在 Keil 上使用 TVM 在 AVH 环境下运行 Paddle 模型
1 简介
截止至目前为止,在裸机设备上运行机器学习任务是比较困难的,其难点我认为主要集中在运行性能有限、跨设备难度高、跨框架难度高这两点上。在裸机上部署机器学习任务时,除了芯片产商自带的推理框架外,比较经典的跨设备框架就是 TFLite,但是 TFLite 也有其自己的缺点,那就是不能跨框架。TVM 推出了 microTVM 很好的解决了上述问题(即使性能上对比 TFLite 确实还有所差距),为任何人轻松快速地实现这一目标奠定开源基础。
microTVM 在性能上虽然和 TFLite 还有所差距,但是其兼顾了性能、跨设备、跨框架三个痛点问题,已经逐渐成为了裸机设备上部署机器学习模型的新宠。TVM 的官方教程使用的也是 AVH,但是其没有提供 Keil 例程,对个人开发者不太友好,这里介绍一下如何移植 TVM 项目到 Keil 上。
2 前期准备
为了便捷开发,我使用的是 AVH 来运行代码。在继续开始之前,请至少浏览以下文章,保证你对 TVM 和如何在 Keil 上运行 AVH 程序有一定的了解。
【Keil&AVH】使用Keil新建Arm Visual Hardware(AVH)项目
3 使用 TVM 编译模型并生成代码
我对 Paddle 模型比较熟悉,因此我以 Paddle 模型作为例子来展示如何编译。
# Download paddlepaddle model
wget "https://paddle-imagenet-models-name.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph/inference/PPLCNet_x0_75_infer.tar"
tar -xf PPLCNet_x0_75_infer.tar
# Export paddlepaddle model to onnx model
paddle2onnx --model_dir "${PWD}/PPLCNet_x0_75_infer" \
--model_filename inference.pdmodel \
--params_filename inference.pdiparams \
--save_file inference.onnx
# Convert onnx model to tvm model
python3 -m tvm.driver.tvmc compile --target=cmsis-nn,c \
--target-cmsis-nn-mcpu=cortex-m55 \
--target-c-mcpu=cortex-m55 \
--runtime=crt \
--executor=aot \
--executor-aot-interface-api=c \
--executor-aot-unpacked-api=1 \
--pass-config tir.usmp.enable=1 \
--pass-config tir.usmp.algorithm=hill_climb \
--pass-config tir.disable_storage_rewrite=1 \
--pass-config tir.disable_vectorize=1 \
inference.onnx \
--output-format=mlf \
--model-format=onnx \
--input-shapes x:[1,3,224,224] \
--module-name=cls \
--output=cls.tar
tar -xvf cls.tar
接下来你会得到 cls 文件夹,将其拷贝到 Keil 项目的根目录下,文件夹中的内容如下:
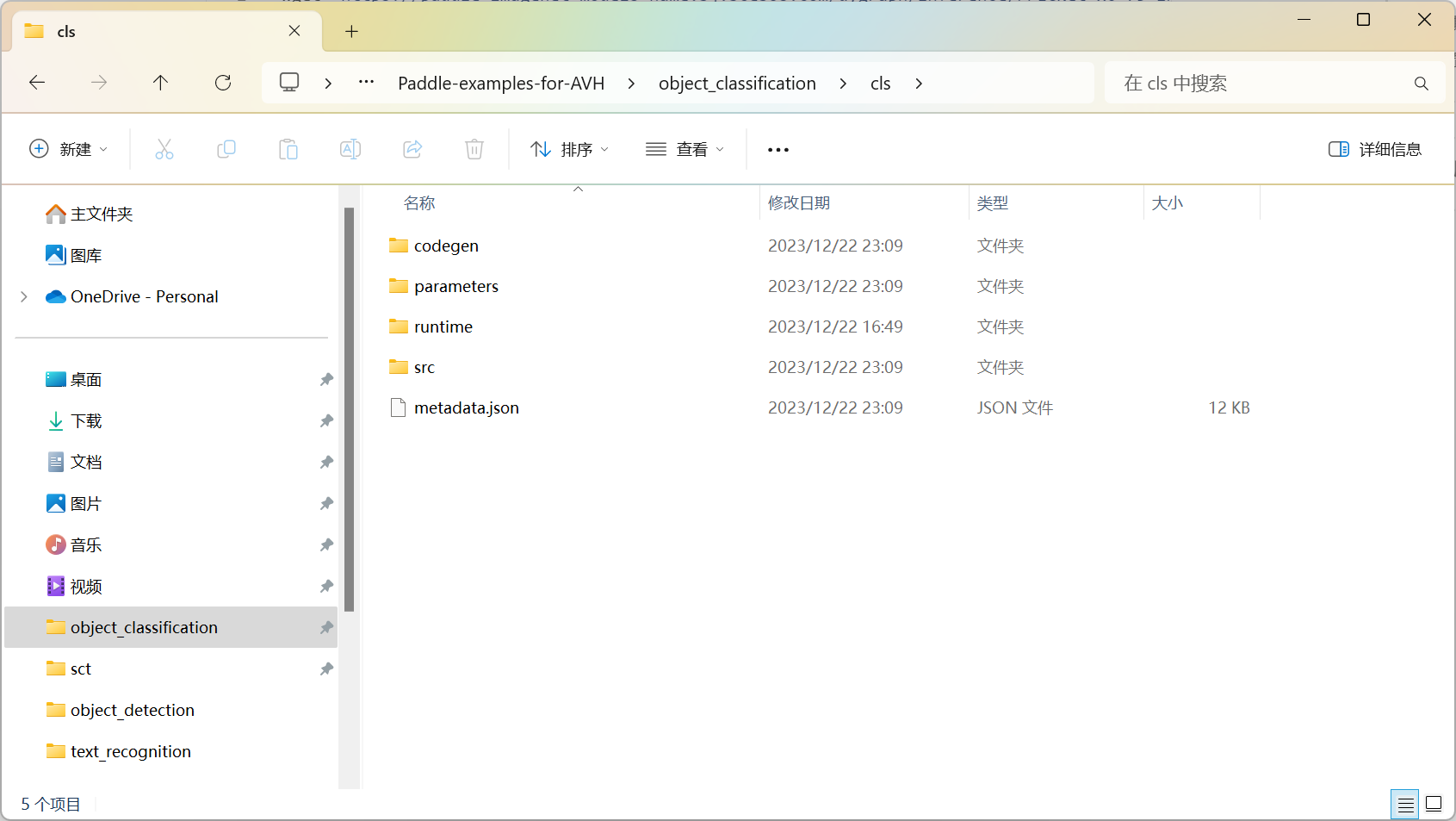
4 构建辅助数组
TVM 帮助我们解决了模型的推理工作,我们要自己设置模型的输入和输出。笔者编写了几个 Python 脚本用于处理模型的输入以及输出。
4.1 获取模型输入输出数组
convert_image.py 用于构建模型的输入和输出数组,我特别对齐了 PaddleClas 中对模型输入的处理,执行该脚本后,include文件夹 下将生成 inputs.h 和 output.h。
import pathlib
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
def decode_image(img_bgr):
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
return img_rgb
def resize_image(im_rgb, resize_short=256):
img_h = im_rgb.shape[0]
img_w = im_rgb.shape[1]
percent = float(resize_short) / min(img_w, img_h)
w = int(round(img_w * percent))
h = int(round(img_h * percent))
resize_img = cv2.resize(im_rgb, (w, h), cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return resize_img
