test.a={Test.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改了Test.b={Test.b}"); } public class Test { [ThreadStatic] public static int a;//TLS 变量 [ThreadStatic] public static string b;//TLS 变量 } #endregion #region 2.使用Thread的2个方法GetData和SetData //如果不希望一开始就定义TLS变量,可以使用Thread的2个方法GetData和SetData,在运行的时候才将数据存进TLS中;在使用GetData和SetData时需求先申请 //一个“数据槽”(代表TLS上的空间)。数据槽分为命名和未命名的,通过GetNamedDataSlot(数据槽名)申请访问一个命名数据槽,如果数据槽不存在会新建一个。 //通过AllocateDataSlot方法申请一个未命名的数据槽,必须保存该方法的返回值,才能继续后面操作。 public class TestB { public int a; public string b; } static void threadSlotTest() { var testB = new TestB() { a = 100, b = "hello" }; //把a放进槽中,它的值不会被其他线程更改 Thread.SetData(Thread.GetNamedDataSlot("slot1"), testB.a); Console.WriteLine($"子线程未运行时,主线程中b.a={ testB.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程未运行时,主线程中b.b={ testB.b}"); var worker = new Thread(() => go2(testB)); worker.Start(); worker.Join(); //把数据拿出来 var data = (int)Thread.GetData(Thread.GetNamedDataSlot("slot1")); //a依然是100 Console.WriteLine($"子线程执行完成,主线程中a={ data}"); //b被修改成了world Console.WriteLine($"子线程执行完成,主线程中b={ testB.b}"); } static void go2(TestB testB) { //子线程无法访问其他线程的数据槽,因此这句代码会报错,因为子线程的slot1中没有数据 // var a=(int)Thread.GetData(Thread.GetNamedDataSlot("slot1")); testB.a = 999; testB.b = "world"; Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改了 testB.a={testB.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改了 testB.b={testB.b}"); } #endregion #region 3.ThreadLocal<T>是.netframework4.0才加入的,使用方法比getdata和setdata方便而且还消除了装箱。使用ThreadLocal<T>之后,T类型中的 // 所有字段都会使用TLS。 static void ThreadLocalTest() { //创建 ThreadLocal<TestB>对象并设置默认值,每个线程都将拥有一个 TestB独立的副本,对它的访问也会自动使用TLS var t = new ThreadLocal<TestB>( () => { return new TestB() { a = 100, b = "hello" }; }); Console.WriteLine($"子线程未执行时,主线程中Test.a={t.Value.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程未执行时,主线程中Test.b={ t.Value.b}"); var worker = new Thread(()=> { go3(t); }); worker.Start(); worker.Join(); //仍是原来的值 Console.WriteLine($"子线程执行后,主线程中Test.a={t.Value.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程执行后,主线程中Test.b={ t.Value.b}"); } static void go3(ThreadLocal<TestB> t) { Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改前a={t.Value.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改前b={t.Value.b}"); //子线程会修改它自己的TLS 上的值 t.Value.a = 99; t.Value.b = "world"; Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改后a={t.Value.a}"); Console.WriteLine($"子线程中修改后b={t.Value.b}"); } #endregion } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号