Struts2基础2
一、struts中的API
1)完全解耦合的方式
1.1首先创建一个示例工程,在WEB-INF下创建lib文件夹,把struts2核心jar包导入。在工程下创建resource文件夹,并将其设为资源文件夹,把struts.xml放入。在web.xml中配置核心控制器。
1.2创建一个表单jsp,提交到form.action,在struts.xml中配置form.action

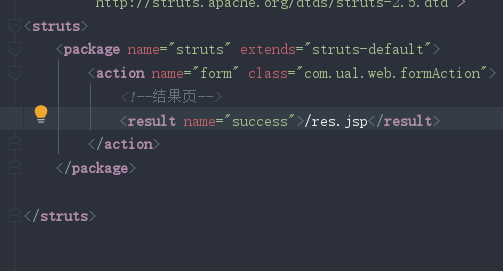
1.3在action类中接收参数并向域中写入
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.HttpParameters; import java.util.Arrays; public class formAction extends ActionSupport { public String execute(){ //接收表单中的参数 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext(); HttpParameters parameters = context.getParameters(); //获取参数 String username = parameters.get("username").getValue(); System.out.println(username); String password = parameters.get("password").getValue(); System.out.println(password); String[] hobbies = parameters.get("hobby").getMultipleValues();//获取多个值 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbies)); System.out.println("接收到表单"); //往域中写入数据 //往request域中: context.put("reqName","reqValue"); //往session: context.getSession().put("sessionName","sessionValue"); //往application域 context.getApplication().put("name","Applicationvalue"); return SUCCESS; } }
接收表单数据:通过ActionContext.getContext获取ActionContext对象,通过该对象获取HttpParameters对象。

获取参数:

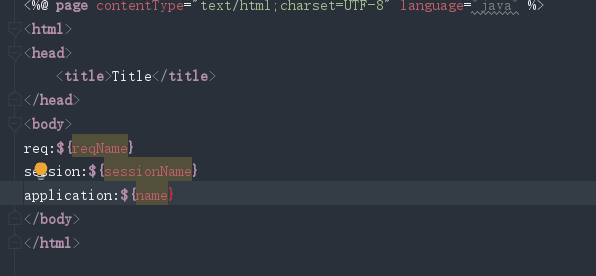
往域中存参

在jsp中获取参数
2)使用Servlet的原声API
public String form2(){ System.out.println("form2"); //获取原生api HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); //获取参数 String username = request.getParameter("username"); String pasword = request.getParameter("password"); String[] hobbies = request.getParameterValues("hobby"); System.out.println(username); System.out.println(pasword); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbies)); //往域中存数据 request.setAttribute("reqNmae2","reqValue2"); request.getSession().setAttribute("sessionName2","sessionValue2"); ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("contextName","contextValue"); return SUCCESS; }
3)接口注入的方式
二、结果页配置
1)局部配置
局部结果页面:在action中的result标签中配置
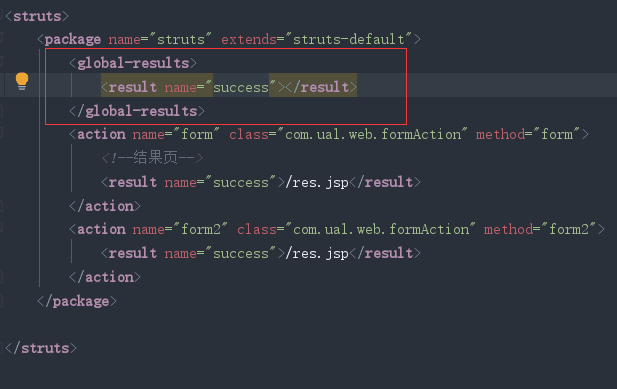
2)全局配置
全局结果页指的是,在包中配置一次,其他的在这个包中的action只要返回这个结果,都可以跳转这个页面。
先在局部找,局部没有找到就到全局找
三、接收参数
一般在开发中不会使用一中提到的方式
当发送一个请求时,除了使用requestAPI来接收参数之外,struts内部提供了三种接收参数方式
1)接收参数方式
1.提供属性set方法的方式
在Action中提供对应属性的set方法,会自动接收参数,并且会自动做类型转换
缺点:接收大量数据时,还需要自己手动封装成对象。
package com.ual.web; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import java.util.List; public class formAction3 extends ActionSupport { //这里的属性值要与表单中提交的name值相同 private String username; private Integer age; private List hobby; //提供set方法 public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public void setHobby(List hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public String form3(){ System.out.println(username); System.out.println(age); System.out.println(hobby); return null; } }
2.页面中提供表达式
2.1创建一个接收参数的domain模型,模型中的字段与提交表单对应。并提供对应get,set方法。
package com.ual.domain; import java.util.List; public class User { private String username; private Integer age; private List hobby; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public List getHobby() { return hobby; } public void setHobby(List hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "username='" + username + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", hobby=" + hobby + '}'; } }
2.2在Action提供对应domain的对象属性,并提供该对象的get,set方法。
package com.ual.web; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.ual.domain.User; import java.util.List; public class formAction4 extends ActionSupport { //页面中提供表达式 private User user; public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } public String form4(){ System.out.println(user); return null; } }
2.3在jsp中页面当中,发送参数时,要带上Action当中的对象属性名