def crop_image(im_rgb, size=224):
if type(size) is int:
size = (size, size)
else:
size = size # (h, w)
w, h = size
img_h, img_w = im_rgb.shape[:2]
w_start = (img_w - w) // 2
h_start = (img_h - h) // 2
w_end = w_start + w
h_end = h_start + h
return im_rgb[h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end, :]
def normalize_image(im_rgb, mean, std):
im_rgb = im_rgb.astype('float32')
im_rgb = im_rgb * 0.00392157
shape = (1, 1, 3)
mean = np.array(mean).reshape(shape).astype('float32')
std = np.array(std).reshape(shape).astype('float32')
im_rgb = (im_rgb.astype('float32') - mean) / std
return im_rgb.astype('float32')
def resize_norm_img(img):
image = np.array(img)
image = decode_image(image)
image = resize_image(image)
image = crop_image(image)
image = normalize_image(image, [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
return image
def create_header_file(name, tensor_name, tensor_data, output_path):
"""
This function generates a header file containing the data from the numpy array provided.
"""
file_path = pathlib.Path(f"{output_path}/" + name).resolve()
# Create header file with npy_data as a C array
raw_path = file_path.with_suffix(".h").resolve()
with open(raw_path, "w+") as header_file:
header_file.write(
"\n"
+ f"const size_t {tensor_name}_len = {tensor_data.size};\n"
+ f'__attribute__((section(".data.tvm"), aligned(16))) float {tensor_name}[] = '
)
header_file.write("{")
for i in np.ndindex(tensor_data.shape):
header_file.write(f"{tensor_data[i]}, ")
header_file.write("};\n\n")
def create_headers(img_path):
"""
This function generates C header files for the input and output arrays required to run inferences
"""
# Create input header file
# Resize image to 32x320
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = resize_norm_img(img)
img_data = img.astype("float32")
# Add the batch dimension, as we are expecting 4-dimensional input: NCHW.
img_data = np.expand_dims(img_data, axis=0)
create_header_file("inputs", "input", img_data, "include")
# Create output header file
output_data = np.zeros([1000], np.float32)
create_header_file("outputs", "output", output_data, "include")
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_headers(sys.argv[1])
4.2 获取模型的 labels 数组
分类模型的后处理中一般都会有一个label来存储类别信息,convert_labels.py 用于构建模型的类别数组,执行该脚本后,include文件夹 下将生成 labels.h。
