BLOG-3
一、前言
1. 知识点:
(1)类和对象:类(class)和对象(object)是两种以计算机为载体的计算机语言的合称。对象是对客观事物的抽象,类是对对象的抽象。类是一种抽象的数据类型。
它们的关系是,对象是类的实例,类是对象的模板。对象是通过new classname产生的,用来调用类的方法;类的构造方法 。
(2)对象交互:当一个对象里有多个对象的时候,那些对象之间是如何交互的,对象和对象之间的联系是如何建立的,对象如何和其他对象交流。
(3)继承与多态:
继承:就是保持已有类的特性而构造新类的过程。继承后,子类能够利用父类中定义的变量和方法,就像它们属于子类本身一样。
多态:(1)一个类继承自某个父类时,对父类中的方法进行改写。
(2)重载是两个方法的名称相同,但参数不同,重载与多态没有关系。
(3)抽象类:Java语言中,用abstract 关键字来修饰一个类时,这个类叫作抽象类。抽象类是它的所有子类的公共属性的集合,是包含一个或多个抽象方法的类。 抽象类可以看作是对类的进一步抽象。在面向对象领域,抽象类主要用来进行类型隐藏。
(4)接口(interface)。
2. 题目:7-1 电信计费系列1-座机计费、7-1 电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费、7-1 电信计费系列3-短信计费
二、设计与分析
7-1 电信计费系列1-座机计费
实现一个简单的电信计费程序:
假设南昌市电信分公司针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式:
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
南昌市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
输入格式:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码除区号外由是7-8位数字组成。
本题只考虑计费类型0-座机计费,电信系列2、3题会逐步增加计费类型。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
注意:
本题非法输入只做格式非法的判断,不做内容是否合理的判断(时间除外,否则无法计算),比如:
1、输入的所有通讯信息均认为是同一个月的通讯信息,不做日期是否在同一个月还是多个月的判定,直接将通讯费用累加,因此月租只计算一次。
2、记录中如果同一电话号码的多条通话记录时间出现重合,这种情况也不做判断,直接 计算每条记录的费用并累加。
3、用户区号不为南昌市的区号也作为正常用户处理。
输出格式:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,
单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯信息单独计费后累加,不是将所有时间累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3,可根据理解自行调整:
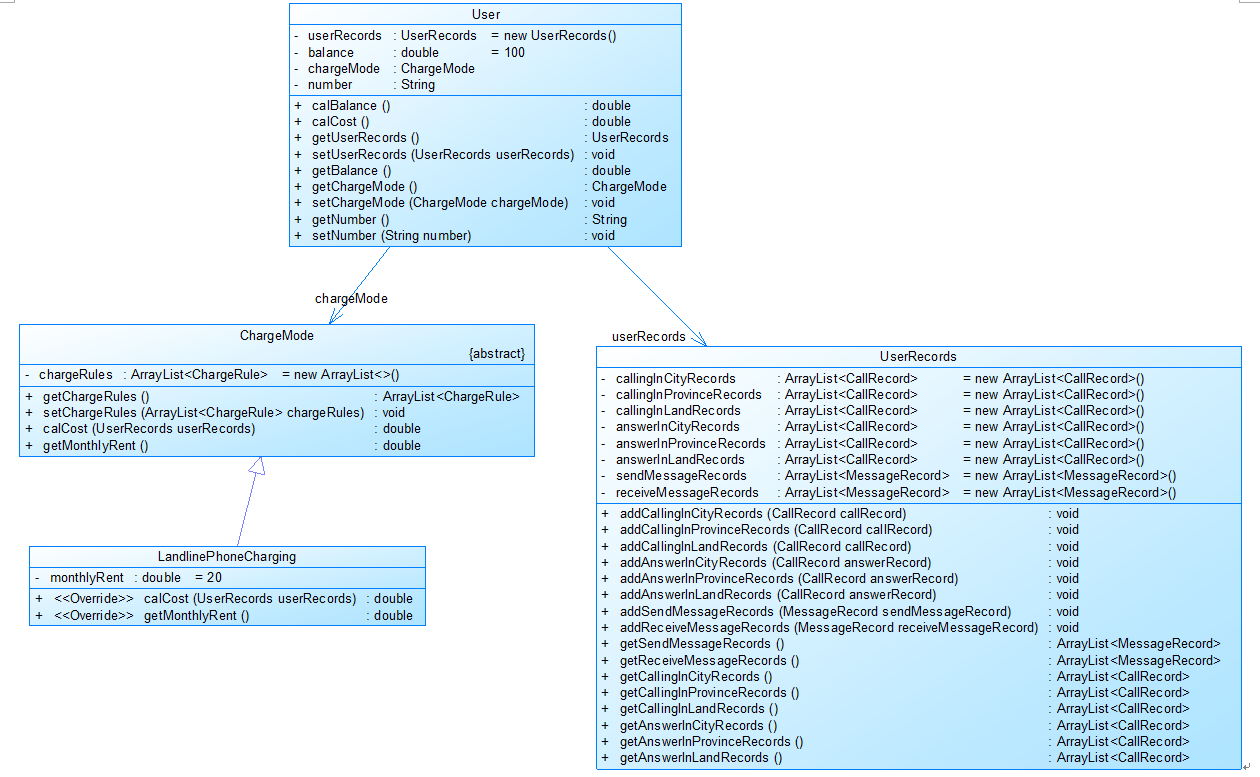
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
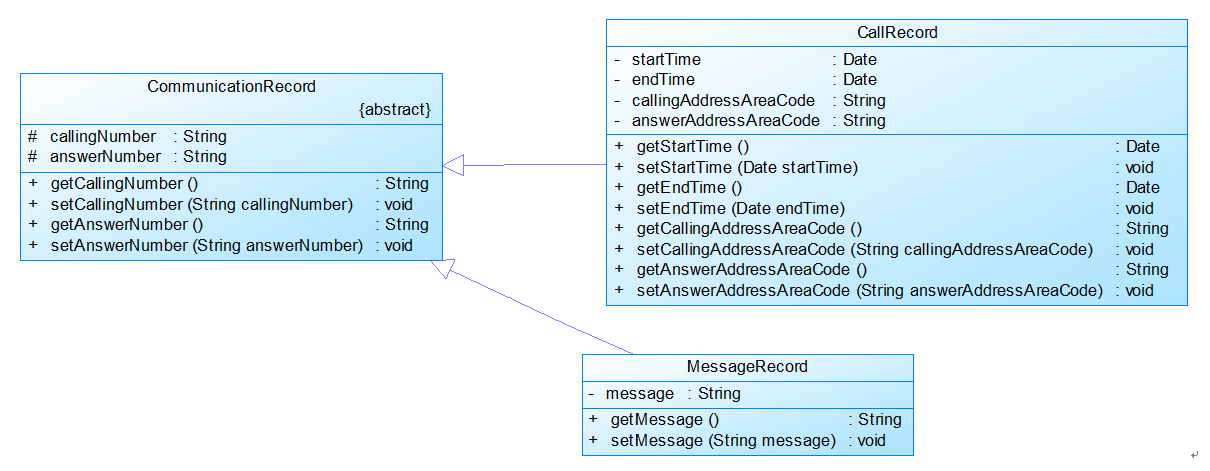
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。
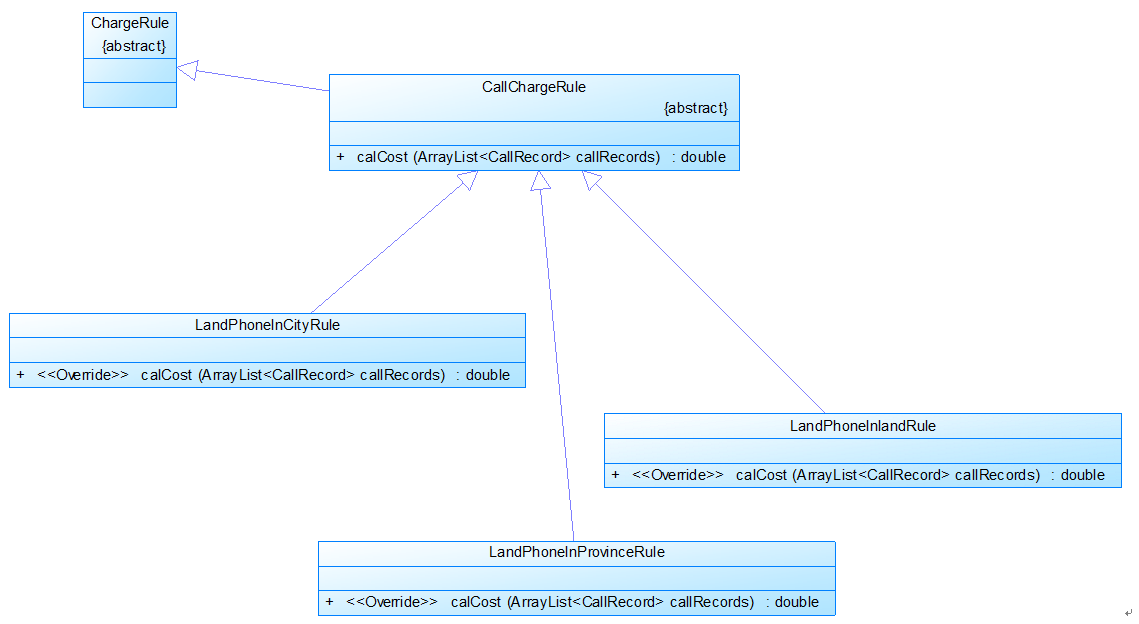
图3
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是
座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
后续扩展说明:
后续题目集将增加手机用户,手机用户的计费方式中除了与座机计费类似的主叫通话费之外,还包含市外接听电话的漫游费以及发短信的费用。在本题的设计时可统一考虑。
通话记录中,手机需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
短信的格式:m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you
源码:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.*; import java.util.Date; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); SimpleDateFormat dateFormat=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss");//时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。 TreeMap<String,User> users=new TreeMap<>();//数字升序排列 String s=in.nextLine(); String check = "u-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s0"; while(!s.equals("end")) { String check1 = "t-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s([0-9]{10,12})\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])"; String check2 = "0791([0-9]{7,8})"; if(s.matches(check)) { String []s1=s.split("-| "); users.put(s1[1], new User(new UserRecords(), 100, new LandlinePhoneCharging())); } else if(s.matches(check1)) { String []s1 = s.split("-| "); for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { String c1 = s1[3] + ' ' + s1[4]; String c2 = s1[5] + ' ' + s1[6]; try { Date date1 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date2 = dateFormat.parse(c2); if (s1[1].equals(entry.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date1, date2); if (s1[2].charAt(0) == '0' && s1[2].charAt(1) == '7' && s1[2].charAt(2) == '9' && s1[2].charAt(3) == '1') { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } else if ((s1[2].charAt(0) == '0' && s1[2].charAt(1) == '7' && ((s1[2].charAt(2) == '9' && s1[2].charAt(3) >= '0' && s1[2].charAt(3) <= '9') || (s1[2].charAt(2) == '0' && s1[2].charAt(3) == '1')))) { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } else { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } s=in.nextLine(); } for(Map.Entry<String,User>entry:users.entrySet()) { System.out.print(entry.getKey()+" "); System.out.printf("%.1f %.1f\n",(new LandlinePhoneCharging().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords)-20),(100-new LandlinePhoneCharging().