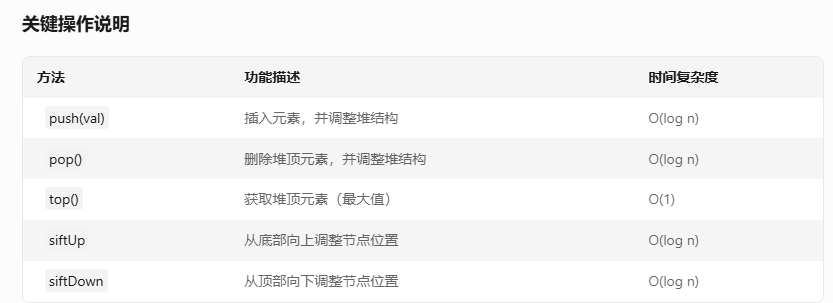
【数据结构】堆(大根堆、小根堆)的C++代码模板
大根堆/最大堆
以下是 大根堆(Heap)的C++代码模板,包含最大堆的基本操作(插入、删除堆顶、堆化等),注释详细说明关键步骤:
class MaxHeap {
private:
vector<int> heap;
// 获取父节点索引
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
// 获取左子节点索引
int left(int i) { return 2 * i + 1; }
// 获取右子节点索引
int right(int i) { return 2 * i + 2; }
// 上浮操作:将节点i向上调整,维护堆性质
void siftUp(int i) {
while (i > 0 && heap[i] > heap[parent(i)]) {
swap(heap[i], heap[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
// 下沉操作:将节点i向下调整,维护堆性质
void siftDown(int i, int n) {
int maxIndex = i;
int l = left(i), r = right(i);
if (l < n && heap[l] > heap[maxIndex])
maxIndex = l;
if (r < n && heap[r] > heap[maxIndex])
maxIndex = r;
if (maxIndex != i) {
swap(heap[i], heap[maxIndex]);
siftDown(maxIndex, n); // 递归调整
}
}
public:
// 构造函数1:通过数组建堆
MaxHeap(vector<int>& nums) {
heap = nums;
// 从最后一个非叶子节点开始调整
for (int i = heap.size() / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
siftDown(i, heap.size());
}
}
// 构造函数2:空堆
MaxHeap() {}
// 插入元素
void push(int val) {
heap.push_back(val);
siftUp(heap.size() - 1); // 新元素上浮
}
// 删除堆顶元素(最大值)
void pop() {
if (heap.empty()) return;
swap(heap[0], heap.back());
heap.pop_back();
siftDown(0, heap.size()); // 新堆顶下沉
}
// 获取堆顶元素(最大值)
int top() {
if (!heap.empty()) return heap[0];
throw out_of_range("Heap is empty");
}
// 判断堆是否为空
bool empty() { return heap.empty(); }
// 获取堆大小
int size() { return heap.size(); }
};
使用示例
int main() {
// 示例1:通过数组建堆
vector<int> arr = {3, 1, 6, 5, 2, 4};
MaxHeap maxHeap(arr);
while (!maxHeap.empty()) {
cout << maxHeap.top() << " "; // 输出:6 5 4 3 2 1
maxHeap.pop();
}
// 示例2:逐个插入元素
MaxHeap heap;
heap.push(3);
heap.push(1);
heap.push(6);
heap.push(5);
cout << heap.top(); // 输出:6
heap.pop();
cout << heap.top(); // 输出:5
return 0;
}