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
# under the License.
import os
import pathlib
import sys
def create_labels_header(labels_file, section, output_path):
"""
This function generates a header file containing the ImageNet labels as an array of strings
"""
labels_path = pathlib.Path(labels_file).resolve()
file_path = pathlib.Path(f"{output_path}/labels.h").resolve()
with open(labels_path) as f:
labels = f.readlines()
with open(file_path, "w+") as header_file:
header_file.write(f'char* labels[] __attribute__((section("{section}"), aligned(16))) = {{')
for _, label in enumerate(labels):
header_file.write(f'"{label.rstrip()}",')
header_file.write("};\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_labels_header(sys.argv[1], ".data.tvm", "./include")
4.3 构建 TVM 配置模板代码
使用 microTVM 需要配置一些 TVM 相关的模板代码,这里参考了 TVM 官方例程来编写。
请在include新建 tvm_runtime.h 并输入以下内容:
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <tvm/runtime/c_runtime_api.h>
#include <tvm/runtime/crt/stack_allocator.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void __attribute__((noreturn)) TVMPlatformAbort(tvm_crt_error_t error_code) {
printf("TVMPlatformAbort: %d\n", error_code);
printf("EXITTHESIM\n");
exit(-1);
}
tvm_crt_error_t TVMPlatformMemoryAllocate(size_t num_bytes, DLDevice dev, void** out_ptr) {