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords))); } } } //用户类 class User//User是用户类,包括属性:userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码) { UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); private double balance = 100; LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging; private String number; public User(UserRecords userRecords, double balance, LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging) { this.userRecords = userRecords; this.balance = balance; this.landlinePhoneCharging = landlinePhoneCharging; } public User(UserRecords userRecords) { } public double calBalance(){ return 0; } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public LandlinePhoneCharging getLandlinePhoneCharging() { return landlinePhoneCharging; } public void setLandlinePhoneCharging(LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging) { this.landlinePhoneCharging = landlinePhoneCharging; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } class UserRecords//UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录 { ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords (CallRecord callRecord){ callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } } abstract class ChargeMode//ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类 { ArrayList <ChargeRule> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); public ChargeMode() { this.arrayList = arrayList; } public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getArrayList() { return arrayList; } public void setArrayList(ArrayList<ChargeRule> arrayList) { this.arrayList = arrayList; } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords){ return 0; } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return 20; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { double monthlyRent=20;//月租 public LandlinePhoneCharging() { super(); } public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { LandPhoneInlandRule landPhoneInlandRule = new LandPhoneInlandRule(); LandPhoneInCityRule landPhoneInCityRule = new LandPhoneInCityRule(); LandPhoneInProvinceRule landPhoneInProvinceRule = new LandPhoneInProvinceRule(); return landPhoneInCityRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInCityRecords)+landPhoneInProvinceRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords)+landPhoneInlandRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInLandRecords)+getMonthlyRent(); } } //计费规则的相关类 class ChargeRule{ } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { return 0; } } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule//市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟 { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.1; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule//省内长途0.3元/分钟 { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule//国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟 { public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double sum=0; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.6; } } //通话记录类 class CallRecord { private Date startTime;//开始时间 private Date endTime;//结束时间 private String callingAddressAreaCode;//拨号地点的区号 private String answerAddressAreaCode;//接听地点的区号 public CallRecord(Date startTime,Date endTime) { this.startTime=startTime; this.endTime=endTime; } public long Day() { long startTimeLong=getStartTime().getTime(); long endTimeLong=getEndTime().getTime(); long second = (endTimeLong-startTimeLong)/1000; return second; } public Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } public void setStartTime(Date startTime) { this.startTime = startTime; } public Date getEndTime() { return endTime; } public void setEndTime(Date endTime) { this.endTime = endTime; } public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } }
类图:
7-1 电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费
实现南昌市电信分公司的计费程序,假设该公司针对手机和座机用户分别采取了两种计费方案,分别如下:
1、针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式(与电信计费系列1内容相同):
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
假设本市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
2、针对手机用户采用实时计费方式:
月租15元,市内省内接电话均免费,市内拨打市内电话0.1元/分钟,市内拨打省内电话0.2元/分钟,市内拨打省外电话0.3元/分钟,省内漫游打电话0.3元/分钟,省外漫游接听0.3元/分钟,省外漫游拨打0.6元/分钟;
注:被叫电话属于市内、省内还是国内由被叫电话的接听地点区号决定,比如以下案例中,南昌市手机用户13307912264在区号为020的广州接听了电话,主叫号码应被计算为拨打了一个省外长途,同时,手机用户13307912264也要被计算省外接听漫游费:
u-13307912264 1
t-079186330022 13307912264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
输入:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,含手机和座机用户
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题在电信计费系列1基础上增加类型1-手机实时计费。
手机设置0或者座机设置成1,此种错误可不做判断。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
输入格式增加手机接打电话以及收发短信的格式,手机接打电话的信息除了号码之外需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:
