搜索二叉树,AVL树,SB树,红黑树,跳表(二)
SB树(SizeBalance树)
每个结点所在子树的结点个数不小于其兄弟的两个孩子所在子树的结点个数。不算重复的key,只算这个树上有多少不同的key。AVL维持了高度,SB树维持了节点的个数。
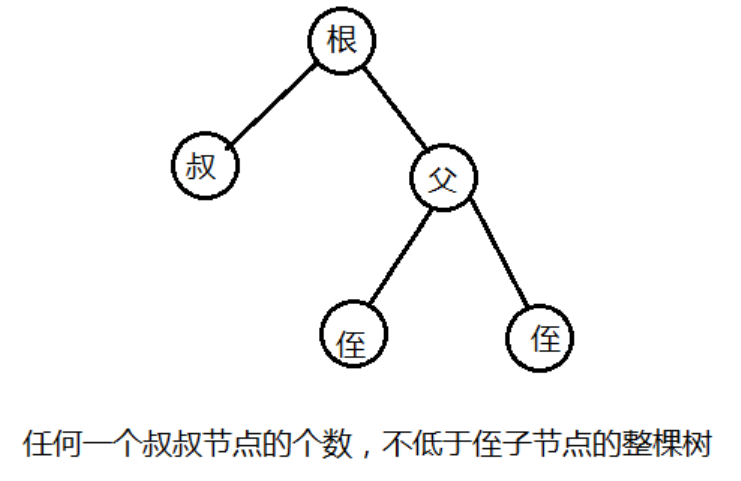
检查平衡性图解
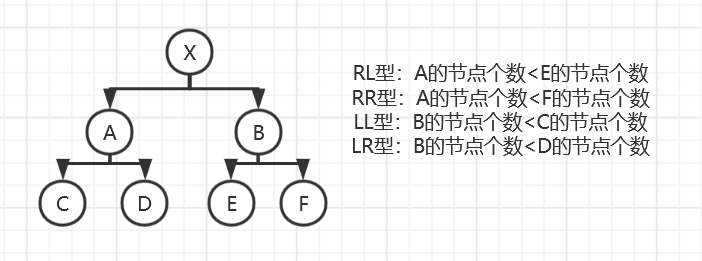
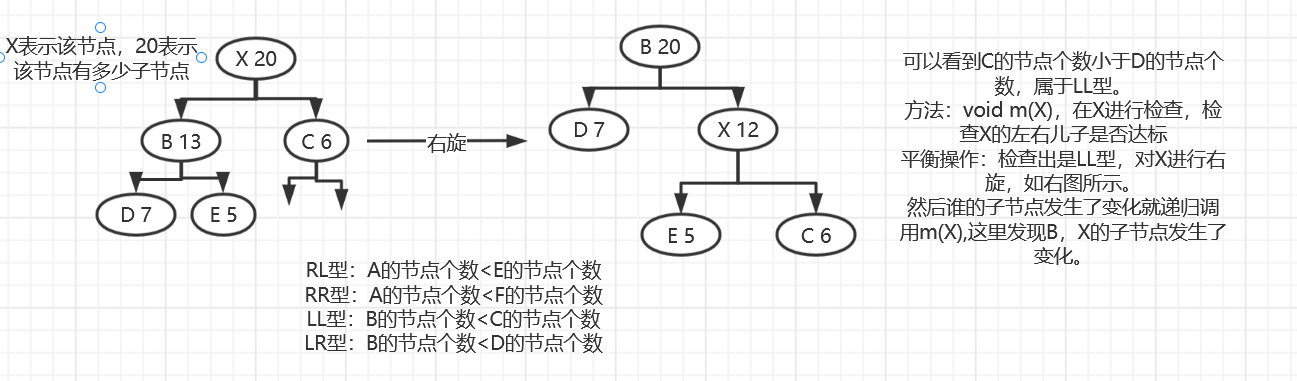
LL:对X进行右旋
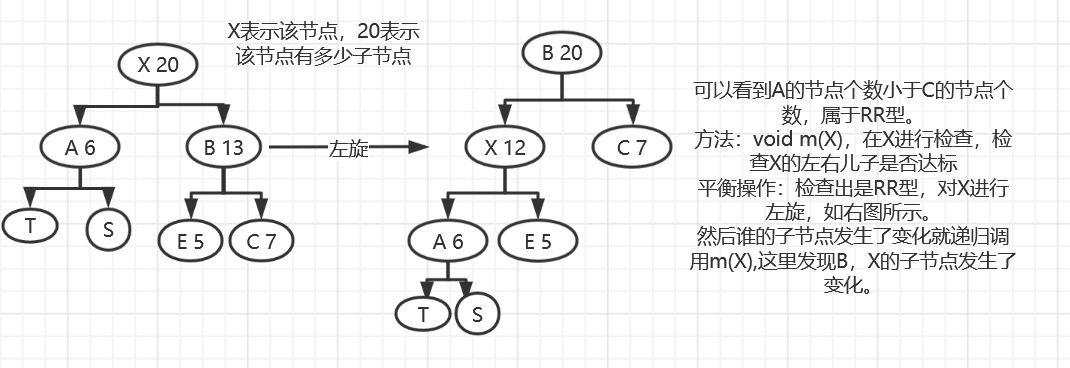
RR:对X进行左旋
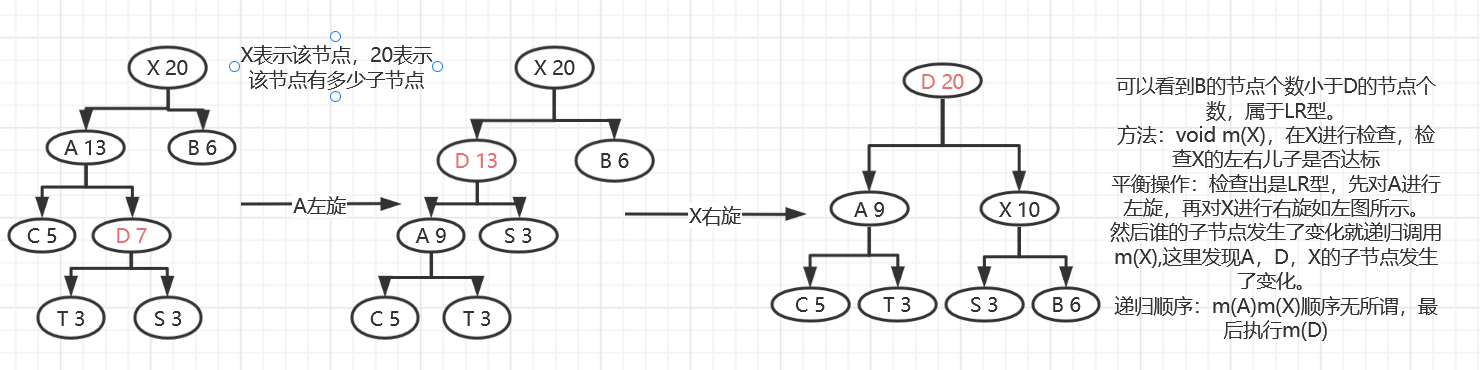
LR: 将有问题的孙子节点旋转到整体顶部
SizeBalance树实现代码:
public static class SBTNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> { public K key; public V value; public SBTNode<K, V> l; public SBTNode<K, V> r; public int size; // 不同的key的数量 public SBTNode(K key, V value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; size = 1; } } public static class SizeBalancedTreeMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> { private SBTNode<K, V> root; //右旋,返回新的头部 private SBTNode<K, V> rightRotate(SBTNode<K, V> cur) { SBTNode<K, V> leftNode = cur.l; cur.l = leftNode.r; leftNode.r = cur; //交换节点的size互换,leftNode到顶部,size与cursize一样 leftNode.size = cur.size; cur.size = (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) + (cur.r != null ? cur.r.size : 0) + 1; return leftNode; } //左旋,返回新的头部 private SBTNode<K, V> leftRotate(SBTNode<K, V> cur) { SBTNode<K, V> rightNode = cur.r; cur.r = rightNode.l; rightNode.l = cur; rightNode.size = cur.size; cur.size = (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) + (cur.r != null ? cur.r.size : 0) + 1; return rightNode; } //调整平衡性,返回新头部 private SBTNode<K, V> maintain(SBTNode<K, V> cur) { if (cur == null) { return null; } int leftSize = cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0; int leftLeftSize = cur.l != null && cur.l.l != null ? cur.l.l.size : 0; int leftRightSize = cur.l != null && cur.l.r != null ? cur.l.r.size : 0; int rightSize = cur.r != null ? cur.r.size : 0; int rightLeftSize = cur.r != null && cur.r.l != null ? cur.r.l.size : 0; int rightRightSize = cur.r != null && cur.r.r != null ? cur.r.r.size : 0; //LL型:左孩子的左孩子的size>右孩子的size,右旋一次,俩次递归 if (leftLeftSize > rightSize) { cur = rightRotate(cur); cur.r = maintain(cur.r); cur = maintain(cur); //LR型:左孩子的右孩子的size>右孩子的size,俩次调整,三次递归 } else if (leftRightSize > rightSize) { cur.l = leftRotate(cur.l); cur = rightRotate(cur); cur.l = maintain(cur.l); cur.r = maintain(cur.r); cur = maintain(cur); //RR型:右孩子的右孩子的size>左孩子的size,左旋一次,俩次调用 } else if (rightRightSize > leftSize) { cur = leftRotate(cur); cur.l = maintain(cur.l); cur = maintain(cur); //RL型:右孩子的左孩子的size>左孩子的size,俩次调整,三次递归 } else if (rightLeftSize > leftSize) { cur.r = rightRotate(cur.r); cur = leftRotate(cur); cur.l = maintain(cur.l); cur.r = maintain(cur.r); cur = maintain(cur); } return cur; } //找到这个key返回,没找到返回最近的不空的节点 private SBTNode<K, V> findLastIndex(K key) { SBTNode<K, V> pre = root; SBTNode<K, V> cur = root; while (cur != null) { pre = cur; if (key.compareTo(cur.key) == 0) { break; } else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) { cur = cur.l; } else { cur = cur.r; } } return pre; } private SBTNode<K, V> findLastNoSmallIndex(K key) { SBTNode<K, V> ans = null; SBTNode<K, V> cur = root; while (cur != null) { if (key.compareTo(cur.key) == 0) { ans = cur; break; } else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) { ans = cur; cur = cur.l; } else { cur = cur.r; } } return ans; } private SBTNode<K, V> findLastNoBigIndex(K key) { SBTNode<K, V> ans = null; SBTNode<K, V> cur = root; while (cur != null) { if (key.compareTo(cur.key) == 0) { ans = cur; break; } else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) { cur = cur.l; } else { ans = cur; cur = cur.r; } } return ans; } // 现在,以cur为头的树上,新增,加(key, value)这样的记录 // 加完之后,会对cur做检查,该调整调整 // 返回,调整完之后,整棵树的新头部 private SBTNode<K, V> add(SBTNode<K, V> cur, K key, V value) { if (cur == null) { return new SBTNode<K, V>(key, value); } else { cur.size++; if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) { //因为add后可能换头部,让左孩子把原本的左孩子加完key的新头部抓住 cur.l = add(cur.l, key, value); } else { cur.r = add(cur.r, key, value); } //当前节点的平衡性调整 return maintain(cur); } } // 在cur这棵树上,删掉key所代表的节点 // 返回cur这棵树的新头部 private SBTNode<K, V> delete(SBTNode<K, V> cur, K key) { cur.size--; if (key.compareTo(cur.key) > 0) { cur.r = delete(cur.r, key); } else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) { cur.l = delete(cur.l, key); } else { // 当前要删掉cur if (cur.l == null && cur.r == null) { // free cur memory -> C++ cur = null; } else if (cur.l == null && cur.r != null) { // free cur memory -> C++ cur = cur.r; } else if (cur.l != null && cur.r == null) { // free cur memory -> C++ cur = cur.l; } else { // 有左有右 SBTNode<K, V> pre = null; SBTNode<K, V> des = cur.r; des.size--; while (des.l != null) { pre = des; des = des.l; des.size--; } if (pre != null) { pre.l = des.r; des.r = cur.r; } des.l = cur.l; des.size = des.l.size + (des.r == null ? 