return kTvmErrorFunctionCallNotImplemented;
}
tvm_crt_error_t TVMPlatformMemoryFree(void* ptr, DLDevice dev) {
return kTvmErrorFunctionCallNotImplemented;
}
void TVMLogf(const char* msg, ...) {
va_list args;
va_start(args, msg);
vfprintf(stdout, msg, args);
va_end(args);
}
TVM_DLL int TVMFuncRegisterGlobal(const char* name, TVMFunctionHandle f, int override) { return 0; }
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
请在include新建 crt_config.h 并输入以下内容:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*/
/*!
* \file tvm/runtime/crt_config.h.template
* \brief Template for CRT configuration, to be modified on each target.
*/
#ifndef TVM_RUNTIME_CRT_CRT_CONFIG_TEMPLATE_H_
#define TVM_RUNTIME_CRT_CRT_CONFIG_TEMPLATE_H_
/*! Log level of the CRT runtime */
#define TVM_CRT_LOG_LEVEL TVM_CRT_LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
#endif // TVM_RUNTIME_CRT_CRT_CONFIG_TEMPLATE_H_
5 构建主函数
这部分比较简单,主要是设置输入输出数据,推理,后处理。
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <crt_config.h>
#include <tvm_runtime.h>
#include <tvmgen_cls.h>
#include "labels.h"
#include "inputs.h"
#include "outputs.h"
#include "stdout_USART.h"
#if defined (__ARMCC_VERSION) && (__ARMCC_VERSION >= 6010050)
__asm(" .global __ARM_use_no_argv\n");
#endif
int main(){
stdout_init();
struct tvmgen_cls_inputs cls_inputs = {
.x = input,
