对Java第四-六周学习内容及三次作业总结
一、前言概括
Java学习过程中的问题和概括:
1.这几周的课程学习重点是面对对象技术的三大特点:封装、继承、多态。
2.自学内容为:接口、hashmap函数的使用,以及对正则表达式的进一步学习。
3.问题:几次实验和PTA题目集的出现的语法问题和对一些Java提供的类的使用遇见的问题。
此次题目集第4-5周的习题题目难度适中,都有一题需要使用正则表达式进行对数据的进行处理的题目,
但很遗憾依旧不能拿到满分,而第六次的作业题目集较为简易,此外题目的量增加了一些。
二、题目集问题分析
第四次题目集1.水文数据校验及处理

public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
DealDate dealDate = new DealDate();
dealDate.getDealResult();
}
}
这里是主类,直接定义了一个DealDate类型的对象,在直接获取结果,在getDealResult中把所有输出写好。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class HydrologicalInfo {//信息类,存储所有水文信息
private LocalDateTime measureDateTime;
private double actualWaterLevel;
private double objectWaterLevel;
private double actualGateOpening;
private double objectGateOpening;
private double waterFlow;
public HydrologicalInfo() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public HydrologicalInfo(LocalDateTime measureDateTime, double actualWaterLevel, double objectWaterLevel,
double actualGateOpening, double objectGateOpening, double waterFlow) {
super();
this.measureDateTime = measureDateTime;
this.actualWaterLevel = actualWaterLevel;
this.objectWaterLevel = objectWaterLevel;
this.actualGateOpening = actualGateOpening;
this.objectGateOpening = objectGateOpening;
this.waterFlow = waterFlow;
}
public LocalDateTime getMeasureDateTime() {
return measureDateTime;
}
public void setMeasureDateTime(LocalDateTime measureDateTime) {
this.measureDateTime = measureDateTime;
}
public double getActualWaterLevel() {
return actualWaterLevel;
}
public void setActualWaterLevel(double actualWaterLevel) {
this.actualWaterLevel = actualWaterLevel;
}
public double getObjectWaterLevel() {
return objectWaterLevel;
}
public void setObjectWaterLevel(double objectWaterLevel) {
this.objectWaterLevel = objectWaterLevel;
}
public double getActualGateOpening() {
return actualGateOpening;
}
public void setActualGateOpening(double actualGateOpening) {
this.actualGateOpening = actualGateOpening;
}
public double getObjectGateOpening() {
return objectGateOpening;
}
public void setObjectGateOpening(double objectGateOpening) {
this.objectGateOpening = objectGateOpening;
}
public double getWaterFlow() {
return waterFlow;
}
public void setWaterFlow(double waterFlow) {
this.waterFlow = waterFlow;
}
}
设计这个类的目的是,为了在分割好数据的时候将数据存储好,便于后续数据的获取和设置
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DealDate {
private List<CheckDate> list = new ArrayList<CheckDate>();
private int cnt = 0;
private static List<String> list2;
public DealDate() {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String tmpStr = input.nextLine();
int row = 1;
while (tmpStr.compareTo("exit") != 0) {//判断何时停止输入
list.add(new CheckDate(tmpStr, row));
tmpStr = input.nextLine();
row++;//计入输入数据行数
}
this.cnt = row - 1;
}
void getDealResult() {
Iterator<CheckDate> it = list.iterator();
double max = 0;
double sum = 0;
boolean flag = false;
while (it.hasNext()) {
CheckDate tmp = it.next();
if (tmp.validateDateData()) {//检测输入数据合法性
flag = true;
}
list2 = tmp.getList();
}
//若flag为判断是否存在非法输入的情况
//list2是存储着非法输入的信息
if (flag) {//输出内容判断
Iterator<CheckDate> it2 = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
CheckDate tmp = it2.next();
HydrologicalInfo tmp2 = tmp.toHydrologicalInfo();
if (tmp2.getActualGateOpening() > tmp2.getObjectGateOpening()) {
System.out.println("Row:" + tmp.getRow() + " GateOpening Warning");
}
if (tmp2.getActualWaterLevel() > max) {//查找数最大的实际水位
max = tmp2.getActualWaterLevel();
}
sum += tmp2.getWaterFlow();//计算水的总量
}
} else {//若存在非法输入,则输出检测出来的非法输入
Iterator<String> it3 = list2.iterator();
while (it3.hasNext()) {
String tempString = it3.next();
if (it3.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(tempString);
} else {
System.out.print(tempString);
}
}
}
}
}
该类的设计的目的就是对每行的数据的处理,主要进行检查输入合法性校验并若合法则判断输出内容,
由于是分行输入,而我采用了先将输入全部存入Arraylist中在进行判断,由于是每行一旦有输入合
法性错误的就需要输出该行信息,这样的话就需要先把判断得到信息进行存储,判断后然后一起输出。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class CheckDate {// 输入合法性校验
private String data;
private int row;
private int totalCoulmn;
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
private int hour;
private int min;
private double actualWaterLevel;
private double objectWaterLevel;
private double actualGateOpening;
private double objectGateOpening;
private double waterFlow;
private static List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public CheckDate() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public CheckDate(String data, int row) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.row = row;
}
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public String[] getData() {
// String format = "([1-9][0-9]{0,3}/[1-9][0-9]?/[1-9][0-9]?
