一、前言:
第一次大作业:
作为三次作业里面最简单的一次作业,第一次作业里面没有什么涉及到那种特别大的程序,并且对类的使用也没有那么的明显,虽然有9道题,但基本上使用面向过程的思维就可以解决完,主要是对java的一些语法和一些方法的训练而已,对于新手来说难度比较适中。
第二次大作业:
第二次作业的难度主要是集中在了两个菜单的设计程序上。第一次菜单的程序设计考察的知识点不多,在第一次作业中题目已经把菜单给固定好了,只需要输入菜名就可以了,并且对类的使用也并不是那么的明显。主要是为了让大家初步掌握一下类是如何使用的,以及面对一个大程序的时候我们该如何去划分这个类的职责,也就是设计好每个类需要干什么,进一步便是我们该如何去使用类里面的属性和方法。其中涉及到的类也不多,并且题目已经把类的模版给我们设计好了。对于刚刚接触java不久的学者来说可能难度算是中档难度。(现在看来真的已经算是很简单的了)
虽然第一次菜单的作业和第二次菜单的作业都是属于第二次大作业中,并且题目顺序都是挨着的,但是不得不说第二次菜单的作业相比于第一次菜单的作业来说难度陡然上升了很多很多。首先从输入上来说固定的菜单变成了需要我们用户手动输入的菜单,这从一开始可把我给难到了,不知道如何判断用户已经开始输入订单了,后来才想到原来可以从输入的第一个字符串如果是数字的话那么就代表用户开始输入订单了。而后续还要判断用户输入的订单上的菜是否在饭店的菜单上是存在的,这给输入的难度大大增加了很多。本题对类使用的必要性提高了很多很多,需要大家能够对类的使用有了比较清晰的了解。(但我这题基本上是面向过程来写的…)这对于一个接触java不久的人来说难度可能已经算上比较难的了(现在看来感觉可能也就中档难度)
第三次大作业:
这次的第三次菜单的作业难度在第二次菜单作业的难度上又提升了一个档次,继续添加了不同桌号的点菜以及不同时间段的点菜,帮别人点菜的功能。这不光需要判断此时的输入是否是桌号,还需要判断此时的价格是不是需要打折,以及当前这个时间段是不是可以点菜,还有此时的输入是不是在帮其他人点菜(还要判断帮助其他人点的菜是不是饭店菜单上拥有的)。这道题对类使用的必要性是非常非常高的(我一开始用面向过程来写,最多只能拿到10分,后面写的思维就十分混乱了)。基本上不使用面向对象的思维很难能够通过这个测试点了。另外就是这个测试点非常难找,即使放到现在我也感觉这道题的难度可以算得上是很难很难了。
二、设计与分析:
(1)第一次菜单作业:
对于第一次菜单作业其实我基本上就没怎么用到面向对象的思维,基本上就是面向过程。程序复杂度的结果如下
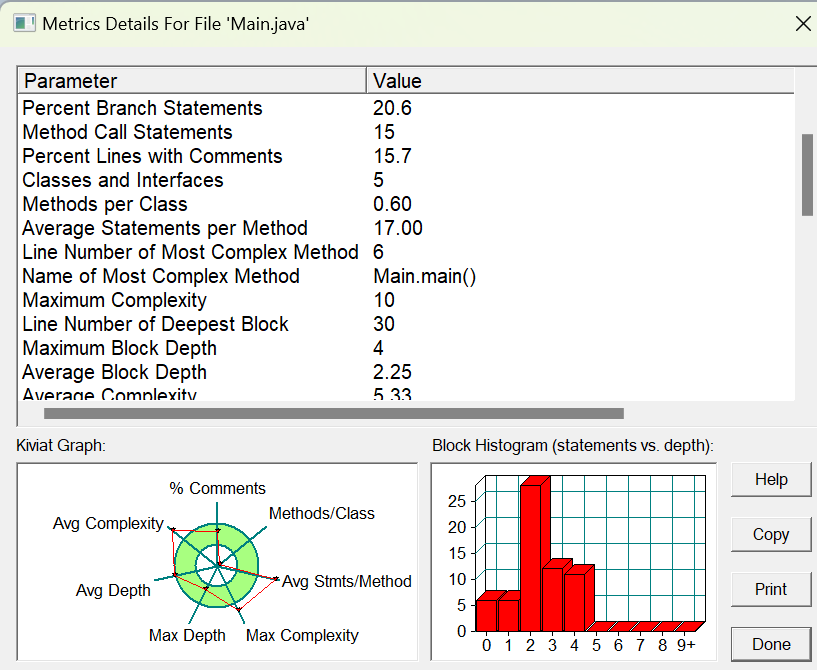
虽然是面向过程的思路,但是由于第一次
菜单作业的题目并不是特别难,因此程序的圈复杂度也只不过是10而已。并且对类的使用是少之又少,基本上就没怎么用到过类。类的设计上面基本上就没用到什么实际的东西,甚至order类基本就没使用过。
public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String name[] = new String[100]; Menu menu = new Menu(); Dish dish = new Dish(); Record record = new Record(); int t = 0, flag = 0; menu.dishes[0] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[1] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[2] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[3] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[0].unit_price = 15; menu.dishes[1].unit_price = 12; menu.dishes[2].unit_price = 12; menu.dishes[3].unit_price = 9; int sumPrice = 0; while (true) { record.d = new Dish(); record.d.name = sc.next(); if (record.d.name.equalsIgnoreCase("西红柿炒蛋")) { record.portion = sc.nextInt(); sumPrice += menu.dishes[0].getPrice(record.portion); //System.out.println(sumPrice); } else if (record.d.name.equalsIgnoreCase("清炒土豆丝")) { record.portion = sc.nextInt(); sumPrice += menu.dishes[1].getPrice(record.portion); //System.out.println(sumPrice); } else if (record.d.name.equalsIgnoreCase("麻婆豆腐")) { record.portion = sc.nextInt(); sumPrice += menu.dishes[2].getPrice(record.portion); //System.out.println(sumPrice); } else if (record.d.name.equalsIgnoreCase("油淋生菜")) { record.portion = sc.nextInt(); sumPrice += menu.dishes[3].getPrice(record.portion); //System.out.println(sumPrice); } else if (record.d.name.equalsIgnoreCase("end")) { break; } else { record.portion = sc.nextInt(); name[t] = record.d.name; t++; flag = 1; } } if (flag == 1) { for(int i = 0;i<t;i++) { System.out.println(name[i] + " does not exist"); } System.out.println(sumPrice); } else System.out.println(sumPrice); } } class Record { //保存订单上的一道菜品记录 Dish d; //菜品 int portion; //份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) } class Menu { //对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 Dish []dishes = new Dish[4]; //菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 /*public Dish searthDish(String dishName){ //根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象 }*/ } class Dish { //对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 String name; //菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 public int getPrice(int portion) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) double price = 0; if (portion == 1) { price = unit_price; } else if (portion == 2) { price = unit_price * 1.5; } else if (portion == 3) { price = unit_price * 2; } int price1 = (int) (run(price)); return price1; } double run(double num) { double a = Math.signum(num); //判断是正数负数还是0,负数返回-1.0,正数返回1.0 if (a < 0.0) return 0.0 - Math.round(Math.abs(num)); return Math.round(num); } } class Order { //保存用户点的所有菜的信息 Record[] records; ////保存订单上每一道的记录 /*int getTotalPrice(){ //计算订单的总价 } Record addARecord(String dishName,int portion){ //添加一条菜品信息到订单中 }*/ }
其中record类用来存储订单上的菜品和份额,menu类中的dish用来存储菜单上的菜品名称和每个菜品的份额,而order类干脆就不使用方法了,甚至唯一一个定义的属性在main方法中都没有被使用过。因此很多东西的使用都放在了主方法里面。直接定义了一个变量sumPrice来求总价。Main方法里面主要是对输入进来的菜品名称进行判断,由于只有四个菜品名称,并且输入还会保证没有输错,因此只需要判断是哪个菜品名称,再把其价格加到总价sumPrice中就行了,在循环的最后再输出sumPrice。
这样的设计对仅仅对第一次菜单作业来说或许是合理的,但是随着菜单程序的不断迭代,后面变得越来越复杂,导致每一次迭代都需要对上一次的代码进行很大程度上的调整,因此这会非常地消耗时间。
(2)第二次菜单作业:
由于在第一次菜单作业当中固有的面向过程的思维当中还没有跳转出来,导致我第二次菜单作业也基本上是使用面向过程的思维,对类的使用也仅仅是调用了极少的方法和一些基本的属性而已。但是第二次难度上升了不少,这种面向过程的思维也导致程序的不可读性上升了很多,程序代码的复杂度也接近了20:
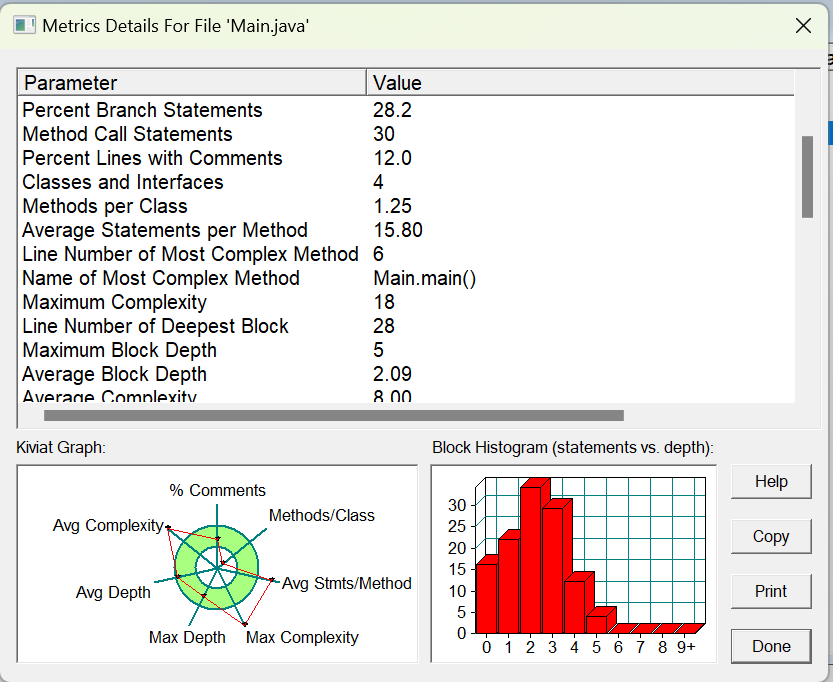
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menu = new Menu(); Record record = new Record(); int sumPrice = 0, flag1 = 0, i = 0, flag = 0, a = 0, b = 0; int price[] = new int[100]; int j = 0, k = 0, flag2 = 0, deleteFlag = 0, jFlag = 0; int lawFlag[] = new int[100]; String definition[] = new String[100]; //用来记录不存在的菜品名称 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < menu.dishes.length; i1++) { menu.dishes[i1] = new Dish(); } for (int i1 = 0; i1 < record.dishs.length; i1++) { record.dishs[i1] = new Dish(); } while (true) { deleteFlag = 0; jFlag = 0; int id = 0; while (true && flag1 == 0) { //菜单上的菜品信息 String name = sc.next(); if (name.equals("1")) { flag1 = 1; break; } else if (name.equals("end")) { System.out.println(0); return; } menu.dishes[i].name = name; menu.dishes[i].unit_price = sc.nextInt(); i++; flag = 1; } if (flag == 1) { String name = sc.next(); //在第一次输入的时候name表示的是订单的菜品名称 if (name.equals("end")) { break; } if (menu.judegeMenu(name, i)) { definition[k++] = name; } record.dishs[j].name = name; record.num[a++] = 1; record.portion = sc.nextInt(); //订单上的菜品的大小份额 record.count = sc.nextInt(); //订单上的菜品的份数 flag = 0;//跳出菜单的输入 int t = -1; for (int i1 = 0; i1 < i; i1++) { if (menu.dishes[i1].name.equals(record.dishs[j].name)) { t = i1; } } if (t != -1) { price[j] = record.count * record.dishs[j].getPrice(record.portion, menu.dishes[t].unit_price); sumPrice += record.count * record.dishs[j].getPrice(record.portion, menu.dishes[t].unit_price); } } else { String name = sc.next();//输入的订单上的序号 if (name.equals("end")) { break; } //判断订单上的序号是否已经存在了, 即是否需要进行delete操作 else if (j != 0 && record.judgeInformation(name, record.num)) { String op = sc.next(); deleteFlag = 1; jFlag = 1; id = Integer.parseInt(name); } //执行到此则订单上的序号不存在,即要么合理输入,要么非法删除 else { String Name = sc.next(); //若此时第二个输入的是delete,即可判断为非法删除 if(Name.equals("delete")){ lawFlag[b++] = j; jFlag = 1; } //执行到此即为正常的订单输入 else{ record.dishs[j].name = Name; //订单上的菜在菜品中不存在 if (menu.judegeMenu(Name, i)) { definition[k++] = Name; } record.portion = sc.nextInt(); record.count = sc.nextInt(); record.num[j] = Integer.parseInt(name); } } int t = -1; //判断订单上的菜是否能在菜品上找到 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < i; i1++) { if (menu.dishes[i1].name.equals(record.dishs[j].name)) { t = i1; } } //能找到的话则价格加入总价格中 if (t != -1) { price[j] = record.count * record.dishs[j].getPrice(record.portion, menu.dishes[t].unit_price); sumPrice += record.count * record.dishs[j].getPrice(record.portion, menu.dishes[t].unit_price); } } //若存在合法删除操作的话,总的价格需要减去此次的价格 if (deleteFlag == 1) { sumPrice -= price[id - 1]; } if (jFlag == 0) { j++; } } for (int i1 = 0; i1 < j; i1++) { flag2 = 0; for (int i2 = 0; i2 < k; i2++) { if (record.dishs[i1].name.equals(definition[i2])) { System.out.println(definition[i2] + " does not exist"); flag2 = 1; } } if (flag2 == 0) { System.out.println(record.num[i1] + " " + record.dishs[i1].name + " " + price[i1]); } for (int i2 = 0; i2 < b; i2++) { if(record.num[i1]==lawFlag[i2]){ System.out.println("delete error;"); } } } System.out.println(sumPrice); } } class Dish { //对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 String name; //菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 public int getPrice(int portion,int money) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) double price = 0; if (portion == 1) { price = money; } else if (portion == 2) { price = money * 1.5; } else if (portion == 3) { price = money * 2; } int price1 = (int) (run(price)); return price1; } double run(double num) { double a = Math.signum(num); //判断是正数负数还是0,负数返回-1.0,正数返回1.0 if (a < 0.0) return 0.0 - Math.round(Math.abs(num)); return Math.round(num); } } class Record { //保存订单上的一道菜品记录 Dish d; //菜品 Dish []dishs = new Dish[100]; int num[] = new int[100];//订单上的序号 int count;//订单上的份数 int portion; //份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) /*int getPrice(String name,int portion){ //计价,计算本条记录的价格 int price = 0; }*/ boolean judgeInformation(String count, int num[]) {//判断序号是否存在 int id = Integer.parseInt(count); for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) { if (id == num[i]) { return true; } } return false; } } class Menu { //对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 Dish []dishes = new Dish[100]; //菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 /*public Dish searchDish(String dishName){ //根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象 }*/ boolean judegeMenu(String name, int length) {//判断菜品的名称在菜单上是否存在 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (dishes[i].name.equals(name)) { return false; } } return true; } }
这次作业相比于第一次菜单作业来说的话呢,菜单从固定变成了自己的输入,最后还需要判断订单上的菜是否在输入中的菜单上存在。
因此在record类上还需要加入了一个序号用来存储用户订单上的序号,其次在record类上还需要加入一个判断序号是否存在的方法,此方法需要将一个序号和一个int类型的数组传进来,然后依次判断该数组的每个元素是否和这个序号相等,若有相等的则返回true,否则最后返回false。
在menu类上又加了一个判断订单上菜品的名称在菜单上是否存在的方法:先将一个菜名和dishes类数组的长度传进来,然后判断dishes类数组每个元素的菜名和传进来的菜名是否相等,若某一次的循环中相等则返回true,否则在循环结束之后返回false。
而主方法的结构由于是半面向过程的,因此算法结构十分复杂,定义了各种各样的数组以及各种各样的判断标志。首先在菜单的输入上,依次判断当前的输入,若不为“1”,则将此次的字符串传进menu类的dish类数组,若为“1”则跳出菜单的输入循环,若为“end”,则直接输出此次的价格为0,然后直接return结束所有程序。结束菜单的输入之后,由于当前是第一次输入,此时序号已经输进来了,当前是要输入菜品名称、份额、份数,而之后的每次输入顺序为订单的序号、菜品名称、份额、份数,因此要把第一次的订单输入和之后的订单输入区分开来。之后再判断序号的输入的时候首先要判断该序号在订单上是否已经存在了,若存在了在该题目的条件下即后续会进行delete的操作,之后就需要把该序号的价钱从总价格上减去。若不存在,则分为两种情况:一种是继续判断后续的输入,若后续的输入为delete,则此时为非法删除,需要输出“delete error”,若后续为菜单的名字,则当前为菜品的合法输入。再每一次的合法输入的时候还需要判断菜名是否在餐馆的菜单上存在了,若不存在,则在最后还需要输出“xxx does not exist”。此外还需要对每次的情况进行判定当前数组的序号是否需要进行j++。
(3)第三次菜单的作业:
第三次作业的可操性更加上升了,不光需要输入桌号进行分类付账,而且还需要判断此时是否在餐馆的正常营业时间以及当前是否需要对用户上的订单进行打折,打折的话又是打几折,如果给其他桌点餐的话那这份钱又需要加入到自己的饭钱里面,并且此次的饭钱又需要进行打折。一开始是继承了前两次的思维继续用面向过程的思维来写的,导致代码的复杂度非常非常的高,并且还有很多很多的测试点没有通过,但这样的情况下改起来会非常的复杂。因此后面被迫真正地使用到了面向对象的思维去构建整个代码的框架以及编写代码。但是即使这样,由于主方法的各种判断语句也导致代码的复杂度非常非常的高:
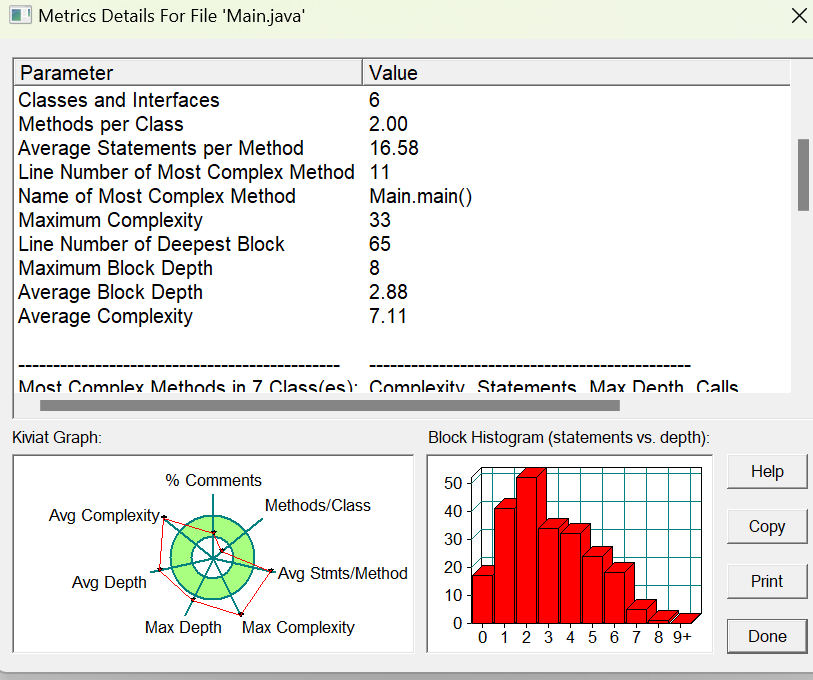
这样的代码的可读性是很低的。
import java.util.Scanner; import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.LocalTime; import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menu = new Menu(); Order order = new Order(); Table table = new Table(); for (int i = 0; i < table.order.length; i++) { table.order[i] = new Order(); for (int i1 = 0; i1 < order.records.length; i1++) { table.order[i].records[i1] = new Record(); } } for (int i = 0; i < menu.dishes.length; i++) { menu.dishes[i] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[i].name = " "; } int flag = 0, tableFlag = 0, tablei = 0, j = 0; int endFlag = 0, accientFlag = 0; int num[] = new int[100]; String accientName = ""; while (true && endFlag == 0) { accientFlag = 0; while (flag == 0) { String dishName = sc.next(); if (dishName.equals("table")) { flag = 1; tableFlag = 1; break; } if (dishName.equals("end")) { return; } int unit_price = sc.nextInt(); menu.addDish(dishName, unit_price); } //输入桌号 if (tableFlag == 1) { table.num[tablei] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[tablei] = sc.next(); table.time[tablei] = sc.next(); table.judgeDiscount(tablei); tablei++; tableFlag = 0; } //输入订单 else { //输入订单上的序号 String id = sc.next(); //System.out.println("id "+id); if(table.num[j] - 1 != 0 && isInteger(id)){ if (tablei - 1 >= 0) { for (int i = 0; i < table.num[tablei - 2]; i++) { if(Integer.parseInt(id) == table.num[i]){ accientFlag = 1; } } } } if (id.equals("end")) { break; } //新的桌号参与进来 else if (id.equals("table")) { //System.out.println("really?"); table.num[tablei] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[tablei] = sc.next(); table.time[tablei] = sc.next(); table.judgeDiscount(tablei); tablei++; j++; while (true) { String dishName = sc.next(); //System.out.println(dishName); if (isInteger(dishName)) { accientName = dishName; break; } if (dishName.equals("end")) { endFlag = 1; break; } String unit_price = sc.next(); } } //正确删除 else if (num[j] != 0 && table.order[tablei - 1].judgeInformation(id)) { String option = sc.next(); if (option.equals("delete")) { table.order[tablei - 1].delARecordByOrderNum(Integer.parseInt(id)); } else if (isInteger(id)) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpTable = Integer.parseInt(id); String dishName = sc.next(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(option); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); if (menu.searchDish(dishName) != null) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); } else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].existFlag = 1; } table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpFlag = 1; num[j]++; } } else if(accientFlag == 1){ //System.out.println("accidentName "+accientName); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpTable = Integer.parseInt(accientName); String dishName = sc.next(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(id); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); if (menu.searchDish(dishName) != null) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); } else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].existFlag = 1; } table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpFlag = 1; num[j]++; } //如果id为菜名的话 else if (!isInteger(id)) { int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = 1; table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(id); table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(id, portion, count); num[j]++; } //非法删除或者合理输入 else { String dishName = sc.next(); //输入的第二个为delete,但在订单上没有此序号,因此判定为非法删除 if (dishName.equals("delete")) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].deleteFlag = 1; table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d.name = dishName; table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, 0, 0); num[j]++; } //正确输入 else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(id); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); if (menu.searchDish(dishName) != null) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); } else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].existFlag = 1; } table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); num[j]++; } } } } for (int i = 0; i < tablei; i++) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + ": "); int m = num[i]; for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m; i1++) { if (table.order[i].records[i1].deleteFlag == 1) { System.out.println("delete error;"); } //不存在 else if (table.order[i].records[i1].existFlag == 1) { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].d.name + " does not exist"); } //有人帮忙付款 else if (table.order[i].records[i1].helpFlag == 1) { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].orderNum + " table " + table.num[i] + " pay for table " + table.order[i].records[i1].helpTable + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].getPrice()); } //正常输出 else { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].orderNum + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].d.name + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].getPrice()); } } } for (int i = 0; i < tablei; i++) { if (table.order[i].workFlag == 0) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + ": " + Math.round(table.order[i].getTotalPrice() * table.order[i].discount)); } else { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + " out of opening hours"); } } } public static boolean isInteger(String str) { Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\\+]?[\\d]*$"); return pattern.matcher(str).matches(); } } class Table { Order order[] = new Order[100]; int num[] = new int[100];//桌子的序号 String date[] = new String[100]; String time[] = new String[100]; int sumPrice[] = new int[100]; //double discount; //...... //int workFlag = 0; void judgeDiscount(int i){ String d[] = date[i].split("/"); String t[] = time[i].split("/"); LocalDate d1 = LocalDate.of(Integer.parseInt(d[0]), Integer.parseInt(d[1]), Integer.parseInt(d[2])); LocalTime d2 = LocalTime.of(Integer.parseInt(t[0]), Integer.parseInt(t[1]), Integer.parseInt(t[2])); LocalTime dRelaxStart = LocalTime.of(9, 30); LocalTime dRelaxEnd = LocalTime.of(21, 30); LocalTime dWorkStart1 = LocalTime.of(10, 30); LocalTime dWorkStart2 = LocalTime.of(17, 0); LocalTime dWorkEnd1 = LocalTime.of(14, 30); LocalTime dWorkEnd2 = LocalTime.of(20, 30); int day = d1.getDayOfWeek().getValue(); if (day == 6 || day == 7) { if (d2.isAfter(dRelaxEnd) || d2.isBefore(dRelaxStart)) { order[i].workFlag = 1; } else{ order[i].discount = 1; } } else { if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart1) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd1))||(d2.until(dWorkStart1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { order[i].discount = 0.6; } else if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart2) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd2))||(d2.until(dWorkStart2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { order[i].discount = 0.8; } else { order[i].workFlag = 1; } } } } class Menu { //对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 Dish[] dishes = new Dish[100];//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 int length = 0; /*public Dish searchDish(int id){ //判断序号是否存在 }*/ boolean judgeMenu(String name, int length) {//判断菜品的名称在菜单上是否存在 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (dishes[i].name.equals(name)) { return false; } } return true; } Dish searchDish(String dishName) { for (int i = 0; i < dishes.length; i++) { if(dishes[i].name.equals(dishName)){ return dishes[i]; } } return null; //未找到 } void addDish(String dishName, int unit_price) { dishes[length].name = dishName; dishes[length].unit_price = unit_price; length++; } } class Order { //保存用户点的所有菜的信息 Record[] records = new Record[100]; ////保存订单上每一道的记录 int length = 0; double discount; int workFlag = 0; int totalPrice = 0; int getTotalPrice() { //计算订单的总价 for (Record record : records) { totalPrice += record.getPrice(); } return totalPrice; } boolean judgeInformation(String n){ int id = Integer.parseInt(n); for (Record record : records) { if(record.orderNum == id){ return true; } } return false; } //添加一条菜品信息到订单中 void addARecord(String dishName, int portion, int count) { records[length].d.name = dishName; records[length].portion = portion; records[length].count = count; length++; } void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (records[i].orderNum == orderNum) { totalPrice -= Math.toIntExact(Math.round(records[i].getPrice())); } } } } class Record { //保存订单上的一道菜品记录 Dish d = new Dish(); //菜品 //Dish[] dishs = new Dish[100]; //int num[] = new int[100];//订单上的序号 int orderNum; int count;//订单上的份数 int portion; //份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) int deleteFlag = 0; int existFlag = 0; int helpFlag = 0; int helpTable; int getPrice(){ return count * d.getPrice(portion); } } class Dish { //对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 String name; //菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 public int getPrice(int portion) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) double price = 0; if (portion == 1) { price = unit_price; } else if (portion == 2) { price = unit_price * 1.5; } else if (portion == 3) { price = unit_price * 2; } int price1 = (int) (run(price)); return price1; } double run(double num) { double a = Math.signum(num); //判断是正数负数还是0,负数返回-1.0,正数返回1.0 if (a < 0.0) return 0.0 - Math.round(Math.abs(num)); return Math.round(num); } }
由于此次需要判断桌号了,因此引入了一个新的类,取名为table类,其中的属性包括了一个order类的数组和两个字符串类型的数组用来存储输入进来的日期,方法包括了判断此时的日期是否在题目所给定的范围之内,以及对order类中的discount进行修改来判断此时是否需要打折。
此次的Menu类修改了一下判断菜品名称的方法,只需要传进来一个菜品的名称,然后在当前的dishes类的数组下寻找是否存在一个元素的菜名与之相等,若有则返回true,循环的最后返回一个false。以及另外定义了一个方法是直接将菜名和单价加入到当前dishes类的数组中,之后数组的索引+1。
此次的record类中定义了一个方法用来求当前订单上此次的价格的,另外还定义了一些新的属性,比如说deleteFlag用来判断是否需要删除一个订单,existFlag用来判断是否此次的菜品名称在菜单上存在,helpFlag用来判断是否需要帮其他桌点餐,helpTable用来存储当前帮其他餐桌点菜时其他餐桌的桌号。
此次终于将order类给用上了,在order类中定义了一个record类型的数组,以及还有用来求所有订单的总价的方法,还有一个判断此时输入的订单号是否存在的方法,以及一个把菜品名称加入到当前record类型的方法,最后就是根据一个序号来删除一条订单的方法。
而对于主方法来说的话,首先就是进行菜单的输入,而当前由于后面会存在第二次菜单的输入,因此当前结束菜单输入的条件分为两种:一种是第一次输入菜单,直接遇到“table”字符串而跳出菜单的输入,第二种是非第一次输入,当前碰到一个数字字符串类型的跳出菜单的输入。之后若是第一次进行桌号的输入的话呢还需要输入桌号、此时吃饭的年月日、时分秒。之后还需要判断是不是有新的桌号输入进来了,(即此时输入的字符串是“table”),以及按照第二次菜单作业的那样判断是否需要删除,是否是合法输入又或者是非法删除,但此时还需要加入一种情况的讨论,也就是当非第一次输入菜单的时候,后面输入的字符串不一定是以数字字符串打头的序号,有可能是菜单的名字,因此还需要加入一个若当前的不是数字字符串的判断。
三、踩坑心得
I. 实然层面上:
(1)第一次菜单作业:
在一开始的时候对最后的那个“xxxx does not exist”的输出的时候选择的语句是:
if (flag == 1) { while (t != 0) { t--; System.out.println(name[t] + " does not exist"); System.out.println(sumPrice); } } else System.out.println(sumPrice);
这就导致输出的顺序跟题目要求的不太一样,从而导致答案的错误,这算是属于没有很好的分析出题目要求的输出顺序。
之后虽然意识到了这个输出顺序的问题,但是对于一些细小的错误,比如说循环结束条件的取等问题依然还是判断错误了:
if (flag == 1) { for(int i = 0;i< = t;i++) { System.out.println(name[i] + " does not exist"); } System.out.println(sumPrice);
}
这里本不应该对这个t取等的,这就导致程序的最后会输出一个null does not exist的形式。
(2)第二次菜单作业:
在最后的一个输出的时候呢将“does not”写成了“dose no”,当时找半天都没有找出来的错误:
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < j; i1++) { flag2 = 0; for (int i2 = 0; i2 < k; i2++) { if (record.dishs[i1].name.equals(definition[i2])) { System.out.println(definition[i2] + " does no exist"); flag2 = 1; } } if (flag2 == 0) { System.out.println(record.num[i1] + " " + record.dishs[i1].name + " " + price[i1]); } }
这里纯粹是属于粗心大意了。
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < j; i1++) { System.out.println(record.num[i1] + " " + record.dishs[i1].name + " " + price[i1]); } /*for (int i1 = 0, m = 0; i1 < j; i1++) { if (N[m] != i1) { //遇到菜单上不存在的菜品不需要输出 System.out.println(record.num[i1] + " " + record.dishs[i1].name + " " + price[i1]); } else { m++; } }*/ //订单上存在菜品上不存在的菜品 if (flag2 == 1) { for (int i1 = 0; i1 < k; i1++) { System.out.println(definition[i1] + " does no exist"); } } //存在错误删除 if (flag5 == 1) { while (amount != 0) { System.out.println("delete error;"); amount--; } } System.out.println(sumPrice);
在最后输出的时候是各自的状态输出各自的状态的,并不是按照顺序输出的,没有考虑算法结构的严谨性。
(3)第三次菜单作业
在一开始选择用面向过程的思想来写,导致整个的复杂度很高。
import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.LocalTime; import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menu = new Menu(); Record record = new Record(); Table table = new Table(); int flag1 = 0, i = 0, flag = 0, a = 0, b = 0; int price[] = new int[100]; int j = 0, k = 0, flag2 = 0, deleteFlag = 0, jFlag = 0, y = 0; int workFlag = 0, eightFlag = 0, sixFlag = 0; int lawFlag[] = new int[100]; String definition[] = new String[100]; //用来记录不存在的菜品名称 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < menu.dishes.length; i1++) { menu.dishes[i1] = new Dish(); } for (int i1 = 0; i1 < record.dishs.length; i1++) { record.dishs[i1] = new Dish(); } for (int i1 = 0; i1 < table.sumPrice.length; i1++) { table.sumPrice[i1] = 0; } int s[] = new int[100]; int count[] = new int[100]; while (true) { deleteFlag = 0; jFlag = 0; int id = 0; workFlag = 0; sixFlag = 0; eightFlag = 0; while (true && flag1 == 0) { //菜单上的菜品信息 String name = sc.next(); if (name.equals("table")) { flag1 = 1; break; } else if (name.equals("end")) { return; } int p = sc.nextInt();//价格 menu.addDish(name, p, i); /*menu.dishes[i].name = name; menu.dishes[i].unit_price = sc.nextInt();*/ i++; flag = 1; } if (flag == 1) { table.num[y] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[y] = sc.next(); table.time[y++] = sc.next(); flag = 0; jFlag = 1; //防止j++; } else { String date[] = table.date[y - 1].split("/"); String time[] = table.time[y - 1].split("/"); LocalDate d1 = LocalDate.of(Integer.parseInt(date[0]), Integer.parseInt(date[1]), Integer.parseInt(date[2])); LocalTime d2 = LocalTime.of(Integer.parseInt(time[0]), Integer.parseInt(time[1]), Integer.parseInt(time[2])); LocalTime dRelaxStart = LocalTime.of(9, 30); LocalTime dRelaxEnd = LocalTime.of(21, 0); LocalTime dWorkStart1 = LocalTime.of(10, 30); LocalTime dWorkStart2 = LocalTime.of(17, 0); LocalTime dWorkEnd1 = LocalTime.of(14, 30); LocalTime dWorkEnd2 = LocalTime.of(20, 30); int day = d1.getDayOfWeek().getValue(); if (day == 6 || day == 7) { if (d2.isAfter(dRelaxEnd) || d2.isBefore(dRelaxStart)) { workFlag = 1; } } else { if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart1) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd1))||(d2.until(dWorkStart1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { sixFlag = 1; } else if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart2) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd2))||(d2.until(dWorkStart2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { eightFlag = 1; } else { workFlag = 1; } } String name = sc.next();//输入的订单上的序号 if (name.equals("end")) { break; } //判断订单上的序号是否已经存在了, 即是否需要进行delete操作 else if (j != 0 && record.judgeInformation(name, record.num)) { String op = sc.next(); deleteFlag = 1; jFlag = 1; id = Integer.parseInt(name); //System.out.println("really?"); } //执行到此则订单上的序号不存在,即要么合理输入,要么非法删除 else { String Name = sc.next(); //若此时第二个输入的是delete,即可判断为非法删除 if (Name.equals("delete")) { lawFlag[b++] = j; jFlag = 1; } //执行到此即为正常的订单输入 else { record.dishs[j].name = Name; //订单上的菜在菜品中不存在 if (menu.judegeMenu(Name, i)) { definition[k++] = Name; } else{ record.num[j] = Integer.parseInt(name); } record.portion = sc.nextInt(); record.count = sc.nextInt(); //record.num[j] = Integer.parseInt(name); count[j] = Integer.parseInt(name); } } int t = -1; //判断订单上的菜是否能在菜品上找到 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < i; i1++) { if (menu.dishes[i1].name.equals(record.dishs[j].name)) { t = i1; } } int p = 0; //能找到的话则价格加入总价格中 if (t != -1) { price[j] = record.count * record.dishs[j].getPrice(record.portion, menu.dishes[t].unit_price); if(sixFlag == 1){ p = (int) Math.round(0.6 * price[j]); s[j] = p; } else if(eightFlag == 1){ p = (int) Math.round(0.8 * price[j]); s[j] = p; //System.out.println("p is "+p); } else{ p = price[j]; s[j] = p; } if (eightFlag == 1) { table.sumPrice[y - 1] += p; //System.out.println("price is " +table.sumPrice[y - 1]); } else if (sixFlag == 1) { table.sumPrice[y - 1] += p; } else{ table.sumPrice[y - 1] += record.count * record.dishs[j].getPrice(record.portion, menu.dishes[t].unit_price); } } } //若存在合法删除操作的话,总的价格需要减去此次的价格 if (deleteFlag == 1) { table.sumPrice[y - 1] -= s[id - 1]; } if (jFlag == 0) { j++; } } for (int i3 = 0; i3 < y; i3++) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i3] + ": "); for (int i1 = 0; i1 < j; i1++) { flag2 = 0; for (int i2 = 0; i2 < k; i2++) { if (record.dishs[i1].name.equals(definition[i2])) { System.out.println(definition[i2] + " does not exist"); flag2 = 1; } } if (flag2 == 0) { System.out.println(record.num[i1] + " " + record.dishs[i1].name + " " + price[i1]); } for (int i2 = 0; i2 < b; i2++) { if (count[i1] == lawFlag[i2]) { System.out.println("delete error;"); } } } if (workFlag == 1) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i3] + " out of opening hours"); } else{ System.out.println("table " + table.num[i3] + ": " + table.sumPrice[i3]); } } } } class Record { //保存订单上的一道菜品记录 Dish d; //菜品 Dish[] dishs = new Dish[100]; int num[] = new int[100];//订单上的序号 int count;//订单上的份数 int portion; //份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) boolean judgeInformation(String count, int num[]) {//判断序号是否存在 int id = Integer.parseInt(count); for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) { if (id == num[i]) { return true; } } return false; } int getPrice(int j,Menu menu,int t){ int sum = 0; sum = count * dishs[j].getPrice(portion,menu.dishes[t].unit_price); return sum; } } class Dish { //对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 String name; //菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 public int getPrice(int portion,int money) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) double price = 0; if (portion == 1) { price = money; } else if (portion == 2) { price = money * 1.5; } else if (portion == 3) { price = money * 2; } int price1 = (int) (run(price)); return price1; } double run(double num) { double a = Math.signum(num); //判断是正数负数还是0,负数返回-1.0,正数返回1.0 if (a < 0.0) return 0.0 - Math.round(Math.abs(num)); return Math.round(num); } } class Table { int num[] = new int[100];//桌子的序号 String date[] = new String[100]; String time[] = new String[100]; int sumPrice[] = new int[100]; } class Menu { //对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 Dish[] dishes = new Dish[100]; //菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 /*public Dish searchDish(int id){ //判断序号是否存在 }*/ boolean judegeMenu(String name, int length) {//判断菜品的名称在菜单上是否存在 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (dishes[i].name.equals(name)) { return false; } } return true; } void addDish(String name, int price, int j){ dishes[j].name = name; dishes[j].unit_price = price; } } class Order { //保存用户点的所有菜的信息 Record[] records; ////保存订单上每一道的记录 /*int getTotalPrice(int i){ //计算订单的总价 int sum = 0; sum = records[i].getPrice(); }*/ void addARecord(String dishName,int portion,int j){//添加一条菜品信息到订单中 records[j].dishs[j].name = dishName; records[j].portion = portion; } }
上面用了各种各样的数组,用了各种各样的判断语句,但是也仅仅拿到了10分而已。