0 : des.r.size) + 1; // free cur memory -> C++ cur = des; } } // cur = maintain(cur); return cur; } private SBTNode<K, V> getIndex(SBTNode<K, V> cur, int kth) { if (kth == (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) + 1) { return cur; } else if (kth <= (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0)) { return getIndex(cur.l, kth); } else { return getIndex(cur.r, kth - (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) - 1); } } public int size() { return root == null ? 0 : root.size; } //查询有没有这个key public boolean containsKey(K key) { if (key == null) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } SBTNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key); return lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.key) == 0 ? true : false; } // (key,value) put -> 有序表 新增、改value public void put(K key, V value) { if (key == null) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } //先去查有没有这个key SBTNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key); //key已经存在,属于修改value if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.key) == 0) { lastNode.value = value; } else { //这个节点不存在,添加新的节点,root可能会换,所以要用root抓住返回值做为新的头部 root = add(root, key, value); } } public void remove(K key) { if (key == null) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } //先查有没有key,有的话delete if (containsKey(key)) { root = delete(root, key); } } public K getIndexKey(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= this.size()) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } return getIndex(root, index + 1).key; } public V getIndexValue(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= this.size()) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } return getIndex(root, index + 1).value; } public V get(K key) { if (key == null) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } SBTNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key); if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.key) == 0) { return lastNode.value; } else { return null; } } public K firstKey() { if (root == null) { return null; } SBTNode<K, V> cur = root; while (cur.l != null) { cur = cur.l; } return cur.key; } public K lastKey() { if (root == null) { return null; } SBTNode<K, V> cur = root; while (cur.r != null) { cur = cur.r; } return cur.key; } public K floorKey(K key) { if (key == null) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } SBTNode<K, V> lastNoBigNode = findLastNoBigIndex(key); return lastNoBigNode == null ? null : lastNoBigNode.key; } public K ceilingKey(K key) { if (key == null) { throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter."); } SBTNode<K, V> lastNoSmallNode = findLastNoSmallIndex(key); return lastNoSmallNode == null ? null : lastNoSmallNode.key; } } // for test public static void printAll(SBTNode<String, Integer> head) { System.out.println("Binary Tree:"); printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17); System.out.println(); } // for test public static void printInOrder(SBTNode<String, Integer> head, int height, String to, int len) { if (head == null) { return; } printInOrder(head.r, height + 1, "v", len); String val = to + "(" + head.key + "," + head.value + ")" + to; int lenM = val.length(); int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2; int lenR = len - lenM - lenL; val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR); System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val); printInOrder(head.l, height + 1, "^", len); } // for test public static String getSpace(int num) { String space = " "; StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer(""); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { buf.append(space); } return buf.toString(); }
跳表skiplist (了解内容)
跳表并不是树结构的,它的每个节点是一个值加一个数组的结构,通过概率而实现的一种和平衡搜索二叉树功能相似的结构,它使用随机的平衡策略取代平衡树严格的强制的树平衡策略。因此它具有更简单有效的插入/删除方法以及更快的搜索速度。目前开源软件 Redis和 LevelDB都有用到它
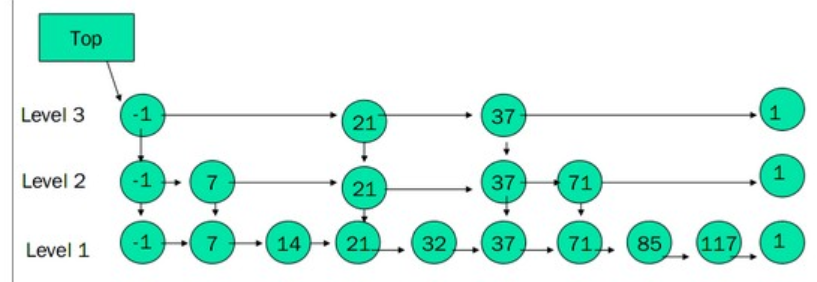
一个跳表,应该具有以下特征:
- 一个跳表应该有几个层(level)组成;
- 跳表的第一层包含所有的元素;
- 每一层都是一个有序的链表;
- 如果元素x出现在第i层,则所有比i小的层都包含x;
- 第i层的元素通过一个down指针指向下一层拥有相同值的元素;
- 在每一层中,-1和1两个元素都出现(分别表示INT_MIN和INT_MAX);
- Top指针指向最高层的第一个元素。
构建有序链表
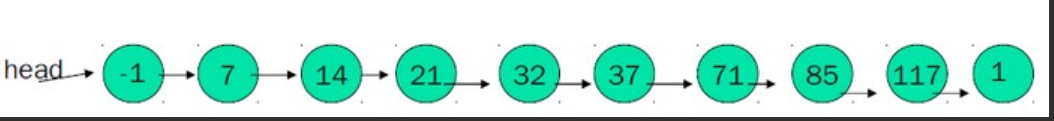
跳表
跳表代码实现:
// 跳表的节点定义 public static class SkipListNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> { public K key; public V val; public ArrayList<SkipListNode<K, V>> nextNodes; public SkipListNode(K k, V v) { key = k; val = v; nextNodes = new ArrayList<SkipListNode<K, V>>(); } // 遍历的时候,如果是往右遍历到的null(next == null), 遍历结束 // 头(null), 头节点的null,认为最小 // node -> 头,node(null, "") node.isKeyLess(!null) true // node里面的key是否比otherKey小,true,不是false public boolean isKeyLess(K otherKey) { // otherKey == null -> false return otherKey != null && (key == null || key.compareTo(otherKey) < 0); } public boolean isKeyEqual(K otherKey) { return (key == null && otherKey == null) || (key != null && otherKey != null && key.compareTo(otherKey) == 0); } } public static class SkipListMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> { private static final double PROBABILITY = 