// [0-9][0-9]?:[0-9][0-9]?)\\|(([1-9][0-9]{0,2}(\\.[0-9]{1,3})?)|([1-9][0-9]{0,2}))\\|(([1-9][0-9]{0,2}(\\.[0-9]{1,3})?)|([1-9][0-9]{0,2}))\\|([0-9]\\.[0-9][0-9])/([0-9]\\.[0-9][0-9])\\|([1-9][0-9]{0,2}(\\.[0-9]{1,3})?)|([1-9][0-9]{0,2})";
String string[] = Pattern.compile("\\|").split(this.data);// 根据|分割数据
this.totalCoulmn = string.length;
for (int i = 1; i < string.length; i++) {
string[i] = string[i].trim();// 去首位括号
}
return string;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getRow() {
return row;
}
public void setRow(int row) {
this.row = row;
}
public boolean validateDateData() {// 对数据进行校验
String[] string = this.getData();
String[] tmpStr = string[3].split("/");
boolean flag = true;
if (this.totalCoulmn != 5) {
list.add("Wrong Format");
list.add("Data:" + this.data);
flag = false;
} else {
if (this.validDateMeasureDateTime(string[0]) == false) {
list.add("Row:" + this.row + ",Column:1Wrong Format");
flag = false; // Row:1,Column:2Wrong Format
}
if (this.validateWaterLevel(string[1]) == false) {
list.add("Row:" + this.row + ",Column:2Wrong Format");
flag = false;
} else {
this.objectWaterLevel = Double.parseDouble(string[1]);
}
if (this.validateWaterLevel(string[2]) == false) {
list.add("Row:" + this.row + ",Column:3Wrong Format");
flag = false;
} else {
this.actualWaterLevel = Double.parseDouble(string[2]);
}
if (this.valiateGateOpening(tmpStr[0]) == false) {
list.add("Row:" + this.row + ",Column:4Wrong Format");
flag = false;
} else {
this.objectGateOpening = Double.parseDouble(tmpStr[0]);
}
if (this.valiateGateOpening(tmpStr[1]) == false) {
list.add("Row:" + this.row + ",Column:5Wrong Format");
flag = false;
} else {
this.actualGateOpening = Double.parseDouble(tmpStr[0]);
}
if (this.validateWaterLevel(string[4]) == false) {
list.add("Row:" + this.row + ",Column:6Wrong Format");
flag = false;
} else {