import java.util.Scanner; import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.LocalTime; import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menu = new Menu(); Order order = new Order(); Table table = new Table(); for (int i = 0; i < table.order.length; i++) { table.order[i] = new Order(); for (int i1 = 0; i1 < order.records.length; i1++) { table.order[i].records[i1] = new Record(); } } for (int i = 0; i < menu.dishes.length; i++) { menu.dishes[i] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[i].name = " "; } int flag = 0, tableFlag = 0, tablei = 0, j = 0; int num[] = new int[100]; while (true) { while (flag == 0) { String dishName = sc.next(); if (dishName.equals("table")) { flag = 1; tableFlag = 1; break; } int unit_price = sc.nextInt(); menu.addDish(dishName, unit_price); } //输入桌号 if (tableFlag == 1) { table.num[tablei] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[tablei] = sc.next(); table.time[tablei] = sc.next(); table.judgeDiscount(tablei); tablei++; tableFlag = 0; } //输入订单 else { //输入订单上的序号 String id = sc.next(); //System.out.println("id "+id); if (id.equals("end")) { break; } //新的桌号参与进来 else if (id.equals("table")) { table.num[tablei] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[tablei] = sc.next(); table.time[tablei] = sc.next(); table.judgeDiscount(tablei); tablei++; j++; while (true) { String dishName = sc.next(); if (dishName.equals("1")) { break; } String unit_price = sc.next(); } } //正确删除 else if (num[j] != 0 && table.order[tablei - 1].judgeInformation(id)) { String option = sc.next(); if (option.equals("delete")) { table.order[tablei - 1].delARecordByOrderNum(Integer.parseInt(id)); } else if(isInteger(id)) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpTable = Integer.parseInt(id); String dishName = sc.next(); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(option); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpFlag = 1; num[j]++; } } //如果id为菜名的话 else if (!isInteger(id)) { int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = 1; table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(id); table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(id, portion, count); num[j]++; } //非法删除或者合理输入 else { String dishName = sc.next(); //System.out.println("dishName "+dishName); //输入的第二个为delete,但在订单上没有此序号,因此判定为非法删除 if (dishName.equals("delete")) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].deleteFlag = 1; table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d.name = dishName; table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, 0, 0); num[j]++; } //正确输入 else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(id); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); if (menu.searchDish(dishName) != null) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); } else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].existFlag = 1; } table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); num[j]++; } } } } for (int i = 0; i < tablei; i++) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + ": "); int m = num[i]; for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m; i1++) { if (table.order[i].records[i1].deleteFlag == 1) { System.out.println("delete error;"); } //不存在 else if (table.order[i].records[i1].existFlag == 1) { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].d.name + " does not exist"); } //有人帮忙付款 else if (table.order[i].records[i1].helpFlag == 1) { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].orderNum + " table " + table.num[i] + " pay for table " + table.order[i].records[i1].helpTable + " "+ table.order[i].records[i1].getPrice()); } //正常输出 else { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].orderNum + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].d.name + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].getPrice()); } } } for (int i = 0; i < tablei; i++) { if (table.order[i].workFlag == 0) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + ": " + Math.round(table.order[i].getTotalPrice() * table.order[i].discount)); } else { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + " out of opening hours"); } } } public static boolean isInteger(String str) { Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\\+]?[\\d]*$"); return pattern.matcher(str).matches(); } } class Table { Order order[] = new Order[100]; int num[] = new int[100];//桌子的序号 String date[] = new String[100]; String time[] = new String[100]; int sumPrice[] = new int[100]; //double discount; //...... //int workFlag = 0; void judgeDiscount(int i){ String d[] = date[i].split("/"); String t[] = time[i].split("/"); LocalDate d1 = LocalDate.of(Integer.parseInt(d[0]), Integer.parseInt(d[1]), Integer.parseInt(d[2])); LocalTime d2 = LocalTime.of(Integer.parseInt(t[0]), Integer.parseInt(t[1]), Integer.parseInt(t[2])); LocalTime dRelaxStart = LocalTime.of(9, 30); LocalTime dRelaxEnd = LocalTime.of(21, 0); LocalTime dWorkStart1 = LocalTime.of(10, 30); LocalTime dWorkStart2 = LocalTime.of(17, 0); LocalTime dWorkEnd1 = LocalTime.of(14, 30); LocalTime dWorkEnd2 = LocalTime.of(20, 30); int day = d1.getDayOfWeek().getValue(); if (day == 6 || day == 7) { if (d2.isAfter(dRelaxEnd) || d2.isBefore(dRelaxStart)) { order[i].workFlag = 1; } else{ order[i].discount = 1; } } else { if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart1) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd1))||(d2.until(dWorkStart1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { order[i].discount = 0.6; } else if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart2) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd2))||(d2.until(dWorkStart2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { order[i].discount = 0.8; } else { order[i].workFlag = 1; } } } } class Menu { //对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 Dish[] dishes = new Dish[100];//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 int length = 0; /*public Dish searchDish(int id){ //判断序号是否存在 }*/ boolean judgeMenu(String name, int length) {//判断菜品的名称在菜单上是否存在 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (dishes[i].name.equals(name)) { return false; } } return true; } Dish searchDish(String dishName) { for (int i = 0; i < dishes.length; i++) { if(dishes[i].name.equals(dishName)){ return dishes[i]; } } return null; //未找到 } void addDish(String dishName, int unit_price) { dishes[length].name = dishName; dishes[length].unit_price = unit_price; length++; } } class Order { //保存用户点的所有菜的信息 Record[] records = new Record[100]; ////保存订单上每一道的记录 int length = 0; double discount; int workFlag = 0; int totalPrice = 0; int getTotalPrice() { //计算订单的总价 for (Record record : records) { totalPrice += record.getPrice(); } return totalPrice; } boolean judgeInformation(String n){ int id = Integer.parseInt(n); for (Record record : records) { if(record.orderNum == id){ return true; } } return false; } //添加一条菜品信息到订单中 void addARecord(String dishName, int portion, int count) { records[length].d.name = dishName; records[length].portion = portion; records[length].count = count; length++; } void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (records[i].orderNum == orderNum) { totalPrice -= Math.toIntExact(Math.round(records[i].getPrice())); } } } } class Record { //保存订单上的一道菜品记录 Dish d = new Dish(); //菜品 //Dish[] dishs = new Dish[100]; //int num[] = new int[100];//订单上的序号 int orderNum; int count;//订单上的份数 int portion; //份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) int deleteFlag = 0; int existFlag = 0; int helpFlag = 0; int helpTable; int getPrice(){ return count * d.getPrice(portion); } } class Dish { //对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 String name; //菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 public int getPrice(int portion) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) double price = 0; if (portion == 1) { price = unit_price; } else if (portion == 2) { price = unit_price * 1.5; } else if (portion == 3) { price = unit_price * 2; } int price1 = (int) (run(price)); return price1; } double run(double num) { double a = Math.signum(num); //判断是正数负数还是0,负数返回-1.0,正数返回1.0 if (a < 0.0) return 0.0 - Math.round(Math.abs(num)); return Math.round(num); } }
后面忽略了考虑当为别人点菜的时候如果点菜的菜名在菜单上是不在的话是需要输出是“xxx does not exist”
import java.util.Scanner; import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.LocalTime; import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menu = new Menu(); Order order = new Order(); Table table = new Table(); for (int i = 0; i < table.order.length; i++) { table.order[i] = new Order(); for (int i1 = 0; i1 < order.records.length; i1++) { table.order[i].records[i1] = new Record(); } } for (int i = 0; i < menu.dishes.length; i++) { menu.dishes[i] = new Dish(); menu.dishes[i].name = " "; } int flag = 0, tableFlag = 0, tablei = 0, j = 0; int endFlag = 0; int num[] = new int[100]; while (true && endFlag == 0) { while (flag == 0) { String dishName = sc.next(); if (dishName.equals("table")) { flag = 1; tableFlag = 1; break; } if(dishName.equals("end")){ return; } int unit_price = sc.nextInt(); menu.addDish(dishName, unit_price); } //输入桌号 if (tableFlag == 1) { table.num[tablei] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[tablei] = sc.next(); table.time[tablei] = sc.next(); table.judgeDiscount(tablei); tablei++; tableFlag = 0; } //输入订单 else { //输入订单上的序号 String id = sc.next(); //System.out.println("id "+id); if (id.equals("end")) { break; } //新的桌号参与进来 else if (id.equals("table")) { //System.out.println("really?"); table.num[tablei] = sc.nextInt(); table.date[tablei] = sc.next(); table.time[tablei] = sc.next(); table.judgeDiscount(tablei); tablei++; j++; while (true) { String dishName = sc.next(); //System.out.println(dishName); if (dishName.equals("1")) { break; } if(dishName.equals("end")){ endFlag = 1; break; } String unit_price = sc.next(); } } //正确删除 else if (num[j] != 0 && table.order[tablei - 1].judgeInformation(id)) { String option = sc.next(); if (option.equals("delete")) { table.order[tablei - 1].delARecordByOrderNum(Integer.parseInt(id)); } else if(isInteger(id)) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpTable = Integer.parseInt(id); String dishName = sc.next(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(option); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); if (menu.searchDish(dishName) != null) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); } else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].existFlag = 1; } table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].helpFlag = 1; num[j]++; } } //如果id为菜名的话 else if (!isInteger(id)) { int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = 1; table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(id); table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(id, portion, count); num[j]++; } //非法删除或者合理输入 else { String dishName = sc.next(); //System.out.println("dishName "+dishName); //输入的第二个为delete,但在订单上没有此序号,因此判定为非法删除 if (dishName.equals("delete")) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].deleteFlag = 1; table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d.name = dishName; table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, 0, 0); num[j]++; } //正确输入 else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].orderNum = Integer.parseInt(id); int portion = sc.nextInt(); int count = sc.nextInt(); if (menu.searchDish(dishName) != null) { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].d = menu.searchDish(dishName); } else { table.order[tablei - 1].records[num[j]].existFlag = 1; } table.order[tablei - 1].addARecord(dishName, portion, count); num[j]++; } } } } for (int i = 0; i < tablei; i++) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + ": "); int m = num[i]; for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m; i1++) { if (table.order[i].records[i1].deleteFlag == 1) { System.out.println("delete error;"); } //不存在 else if (table.order[i].records[i1].existFlag == 1) { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].d.name + " does not exist"); } //有人帮忙付款 else if (table.order[i].records[i1].helpFlag == 1) { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].orderNum + " table " + table.num[i] + " pay for table " + table.order[i].records[i1].helpTable + " "+ table.order[i].records[i1].getPrice()); } //正常输出 else { System.out.println(table.order[i].records[i1].orderNum + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].d.name + " " + table.order[i].records[i1].getPrice()); } } } for (int i = 0; i < tablei; i++) { if (table.order[i].workFlag == 0) { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + ": " + Math.round(table.order[i].getTotalPrice() * table.order[i].discount)); } else { System.out.println("table " + table.num[i] + " out of opening hours"); } } } public static boolean isInteger(String str) { Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-\\+]?