JavaScript基本数据类型
数据类型分类
Js中分为两种数据类型,一种是基本数据类型,一种是object引用数据类型。
当需要去使用object引用数据类型的时候会在栈内存(连续存储)中去调用堆内存(链表存储)中的object引用数据类型对象,这是一个引用过程。
值类型(基本类型):number、boolean、null、undefined、string(在赋值传递中会以引用类型的方式来处理)。
引用类型:对象、数组、函数。
基本类型值:按值访问,操作的是他们实际保存的值;
引用类型值:按引用访问,当查询时,我们需要先从栈中读取内存地址,然后再顺藤摸瓜地找到保存在堆内存中的值;
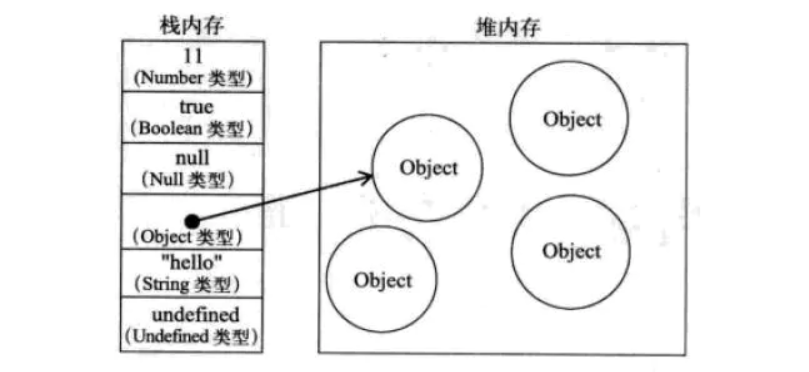
只有对象才有方法使用,但在Js中也可以使用值类型调用方法,因为它会在执行时将值类型转为引用类型,即跑到堆内存中找方法。
类型检测
Js中提供了丰富的数据类型,在实际开发工作中。要根据不同的数据类型做出不同的处理方案,那么类型检测就显得尤为重要。
typeof
typeof 用于返回以下原始类型
number
string
boolean
function
object
undefined
可以使用typeof用于判断数据的类型
<script>"use strict"; let num = 100; let num_string = "100"; let bool_true = true; let bool_false = false; function test(){}; let undef; // 未定义 let dic = {"1":"一","2":"二"}; console.log(typeof num); // number console.log(typeof num_string); // string console.log(typeof bool_true); // boolean console.log(typeof bool_false); // boolean console.log(typeof test); // function console.log(typeof undef); // undefined console.log(typeof dic); // object </script>
instanceof
instanceof 运算符用于检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上。
也可以理解为是否为某个对象的实例,typeof不能区分数组,但instanceof则可以。
<script>"use strict"; let num = 100; let num_string = "100"; let bool_true = true; let bool_false = false; function test(){}; let dic = {"1":"一","2":"二"}; console.log(num instanceof Number); // false console.log(num_string instanceof String); // false console.log(bool_true instanceof Boolean); // false console.log(bool_false instanceof Boolean); // false console.log(test instanceof Function); // true console.log(dic instanceof Object); // true </script>
如果我们用简写的形式生成基本类型,使用instanceof进行判断时会全部变成false。
但是用完整的实例化对象方式生成基本类型则会变成true。
<script>"use strict"; let num = new Number(100); let num_string = new String("100"); let bool_true = new Boolean(true); let bool_false = new Boolean(false); function test(){}; let dic = {"1":"一","2":"二"}; console.log(num instanceof Number); // true console.log(num_string instanceof String); // true console.log(bool_true instanceof Boolean); // true console.log(bool_false instanceof Boolean); // true console.log(test instanceof Function); // true console.log(dic instanceof Object); // true </script>
String
字符串类型是使用非常多的数据类型,也是相对简单的数据类型。
声明定义
使用对象形式创建字符串
<script>"use strict"; let object_string = new String("hello,world"); console.log(typeof object_string); // object </script>
简便创建字符串,即使用字面量来创建。
<script>"use strict"; let value_string = "hello,world"; console.log(typeof value_string); // string </script>
转义字符
有些字符有双层含义,需要使用 \ 转义符号进行含义转换。
下例中引号为字符串边界符,如果输出引号时需要使用转义符号。
<script>"use strict"; console.log("JavaScript是一门非常\'严格\'的语言。"); // JavaScript是一门非常'严格'的语言。 </script>
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| \t | 制表符 |
| \n | 换行 |
| \ | 斜杠符号 |
| \' | 单引号 |
| \" | 双引号R |
连接运算符
使用 + 可以连接多个内容组合成字符串,经常用于组合输出内容使用。
<script>"use strict"; console.log("JavaScript"+"是一门"+"非常优秀的语言。"); // JavaScript是一门非常优秀的语言。 </script>
模板字面量
