牛客网Groundhog Looking Dowdy
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5674/F
来源:牛客网
题目描述 :
Groundhog finds that Apple seems to be less intimate than before.
He is very distressed for this.After pondering for a long time, Groundhog finds that he looks too dowdy.So, Groundhog decided to improve a little.
Because Groundhog is lazy, he only lists the clothes that can be worn for the next n{n}n days. On the ith{i^{th}}ith day, the jth{j^{th}}jth clothes have a dowdiness ai,ja_{i,j}ai,j.
On each day,he will choose one of the clothes and wear it.
And Groundhog should choose m{m}m days from n{n}n days to go out with Apple.
Groundhog wants to know the minimum difference between the maximum dowdiness and the minimum dowdiness in m{m}m days when Groundhog's choice is optimal.
Simplified:
You should choose n clothes for each day and then choose m clothes from those n clothes,
and the problem is to calculate the minimum difference between the maximum dowdiness and the minimum dowdiness.
翻译:
有n天,每天穿一件衣服,第 i 天有 k_i 件衣服可以穿,穿第 j 件衣服的的权值为 a_{i, j} 。
从 n 天中选择 m 天,求这 m 天中,所穿衣服的权值最大与最小值的最小差是多少。
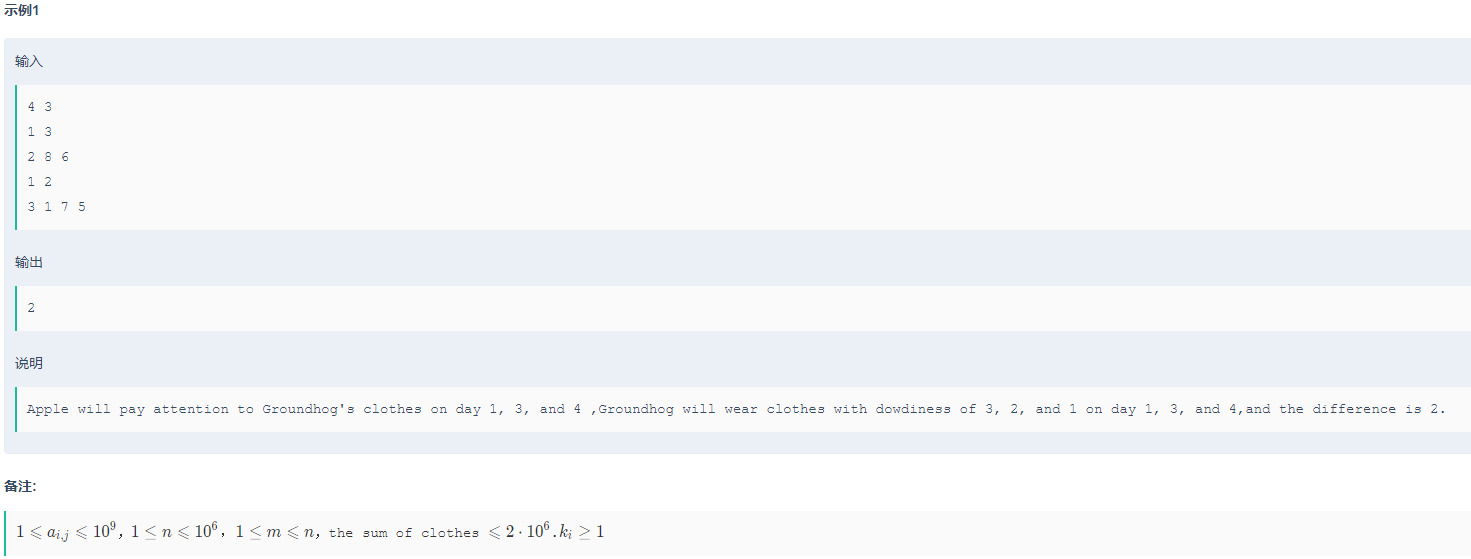
输入描述:
The first line contains two integers n{n}n and m{m}m.
Then n{n}n lines follow,each line contains a integer kik_iki,represents the number of the clothes that can be worn on ith{i^{th}}ith day.Then kik_iki integers ai,ja_{i,j}ai,j follow.
输出描述:
Print in one line the minimum difference.
- 由于要最小化最大值和最小值的差值,因此我们可以把所有衣服按照dowdiness从小到大排个序。
- 排序之后,设最终选出的m件衣服最小覆盖区间为[L,R],则答案为downdiness[R]-downdiness[L]
- 则一个合法的区间至少需要包含m种不同的日期
- 可以对于每个L求出最小的合法的R,这就转化为一个简单的动态窗口问题了。
- 但是由于数据太水,可以求每天的最小全职并求出最小差即可。
正解代码:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node { int v; int h; }a[2000010]; bool cmp(node x,node y) { return x.v < y.v; } int m,cnt=0; int vis[2000010]; int main() { int n,k; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d",&k); for(int j=1;j<=k;j++) { cnt++; scanf("%d",&a[cnt].v); a[cnt].h=i; } } sort(a+1,a+1+cnt,cmp); int ans=1e9; int l=1,r=m; int tmp=0; for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) if(!vis[a[i].h]) vis[a[i].h]++;tmp++; while(tmp<m) { r++; if(!vis[a[r].h]) { vis[a[r].h]++; tmp++; } } for(l,r;r<=cnt;) { ans=min(ans,a[r].v-a[l].v); vis[a[l].h]--; l++; if(vis[a[l-1].h]==0) tmp--; while(tmp<m&&r<=cnt) { r++; if(!vis[a[r].h]) { vis[a[r].h]++; tmp++; } } } printf("%d",ans); }
水代码:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n,m; int l,w; int ans; int a[1000010]; int main() { for (int i=1; i<=1e6; i++) a[i]=1e9+7; ans=1e9+7; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) { scanf("%d",&l); for (int j=1; j<=l; j++) { scanf("%d",&w); a[i]=min(w,a[i]); } } sort(a+1,a+1+n); for (int i=1; i<=n-m; i++) ans=min(ans,a[i+m-1]-a[i]); printf("%d",ans); }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号