mysql索引
索引
mysql官方对索引的定义为:索引(index)是帮助mysql高校获取数据的数据结构。提取句子主干,就可以得到索引的本质:索引就是数据结构。
索引的分类
- 主键索引(primary key)
- 唯一标识,主键不可重复
- 唯一索引(unique key)
- 避免重复的列出现,唯一索引可以重复,多个列都可以被标识为唯一索引
- 常规索引(key|index)
- 默认的,可以使用index或者key关键字设置
- 全文索引(fulltext)
- 在特定的数据库引擎下才有,比如myisam引擎
- 可以快速定位数据
索引的使用
-- 在创建表的时候给字段增加索引
-- 创建完毕后,增加索引
-- 显示所有的索引信息
show index from students
-- 增加一个全文索引
-- 格式
alter table <表名> add fulltext index <索引名>(<列名>);
-- 代码示例
alter table school.students add fulltext index `name`(`name`);
-- 创建一个索引
-- 格式
create <索引类型> <自定义索引名> on <表名>(<字段名>)
-- 自定义索引名格式:id_表名_字段名
-- 代码示例
create index id_students_name on students(`name`)
分析sql执行的状况
-- explain关键字可以分析sql执行状况
-- 非全文索引
explain select * from students;
--
explain select * from students where match(name) against('刘');
mysql是可以编程的
-- 在mysql中编程之前必须加上delimiter这个关键字
delimiter $$ -- 格式是固定的
-- 创建自定义函数,下面必须安装这个格式编写
create function myfunc()
returns int -- 定义返回类型
begin -- 开始执行
中间就是需要执行的函数逻辑
return 1; -- 返回对应定义好的数据类型的数据
end; --结束执行
测试索引
- 创建测试环境
-- 创建实验表
create table `app_user`(
`id` bigint(20) unsigned not null auto_increment,
`name` varchar(50) default '' comment '用户昵称',
`email` varchar(50) not null comment '用户邮箱',
`phone` varchar(20) default '' comment '手机号',
`gender` tinyint(4) unsigned default '0' comment '性别(0:男;1:女)',
`password` varchar(100) not null comment '密码',
`age` tinyint(4) default '0' comment '年龄',
`create_time` datetime default current_timestamp,
`update_time` timestamp null default current_timestamp on update current_timestamp,
primary key(`id`)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8mb4 comment='app用户表'
-- 插入数据代码
insert into app_user(`name`,`email`,`phone`,`gender`,`password`,`age`)
values