在JavaScript中没有format格式化字符串,但是有模板字面量。
你可以使用`${变量\函数\表达式}`来达到格式化字符串的目的。
注意,不是单引号。而是`号。
<script>"use strict"; let username = prompt("请输入您的姓名:").trim(); document.write(`欢迎您:${username},很高兴您回家..`); </script>
使用函数或表达式。
<script>
"use strict";
function show() {
return "云崖先生";
};
document.write(`欢迎您:${show()},很高兴您回家..`);
</script>
另外,换行操作不会产生错误。会保留原样进行输出。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(`经过周密的计算,最后结果是:
${1 + 2},对这个结果满意吗?`);
// 经过周密的计算,最后结果是:
// 3,对这个结果满意吗?
// 会保留原样式
</script>
标签模板
标签模板是提取出普通字符串与变量,交由标签函数处理。
<script>
"use strict";
let username = "云崖先生";
let age = 18;
func`用户名是${username},年龄是${age},看的出来是个小帅哥`;
// ... 是一种语法,可以让形参接收多个参数。用array进行接收。和arguments有点相似,但是要定义形参名称。
function func(s, ...f) {
console.log(s); // (3) ["用户名是", ",年龄是", ",看的出来是个小帅哥", raw: Array(3)]
console.log(f); // (2) ["云崖先生", 18]
};
</script>
获取长度
使用length属性可以获取字符串长度
<script>
"use strict";
console.log("hello,world".length); // 11
</script>
大小写转换
大写转换:toUpperCase()
小写转换:toLowerCase()
<script>
"use strict";
console.log("hello,world".toUpperCase()); // HELLO,WORLD
console.log("HELLO,WORLD".toLowerCase()); // hello,world
</script>
移除空白
使用trim()可移除两侧空白。
使用trimLeft()删除左边空白。
使用trimRight()删除右边空白。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(" 不移除空白 ");
console.log(" 两侧空白 ".trim());
console.log(" 左侧空白".trimLeft());
console.log("右侧空白 ".trimRight());
</script>
获取单字符
索引从0开始,往后数。
可以使用charAt()。
也可使用[]。
使用length-1即可获取最后一位元素,以此类推。
<script>
"use strict";
let str = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMN";
// 取出C
console.log(str[2]);
// 取出D
console.log(str.charAt(3));
// 取出N
console.log(str[str.length - 1]);
// 取出L
console.log(str.charAt(str.length - 3));
</script>
截取子字符串
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| slice() | 参数1:开始索引值 参数2:结束索引值 特点:取头不取尾 |
| substring() | 参数1:开始索引值 参数2:结束索引值 特点:取头不取尾 |
| substr() | 参数1:开始索引值 参数2:指定获取长度 特点:从开始索引值往后数参数2的数值-1即可 |
<script> "use strict"; let str = "0123456789"; // 取出0 1 2 3 4 取头不取尾 console.log(str.slice(0, 5)); // 从2开始取,往后数五个 2 3 4 5 6 7 减去一个 2 3 4 5 6 console.log(str.substr(2, 5)); // 取出0 1 2 3 4 取头不取尾 console.log(str.substring(2, 5)); </script>
查找字符串
查找字符串的索引位置或给出一个布尔值。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| indexOf() | 从开始获取字符串位置,检测不到时返回 -1,第2个参数为从哪个位置开始查找 |
| lastIndexOf() | 从结尾来搜索字符串位置,检测不到时返回 -1,第2个参数为从哪个位置开始查找 |
| search() | 用于检索字符串中指定的子字符串,也可以使用正则表达式搜索。检测不到时返回 -1 |
| includes() | 字符串中是否包含指定的值,第二个参数指查找开始位置,返回的是一个布尔值 |
| startsWith() | 是否已特定子串开头。 参数2为查找的位置。返回的是一个布尔值 |
| endsWith() | 是否已特定子串结束。参数2为查找的位置。返回的是一个布尔值 |
<script> "use strict"; let str = "01234567890123456789abcdef"; // 从下标0的位置开始向后找 console.log(str.indexOf("0123")); // 0 // 从下标3的位置开始向后找 console.log(str.indexOf("ef", 3)); // 24 // 找不到返回 -1 console.log(str.indexOf("z")); // -1 // 从最后一位下标开始往前找 console.log(str.lastIndexOf("9abc")); // 19 // 指定下标位,从下标7的位置向前找 console.log(str.lastIndexOf("123", 7)); // 1 // 找不到返回 -1 console.log(str.lastIndexOf("z")); // -1 // 必须以f结尾 console.log(str.search("f$")); // 25 // 必须以a开头 console.log(str.search("^a")); // -1 // 必须以89开头结尾是英文 console.log(str.search("89[a-z]")); // 18 // 是否包含abc console.log(str.includes("abc")); // true // 是否包含zzz,从索引2向后检索 console.log(str.includes("zzz", 2)); // false // 索引2是否234开始 console.log(str.startsWith("234", 2)); // true // 当前字符串是否已cdef结束 console.log(str.endsWith("cdef")); // true </script>
