2.线性表——栈
1.什么是栈
[1]. 栈是一种只能在一端进行插入和删除操作的线性表;插入:入栈(push);删除:出栈(pop);
[2]. 栈是按照“先进后出”(Last In First Out, LIFO)的原则存储数据;
栈顶(Top):允许删除和插入;
栈底(Botton) ;
[3]. 栈的分类:
静态栈:其核心是数组,类似于一个连续内存的数组,需要提前确定好栈的大小;
动态栈:其核心是链表,内存够用的前提下,可以无穷大,不连续;
[4]. 栈的表示:
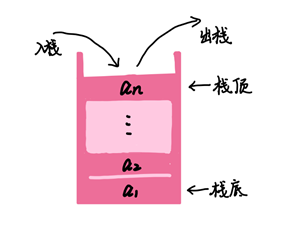
1.1 栈的表示
2. 栈的基本操作
[1]. 栈的存储结构
[2]. 进栈
[3]. 出栈
[4]. 判断空,判断满
[5]. 栈的遍历
[6]. 清空栈
备注:静态栈参考【2.线性表——数组】
动态栈参考【2.线性表——链表】
3. 静态栈的代码实现
[1]. 静态栈的存储结构
public class MyStack { final int STACKSIZE = 5; // 声明栈的容量 // 注意:final 的用法; public int bottom; public int top; public int[] arr; public MyStack() { bottom = top = -1; arr = new int[STACKSIZE]; } }
[2]. 静态栈的基本操作实现
package com.Stack; /* * 静态栈的基本操作: * 1. 初始化,创建 * 2. 入栈 * 3. 出栈 * 4. 判断空;判断满; * 5. 遍历 * 6. 清空 * * */ public class DemoStack { // 判断满 public static boolean isFull(MyStack stack){ if(stack.top >= stack.STACKSIZE-1) // 利用数组构建的静态栈的下标是从0开始的 return true; else return false; // 判断满,简写代码:return stack.top >= stack.STACKSIZE-1; } // 判断空 public static boolean isEmpty(MyStack stack){ if(stack.top == stack.bottom) return true; else return false; // 简写:return stack.top == stack.bottom; } // 进栈 public static boolean poshStack(MyStack stack,int data){ if(isFull(stack)){ System.out.println("当前栈已满!"); return false; }else{ stack.arr[++stack.top] = data; return true; } } // 出栈 public static boolean popStack(MyStack stack){ if(isEmpty(stack)){ System.out.println("当前栈为空!"); return false; }else{ System.out.println("栈顶元素出栈:"+stack.arr[stack.top--]); return true; } } // 遍历输出 public static boolean printOutStack(MyStack stack) { if(isEmpty(stack)){ System.out.println("当前栈为空!无法输出"); return false; }else{ int length = stack.top - stack.bottom; System.out.print("栈遍历输出:"); for(int i=length-1 ; i>=0; i--){ System.out.print(stack.arr[i]+" "); } System.out.println("\n"+"==============分隔符==================="); return true; } } // 清空栈 public static boolean clearStack(MyStack stack){ if(isEmpty(stack)){ System.out.println("当前栈为空!"); return false; }else{ /* int length = stack.top - stack.bottom; for(int i=length-1 ; i>=0; i--){ stack.arr[i] = 0; stack.top--; }*/ stack.arr = null;// java内部会不定时的启动【垃圾回收机制】,对堆内存空间进行回收 stack.top = stack.bottom = -1; return true; } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyStack stack = new MyStack(); poshStack(stack,1); poshStack(stack,2); poshStack(stack,3); poshStack(stack,4); poshStack(stack,5); System.out.println("入栈后"); printOutStack(stack); popStack(stack); popStack(stack); System.out.println("出栈后"); printOutStack(stack); clearStack(stack); if(isEmpty(stack)){ System.out.println("栈已清空 !"); } printOutStack(stack); } }
[3]. 运行结果

4. 动态栈的代码实现
[1]. 动态栈的存储结构
package com.Stack; public class MyDynamicStack { private int data; private MyDynamicStack next; public MyDynamicStack() { } public MyDynamicStack(int data) { this.data = data; } public MyDynamicStack(int data, MyDynamicStack next) { this.data = data; this.next = next; } public int getData() { return data; } public void setData(int data) { this.data = data; } public MyDynamicStack getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(MyDynamicStack next) { this.next = next; } }
[2]. 动态栈的基本操作实现
[3
package com.Stack; // 栈:先进后出 public class DemoListStack { static final int SIZE = 10; // 同样可以不用设置链表的容量,这里是为了验证试验效果添加的SIZE static int stackSize = 0; static MyDynamicStack top = null; static MyDynamicStack bottom = null; public static boolean isFull(){ if(SIZE > stackSize){ return false; } return true; } public static boolean isEmpty(){ if(stackSize==0||top==null){ return true; } return false; } public static void printOutStack(){ MyDynamicStack temp = top; while(null!=temp){ System.out.print(temp.getData()+" "); temp = temp.getNext(); } System.out.println("\n当前栈内元素的个数有:"+stackSize); } // 出栈 public static void popStack(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("动态栈为空!无法出栈!"); return; } int num = top.getData(); System.out.println("\n出栈的元素数据为:"+num); top = top.getNext(); stackSize--; } // 入栈 public static void pushStack(int num){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("动态栈已满!无法进栈!"); return; } MyDynamicStack newnode = new MyDynamicStack(num,null); if(isEmpty()){ top = new MyDynamicStack(num,null); }else{ newnode.setNext(top); top = newnode; } stackSize++; } public static void main(String[] args) { // 进栈 pushStack(10); pushStack(20); pushStack(30); pushStack(40); pushStack(50); printOutStack(); //出栈 popStack(); printOutStack(); } }
[3]. 运行结果

备注:学习过程中难免会出现很多错误,请大家指教!有问题可以直接评论我,谢谢!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号