委托详解
委托
delagate是函数指针(c和c++中)的升级版
函数指针的实例如下:
# include <stdio.h>
int Max(int, int); //函数声明
int main(void)
{
int(*p)(int, int); //定义一个函数指针
int a, b, c;
p = Max; //把函数Max赋给指针变量p, 使p指向Max函数
printf("please enter a and b:");
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
c = (*p)(a, b); //通过函数指针调用Max函数
printf("a = %d\nb = %d\nmax = %d\n", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
int Max(int x, int y) //定义Max函数
{
int z;
if (x > y)
{
z = x;
}
else
{
z = y;
}
return z;
}
//输出结果是:
//please enter a and b:3 4
//a = 3
//b = 4
//max = 4
一切皆地址
变量(数据)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的值
函数(算法)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的一组机器语言指令
所以,变量是寻找数据的地址,函数是寻找算法的地址
直接调用与间接调用
直接调用:通过函数名来调用函数, CPU通过函数名直接获得函数所在地址并开始执行>返回
间接调用:通过函数指针来调用函数, CPU通过读取函数指针存储的值获得函数所在地址并开始执行→返回
JAVA舍弃了函数指针的功能,而C#通过委托保留了这种功能。
C#中有许多现成的委托,比如Action,Function
见下面实例:
class program
{
static void Main[string[] args]
{
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
//Action其实就是无返回值的delegate罢了,Action委托至少0个参数,至多16个参数,无返回值。
Action action = new Action(calculator. Report);
calculator.Report();//直接调用
action.Invoke();//通过委托间接调用
action();
//Function就是有返回值的delegate,也是至多输入16个参数。
Func<int,int,int> func1 = new Func<int,int,int>(calculator.Add);
Func<int,int,int> func2 = new Func<int,int,int>(calculator.Sub);
int x = 100;
int y = 200;
int z = 0;
z = func1.Invoke(x, y);//通过委托间接调用
Console.WriteLine(z);
Z = func2.Invoke(x, y);//通过委托间接调用
Console.Writeline(z);|
//所有的调用都可以省略Invoke
}
}
class Calculator
{
public void Report()
{
Console.Writeline("I have 3 methods.")
}
public int Add(int a,int b)
{
int result = a + b;
return result
}
public int sub(int a,int b)
{
int result = a - b;
return result
}
}
自定义委托
自定义委托重点:委托与所封装的方法必须“类型兼容”
返回值的数据类型一致
参数列表在个数和数据类型上一致(参数名不需要一样)
using System;
delegate int NumberChanger(int n);//声明委托
namespace DelegateAppl
{
class TestDelegate
{
static int num = 10;
public static int AddNum(int p)
{
num += p;
return num;
}
public static int MultNum(int q)
{
num *= q;
return num;
}
public static int getNum()
{
return num;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建委托实例
NumberChanger nc1 = new NumberChanger(AddNum);//封装AddNum,MultNum方法
NumberChanger nc2 = new NumberChanger(MultNum);
// 使用委托对象调用方法
nc1(25);
Console.WriteLine("Value of Num: {0}", getNum());
nc2(5);
Console.WriteLine("Value of Num: {0}", getNum());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
声明委托的位置:委托尽量声明在命名空间里,不要放在别的类里。
委托的一般使用
实例:把方法当作参数传给另一个方法
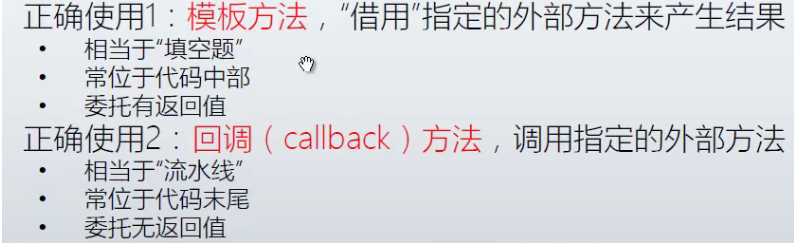
注意:

模板方法实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 产品
/// </summary>
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 包装
/// </summary>
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 包装工厂
/// </summary>
class WrapFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// 模板方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="getProduct">委托变量</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct)