替换字符串
replace() 方法用于字符串的替换操作。
参数1:查找的子串
参数2:替换的子串
注意,默认只替换一次。
<script>
"use strict";
let str = "hello,world";
let new_str = str.replace("world","Js");
console.log(new_str); // hello,Js
</script>
重复生成
使用repeat()方法可进行重复生成。
<script>
"use strict";
// 生成20个星号
console.log("*".repeat(20));
// ********************
</script>
将电话号码中间四位隐藏。
<script>
"use strict";
let phone = "13811112457";
let new_phone = phone.replace(phone.slice(3, 7), "*".repeat(4));
console.log(new_phone);
// 138****2457
</script>
拆分字符串
使用split()方法可将字符串进行拆分,拆分结果为array类型。
<script>
"use strict";
let str = "hello,world";
console.log(str.split(",")); // ["hello", "world"]
</script>
split()方法的第二个参数可以指定要拿几次拆分,默认是都拿。
<script>
"use strict";
let str = "hello,wor,ld";
// 代表拆分出来只拿前两个,而不是都拿
console.log(str.split(",", 2)); //["hello", "wor"]
</script>
合并字符串
使用concat()方法可将多个字符串合并为一个新的字符串。
<script>
"use strict";
let s1 = "hello",s2 = "world";
// 指定拼接符号 指定要拼接的字符串 指定新添加的内容
let s3 = s1.concat(",",s2,"新添加的内容");
console.log(s3);
// hello,world新添加的内容
</script>
类型转换
如果想让一个对象变为字符串,可以使用Strint()将它包裹。
<script>
"use strict";
let num = 123321;
let num_string = String(num);
console.log(num_string); // 123321
console.log(typeof num_string); // string
let arr = ["a",1,23];
let arr_string = String(arr);
console.log(arr_string); // a,1,23
console.log(typeof arr_string); // string
</script>
此外,我们也可以直接对象+""完成类型转换,,这是属于隐式转换。
<script>
"use strict";
let num = 123321;
let num_string = num+"";
console.log(num_string); // 123321
console.log(typeof num_string); // string
let arr = ["a",1,23];
let arr_string = arr+"";
console.log(arr_string); // a,1,23
console.log(typeof arr_string); // string
</script>
我们也可以调用对象下的toString()方法,来将对象转换为string类型。
<script>
"use strict";
let num = 123321;
let num_string = num.toString();
console.log(num_string); // 123321
console.log(typeof num_string); // string
let arr = ["a",1,23];
let arr_string = arr.toString();
console.log(arr_string); // a,1,23
console.log(typeof arr_string); // string
</script>
常用方法大全
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| length | 获取长度 |
| 大小写转换 | |
| toUpperCase() | 大写转换 |
| toLowerCase() | 小写转换 |
| 移除空白 | |
| trim() | 移除两侧空白 |
| trimLeft() | 移除左侧空白 |
| trimeRight() | 移除右侧空白 |
| 获取单字符 | |
| charAt() | 获取单字符,与[]使用方法相同 |
| 截取字符串 | |
| slice() | 参数1:开始索引值 参数2:结束索引值 特点:取头不取尾 |
| substring() | 参数1:开始索引值 参数2:结束索引值 特点:取头不取尾 |
| substr() | 参数1:开始索引值 参数2:指定获取长度 特点:从开始索引值往后数参数2的数值-1即可 |
| 查找字符串 | |
| indexOf() | 从开始获取字符串位置,检测不到时返回 -1,第2个参数为从哪个位置开始查找 |
| lastIndexOf() | 从结尾来搜索字符串位置,检测不到时返回 -1,第2个参数为从哪个位置开始查找 |