t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:
t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
输出:
根据输入的详细通讯信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月费用(精确到小数点后2位,单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条通讯、短信信息均单独计费后累加,不是将所有信息累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
本题只做格式的错误判断,无需做内容上不合理的判断,比如同一个电话两条通讯记录的时间有重合、开户号码非南昌市的号码等,此类情况都当成正确的输入计算。但时间的输入必须符合要求,比如不能输入2022.13.61 28:72:65。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3:
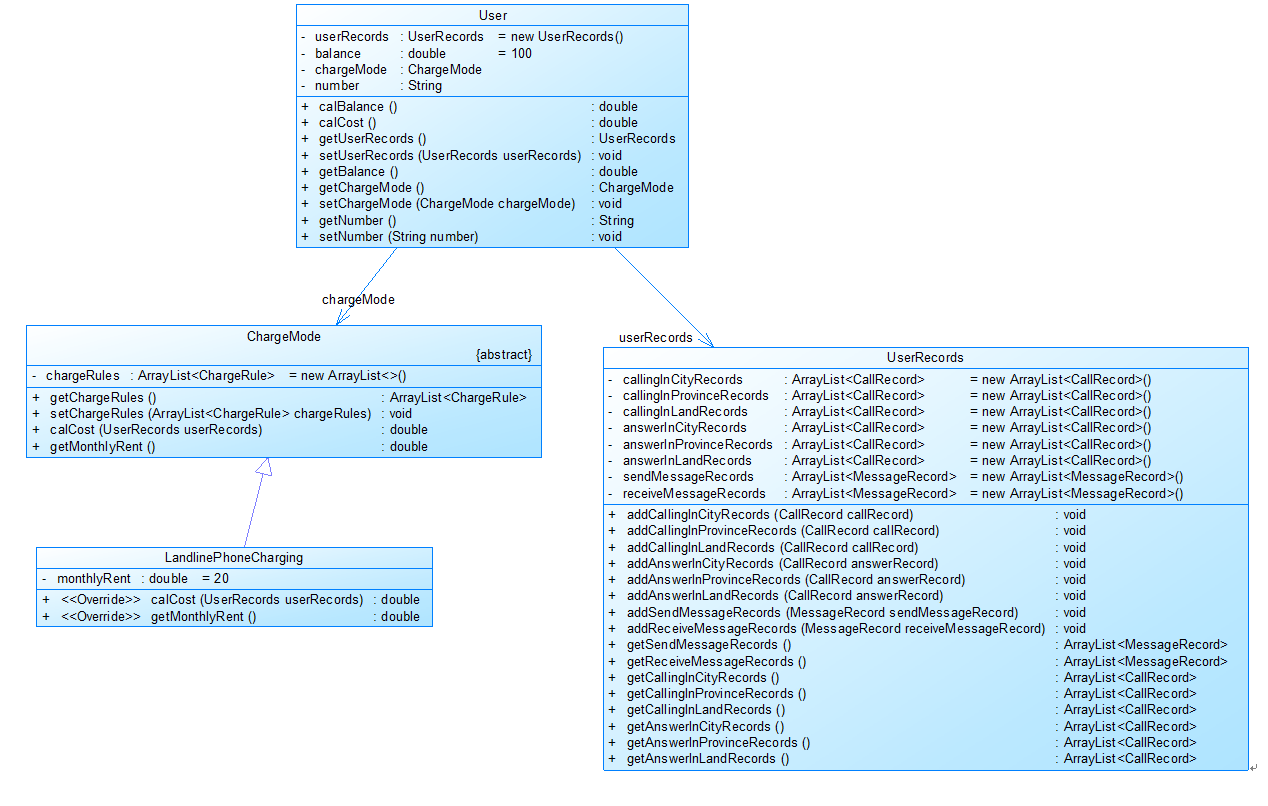
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
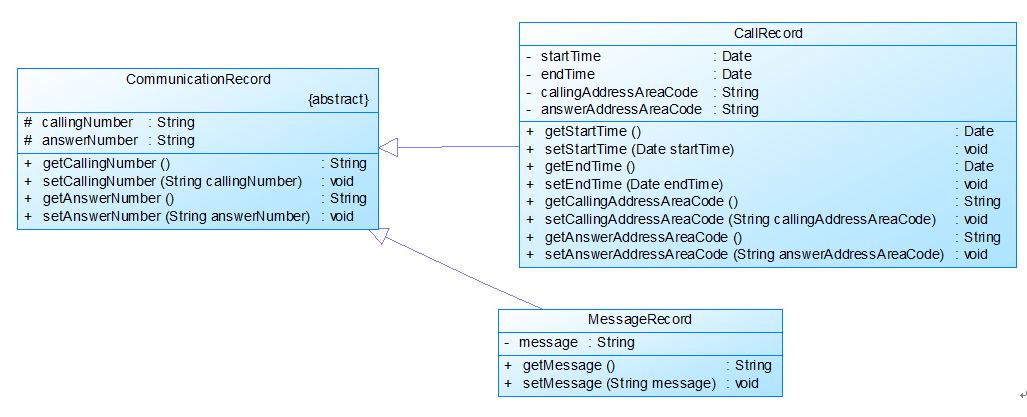
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。CallRecord(通话记录类)包含属性:
通话的起始、结束时间以及
拨号地点的区号(callingAddressAreaCode)、接听地点的区号(answerAddressAreaCode)。
区号用于记录在哪个地点拨打和接听的电话。座机无法移动,就是本机区号,如果是手机号,则会有差异。
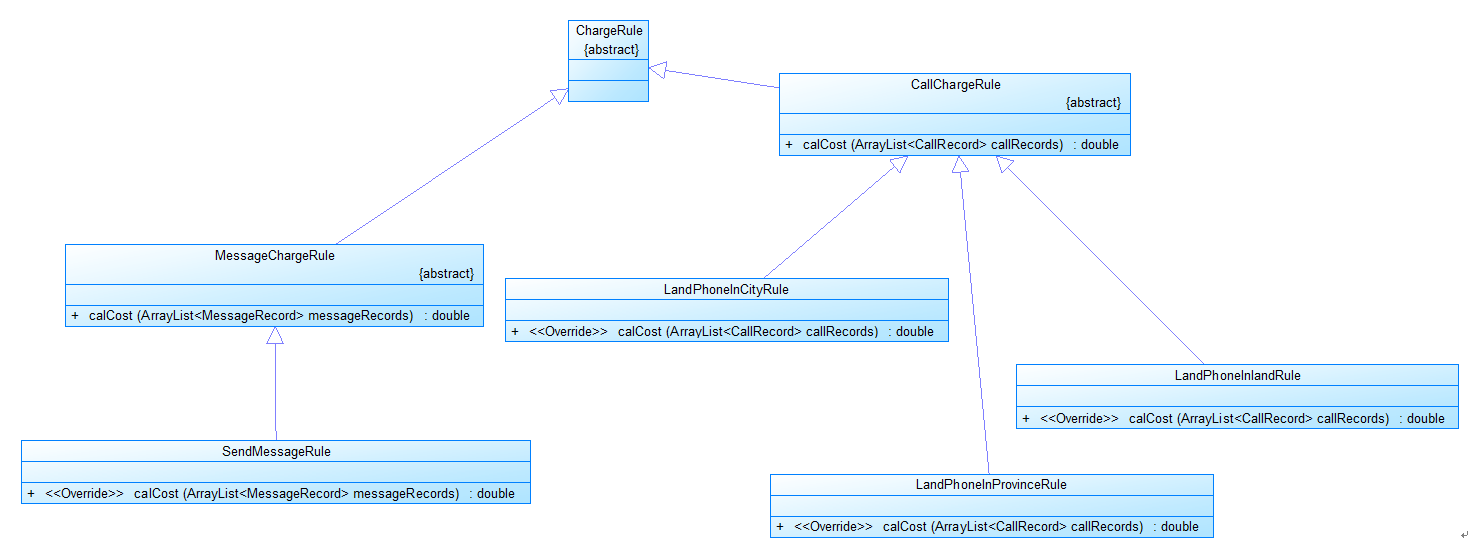
图3
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
SendMessageRule是发送短信的计费规则类,用于计算发送短信的费用。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
源码:
import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.*; import java.util.Date; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); TreeMap<String,User> users = new TreeMap<>(); String s = in.nextLine(); String check = "u-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s0"; while( !s.equals("end")) { String check1 = "t-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s([0-9]{10,12})\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])"; String check2 = "u-1([0-9]{10})\\s1"; String check3 = "t-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])"; String check4 = "t-1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s([0-9]{10,12})\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])"; String check5 = "07((9[0-9])|(01))"; String check7 = "t-1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])"; String check8 = "0791([0-9]{7,8})"; if(s.matches(check)||s.matches(check2)) { String []s1 = s.split("-| "); users.put(s1[1], new User(new UserRecords(), 100, new LandlinePhoneCharging())); } else if (s.matches(check1)||s.matches(check3)||s.matches(check4)||s.matches(check7)) { String []s1 = s.split("-| "); if(s1.length==7) { for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { String c1 = s1[3] + ' ' + s1[4]; String c2 = s1[5] + ' ' + s1[6]; try { Date date1 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date2 = dateFormat.parse(c2); if (s1[1].equals(entry.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date1, date2); if (s1[2].charAt(0) == '0' && s1[2].charAt(1) == '7' && s1[2].charAt(2) == '9' && s1[2].charAt(3) == '1') { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } else if ((s1[2].charAt(0) == '0' && s1[2].charAt(1) == '7' && ((s1[2].charAt(2) == '9' && s1[2].charAt(3) >= '0' && s1[2].charAt(3) <= '9') || (s1[2].charAt(2) == '0' && s1[2].charAt(3) == '1')))) { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } else { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } }catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } else if(s1.length == 8&&s1[3].length()<=4) { String c1 = s1[4] + ' ' + s1[5]; String c2 = s1[6] + ' ' + s1[7]; try { Date date11 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date22 = dateFormat.parse(c2); for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry1 : users.entrySet()) { if (s1[2].equals(entry1.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date11, date22); if (!s1[3].matches(check5)) { entry1.getValue().userRecords.answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } } }catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { try { Date date1 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date2 = dateFormat.parse(c2); if (s1[1].equals(entry.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date1, date2); if (s1[3].equals("0791")) { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } else if (s1[3].matches(check5)) { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } else { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } }catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } else if(s1.length ==9) { String c1 = s1[5] + ' ' + s1[6]; String c2 = s1[7] + ' ' + s1[8]; try { Date date11 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date22 = dateFormat.parse(c2); for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry1 : users.entrySet()) { if (s1[3].equals(entry1.