this.waterFlow = Double.parseDouble(string[4]);
}
}
if (flag == false) {
list.add("Data:" + this.data);
}
return flag;
}
public boolean validDateMeasureDateTime(String measureDateTime) {// 对输入时间部分进行校验
if (measureDateTime.matches("([1-9][0-9]{0,3}/[1-9][0-9]?/[1-9][0-9]? [1-9][0-9]{0,1}:[0][0])")) {
String string[] = measureDateTime.split("/");
this.year = Integer.parseInt(string[0]);
this.month = Integer.parseInt(string[1]);
String string2[] = string[2].split(" ");
this.day = Integer.parseInt(string2[0]);
String string3[] = string2[1].split(":");
this.hour = Integer.parseInt(string3[0]);
this.min = (string3[1].charAt(0) - '0') * 10 + (string3[1].charAt(1) - '0');// 数字转换
if (hour % 2 != 0) {
return false;
}
return this.checkInputValidity(year, month, day, hour, min);
}
return false;
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0))
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(int year, int month, int day, int hour, int min) {// 时间合法性检测
if (year < 1 || year > 9999 || month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > 31 || day > monthDays(year, month)
|| min > 60 || min < 0 || hour > 24 || hour < 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static int monthDays(int year, int month) {
int day = 0;
switch (month) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
day = 31;
break;
case 2:
if (isLeapYear(year))
day = 29;
else
day = 28;
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
day = 30;
break;
}
return day;
}
public boolean validateWaterLevel(String waterLevel) {// 对水位的合法性检测
if (waterLevel.matches("([1-9][0-9]{0,2}(\\.[0-9]{1,3})?)|([1-9][0-9]{0,2})")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean valiateGateOpening(String gateOpening) {// 开度合法性检测
return gateOpening.matches("([0-9]\\.[0-9][0-9])");
}
public HydrologicalInfo toHydrologicalInfo() {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(year, month, day, hour, min);
