Transformer 学习笔记
自注意力
可以将 \(q^{<i>}\) 理解为单词 \(x^{<i>}\) 提出的问题,将 \(k^{<j>}\) 理解为单词 \(x^{<j>}\) 做出的回答。将 \(v^{<z>}\) 理解为单词 \(x^{<z>}\) 的含义。
多头注意力
一个注意力头可以理解为一个类型的问题。多个注意力头就是多个类型的问题。
参考:Multi-Head Attention | Coursera
交叉注意力
当注意力网络的 \(Q\) 和 \(K, V\) 来源于不同输入序列时,就是在计算交叉注意力。在 Transformer 网络中,解码器的第二个 Multi-Head Attention 层输入的 \(Q\) 来自于编码器,而 \(K, V\) 来自于第一个 Multi-Head Attention 层,这里就在计算交叉注意力。
Transformer 网络
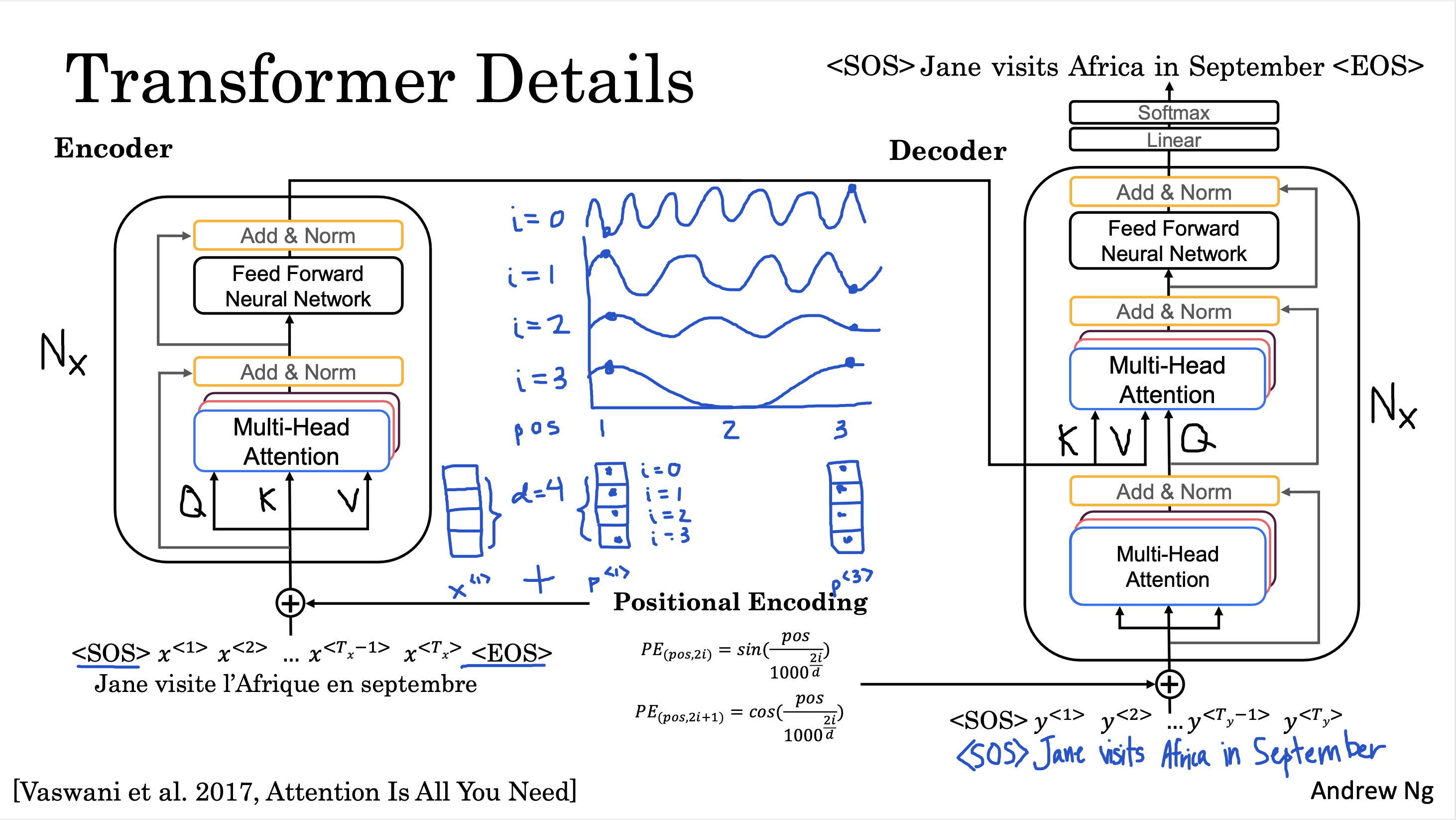
位置编码
\[PE(pos, 2i) = \sin\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{2i/d}}\right)
\]
\[PE(pos, 2i+1) = \cos\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{2i/d}}\right)
\]
- \(10000^{2i/d}\):频率,不同的维度(\(i\))有不同的频率
- \(d\):嵌入向量的总维度
- \(i\):特征在嵌入向量中的维度,是总维度的一半(\(2i \in [0, d)\))
- \(pos\):嵌入向量在向量序列中的位置
比如 \(x^{<1>}\) 的位置编码可能为:\([\sin(1/10000^0), \cos(1/10000^0), \sin(1/10000^{0.5}), \cos(1/10000^{0.5})]\)
这种位置编码也叫绝对位置编码
import torch as th
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_angles(pos, k, d):
i = k // 2
angles = pos / th.pow(10000, 2 * i / d)
return angles
def positional_encoding(positions, d):
angle_rads = get_angles(th.arange(positions).unsqueeze(1), th.arange(d).unsqueeze(0), d)
angle_rads[:, 0::2] = th.sin(angle_rads[:, 0::2])
angle_rads[:, 1::2] = th.cos(angle_rads[:, 1::2])
pos_encoding = angle_rads.unsqueeze(0)
return pos_encoding.numpy()
pos_encoding = positional_encoding(50, 512)
plt.pcolormesh(pos_encoding[0], cmap='RdBu')
plt.xlabel('d')
plt.xlim((0, 512))
plt.ylabel('Position')
plt.colorbar()
plt.savefig('positional_encoding.svg')
每一行代表一个位置编码,可以看到没有任何两行是相同的。
参考:Transformer Network | Coursera
参见:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号