[\\d]*$"); return pattern.matcher(str).matches(); } } class Table { Order order[] = new Order[100]; int num[] = new int[100];//桌子的序号 String date[] = new String[100]; String time[] = new String[100]; int sumPrice[] = new int[100]; //double discount; //...... //int workFlag = 0; void judgeDiscount(int i){ String d[] = date[i].split("/"); String t[] = time[i].split("/"); LocalDate d1 = LocalDate.of(Integer.parseInt(d[0]), Integer.parseInt(d[1]), Integer.parseInt(d[2])); LocalTime d2 = LocalTime.of(Integer.parseInt(t[0]), Integer.parseInt(t[1]), Integer.parseInt(t[2])); LocalTime dRelaxStart = LocalTime.of(9, 30); LocalTime dRelaxEnd = LocalTime.of(21, 0); LocalTime dWorkStart1 = LocalTime.of(10, 30); LocalTime dWorkStart2 = LocalTime.of(17, 0); LocalTime dWorkEnd1 = LocalTime.of(14, 30); LocalTime dWorkEnd2 = LocalTime.of(20, 30); int day = d1.getDayOfWeek().getValue(); if (day == 6 || day == 7) { if (d2.isAfter(dRelaxEnd) || d2.isBefore(dRelaxStart)) { order[i].workFlag = 1; } else{ order[i].discount = 1; } } else { if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart1) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd1))||(d2.until(dWorkStart1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd1, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { order[i].discount = 0.6; } else if ((d2.isAfter(dWorkStart2) && d2.isBefore(dWorkEnd2))||(d2.until(dWorkStart2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0||d2.until(dWorkEnd2, ChronoUnit.SECONDS)==0)) { order[i].discount = 0.8; } else { order[i].workFlag = 1; } } } } class Menu { //对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 Dish[] dishes = new Dish[100];//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 int length = 0; /*public Dish searchDish(int id){ //判断序号是否存在 }*/ boolean judgeMenu(String name, int length) {//判断菜品的名称在菜单上是否存在 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (dishes[i].name.equals(name)) { return false; } } return true; } Dish searchDish(String dishName) { for (int i = 0; i < dishes.length; i++) { if(dishes[i].name.equals(dishName)){ return dishes[i]; } } return null; //未找到 } void addDish(String dishName, int unit_price) { dishes[length].name = dishName; dishes[length].unit_price = unit_price; length++; } } class Order { //保存用户点的所有菜的信息 Record[] records = new Record[100]; ////保存订单上每一道的记录 int length = 0; double discount; int workFlag = 0; int totalPrice = 0; int getTotalPrice() { //计算订单的总价 for (Record record : records) { totalPrice += record.getPrice(); } return totalPrice; } boolean judgeInformation(String n){ int id = Integer.parseInt(n); for (Record record : records) { if(record.orderNum == id){ return true; } } return false; } //添加一条菜品信息到订单中 void addARecord(String dishName, int portion, int count) { records[length].d.name = dishName; records[length].portion = portion; records[length].count = count; length++; } void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) { for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (records[i].orderNum == orderNum) { totalPrice -= Math.toIntExact(Math.round(records[i].getPrice())); } } } } class Record { //保存订单上的一道菜品记录 Dish d = new Dish(); //菜品 //Dish[] dishs = new Dish[100]; //int num[] = new int[100];//订单上的序号 int orderNum; int count;//订单上的份数 int portion; //份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) int deleteFlag = 0; int existFlag = 0; int helpFlag = 0; int helpTable; int getPrice(){ return count * d.getPrice(portion); } } class Dish { //对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 String name; //菜品名称 int unit_price; //单价 public int getPrice(int portion) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) double price = 0; if (portion == 1) { price = unit_price; } else if (portion == 2) { price = unit_price * 1.5; } else if (portion == 3) { price = unit_price * 2; } int price1 = (int) (run(price)); return price1; } double run(double num) { double a = Math.signum(num); //判断是正数负数还是0,负数返回-1.0,正数返回1.0 if (a < 0.0) return 0.0 - Math.round(Math.abs(num)); return Math.round(num); } }
这种情况下如果输入中的非法删除在菜单的正确输入的前面的话,会导致整个程序的输出出现问题,原因就在于当时判断非法删除的时候选择了num[j]++,但是加了之后序号也变了,算法考虑还是没有严密。
II.因然层面上:
纵观三次的代码,自己使用的永远都是复杂的判断语句,设置各种各样的循环和数组用来处理事情,或许解决前两次作业还是勉强可以,但是面对第三次作业如此复杂的程度上,使用此方法会消耗大量的脑力去处理复杂的程序结构,并且一旦出了错也需要花大量的时间去找BUG,时间成本和脑力成本都大大增加,这也导致了为什么第三次作业没有拿到满分的结果。
四、主要困难以及改进建议:
I. 主要困难:
(1)从思维上来看的话目前主要困难还是在于没有很好地弄清楚面向对象的思维到底是如何的,而且C语言的面向过程的思想已经可以说是根深蒂固了,对于以后的越来越难的大作业来说,自己还是得尽快地掌握面向对象的思维和面向对象的逻辑。
(2)从逻辑上来看的话,对java的一些方法还没有形成一种“本能的反应”,比如说第三次菜单大作业中的输入本来可以直接使用java当中提供的substring方法,直接通过长度来判断每一次的输入是什么状态,但是自己没有意识到这一点,而是本能的用C语言那一套逻辑,选择去判断是不是菜名,是不是数字,是数字的话后面跟着的又是不是数字,不是数字的话那是不是正确的输入呢?导致一系列判断语句下来,代码的复杂度上升了,自己的头也快秃了。
II.改进建议:
(1)先通过一些小的练习题来让自己能够理解并掌握一下面向对象的思维和逻辑框架。
(2)通过包括但不仅限于看网上的资料,写小题目,看书等方式让自己对java的一些语法和方法形成一种“条件反射”,能够在以后的学习中遇到什么样的困难能够直接联想到java当中是不是有更为简便,更为直接的方法来使用,这样可以减少时间成本,也可以简化一下自己的算法。
(3)对教学相关的建议:
I. 老师方面:以自己的理解力来说的话感觉老师讲的有点儿太快了点儿,有些挺难的知识点老师很快的就讲完了,但是自己连反应过来的时间都没有。有的时候在QQ上问老师问题,老师没有理我,不知道是不是自己的问题好愚蠢还是老师忘记回了(哭哭)。
II. 课程方面:课程设置体系是让学生自学语法,上课主要讲其他知识点,但其实说实话能够真正的去学习语法的学生是很少的,我的建议是应该是每周加一次java课用来补语法。
III. 作业:其实每周都要做一次大作业我是能够理解的,但是类似于第二次作业这种上来就两个菜单大作业我觉得对我们有一些过于自信了,我觉得每次的作业里面设置一道这种很复杂的程序就行了,设置两道的话着实有一些应付不过来。
IV. 实验:由于实验和pta大作业是同一周完成的,基于此来说的话实验的时间相对来说有一些紧张,如果能宽松到跟pta截止时间一样的话或许会好一点。
V. 课上课下的组织方式:老师为了大家能够及时掌握一下课堂上的所学知识,课后会布置一个作业,但是pta的大作业我们都应付不过来,再加上每一次的作业或许会成为最后一根稻草,我想如果能把每一次的作业在课堂上完成的话或许结果会好一点儿。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号