HydrologicalInfo hydrologicalInfo = new HydrologicalInfo(localDateTime, actualWaterLevel, objectWaterLevel,
actualGateOpening, objectGateOpening, waterFlow);
return hydrologicalInfo;
}
}
该类是用于检测数据合法性的,首先是采用了split函数进行分割数据,根据|分割成5份,
在进行判断若没有5份则说明整体输入格式非法,若为5分则分别对五份进行检测,若都为合法
输入则将数据字符串转化为数值。
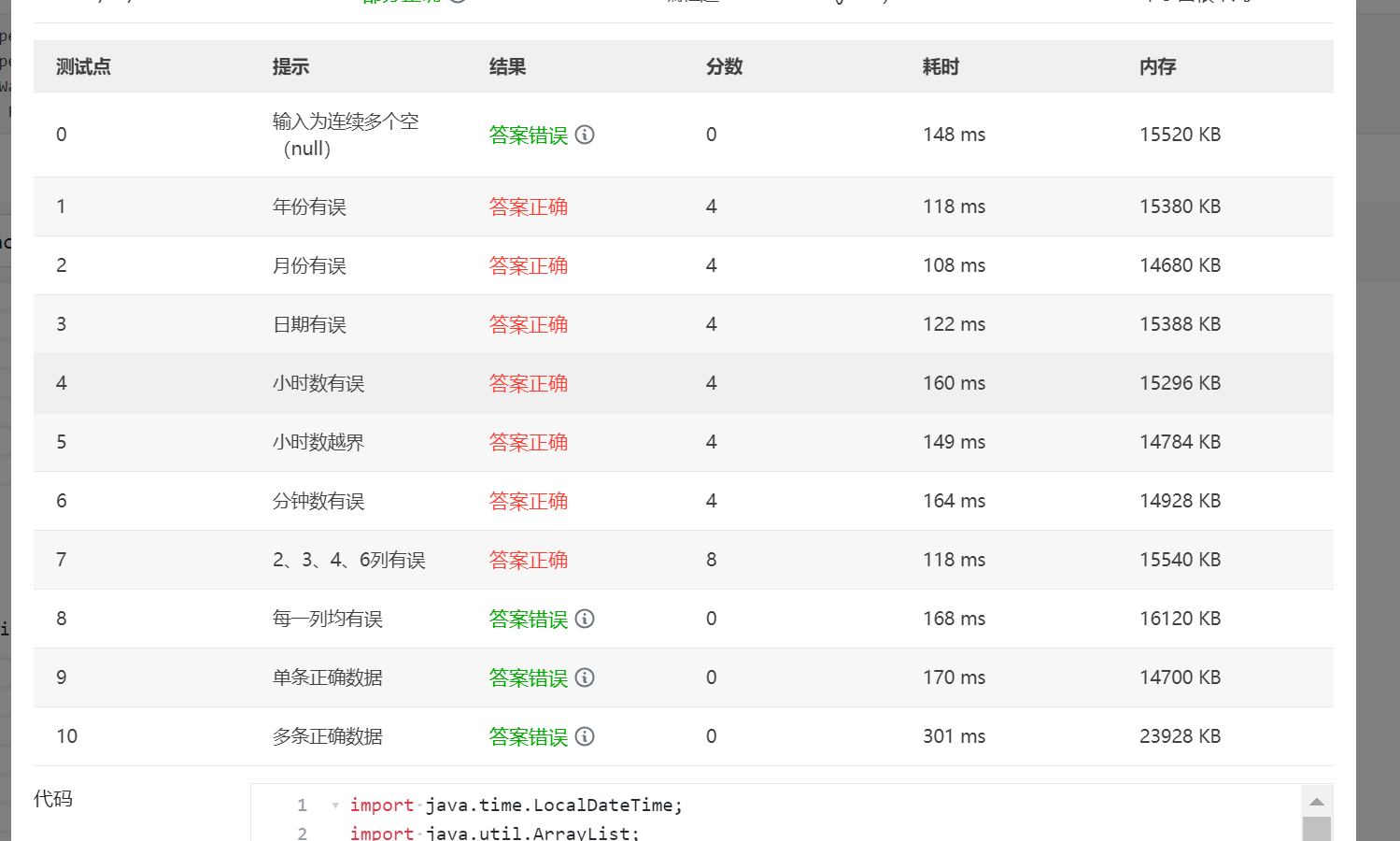
还有四个测试点未过,分析了一下可能因为正则表达式并没有检测出所有错误,
比如说在数据中间加空格的情况没有进行排除,同时数据又字符串转化为数值时
出现错误。而且其中一个类并没有用上存在多项问题。
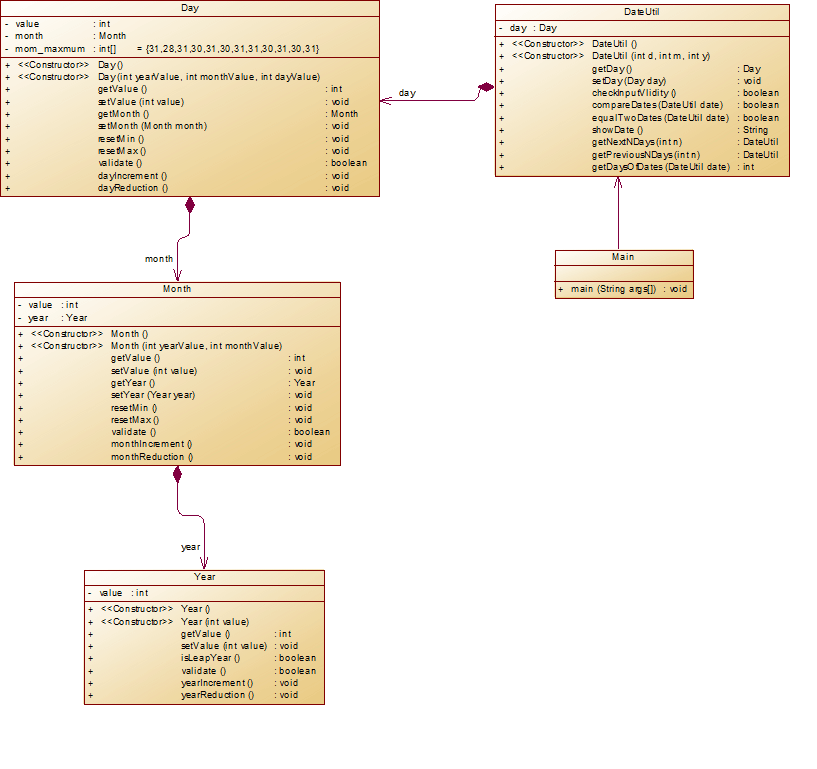
类图:
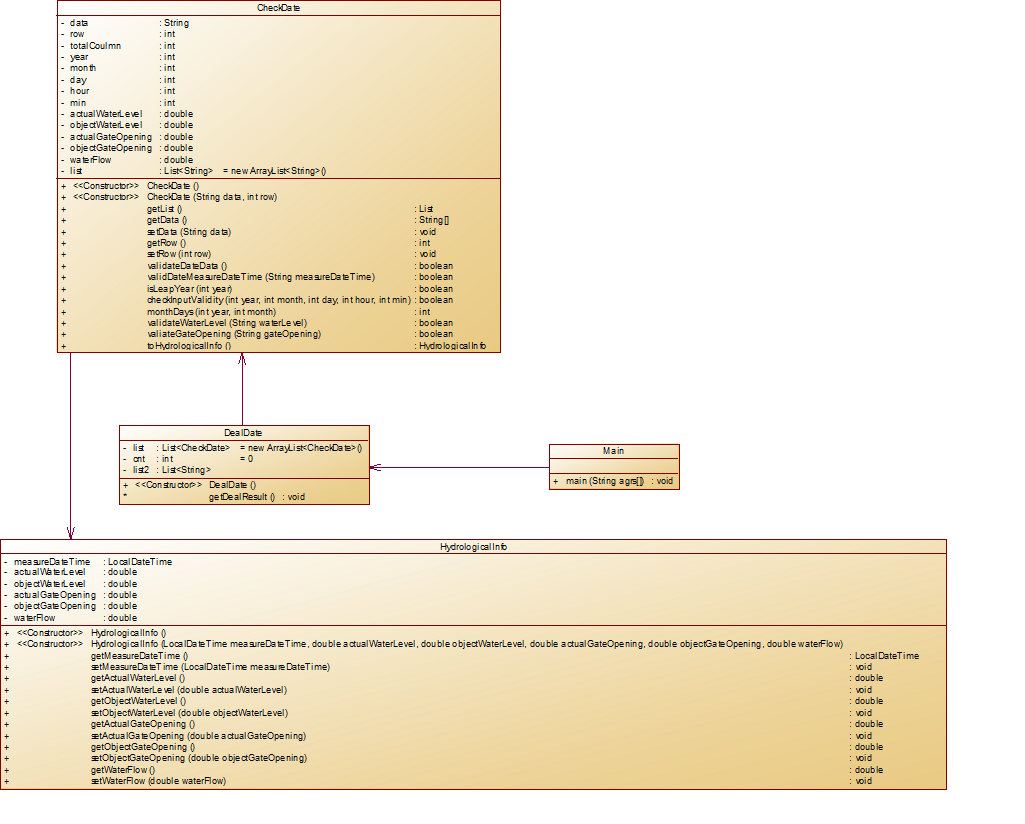
在设计类的时候准备将checkData用在检测数据,但是为了方便我把数据拆分为5个部分进行分别检测合法性
而此时顺便将各部分转变为数值
dealDate类是为了处理数据,和checkData类为聚合关系
HydrologicalInfo虽然设计成了与checkData类为关联关系但是实际上并没有用到该类
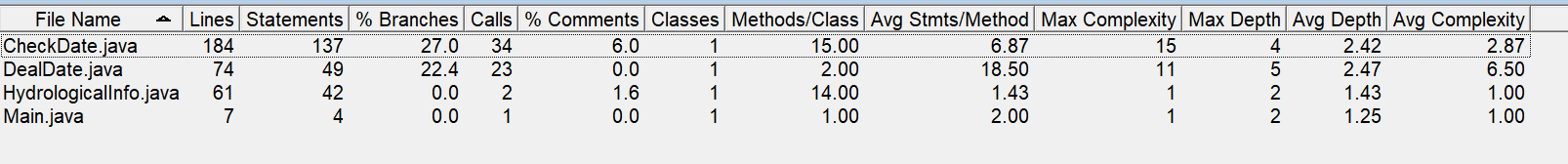
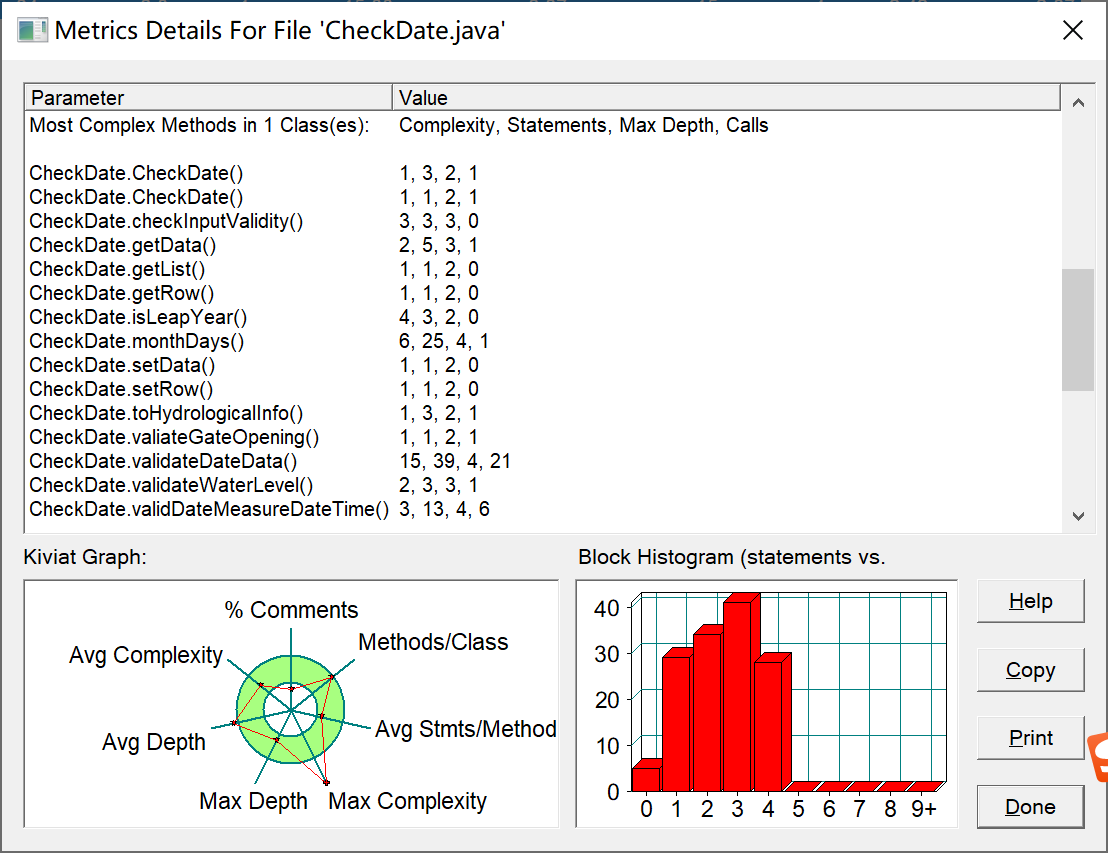
问题:
复杂度较高,而类的多有重复之处,且功能混乱,最好执行类的单一职责原则,
暂且无好的改进思路。
第四次题目集2. 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = input.nextInt();
int year ;
int month ;
int day ;
int year2 ;
int month2 ;
int day2 ;
int n ;
switch(option) {//操作选择
case 1://获取N天后的日期
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
n = input.nextInt();
DateUtil dateUtil = new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(dateUtil.checkInputVlidity()) {
DateUtil newDateUtil = dateUtil.getNextNDays(n);
System.out.println(newDateUtil.showDate());
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
break;
case 2://获取前N天的日期
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
n = input.nextInt();
DateUtil dateUtil2 = new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(dateUtil2.checkInputVlidity()) {
DateUtil newDateUtil2 = dateUtil2.getPreviousNDays(n);
System.out.println(newDateUtil2.showDate());
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
break;
case 3://获取两个日期之间相差天数
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
year2 = input.nextInt();
month2 = input.nextInt();