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = getProduct.Invoke();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 生产工厂
/// </summary>
class ProductFactory
{
public Product MakePizza()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
return product;
}
}
}
//输出:Pizza,Toy Car
委托的多播
委托对象可使用 "+" 运算符进行合并。一个合并委托调用它所合并的两个委托。只有相同类型的委托可被合并。"-" 运算符可用于从合并的委托中移除组件委托。
using System;
delegate int NumberChanger(int n);
namespace DelegateAppl
{
class TestDelegate
{
static int num = 10;
public static int AddNum(int p)
{
num += p;
return num;
}
public static int MultNum(int q)
{
num *= q;
return num;
}
public static int getNum()
{
return num;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建委托实例
NumberChanger nc;
NumberChanger nc1 = new NumberChanger(AddNum);
NumberChanger nc2 = new NumberChanger(MultNum);
nc = nc1;
nc += nc2;
// 调用多播
nc(5);
Console.WriteLine("Value of Num: {0}", getNum());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
//输出:Value of Num: 75
隐式异步调用委托
同步与异步的简介
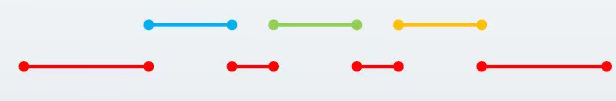
同步:你做完了我(在你的基础上)接着做
异步:咱们两个同时做(相当于汉语中的“同步进行”)
同步:红色代表主线程
异步:
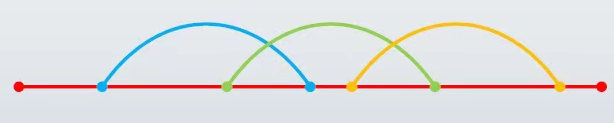
同步调用与异步调用的对比
每一个运行的程序是一个进程 ( process )
每个进程可以有一个或者多个线程( thread )
同步调用是在同一线程内
异步调用的底层机理是多线程
串行同步单线程,并行异步多线程
invoke是同步调用,BeginInvoke是隐式异步调用
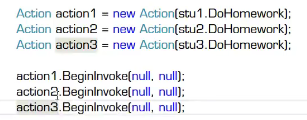
显示异步调用:使用Thread
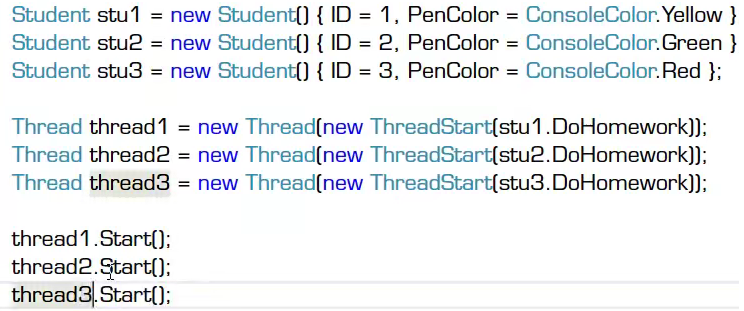
也可以使用Task:
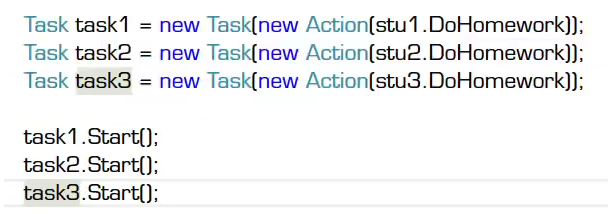
程序中尽量使用接口去替代委托。
如以下代码代替上面工厂实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DelegateExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IProductFactory pizzaFactory = new PizzaFactory();
IProductFactory toycarFactory = new ToyCarFactory();
WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();
Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(pizzaFactory);
Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(toycarFactory);
Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);
}
}
interface IProductFactory
{
Product Make();
}
class PizzaFactory : IProductFactory
{
Product IProductFactory.Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
}
class ToyCarFactory : IProductFactory
{
Product IProductFactory.Make()
{
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Toy Car";
return product;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 产品
/// </summary>
class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 包装
/// </summary>
class Box
{
public Product Product { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 包装工厂
/// </summary>
class WrapFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// 模板方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="getProduct">委托变量</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Box WrapProduct(IProductFactory productFactory)
{
Box box = new Box();
Product product = productFactory.Make();
box.Product = product;
return box;
}
}
}
委托的优点
转载自委托的好处


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号