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date11, date22); if (!s1[4].matches(check5)) { entry1.getValue().userRecords.answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } } } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { try { Date date1 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date2 = dateFormat.parse(c2); if (s1[1].equals(entry.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date1, date2); if (s1[2].equals("0791")) { if (s1[4].equals("0791")) { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } else if (s1[4].matches(check5)) { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } else { entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } else if(s1[2].matches(check5)) { entry.getValue().userRecords.manYouCallingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } else { entry.getValue().userRecords.manYouCallingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } else { String c1 = s1[4] + ' ' + s1[5]; String c2 = s1[6] + ' ' + s1[7]; for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { try { Date date1 = dateFormat.parse(c1); Date date2 = dateFormat.parse(c2); if (s1[1].equals(entry.getKey())) { CallRecord callRecord = new CallRecord(date1, date2); if(s1[2].equals("0791")&&s1[3].matches(check8)){ entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } else if(s1[2].equals("0791")&&s1[3].matches(check5)){ entry.getValue().userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } else{ entry.getValue().userRecords.manYouCallingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } } } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } s = in.nextLine(); } for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { if (entry.getKey().charAt(0) == '0') { System.out.print(entry.getKey() + " "); System.out.printf("%.1f %.1f\n", (new LandlinePhoneCharging().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords) - 20), (100 - new LandlinePhoneCharging().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords))); } else { System.out.print(entry.getKey() + " "); System.out.printf("%.1f %.1f\n",new MobliePhoneCharging().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords)-15,100-new MobliePhoneCharging().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords)); } } } } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ return 0; } } class CallRecord { private Date startTime; private Date endTime; private String callingAddressAreaCode; private String answerAddressAreaCode; public CallRecord(Date startTime, Date endTime) { this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; } public CallRecord(Date startTime, Date endTime, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } public long Day(){ long stateTimeLong = getStartTime().getTime(); long endTimeLong = getEndTime().getTime(); long second = (endTimeLong-stateTimeLong)/1000; return second; } public Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } public void setStartTime(Date startTime) { this.startTime = startTime; } public Date getEndTime() { return endTime; } public void setEndTime(Date endTime) { this.endTime = endTime; } public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } } abstract class ChargeMode { ArrayList <ChargeRule> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); public ChargeMode() { this.arrayList = arrayList; } public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getArrayList() { return arrayList; } public void setArrayList(ArrayList<ChargeRule> arrayList) { this.arrayList = arrayList; } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords){ return 0; } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return 20; } } class ChargeRule { } abstract class CommunicationRecord { private String callingNumber; private String answerNumber; public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumber() { return answerNumber; } public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber) { this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging() { super(); } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords) { LandPhoneInlandRule landPhoneInlandRule = new