};
struct tvmgen_cls_outputs cls_outputs = {
.output = output,
};
tvmgen_cls_run(&cls_inputs, &cls_outputs);
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < output_len;i++){
if(output[i] > output[index]){
index = i;
}
}
printf("Index is %d; Confidence is %f; Label is %s\n", index, output[index], labels[index]);
printf("EXITTHESIM\r\n");
}
6 配置 Keil 项目
在前期准备中,笔者已经介绍了从零在 Keil 中配置一个 AVH 项目,这里需要修改一个简单的修改。
6.1 导入项目文件
需要导入的项目文件主要有以下几个部分组成:
main.c:控制主函数运行
cls_lib0.c:存放了模型的各种参数
cls_lib1.c:调用后端并执行各种模型推理任务
crt_backend_api.c:后端核心推理框架代码
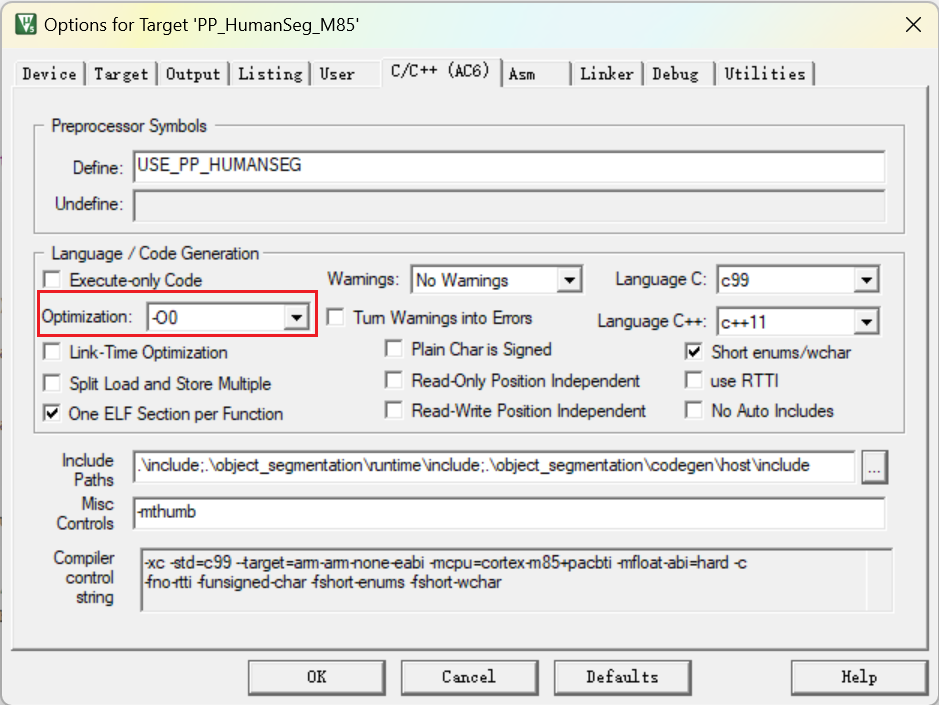
6.2 修改代码优化级别
把代码优化级别改为不优化,否则可能因为优化执行顺序而产生错误。
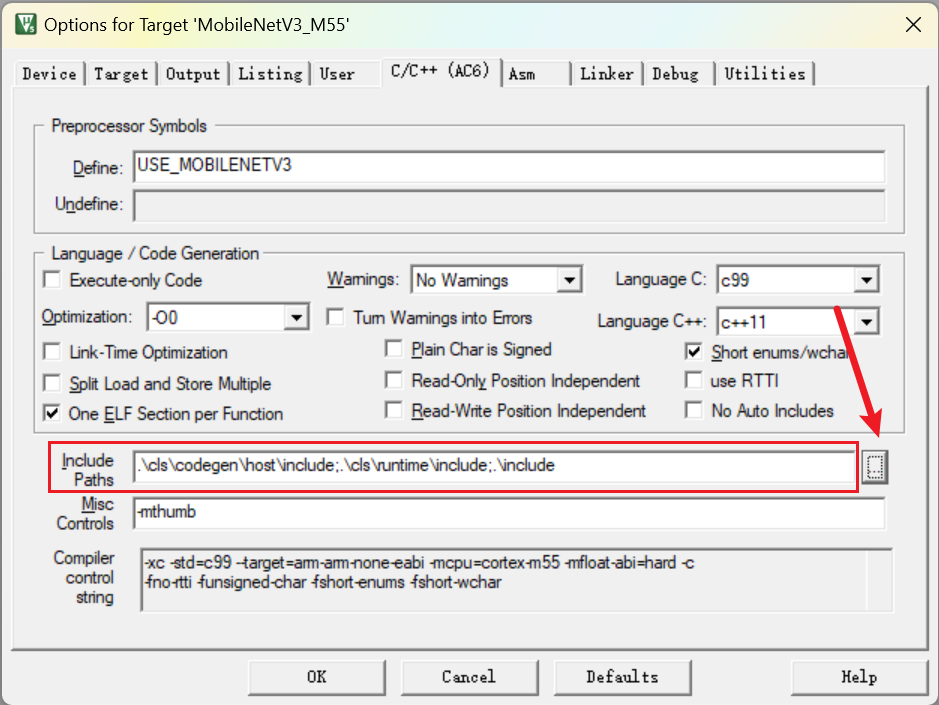
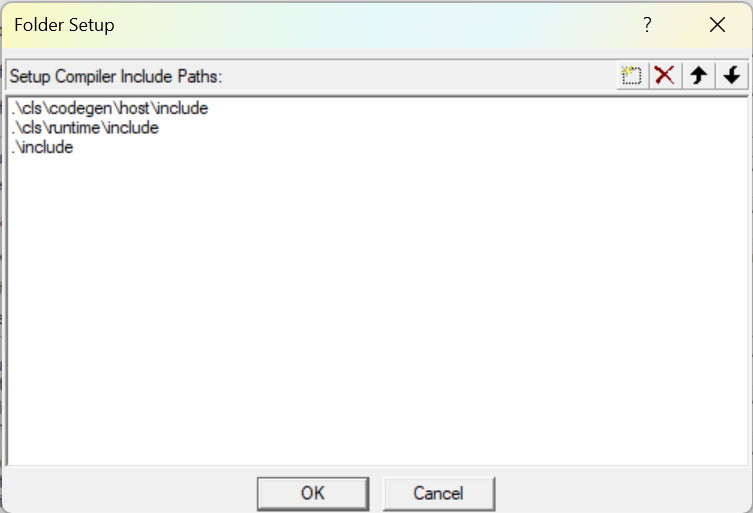
6.3 设置头文件文件夹路径
6.4 导入 CMSIS-DSP 和 CMSIS-NN
在Keil中导入 CMSIS-DSP 和 CMSIS-NN
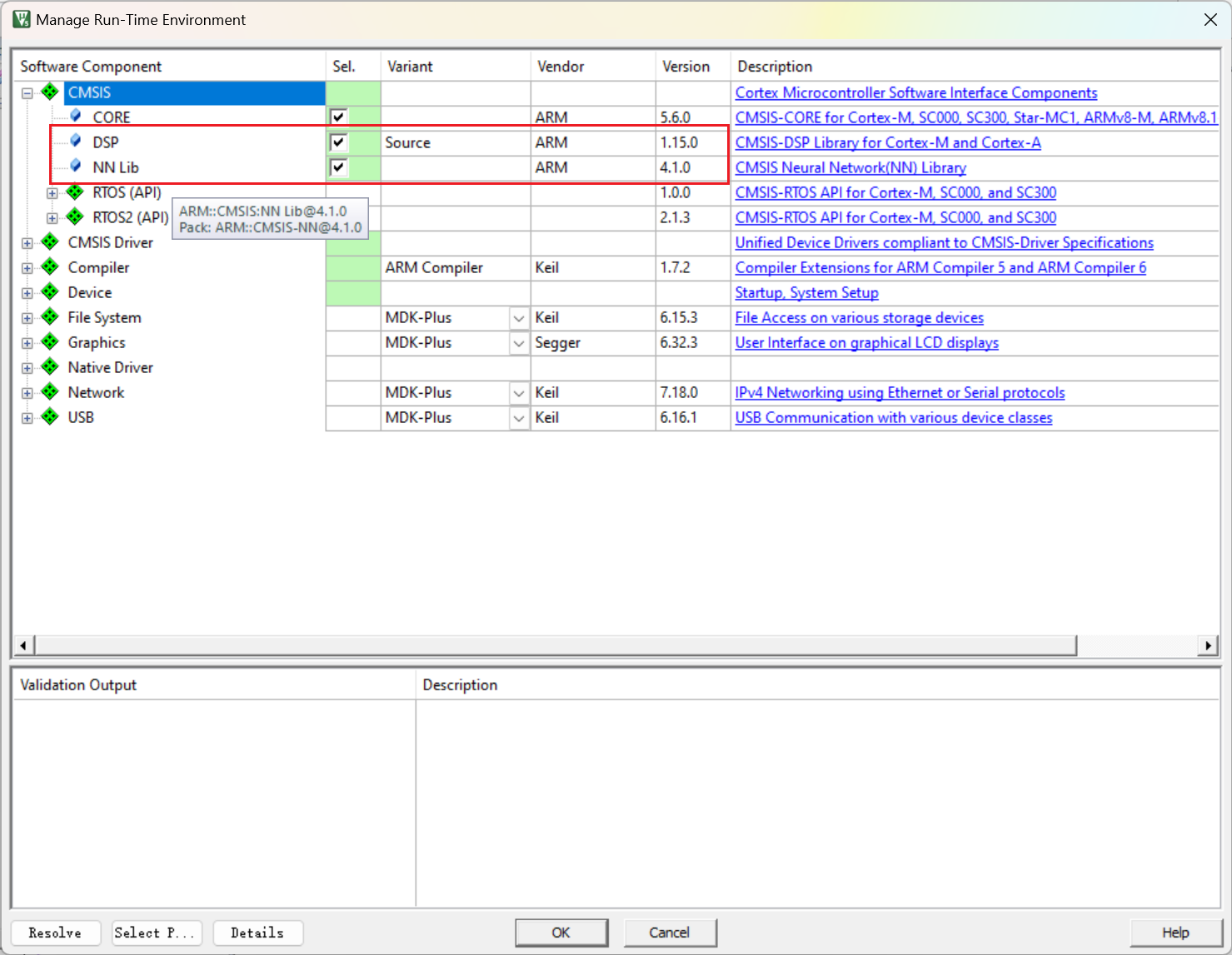
6.5 配置 sct 文件
TVM 的例程中使用的是 ld 文件的形式来定义变量储存在什么位置,Keil 中则是用 sct 文件的形式来定义该内容。
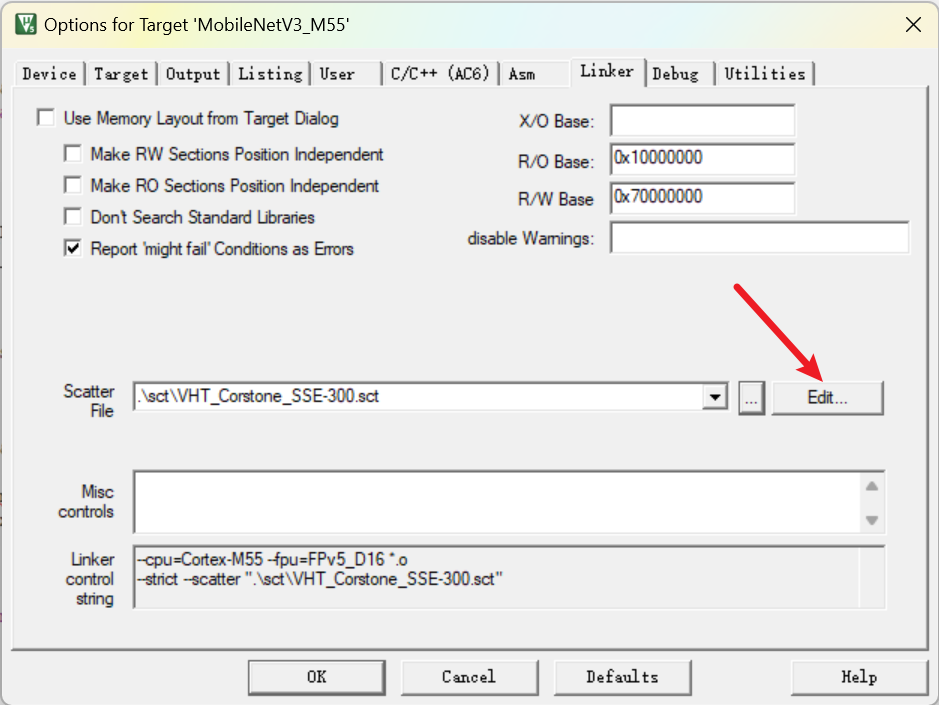
如果你使用的模拟器是 VHT_MPS3_Corstone_SSE-300,修改 sct 文件如下:
#! armclang --target=arm-arm-none-eabi -march=armv8.1-m.main -E -xc
LOAD_REGION_0 0x00000000 0x00080000
{
; ITCM is used for code
itcm.bin 0x00000000 0x00080000
{
*.o (RESET, +First)
.ANY (+RO)
}
; DTCM is used for any other RW or ZI data.
dtcm.bin 0x20000000 0x00060000
{
.ANY(+ZI +RW)
}
; 32 kiB of stack space within the DTCM region.