3.采用模型驱动方式
3.1创建一个接收参数的domain模型
3.2在Action中实现ModelDriven<T>接口,其中T为domain模型类
3.3实现接口方法getModel()
3.4创建一个domain模型对象,在接口方法中返回。
package com.ual.web; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven; import com.ual.domain.User; public class formAction5 extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User> { //采用模型驱动方式 private User user=new User(); @Override public User getModel() { return user; } public String form5(){ System.out.println("user===="+user); return null; } }
4)接收参数错误
只要任何一个拦截器在执行过程中,出现错误都会向错误信息中添加错误信息。最后workfllow会检查错误信息当中是否有错误,如果没有,就会到目标action,如果有,就会跳转input逻辑视图。
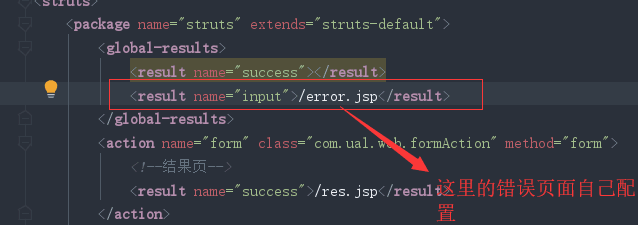
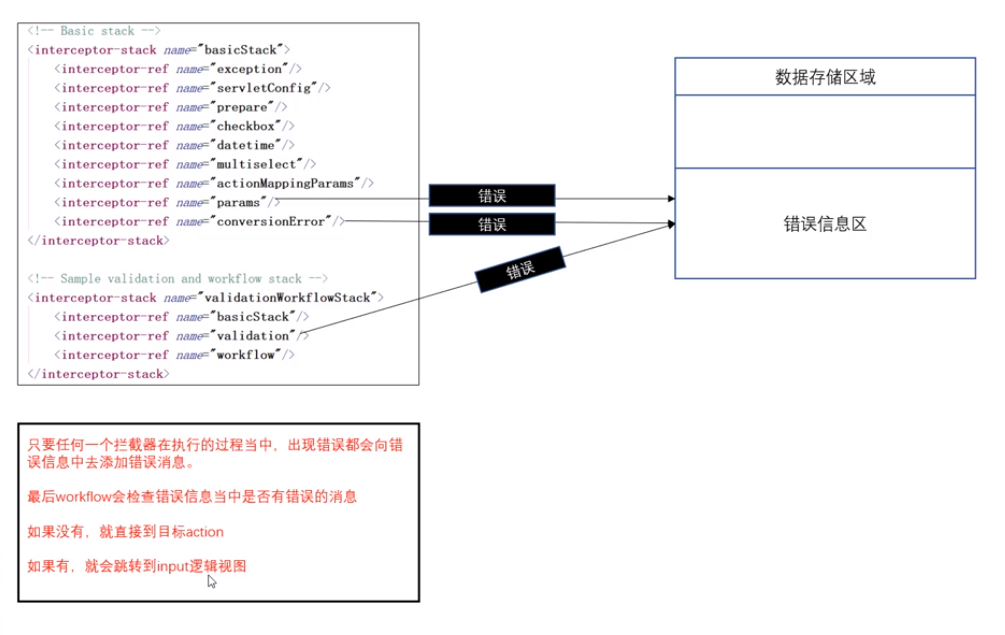
在开发时,可以配置一个input逻辑视图,错误时,可以跳转到自己指定界面,在页面中可以显示错误信息。
5)通过List集合接收多组相同参数
1.定义domain类
package com.ual.domain; public class goods { private String name; private double price; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "goods{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", price=" + price + '}'; } }
2.在Action中,采用页面中提供表达式方法
package com.ual.web; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven; import com.ual.domain.goods; import java.util.List; public class formAction6 extends ActionSupport { private List<goods> goodsList;//定义一个List集合,其中装入domain类,提供getset方法。 public List<goods> getGoodsList() { return goodsList; } public void setGoodsList(List<goods> goodsList) { this.goodsList = goodsList; } public String form6(){ System.out.println(goodsList); return null; } }
3.jsp中,参数名前写入Action中定义的List集合加下标

6)使用map接收参数
1.定义domain类
2.在Action中,采用页面中提供表达式方法
package com.ual.web; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.ual.domain.goods; import java.util.Map; public class formAction7 extends ActionSupport { private Map<String , goods> goodsMap;//定义存domain类对象的map,键是string类型,值是domain对象 public Map<String, goods> getGoodsMap() {//提供getset方法。 return goodsMap; } public void setGoodsMap(Map<String, goods> goodsMap) { this.goodsMap = goodsMap; } public String form7(){ System.out.println(goodsMap); return null; } }
3.jsp中参数值设置



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号