LandPhoneInlandRule(); LandPhoneInCityRule landPhoneInCityRule = new LandPhoneInCityRule(); LandPhoneInProvinceRule landPhoneInProvinceRule = new LandPhoneInProvinceRule(); return landPhoneInCityRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInCityRecords)+landPhoneInProvinceRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords) +landPhoneInlandRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInLandRecords)+getMonthlyRent(); } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return monthlyRent; } } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.1; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.6; } public double phoneCalCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } public double answerInLandCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } public double manYouCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.6; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } public double phoneCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.2; } public double manYouCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } } class MobliePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { double monthlyRent = 15; public MobliePhoneCharging() { super(); } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords){ LandPhoneInlandRule landPhoneInlandRule = new LandPhoneInlandRule(); LandPhoneInCityRule landPhoneInCityRule = new LandPhoneInCityRule(); LandPhoneInProvinceRule landPhoneInProvinceRule = new LandPhoneInProvinceRule(); return landPhoneInCityRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInCityRecords)+landPhoneInProvinceRule.phoneCalCost(userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords) +landPhoneInlandRule.phoneCalCost(userRecords.callingInLandRecords)+landPhoneInlandRule.answerInLandCalCost(userRecords.answerInLandRecords)+ landPhoneInProvinceRule.manYouCalCost(userRecords.manYouCallingInProvinceRecords)+getMonthlyRent()+ landPhoneInlandRule.manYouCalCost(userRecords.manYouCallingInLandRecords); } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return monthlyRent; } } class User { UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); private double balance = 100; LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging; private String number; public User(UserRecords userRecords, double balance, LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging) { this.userRecords = userRecords; this.balance = balance; this.landlinePhoneCharging = landlinePhoneCharging; } public User(UserRecords userRecords) { } public double calBalance(){ return 0; } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public LandlinePhoneCharging getLandlinePhoneCharging() { return landlinePhoneCharging; } public void setLandlinePhoneCharging(LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging) { this.landlinePhoneCharging = landlinePhoneCharging; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } class UserRecords { ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> manYouCallingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> manYouCallingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords (CallRecord callRecord){ callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord messageRecord){ sendMessageRecords.add(messageRecord); } public void addReceiveMessageRecords(MessageRecord messageRecord){ receiveMessageRecords.add(messageRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() { return sendMessageRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords() { return receiveMessageRecords; } } class MessageRecord { private String message; public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } }
类图:
7-1 电信计费系列3-短信计费
实现一个简单的电信计费程序,针对手机的短信采用如下计费方式:
1、接收短信免费,发送短信0.1元/条,超过3条0.2元/条,超过5条0.3元/条。
2、如果一次发送短信的字符数量超过10个,按每10个字符一条短信进行计算。
输入:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市手机用户开户的信息,每行一个用户。
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐 3-手机短信计费)
例如:u-13305862264 3
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题只针对类型3-手机短信计费。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的短信信息,短信的格式:
m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容 (短信内容只能由数字、字母、空格、英文逗号、英文句号组成)
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi.
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you.