ARM_LIB_STACK 0x20060000 EMPTY ALIGN 8 0x00008000
{}
; This region should have 3 cycle read latency from both Cortex-M55 and Ethos-U NPU
isram.bin 0x31000000 UNINIT ALIGN 16 0x00200000
{
}
}
; Second load region (DDR)
LOAD_REGION_1 0x60000000 0x02000000
{
; 32 MiB of DDR space for neural network model input vectors and labels.
ddr.bin 0x60000000 ALIGN 16 0x02000000
{
*.o (.bss.noinit.*)
*.o (.rodata.tvm)
*.o (.data.tvm)
}
; First 256kiB of BRAM (FPGA SRAM) used for RO data.
bram.bin 0x11000000 ALIGN 8 0x00040000
{
; RO data (incl. unwinding tables for debugging)
;.ANY (+RO-DATA)
}
; 768 KiB of remaining part of the 1MiB BRAM used as heap space.
ARM_LIB_HEAP 0x11040000 EMPTY ALIGN 8 0x000C0000
{
}
; 32 MiB of model space for run-time load of model
runtime_model 0x90000000 EMPTY ALIGN 16 0x02000000
{
}
; 16 MiB of IFM space for run-time loading (FVP only)
runtime_ifm 0x92000000 EMPTY ALIGN 16 0x01000000
{}
; 16 MiB of OFM space for run-time loading (FVP only)
runtime_ofm 0x93000000 EMPTY ALIGN 16 0x01000000
{}
}
如果你使用的模拟器是 VHT_Corstone_SSE-310,修改 sct 文件如下:
LOAD_REGION_0 0x11000000 0x00200000
{
bram.bin 0x11000000 0x00080000
{
*.o (RESET, +First)
.ANY (+RO)
}
data.bin 0x11080000 ALIGN 8 0x00080000
{
.ANY(+ZI +RW)
}
ARM_LIB_HEAP 0x11100000 EMPTY ALIGN 8 0x000C0000
{}
ARM_LIB_STACK 0x30000000 EMPTY ALIGN 8 0x00008000
{}
isram.bin 0x31000000 UNINIT ALIGN 16 0x00200000
{
}
}
LOAD_REGION_1 0x70000000 0x02000000
{
ddr.bin 0x70000000 ALIGN 16 0x02000000
{
*.o (.bss.noinit.*)
*.o (.rodata.tvm)
*.o (.data.tvm)
}
runtime_model 0x90000000 EMPTY ALIGN 16 0x02000000
