2022-08-23 吉林化工学院 第五组 韩嘉宁
CSS续
目录
CSS三大特性
层叠性
(1)标签可以有多个CSS样式
(2)浏览器处理冲突的能力,如果一个属性通过两个相同的选择器设置到元素上
层叠规则:
前提:相同类型选择器才可重叠!!!!
按照样式的声明顺序来层叠(就近原则)
样式不冲突,不会层叠
继承性
子标签会继承父标签的某些样式
如文本颜色和字号
优先级
- 继承优先级最低(0)
- 行内样式(100)
- 权重相同,采用就近原则
- !import命令 无限大
CSS权重公式:
| 继承、* | 0,0,0,0 |
| 标签选择器 | 0,0,0,1 |
| 类、伪类选择器 | 0,0,1,0 |
| ID选择器 | 0100 |
| 行内样式 | 1000 |
| !improtant | 无穷大 |
| width , height | 大于无穷大 |
权重不能被继承
贡献值没有进位
如果同时有max- width,max-height,min-width,min-height, 则 !important 不优先显示
CSS常用单位
| em:绝对单位 。相对于其父级。如父级为16px,子级为 2em 则子级为 32px |
| px (像素):最常用 |
| rem :由整个HTML字号决定。当我们改变浏览器字号时,我们的页面也随之更改。 |
| 百分比:相对父级元素的比例 |
CSS字体
| 字体大小 | font-size |
| 字体粗细 | font-weight |
| 字体修饰 | text-decoration |
| 字体 | font-family |
| 字体样式 | font-style |
| 复合类型 | font: ; |
| (只有font类型可复合) |
列表样式
边框样式
- width
- height
- border -radius : 圆角半径
- border- color : 边框颜色
- border -style :边框样式
- border- bottom-left :边框左上
案例:360管家图标
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.oo {
background-color: green;
border-top-right-radius: 50%;
border-bottom-left-radius: 50%;
width: 500px;
}
.ot {
background-color: rgb(0, 0, 248);
border-top-left-radius: 50%;
border-bottom-right-radius: 50%;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
.to {
background-color: rgb(232, 188, 9);
border-top-left-radius: 50%;
border-bottom-right-radius: 50%;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
.tt {
background-color: rgb(238, 14, 14);
border-top-right-radius: 50%;
border-bottom-left-radius: 50%;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div>
<table>
<tr>
<td class="oo">
<div></div>
</td>
<td class="ot">
<div></div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="to">
<div></div>
</td>
<td class="tt">
<div></div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
效果图如下:

盒子模型
定位
文档流:在网页窗体中有很多行(网页默认布局方式)
(1)static : 文档流,网页默认布局
(2)absolute:绝对定位(相对于父元素)
(3)relative :相对定位(相对于上一个元素位置)
(4)fixed:固定定位
【子绝父相】
-
- 子元素是绝对定位
-
- 父元素是相对定位
【定位left与盒子模型margin-left有什么区别】
- 定位left是相对于父元素的位置,margin是相对于自己的位置
- left是定位的属性
- 盒子模型用margin
- 定位用 left,top,right,bottom
网页常用布局
双列布局
三列布局
可见性
visibility:
visibility: hidden; /*隐藏*/
/* 溢出策略 */
overflow:scroll;
<style>
div{
width: 300px;
height: 1122px;
overflow: hidden;
/* 平铺 */
display: inline-block;
}
div:hover{
overflow: visible;
width: 800px;
height: 1122px;
}
</style>
<body>
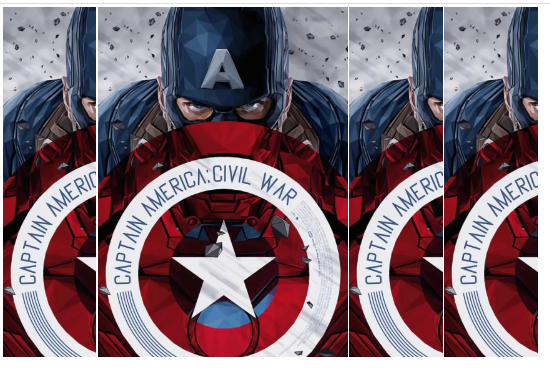
<div>
<img src="美队.png" alt="" >
</div>
<div>
<img src="美队.png" alt="" >
</div>
<div>
<img src="美队.png" alt="" >
</div>
<div>
<img src="美队.png" alt="" >
</div>
</body>
效果图如下:
transition 和animate区别
- transition只能通过固定属性来开始与结束值
- animinate只能一帧一帧的去实现效果
flex布局
块级元素和行内块级元素
1.父容器要加上 display:flex(设置流式布局)
2.排列方向:(flex-direction)
从左到右 row
从右到左 row-reverse
若一行装不下,换行:(flex -wrap :wrap-reverse)
同时设置排序方向换行:flex-flow:row wrap-reverse
前端CSS端必须掌握
- 选择器【十分重要】
- css三大特征:层叠性,继承性,优先级
- 盒子模型
- 定位
- 浮动,清除浮动(****)
- 常见的属性——字体,背景,列表,边框等等
- 元素的隐藏,元素内容的溢出,【overflow,fisplay,visibility】
- 【开发中,推荐使用外部引入的方式】



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号