day2 = input.nextInt();
DateUtil dateUtil3 = new DateUtil(day,month,year);
DateUtil dateUtil4 = new DateUtil(day2,month2,year2);
if(dateUtil3.compareDates(dateUtil4)) {//比较哪个日期更小
if(dateUtil4.checkInputVlidity()&&dateUtil3.checkInputVlidity()) {
int sum = dateUtil4.getDaysOfDates(dateUtil3);
System.out.println(sum);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}else {
if(dateUtil3.checkInputVlidity()&&dateUtil4.checkInputVlidity()) {
int sum = dateUtil3.getDaysOfDates(dateUtil4);
System.out.println(sum);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
break;
default ://若选择操作越界
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
main类主要控制选择操作和组织类与方法,在case3中由于特殊的函数算法要把日期小的数据放前面。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DateUtil {
private Day day;
public DateUtil() {
}
public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) {
day = new Day(y, m, d);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean checkInputVlidity() {//检测年月日输入合法性
if (day.getMonth().validate() == false || day.getMonth().getYear().validate() == false) {
return false;
} else if (day.validate() == false) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {//比较两个日期大小
if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return false;
} else {
if (day.getMonth().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
} else if (day.getMonth().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
return false;
} else {
if (day.getValue() > date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {//判断两个日期是否相等
if (this.compareDates(date) == false && day.getValue() == date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public String showDate() {//格式化输出
String temp;
Integer x = this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();
Integer z = this.day.getMonth().getValue();
Integer c = this.day.getValue();