{}
runtime_ifm 0x92000000 EMPTY ALIGN 16 0x01000000
{}
runtime_ofm 0x93000000 EMPTY ALIGN 16 0x01000000
{}
}
7 编译并运行代码
点击编译并进入 Debug 模型
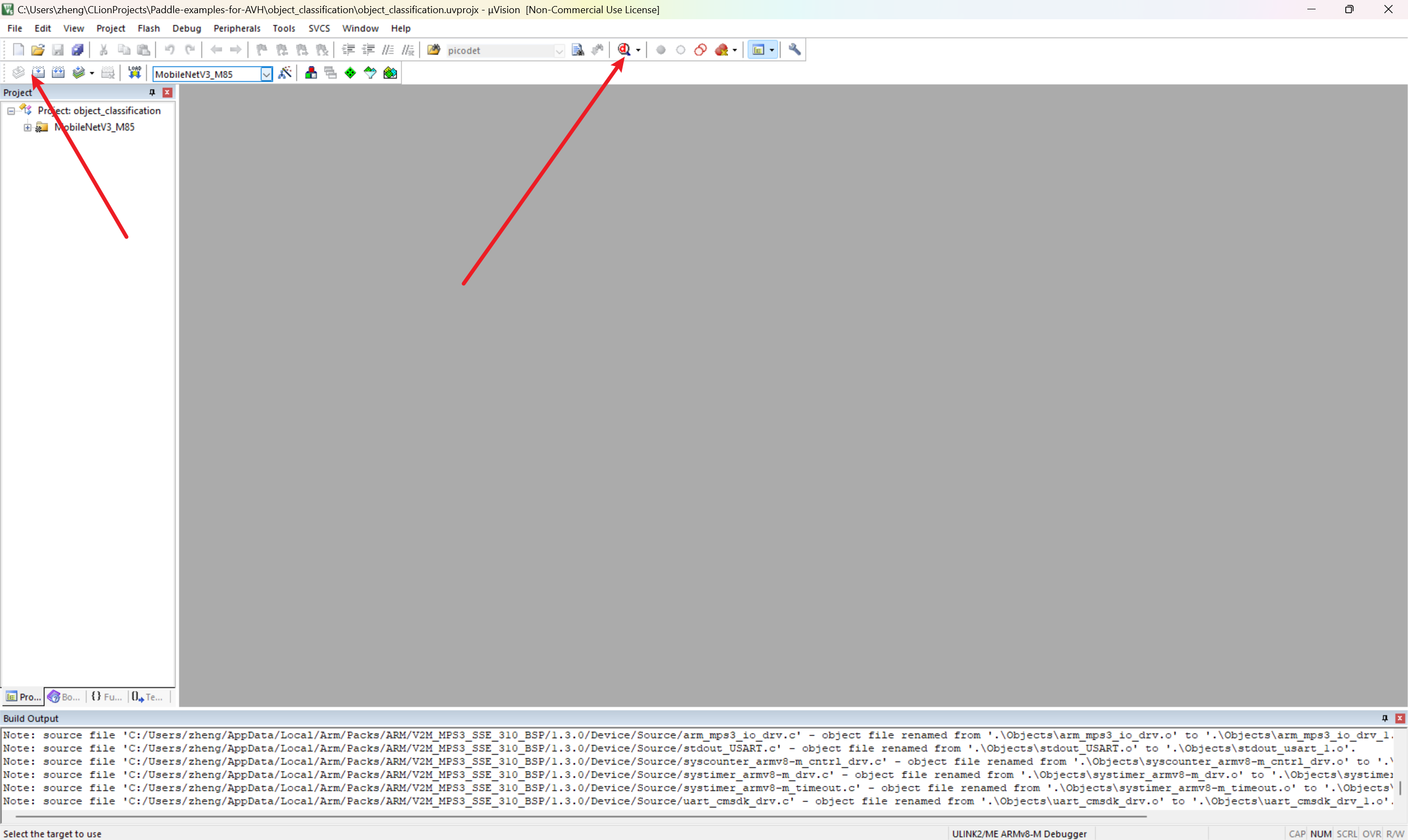
开始执行代码
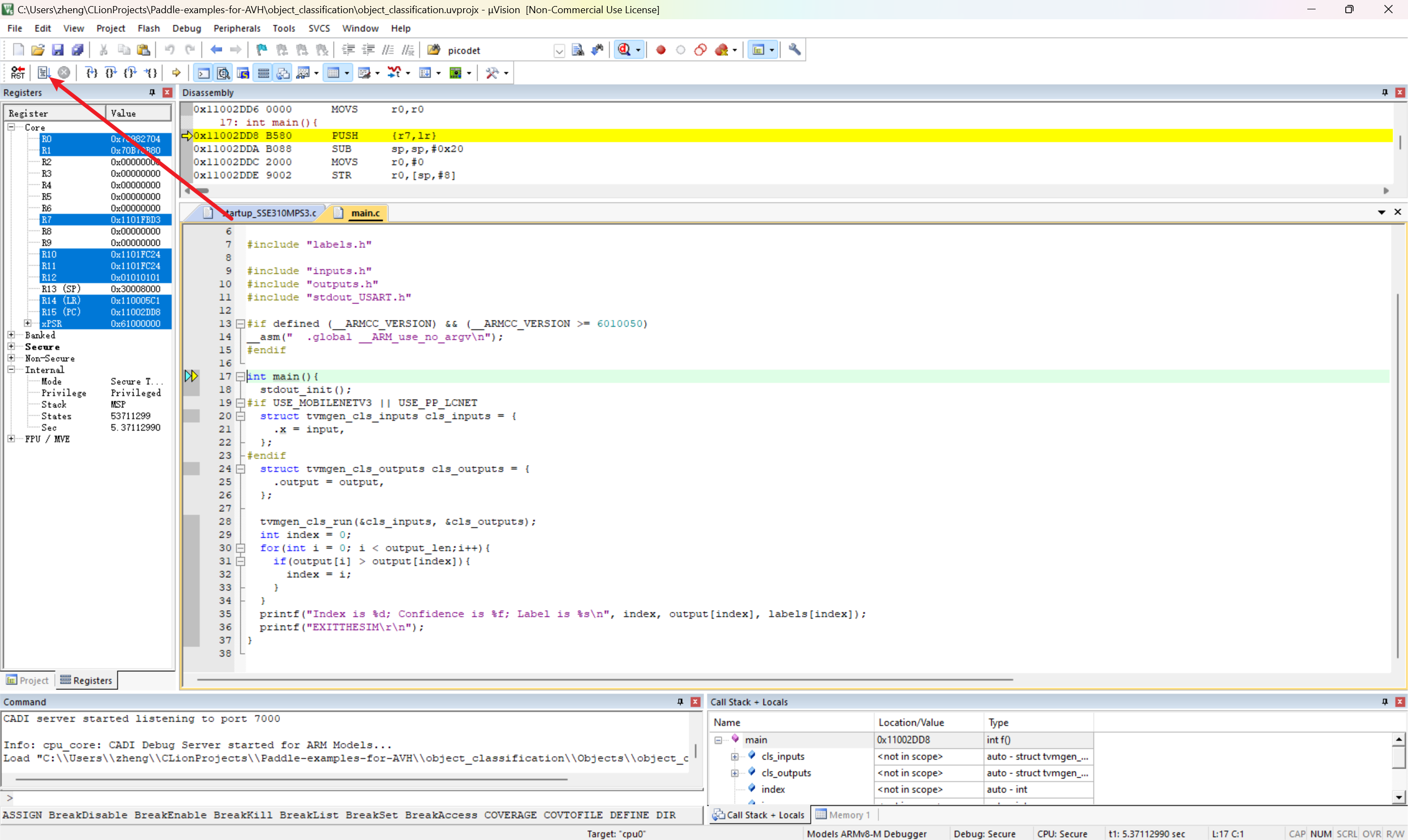
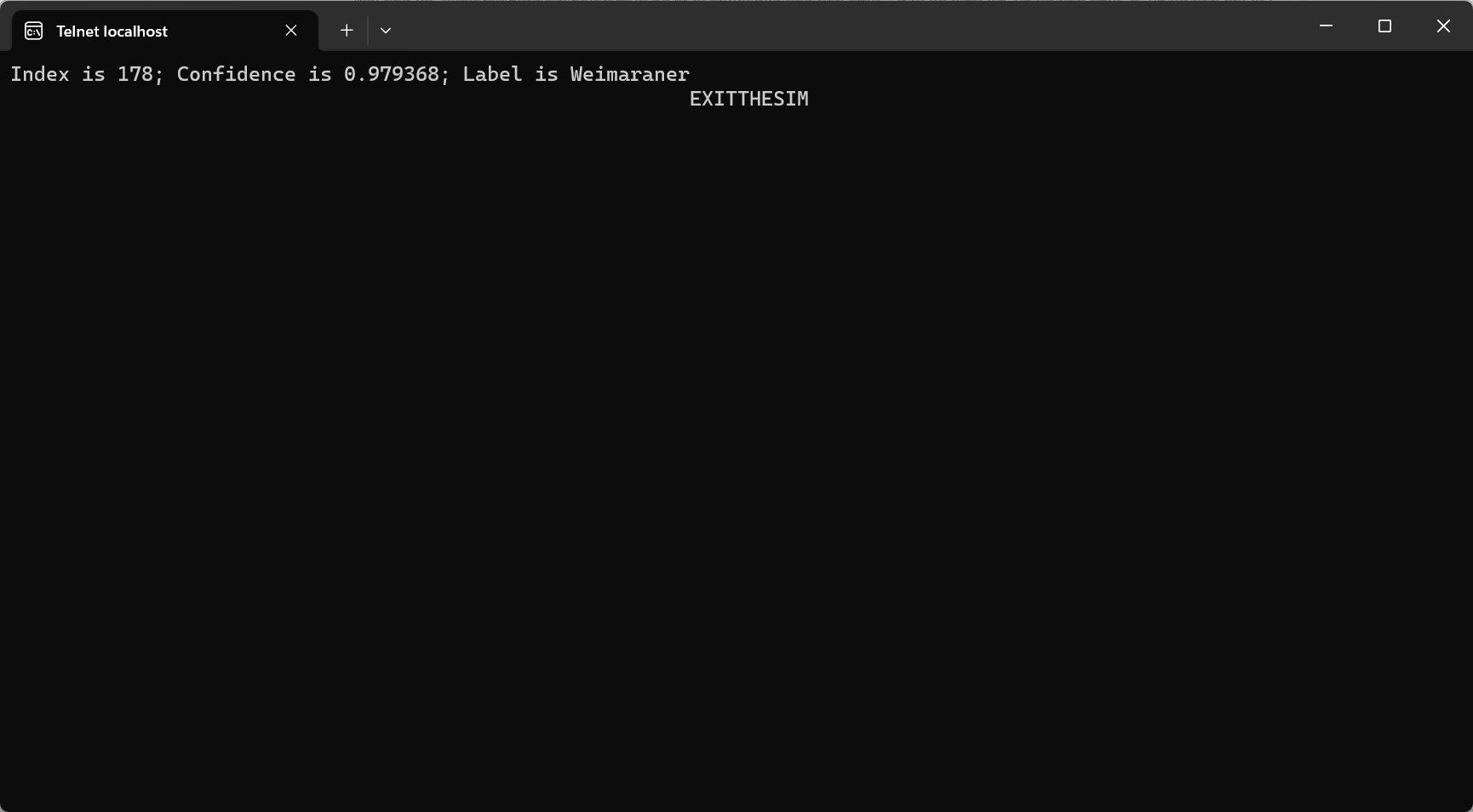
模拟器成功输出类别信息
8 参考资料
以下资料可能会帮助到你
- TVM TinyML Optimization
- tvm/apps/microtvm/cmsisnn at main · apache/tvm
- mlek-cmsis-pack-examples/object-detection at main · Arm-Examples/mlek-cmsis-pack-examples
- GitHub - ArmDeveloperEcosystem/Paddle-examples-for-AVH: 🤖 Use PaddlePaddle for OCR and Object Detection on Arm Cortex-M with Arm Virtual Hardware (AVH)
- GitHub - apache/tvm: Open deep learning compiler stack for cpu, gpu and specialized accelerators




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号