注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
输出:
根据输入的详细短信信息,计算所有已开户的用户的当月短信费用(精确到小数点后2位,单位元)。假设每个用户初始余额是100元。
每条短信信息均单独计费后累加,不是将所有信息累计后统一计费。
格式:号码+英文空格符+总的话费+英文空格符+余额
每个用户一行,用户之间按号码字符从小到大排序。
错误处理:
输入数据中出现的不符合格式要求的行一律忽略。
本题只做格式的错误判断,无需做内容上不合理的判断,比如同一个电话两条通讯记录的时间有重合、开户号码非南昌市的号码、自己给自己打电话等,此类情况都当成正确的输入计算。但时间的输入必须符合要求,比如不能输入2022.13.61 28:72:65。
本题只考虑短信计费,不考虑通信费用以及月租费。
建议类图:
参见图1、2、3:
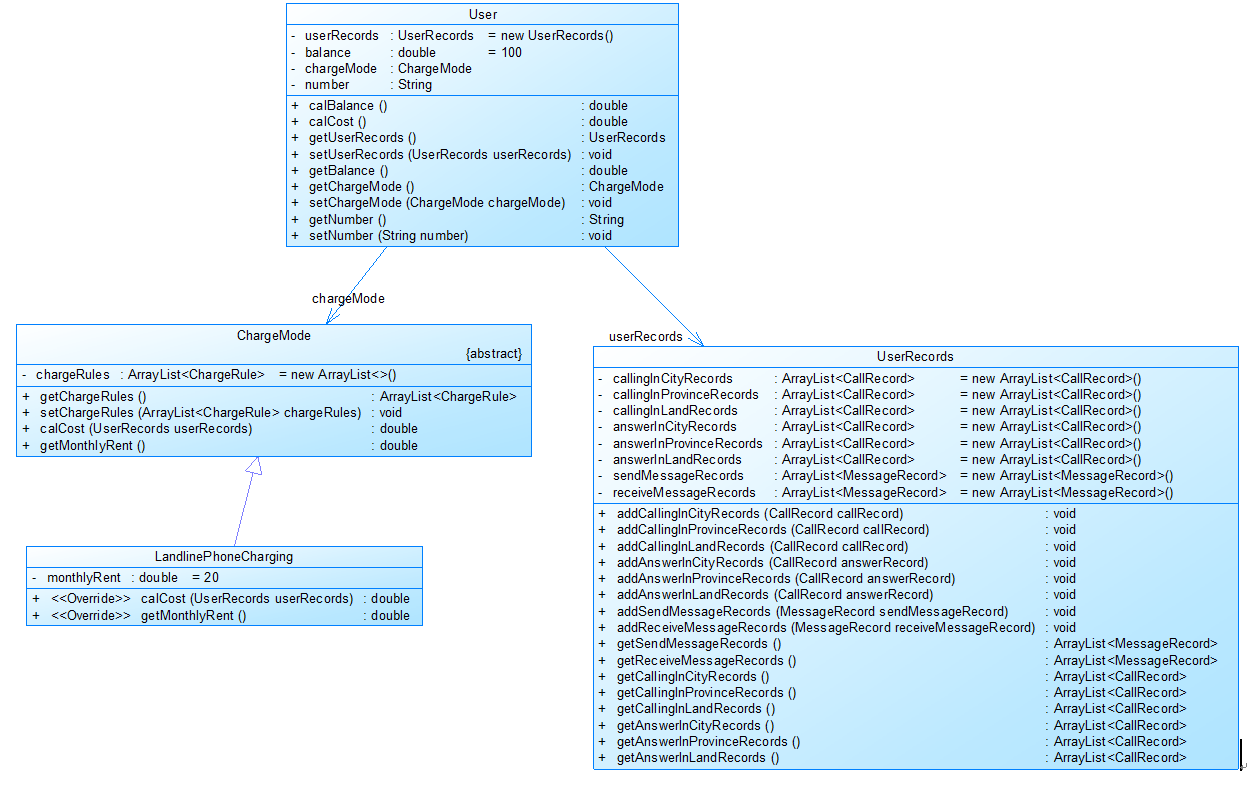
图1
图1中User是用户类,包括属性:
userRecords (用户记录)、balance(余额)、chargeMode(计费方式)、number(号码)。
ChargeMode是计费方式的抽象类:
chargeRules是计费方式所包含的各种计费规则的集合,ChargeRule类的定义见图3。
getMonthlyRent()方法用于返回月租(monthlyRent)。
UserRecords是用户记录类,保存用户各种通话、短信的记录,
各种计费规则将使用其中的部分或者全部记录。
其属性从上到下依次是:
市内拨打电话、省内(不含市内)拨打电话、省外拨打电话、
市内接听电话、省内(不含市内)接听电话、省外接听电话的记录
以及发送短信、接收短信的记录。
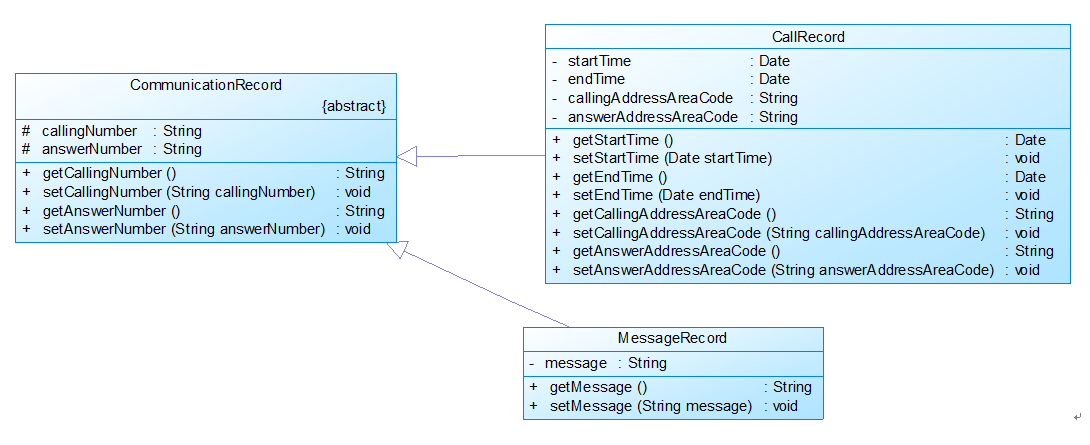
图2
图2中CommunicationRecord是抽象的通讯记录类:
包含callingNumber拨打号码、answerNumber接听号码两个属性。
CallRecord(通话记录)、MessageRecord(短信记录)是它的子类。
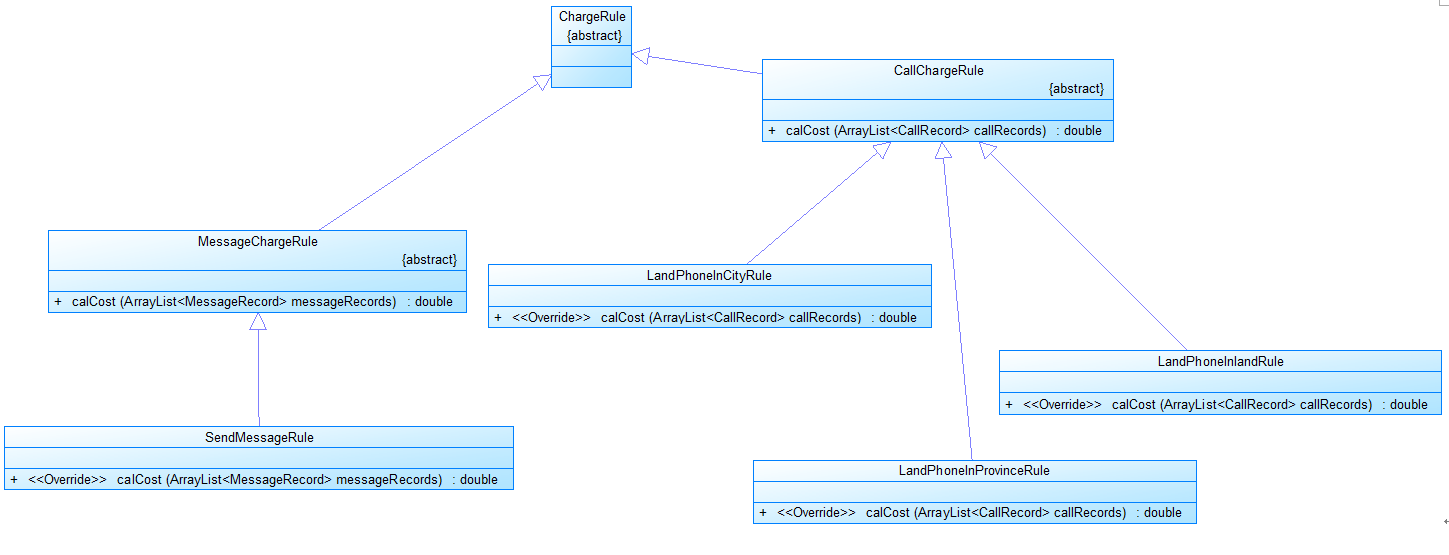
图3
图3是计费规则的相关类,这些类的核心方法是:
calCost(ArrayList callRecords)。
该方法针根据输入参数callRecords中的所有记录计算某用户的某一项费用;如市话费。
输入参数callRecords的约束条件:必须是某一个用户的符合计费规则要求的所有记录。
SendMessageRule是发送短信的计费规则类,用于计算发送短信的费用。
LandPhoneInCityRule、LandPhoneInProvinceRule、LandPhoneInLandRule三个类分别是座机拨打市内、省内、省外电话的计费规则类,用于实现这三种情况的费用计算。
(提示:可以从UserRecords类中获取各种类型的callRecords)。
注意:以上图中所定义的类不是限定要求,根据实际需要自行补充或修改。
源码:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.*; import java.util.Date; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); TreeMap<String,User> users = new TreeMap<>(); String s = in.nextLine(); while( !s.equals("end")) { String check2 = "[u][-]1[3-9]\\d{9}[ ][3]"; String messagejudge = "m-1[3-9]\\d{9} 1[3-9]\\d{9} [a-z|0-9| |,|.]++"; if(s.matches(check2)) { String []s1 = s.split("-| "); users.put(s1[1], new User(new UserRecords(), 100, 0)); } if(s.matches(messagejudge)) { for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { String []s2 = s.split("-| ",4); if (s2[1].equals(entry.getKey())){ String s3 =s2[3]; MessageRecord messageRecord = new MessageRecord(s3.length()); entry.getValue().userRecords.sendMessageRecords.add(messageRecord); } } } s = in.nextLine(); } for (Map.Entry<String, User> entry : users.entrySet()) { System.out.print(entry.getKey() + " "); System.out.printf("%.1f %.1f\n",100-new SendMessageRule().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords.sendMessageRecords),new SendMessageRule().calCost(entry.getValue().userRecords.sendMessageRecords)); } } } class SendMessageRule extends MessageChargeRule { public double calCost(ArrayList<MessageRecord> callRecords) { double sum = 0; int num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < callRecords.size(); i++) { if (callRecords.get(i).getLength() % 10 == 0) { num += callRecords.get(i).getLength() / 10; } else { num+=callRecords.get(i).getLength()/10+1; } } if(num<=3){ return 100-num*0.1; }else if(num<=5){ return 100-3*0.1-(num-3)*0.2; }else{ return 100-3*0.1-2*0.2+0.3*(num-5); } } } class MessageRecord { private int length; public MessageRecord(int length) { this.length = length; } public int getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(int length) { this.length = length; } } class MessageChargeRule extends ChargeRule{ } class User { UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); private double balance = 100; LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging; private String number; private int num; public User(UserRecords userRecords, double balance, LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging) { this.userRecords = userRecords; this.balance = balance; this.landlinePhoneCharging = landlinePhoneCharging; } public User(UserRecords userRecords,double balance,int num) { this.userRecords = userRecords; this.balance = balance; this.num = num; } public double calBalance(){ return 0; } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public LandlinePhoneCharging getLandlinePhoneCharging() { return landlinePhoneCharging; } public void setLandlinePhoneCharging(LandlinePhoneCharging landlinePhoneCharging) { this.landlinePhoneCharging = landlinePhoneCharging; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } class UserRecords { ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> manYouCallingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> manYouCallingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList <MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords (CallRecord callRecord){ callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord messageRecord){ sendMessageRecords.add(messageRecord); } public void addReceiveMessageRecords(MessageRecord messageRecord){ receiveMessageRecords.add(messageRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord){ answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() { return sendMessageRecords; } public ArrayList<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords() { return receiveMessageRecords; } } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ return 0; } } class CallRecord { private Date startTime; private Date endTime; private String callingAddressAreaCode; private String answerAddressAreaCode; public CallRecord(Date startTime, Date endTime) { this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; } public CallRecord(Date startTime, Date endTime, String callingAddressAreaCode, String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.startTime = startTime; this.endTime = endTime; this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } public long Day(){ long stateTimeLong = getStartTime().getTime(); long endTimeLong = getEndTime().getTime(); long second = (endTimeLong-stateTimeLong)/1000; return second; } public Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } public void setStartTime(Date startTime) { this.startTime = startTime; } public Date getEndTime() { return endTime; } public void setEndTime(Date endTime) { this.endTime = endTime; } public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } } abstract class ChargeMode { ArrayList <ChargeRule> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); public ChargeMode() { this.arrayList = arrayList; } public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getArrayList() { return arrayList; } public void setArrayList(ArrayList<ChargeRule> arrayList) { this.arrayList = arrayList; } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords){ return 0; } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return 20; } } class ChargeRule { } abstract class CommunicationRecord { private String callingNumber; private String answerNumber; public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumber() { return answerNumber; } public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber) { this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging() { super(); } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords){ LandPhoneInlandRule landPhoneInlandRule = new LandPhoneInlandRule(); LandPhoneInCityRule landPhoneInCityRule = new LandPhoneInCityRule(); LandPhoneInProvinceRule landPhoneInProvinceRule = new LandPhoneInProvinceRule(); return landPhoneInCityRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInCityRecords)+landPhoneInProvinceRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords) +landPhoneInlandRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInLandRecords)+getMonthlyRent(); } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return monthlyRent; } } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.1; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.6; } public double phoneCalCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } public double answerInLandCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } public double manYouCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.6; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { public double calCost (ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } public double phoneCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.2; } public double manYouCalCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords){ double sum = 0; for (CallRecord callRecord : callRecords) { sum+=Math.ceil(callRecord.Day()/60.0); } return sum*0.3; } } class MobliePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { double monthlyRent = 15; public MobliePhoneCharging() { super(); } public double calCost (UserRecords userRecords){ LandPhoneInlandRule landPhoneInlandRule = new LandPhoneInlandRule(); LandPhoneInCityRule landPhoneInCityRule = new LandPhoneInCityRule(); LandPhoneInProvinceRule landPhoneInProvinceRule = new LandPhoneInProvinceRule(); return landPhoneInCityRule.calCost(userRecords.callingInCityRecords)+landPhoneInProvinceRule.phoneCalCost(userRecords.callingInProvinceRecords) +landPhoneInlandRule.phoneCalCost(userRecords.callingInLandRecords)+landPhoneInlandRule.answerInLandCalCost(userRecords.answerInLandRecords)+ landPhoneInProvinceRule.manYouCalCost(userRecords.manYouCallingInProvinceRecords)+getMonthlyRent()+ landPhoneInlandRule.manYouCalCost(userRecords.manYouCallingInLandRecords); } public double getMonthlyRent (){ return monthlyRent; } }
类图:
三、采坑心得
正则表达式的在三次电话计费题目中有着很大的作用,在这三次电话计费题目中对于正则表达式的使用有:
1、确定输入电话号码的位数;
2、确定开头标志符号是否正确;
3、确定输入的电话号码是否合法;
4、确定时间和日期是否正确;
5、确定区域是否准确。
String check1 = "t-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s([0-9]{10,12})\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])";
String check2 = "0791([0-9]{7,8})";
String check1 = "t-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s([0-9]{10,12})\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])";
String check2 = "u-1([0-9]{10})\\s1";
String check3 = "t-0791([0-9]{7,8})\\s1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])";
String check4 = "t-1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s([0-9]{10,12})\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])";
String check5 = "07((9[0-9])|(01))";
String check7 = "t-1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s1([0-9]{10})\\s\\d{3,4}\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|1[012])\\.([1-9]|([1-2][0-9])|[3][0,1])\\s((0[0-9])|(1[0-9])|(2[0-3])):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])";
String check8 = "0791([0-9]{7,8})";
String check2 = "[u][-]1[3-9]\\d{9}[ ][3]";
String messagejudge = "m-1[3-9]\\d{9} 1[3-9]\\d{9} [a-z|0-9| |,|.]++";
四、改进建议
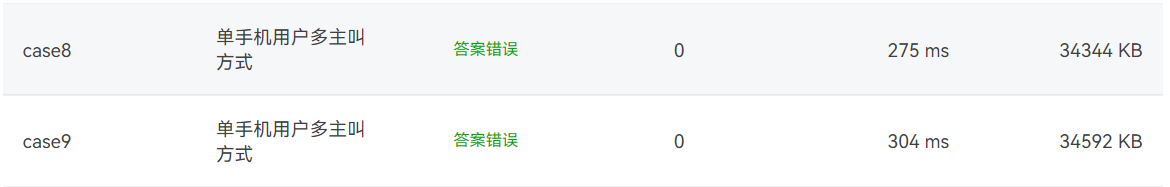
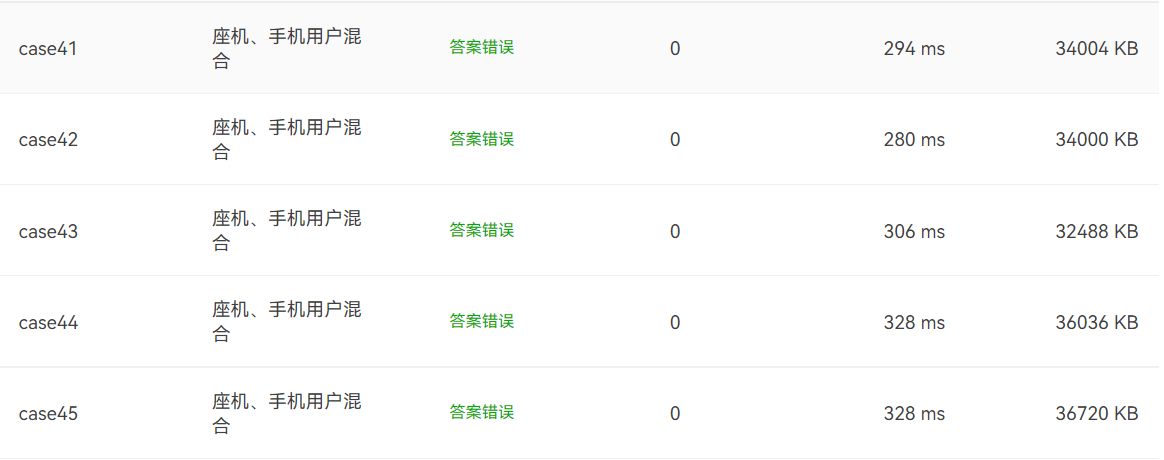
7-1 电信计费系列1-座机计费
7-1 电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费

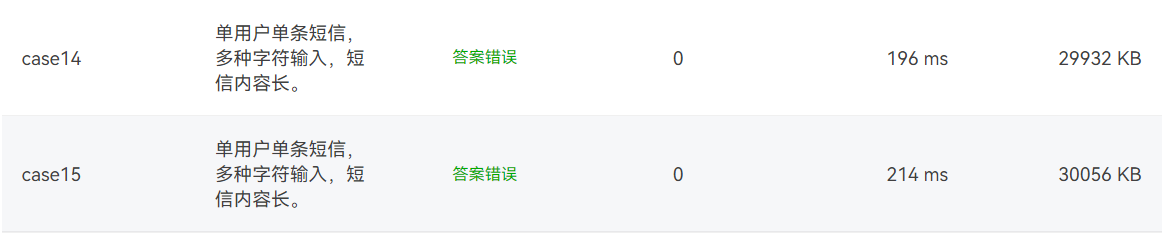
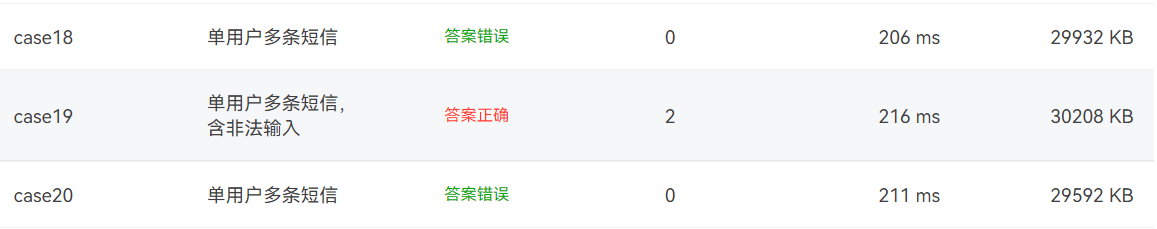
7-1 电信计费系列3-短信计费
五、总结
对本阶段(10-16周)综合性总结:对java的类和对象了解更加深刻,代码的优化程度有所提高,程序的可读性更好,但对于Java的熟练程度有待提高,Java编码的思路还有待加强,还是过于依赖之前C语言的固有思维。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号