IO流
File和IO流概述:

File类:
- 可以将File理解为文件或者文件夹的路径
- File封装的并不是一个真正的文件
- 它仅仅是一个路径名,可以存在,也可以不存在
File类的构造方法:

绝对路径和相对路径:

File类的创建功能:
File file =new File("路径");
- file.creatNewFile(); 创建一个新文件
- file.mkdir();创建单级文件夹
- file.mkdirs();创建多级文件夹
File类的删除功能:
文件直接删,文件夹需为空

File类的获取和判断方法:
File file=new File("路径");
File类的判断方法:
file.isDirectory();判断是否是文件夹
file.isFile();判断是否是文件
file.exists();判断文件是否存在
File类的获取方法:
file.getAbsoPath();获取绝对路径
file.getPath();获取构造方法中的路径
file.getName();获取文件或文件夹的名称
File的listFiles方法:
进入不了则为null

删除多级文件夹:
以桌面考试文件夹为例(反正我也不想要里面的东西了)
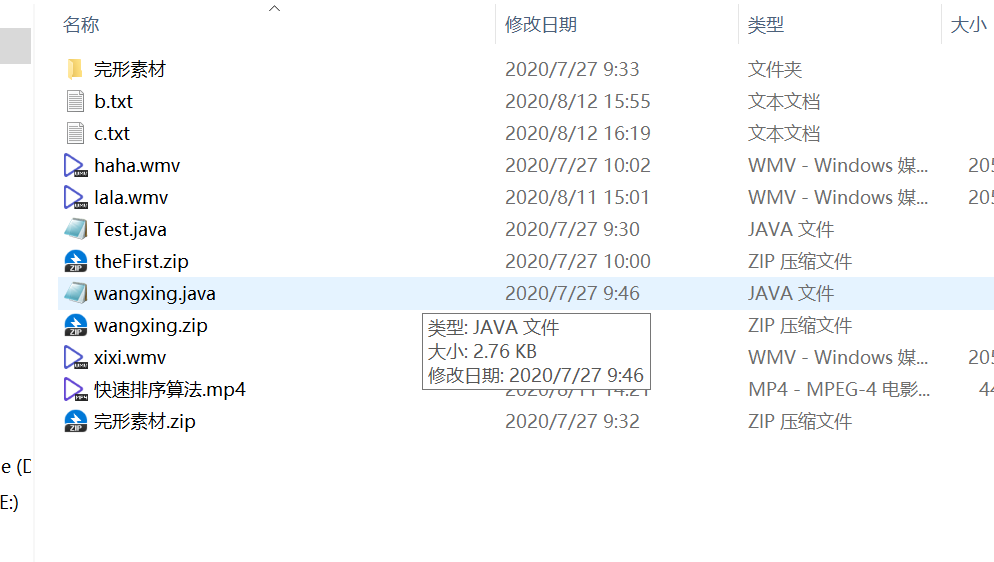
这是里面的目录:
删除递归代码如下:
1 public class TestDelete { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 File file = new File("C:\\Users\\ZYH\\Desktop\\考试"); 4 Mydelete(file); 5 } 6 private static void Mydelete(File file) { 7 //获取删除文件夹file集合 8 File[] files = file.listFiles(); 9 //增强for遍历: 10 for (File file1 : files) { 11 //判断 12 if (file1.isFile()) { 13 file1.delete(); 14 } else { 15 Mydelete(file1); 16 } 17 } 18 file.delete(); 19 } 20 21 22 }
案例:统计一个文件夹中每种文件的个数并打印:
思路:

代码如下:
1 public class CuntFile { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 File file = new File("C:\\Users\\ZYH\\Desktop\\文件\\基础题目"); 4 HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); 5 theCount(file, hashMap); 6 System.out.println(hashMap); 7 8 9 } 10 11 private static void theCount(File file, HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap) { 12 13 File[] files = file.listFiles(); 14 for (File file1 : files) { 15 if (file1.isFile()) { 16 String name = file1.getName(); 17 18 String[] split = name.split("\\."); 19 20 String s = split[1]; 21 Set<String> set = hashMap.keySet(); 22 if (!set.contains(s)) { 23 hashMap.put(s, 1); 24 25 26 } else { 27 Integer s1 = hashMap.get(s); 28 s1 += 1; 29 hashMap.put(s, s1); 30 31 32 } 33 } else { 34 theCount(file1, hashMap); 35 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 41 } 42 }
IO流的分类:

字节流:
字节输出流FileOutputStream:
注意事项:
- 如果目的地指向的文件不存在,会自动帮我们创建
- 如果存在会清空,再进行写入数据(加true后不清空)
- 通过IO流操作文件后,必须关流释放资源,否则文件会一直被占用
字节流写数据的三种方式:
- write(int b); 一次写一个字节数据
- write(byte[]arr) 一次写一个字节数组
- write(byte[]arr,int index,int len) 一次写数组的指定部分
如何换行和续写:

字节输入流FileInputStream:

字节流赋值文件模板:
1 public class read { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 3 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day10\\a.txt"); 4 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day10\\a1.txt"); 5 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; 6 int len; 7 while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) { 8 fos.write(bytes, 0, len); 9 } 10 fis.close(); 11 fos.close(); 12 13 14 } 15 }
复制文件就用字节流
字节缓冲流:
- BufferOutputStream 字节缓冲输出流
- BufferInputStream 字节缓冲输入流

缓冲流使用字节流的方法
缓冲流是通过定义一个8192字节长度的数组来实现缓冲区
字符流(字节流+编码表)
- FileWrite字符写出流
- FileRedar字符写入流
字符流编码表:

字符流有五种方法:

字符流写数据注意事项:

字符流flush和close方法

字符流读数据的两种方法:

字符缓冲流
字符缓冲输入流:
BufferReader(传参用FileReader)

字符缓冲输出流:
BufferWriter(传参用FileWriter)

字符缓冲流特有的方法:

从硬盘到内存或者从内存到硬盘用字符流。
IO流小结:
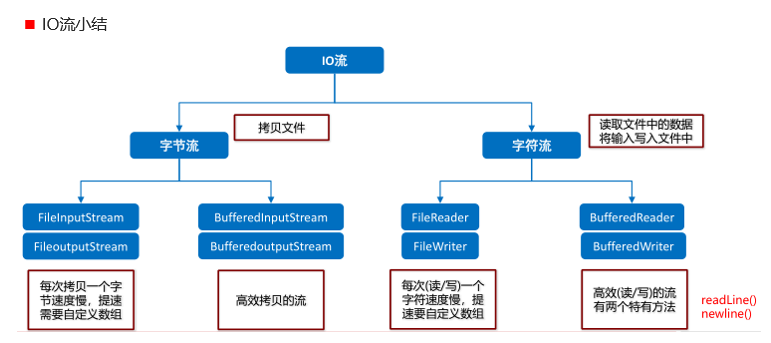
个人小总结:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("C:\\"); 3 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("C:\\"); 4 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);//缓冲流里面放对应的输入输出流 5 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis); 6 FileReader fr=new FileReader("C:\\"); 7 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("C:\\"); 8 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr); 9 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);//缓冲流里放对应的输入输出流 10 //因为字符流中的字符都是人类可以看懂的,所以字符流或者字符缓冲流名字里都会有 11 //reader,writer 12 //子节流人类看不懂只能inputStream和outputStream来表示
- 因为字符流中的字符都是人类可以看懂的,所以字符流或者字符缓冲流名字里都会有reader,writer
- 子节流人类看不懂只能inputStream和outputStream来表示
- 缓冲流里放对应的输入输出流
迎风少年


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号