MOOC数据结构PTA-03-树3 Tree Traversals Again
题目表述
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
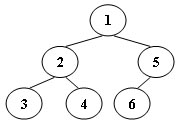
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
结尾无空行
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
结尾无空行
题目解析
本题借鉴了一些算法:通过输入可以构建前序遍历数组,和中序遍历数组,然后通过递归,根据前项遍历数组和中序遍历数组得出后续遍历数组。
1.首先栈push的过程即是前序遍历的数组;
pop的过程即是中序遍历的数组。
2.后序遍历:将前序的第一个放到后序的最后一个,然后通过中序得到左节点数L和右节点数R,将前序的下一个放到后序数组的左边的最后一个,右边同,然后递归实现。(每次递归前序数组后移一个,中序用来找左数L和右数R,将前序的本节点赋值给后序数组的L或R个元素的最后一个)
代码
// Tree traversal again
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define Max 30
int pre[Max], in[Max], post[Max];
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
} Node, *Stack;
typedef struct tnode {
int data;
struct tnode *lchild, *rchild;
} TNode, *Tree;
//函数声明
Stack Init_stack();
void push(Stack S, int x);
bool pop(Stack S, int* x);
bool isempty(Stack S);
void buildTree(int N);
void PostTree(int pre_r, int in_r, int post_r, int N);
//主函数
int main() {
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
buildTree(N);
PostTree(0, 0, 0, N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("%d", post[i]);
if (i < N - 1)
putchar(' ');
}
return 0;
}
//函数定义
Stack Init_stack() {
Stack p = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->next = NULL;
return p;
}
void push(Stack S, int x) {
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->data = x;
p->next = S->next;
S->next = p;
}
bool pop(Stack S, int* x) {
if (isempty(S))
return false;
Node* p = S->next;
*x = p->data;
S->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
bool isempty(Stack S) {
if (S->next == NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void buildTree(int N) {
Stack S = Init_stack();
int index_in = 0; //中序数组角标
int index_pre = 0; //前序数组角标
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * N; i++) {
char order[5];
int data;
scanf("%s", order);
if (strcmp(order, "Push") == 0) {
scanf("%d", &data);
pre[index_pre++] = data;
push(S, data);
} else {
pop(S, in + index_in);
index_in++;
}
}
return;
}
void PostTree(int pre_r, int in_r, int post_r, int N) {
if (N == 0)
return;
if (N == 1)
post[post_r] = pre[pre_r];
int i;
int root = pre[pre_r];
post[post_r + N - 1] = root;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (in[in_r + i] == root)
break;
}
int L = i, R = N - i - 1;
PostTree(pre_r + 1, in_r, post_r, L);
PostTree(pre_r + 1 + L, in_r + L + 1, post_r + L, R);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号