| search() | 用于检索字符串中指定的子字符串,也可以使用正则表达式搜索。检测不到时返回 -1 |
| includes() | 字符串中是否包含指定的值,第二个参数指查找开始位置,返回的是一个布尔值 |
| startsWith() | 是否已特定子串开头。 参数2为查找的位置。返回的是一个布尔值 |
| endsWith() | 是否已特定子串结束。参数2为查找的位置。返回的是一个布尔值 |
| 替换与重复生成 | |
| replace() | 用于字符串的替换操作。参数1:查找的子串 参数2:替换的子串 |
| repeat() | 重复生成的次数 |
| 合并与拆分 | |
| split() | 拆分字符串,拆分结果为数组类型 |
| concat() | 合并字符串,产生一个新的字符串 |
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| charCodeAt() | 通过index下标取出元素的Unicode编码 |
| anchor( ) | 为字符串添加上a标签 |
| italics( ) | 为字符串添加上i标签 |
| bold( ) | 为字符串添加上b标签 |
Boolean
布尔类型包括 true 与 false 两个值,是开发中使用较多的数据类型。
声明定义
使用对象形式创建布尔类型
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(new Boolean(true)); // true
console.log(new Boolean(false)); // false
</script>
但建议使用字面量创建布尔类型
<script>
"use strict";
let status = true;
</script>
隐式转换
基本上所有类型都可以隐式转换为 Boolean类型。
| 数据类型 | true | false |
|---|---|---|
| String | 非空字符串 | 空字符串 |
| Number | 非0的数值 | 0 、NaN |
| Array | 数组不参与比较时 | 参与比较的空数组 |
| Object | 所有对象 | |
| undefined | 无 | undefined |
| null | 无 | null |
| NaN | 无 | NaN |
当与Boolean类型比较时,会将两边类型统一为数字1或0。
如果使用Boolean与数值比较时,会进行隐式类型转换 true转为1,false转为0。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(3 == true); //false
console.log(0 == false); //true
</script>
当String类型与Boolean类型做比较时,会都转换为Number类型进行比较。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(true == "1"); // true
console.log(true > "0"); // true
</script>
数组的表现与字符串原理一样,会先转换为数值。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(Number([])); // 0
console.log(Number([3])); // 3
console.log(Number([1, 2, 3])); // NaN
console.log([] == false); // true
console.log([1] == true); // true
console.log([1, 2, 3] == true); // false
</script>
引用类型的Boolean值为真,如键值对对象和数组。
<script>
"use strict";
if ([]) { console.log("true") } else { console.log("false"); }; // true
if ({}) { console.log("true") } else { console.log("false"); }; // true
</script>
显式转换
使用 !! 转换布尔类型。
首先
!代表非,取反的意思。如果是
true则取false,如果是false则去true。这会得到一个相反的布尔值。再来一个
!,将之前的布尔值再去反。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(!![]); // true
console.log(!!{}); // true
console.log(!!""); // false
console.log(!!"0"); // true
console.log(!!"1"); // true
console.log(!!0); // false
console.log(!!1); // true
</script>
使用 Boolean() 函数可以显式转换为布尔类型
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(Boolean([])); // true
console.log(Boolean({})); // true
console.log(Boolean("")); // false
console.log(Boolean("0")); // true
console.log(Boolean("1")); // true
console.log(Boolean(0)); // false
console.log(Boolean(1)); // true
</script>
Number
在JavaScript中,Number包含整数与小数。
声明定义
使用对象方式声明
<script>
"use strict";
let num_obj = new Number(100);
console.log(typeof num_obj); // object
console.log(num_obj); // Number {100}
</script>
简便的字面量形式声明
<script>
"use strict";
let num_value = 100;
console.log(typeof num_value); // number
console.log(num_value); // 100
</script>
类型判断
使用isInteger()方法可判断是否为整数。