0.5; // < 0.5 继续做,>=0.5 停 private SkipListNode<K, V> head; private int size; private int maxLevel; public SkipListMap() { head = new SkipListNode<K, V>(null, null); head.nextNodes.add(null); // 0 size = 0; maxLevel = 0; } // 从最高层开始,一路找下去, // 最终,找到第0层的<key的最右的节点 private SkipListNode<K, V> mostRightLessNodeInTree(K key) { if (key == null) { return null; } int level = maxLevel; SkipListNode<K, V> cur = head; while (level >= 0) { // 从上层跳下层 // cur level -> level-1 cur = mostRightLessNodeInLevel(key, cur, level--); } return cur; } // 在level层里,如何往右移动 // 现在来到的节点是cur,来到了cur的level层,在level层上,找到<key最后一个节点并返回 private SkipListNode<K, V> mostRightLessNodeInLevel(K key, SkipListNode<K, V> cur, int level) { SkipListNode<K, V> next = cur.nextNodes.get(level); while (next != null && next.isKeyLess(key)) { cur = next; next = cur.nextNodes.get(level); } return cur; } public boolean containsKey(K key) { if (key == null) { return false; } SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key); SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0); return next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key); } // 新增、改value public void put(K key, V value) { if (key == null) { return; } // 0层上,最右一个,< key 的Node -> >key SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key); SkipListNode<K, V> find = less.nextNodes.get(0); if (find != null && find.isKeyEqual(key)) { find.val = value; } else { // find == null 8 7 9 size++; int newNodeLevel = 0; while (Math.random() < PROBABILITY) { newNodeLevel++; } // newNodeLevel while (newNodeLevel > maxLevel) { head.nextNodes.add(null); maxLevel++; } SkipListNode<K, V> newNode = new SkipListNode<K, V>(key, value); for (int i = 0; i <= newNodeLevel; i++) { newNode.nextNodes.add(null); } int level = maxLevel; SkipListNode<K, V> pre = head; while (level >= 0) { // level 层中,找到最右的 < key 的节点 pre = mostRightLessNodeInLevel(key, pre, level); if (level <= newNodeLevel) { newNode.nextNodes.set(level, pre.nextNodes.get(level)); pre.nextNodes.set(level, newNode); } level--; } } } public V get(K key) { if (key == null) { return null; } SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key); SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0); return next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key) ? next.val : null; } public void remove(K key) { if (containsKey(key)) { size--; int level = maxLevel; SkipListNode<K, V> pre = head; while (level >= 0) { pre = mostRightLessNodeInLevel(key, pre, level); SkipListNode<K, V> next = pre.nextNodes.get(level); // 1)在这一层中,pre下一个就是key // 2)在这一层中,pre的下一个key是>要删除key if (next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key)) { // free delete node memory -> C++ // level : pre -> next(key) -> ... pre.nextNodes.set(level, next.nextNodes.get(level)); } // 在level层只有一个节点了,就是默认节点head if (level != 0 && pre == head && pre.nextNodes.get(level) == null) { head.nextNodes.remove(level); maxLevel--; } level--; } } } public K firstKey() { return head.nextNodes.get(0) != null ? head.nextNodes.get(0).key : null; } public K lastKey() { int level = maxLevel; SkipListNode<K, V> cur = head; while (level >= 0) { SkipListNode<K, V> next = cur.nextNodes.get(level); while (next != null) { cur = next; next = cur.nextNodes.get(level); } level--; } return cur.key; } public K ceilingKey(K key) { if (key == null) { return null; } SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key); SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0); return next != null ? next.key : null; } public K floorKey(K key) { if (key == null) { return null; } SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key); SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0); return next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key) ? next.key : less.key; } public int size() { return size; } }
红黑树
- 所有的节点非红即黑
- 整棵树的头节点必然是黑
- 底节点(叶节点的子节点)是黑,指为空的节点
- 红节点的子节点为黑节点,黑节点的子节点可以是黑
- 任何一个节点任何一条链(一条分支)里的黑节点数量

之前那些平衡性的要求做了一件这样的事,就是,一条链长度不会超过另一条链长度两倍链都是红黑红黑这样排布的。AVL树,SB树只有LL,LR,RR,RL四种违规情况,红黑树插入违规情况5种,删除违规情况8种。
总结
AVL树、SB树、红黑树,本质都是二叉搜索树,只不过,在搜索树的前提下,提供了左旋和右旋调整平衡的操作,注意,这三种结构调整平衡的步骤都是左旋右旋。因此,由于这三种结构对平衡的定义不同,因此,出现不平衡的判断条件不同,导致他们调用左旋右旋的策略不同,他们的区别,仅此而已。跳表并不是树结构的,它的每个节点是一个值加一个数组的结构,通过概率而实现的一种和平衡搜索二叉树功能相似的结构。AVL树平衡定义是任意一个节点的左右子树的高度差不能超过1,因此,AVL树的不平衡状态,就包括四种情况LL,LR,RR,RL。SB树的平衡定义是每个结点所在子树的结点个数不小于其兄弟的两个孩子所在子树的结点个数。不算重复的key,只算这个树上有多少不同的key。SB树的不平衡状态也包括LL,LR,RR,RL这四种情况。因此我们发现AVL树维持了高度,SB树维持了节点的个数。红黑树是通过颜色的约束维持着二叉搜索树的平衡性,它的违规情况是插入违规情况5种,删除违规情况8种。
Reference:
1.对比AVL树,SB树,红黑树
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43923436/article/details/117964247
2.二叉树专题(平衡二叉排序树 AVL树 红黑树 SB树 跳表)
https://blog.csdn.net/wdays83892469/article/details/79343718
3.平衡二叉树-AVL树(LL,LR,RR,RL旋)
https://www.cnblogs.com/ybf-yyj/p/9513706.html
4.跳表数据结构
https://www.cnblogs.com/likui360/p/6124640.html
5.红黑树数据结构剖析
https://www.cnblogs.com/fanzhidongyzby/p/3187912.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号