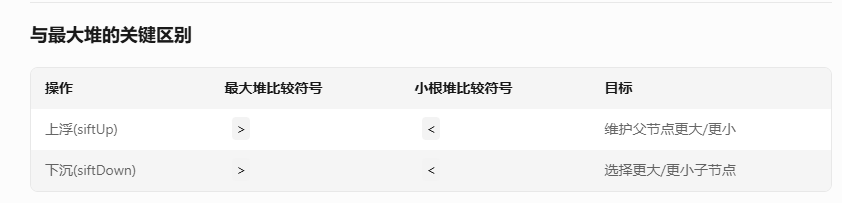
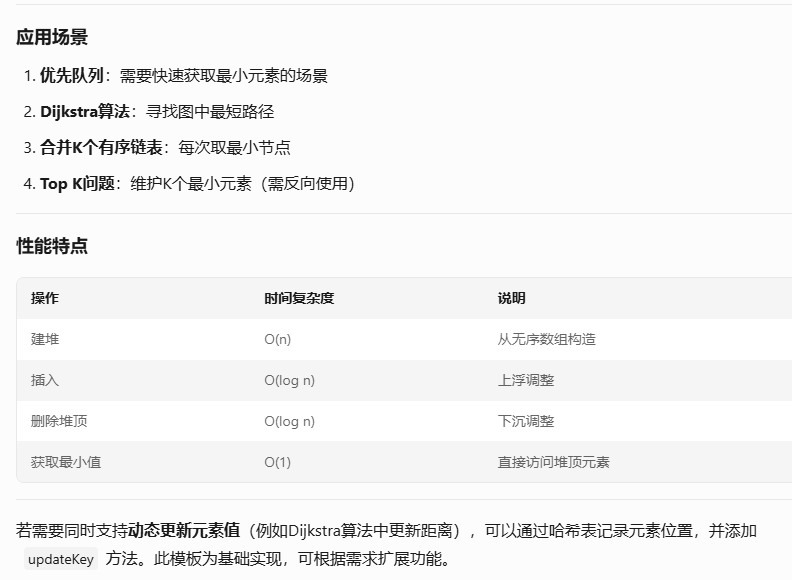
小根堆/最小堆
以下是 小根堆(Min Heap)的C++代码模板,包含插入、删除堆顶、堆化等基本操作,注释详细说明修改关键点:
class MinHeap {
private:
vector<int> heap;
// 获取父节点索引(与最大堆相同)
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
// 获取左子节点索引(与最大堆相同)
int left(int i) { return 2 * i + 1; }
// 获取右子节点索引(与最大堆相同)
int right(int i) { return 2 * i + 2; }
// 上浮操作:修改比较符号为 <
void siftUp(int i) {
while (i > 0 && heap[i] < heap[parent(i)]) { // 仅此处改为 <
swap(heap[i], heap[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
// 下沉操作:修改比较符号为 <
void siftDown(int i, int n) {
int minIndex = i;
int l = left(i), r = right(i);
// 比较子节点中的较小者
if (l < n && heap[l] < heap[minIndex]) // 改为 <
minIndex = l;
if (r < n && heap[r] < heap[minIndex]) // 改为 <
minIndex = r;
if (minIndex != i) {
swap(heap[i], heap[minIndex]);
siftDown(minIndex, n); // 递归调整
}
}
public:
// 构造函数1:通过数组建堆(调整比较方向)
MinHeap(vector<int>& nums) {
heap = nums;
// 从最后一个非叶子节点开始调整
for (int i = heap.size()/2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
siftDown(i, heap.size());
}
}
// 构造函数2:空堆
MinHeap() {}
// 插入元素(与最大堆逻辑相同)
void push(int val) {
heap.push_back(val);
siftUp(heap.size() - 1);
}
// 删除堆顶元素(最小值)
void pop() {
if (heap.empty()) return;
swap(heap[0], heap.back());
heap.pop_back();
siftDown(0, heap.size());
}
// 获取堆顶元素(最小值)
int top() {
if (!heap.empty()) return heap[0];
throw out_of_range("Heap is empty");
}
// 判断堆是否为空
bool empty() { return heap.empty(); }
// 获取堆大小
int size() { return heap.size(); }
};
使用示例
int main() {
// 示例1:通过数组建堆
vector<int> arr = {3, 1, 6, 5, 2, 4};
MinHeap minHeap(arr);
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
cout << minHeap.top() << " "; // 输出:1 2 3 4 5 6
minHeap.pop();
}
// 示例2:逐个插入元素
MinHeap heap;
heap.push(3);
heap.push(1);
heap.push(6);
heap.push(5);
cout << heap.top(); // 输出:1
heap.pop();
cout << heap.top(); // 输出:3
return 0;
}
模板题 P3378 【模板】堆
// Problem: P3378 【模板】堆
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3378
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class MinHeap {
private:
vector<int> heap;
// 获取父节点索引(与最大堆相同)
int parent(int i) {
return (i - 1) / 2;
}
// 获取左子节点索引(与最大堆相同)
int left(int i) {
return 2 * i + 1;
}
// 获取右子节点索引(与最大堆相同)
int right(int i) {
return 2 * i + 2;
}
// 上浮操作:修改比较符号为 <
void siftUp(int i) {
while (i > 0 && heap[i] < heap[parent(i)]) { // 仅此处改为 <
swap(heap[i], heap[parent(i)]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
// 下沉操作:修改比较符号为 <
void siftDown(int i, int n) {
int minIndex = i;
int l = left(i), r = right(i);
// 比较子节点中的较小者
if (l < n && heap[l] < heap[minIndex]) // 改为 <
minIndex = l;
if (r < n && heap[r] < heap[minIndex]) // 改为 <
minIndex = r;
if (minIndex != i) {
swap(heap[i], heap[minIndex]);
siftDown(minIndex, n); // 递归调整
}
}
public:
// 构造函数1:通过数组建堆(调整比较方向)
MinHeap(vector<int>& nums) {
heap = nums;
// 从最后一个非叶子节点开始调整
for (int i = heap.size() / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
siftDown(i, heap.size());
}
}
// 构造函数2:空堆
MinHeap() {}
// 插入元素(与最大堆逻辑相同)
void push(int val) {
heap.push_back(val);
siftUp(heap.size() - 1);
}
// 删除堆顶元素(最小值)
void pop() {
if (heap.empty()) return;
swap(heap[0], heap.back());
heap.pop_back();
siftDown(0, heap.size());
}
// 获取堆顶元素(最小值)
int top() {
if (!heap.empty()) return heap[0];
throw out_of_range("Heap is empty");
}
// 判断堆是否为空
bool empty() {
return heap.empty();
}
// 获取堆大小
int size() {
return heap.size();
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
MinHeap heap;
while (n--) {
int op;
cin >> op;
if (op == 1) {
int x;
cin >> x;
heap.push(x);
} else if (op == 2) {
cout << heap.top() << '\n';
} else {
heap.pop();
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
建堆过程详解


void siftDown(vector<int>& arr, int i, int n) {
int maxIndex = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[maxIndex])
maxIndex = left;
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[maxIndex])
maxIndex = right;
if (maxIndex != i) {
swap(arr[i], arr[maxIndex]);
siftDown(arr, maxIndex, n); // 递归调用
}
}
// 建堆函数
void buildHeap(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
siftDown(arr, i, n);
}
}

建堆时间复杂度分析





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号