(concat('用户',1),'11111111@qq.com',concat('18',floor(rand()*((999999999-100000000)+100000000))),floor(rand()*2),uuid(),floor(rand()*100))
-- 创建函数,并把插入数据的代码放入循环中,把concat('用户',1)改成concat('用户',i)
delimiter $$
create function mock_data()
returns int
begin
declare num int default 1000000;
declare i int default 0;
while i<num do
insert into app_user(`name`,`email`,`phone`,`gender`,`password`,`age`)
values
(concat('用户',i),'11111111@qq.com',concat('18',floor(rand()*((999999999-100000000)+100000000))),floor(rand()*2),uuid(),floor(rand()*100));
set i=i+1;
end while;
return i;
end;
select mock_data();
-
数据插入效果图
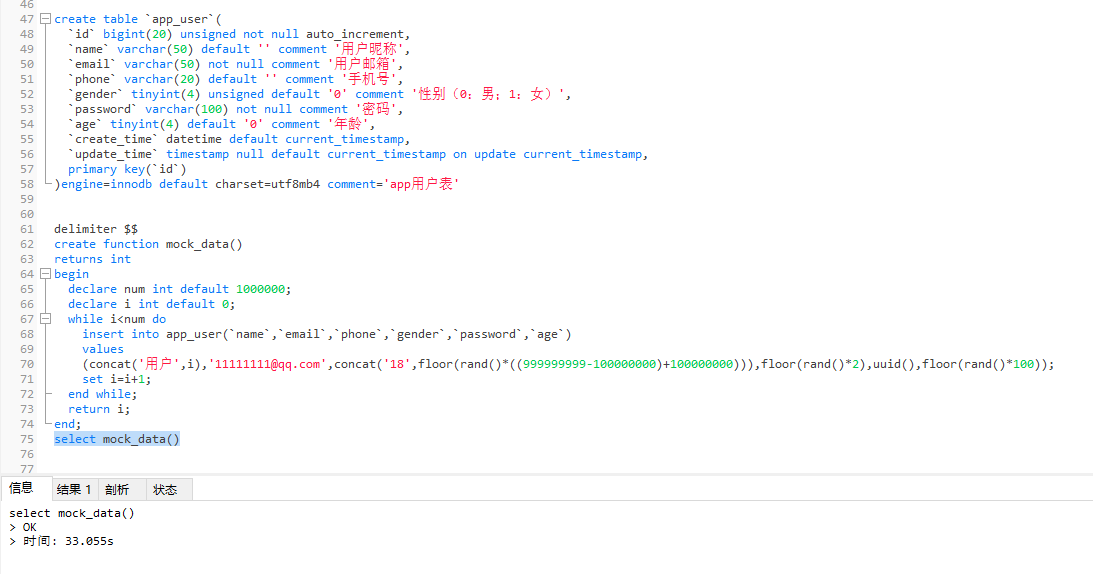
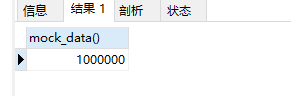
嗯,我用了33.055s -
对比有索引和无索引的区别
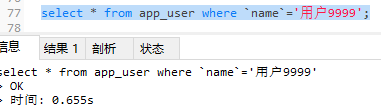
-- 没有索引查询比较靠后的数据
select * from app_user where `name`='用户9999';
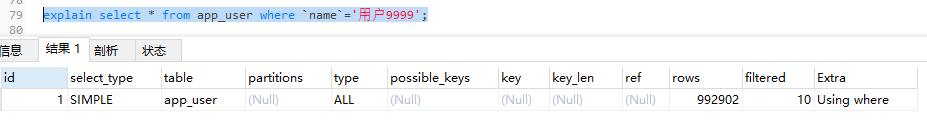
-- 分析没有索引的时候使用查询语句查询靠后的数据
explain select * from app_user where `name`='用户9999';
-- 创建索引
create index id_app_user_name on app_user(`name`);
-- 创建索引会耗费较长时间
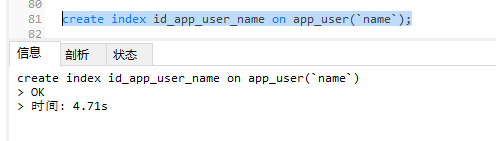
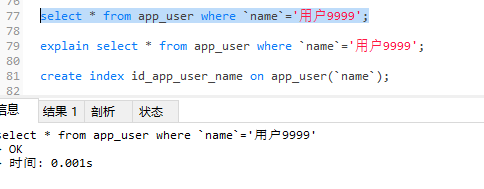
-- 有索引查询比较靠后的数据
select * from app_user where `name`='用户9999';
-- 分析有索引的时候使用查询语句查询靠后的数据
explain select * from app_user where `name`='用户9999';
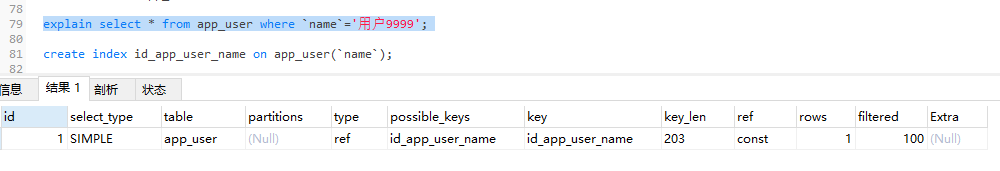
-
索引原则
- 索引不是越多越好
- 不要对经常变动的数据加索引
- 小数据量的表不需要加索引
- 索引一般加在常用来查询的字段上
-
结论
索引在小数据量的时候,用处不大,但是在大数据的时候,区别十分明显。同时我们也会发现,当数据量过大并且创建索引后,插入数据的时间其实是会翻倍的,原因就是每次插入新数据都会影响索引。创建索引的时候其实是比较费时间的。 -
索引的数据结构
hash 类型的索引
btree:innodb的默认数据结构
参考文章
https://blog.csdn.net/jiadajing267/article/details/81269067
http://blog.codinglabs.org/articles/theory-of-mysql-index.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号