返回一个布尔值。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(Number.isInteger(39.5)); // false
</script>
使用isNaN()方法可判断是否为NaN。
返回一个布尔值。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(Number.isNaN(39.5)); // false
</script>
NaN
NaN表示无效的数值,并且不能使用 == 比较。
除了可以使用isNaN()方法外,也可以使用Object对象的is方法进行判定。
<script>
"use strict";
// NaN代表无效的数值
let res = "两百" / 2;
console.log(res);
// 使用isNaN()
console.log(Number.isNaN(res)); // true
// 使用Object.is()
console.log(Object.is(res,NaN)); // true
</script>
浮点舍入
使用toFixed()方法对数值进行四舍五入操作,可指定保留小数点后的位数。
<script>
"use strict";
let float_num = 123.456;
// 四舍五入,保留小数点后两位。
console.log(float_num.toFixed(2)); // 123.46
</script>
浮点精度
大部分编程语言在浮点数计算时都会有精度误差问题,Js也不例外。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(0.1+0.2); // 0.30000000000000004
</script>
这是因为计算机以二进制处理数值类型,上面的0.1与0.2转为二进制后是无穷的。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log((0.1).toString(2)) //0.0001100110011001100110011001100110011001100110011001101
console.log((0.2).toString(2)) //0.001100110011001100110011001100110011001100110011001101
</script>
一种方式使用toFixed()方法进行小数截取
<script>
"use strict";
// 保留小数点后两位
console.log((0.1 + 0.2).toFixed(2)); // 0.30
</script>
也可通过一些第三方库进行操作,下面演示decimal.js库来进行处理。
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/decimal.js/10.2.0/decimal.min.js"></script>
<script>
"use strict";
// 保留小数点后两位
console.log(Decimal.add(0.1, 0.2).valueOf()) // 0.3
</script>
普通转换
使用Number()函数包裹住需要转换的对象。
基本上所有的数据类型都能转换为Number类型,区别是有的会转换为有效数值,有的会转换为NaN即无效数值。
<script>
"use strict";
console.log(Number('hello')); //NaN
console.log(Number(true)); //1
console.log(Number(false)); //0
console.log(Number('99')); //99
console.log(Number([])); //0
console.log(Number([51])); //51
console.log(Number([5, 2])); //NaN
console.log(Number({})); //NaN
</script>
我们也可以使用算术运算符进行隐式转换。
<script>
"use strict";
let str = "123";
let res = str * 1;
console.log(res); // 123
console.log(typeof res); // number
</script>
强制转换
如果一个String即包含数字又包含其他字符,可使用强制转换。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| parseInt() | 提取字符串开始去除空白后的数字转为整数。 |
| parseFloat() | 转换字符串为浮点数,忽略字符串前面空白字符。 |
<script> "use strict"; let str = " 123.4这是一个字符串" // 强制转换为整数 console.log(parseInt(str)); // 123 // 强制转换为小数 console.log(parseFloat(str)); // 123.4 </script>
undefined
undefined更多代表的是未定义。
第一种情况:定义好变量 但是未进行赋值
<script>
"use strict";
let num;
console.log(num); // undefined
</script>
第二种情况:函数无返回值
<script>
"use strict";
function test() {
console.log("执行了...");
};
let res = test();
console.log(res); // undefined
</script>
null
表示未存在的对象。如果函数或方法要返回的是对象,那么找不到该对象时,返回的通常是 null。
<script>
"use strict";
let n = null; // null代表未引用任何对象,也就是为被实例化。此时它所属object对象
let a = []; // 虽然是一个空数组,但是它是Array的实例对象
console.log(n); // null
console.log(a); // []
console.log(typeof n); // object
console.log(typeof a); // object
</script>
在ECMA中,认为null与undefined是相等的。
并且值undefined是值null


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号