temp = x.toString() + "-" + z.toString() + "-" + c.toString();
return temp;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {//获取N天后日期
int[] mom_maxmum = { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int year = this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int month = this.day.getMonth().getValue();
int day = this.day.getValue();
int totalDays = 365;
n = n + day;//这里是调整日期号为0,更好实现月的递加
DateUtil newday = new DateUtil(0, month, year);
while (true) {
if (newday.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
totalDays = 366;
mom_maxmum[1] = 29;
} else {
totalDays = 365;
mom_maxmum[1] = 28;
}
if (n > mom_maxmum[newday.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1]) {
n -= mom_maxmum[newday.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1];
newday.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();
if (newday.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > 12) {
newday.getDay().getMonth().resetMin();
newday.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
}
} else {
newday.getDay().setValue(n);
break;
}
}
return newday;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {
int[] mom_maxmum = { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int year = this.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int month = this.day.getMonth().getValue();
int day = this.day.getValue();
int totalDays = 365;
n = n - day;//这一段为了使日期号day为上个月最大数,便于后面的日期号直接减去剩余的n
month--;
if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)) {
mom_maxmum[1] = 29;
} else {
mom_maxmum[1] = 28;
}
if(month<1) {
month = 12;
year--;
}
DateUtil newday = new DateUtil(mom_maxmum[month - 1], month, year);
while (true) {
if (newday.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
totalDays = 366;
mom_maxmum[1] = 29;
} else {
totalDays = 365;
mom_maxmum[1] = 28;
}
if (n > mom_maxmum[newday.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1]) {
n -= mom_maxmum[newday.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1];
newday.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction();
if (newday.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < 1) {
newday.getDay().getMonth().resetMax();
newday.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
}
} else {
int temp = newday.getDay().getValue() - n;
newday.day.setValue(temp);
break;
}
}
return newday;
}
public int getDaysOfDates(DateUtil date) {//获取两个日期之间的相差天数
int left = 0;
int right = 1000;
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
DateUtil newday = this.getNextNDays(right);//使用了本类里的获取下N天,所以日期小的数据在前
while (true) {//保证right的值代入得到的日期比第二个日期大
if (newday.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
left = right;
right = right * 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(right);
} else {
break;
}
}
mid = (left + right) / 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
while (right > left) {//在使用折半查找进行得到符合要求的N
if (newday.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
right = mid - 1;
mid = (int) ((right + left) / 2);
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
} else if (newday.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
left = mid + 1;
mid = (right + left) / 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
} else if (newday.day.getMonth().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getValue()) {
right = mid - 1;
mid = (right + left) / 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
} else if (newday.day.getMonth().getValue() < date.day.getMonth().getValue()) {
left = mid + 1;
mid = (right + left) / 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
} else if (newday.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue()) {
right = mid - 1;
mid = (right + left) / 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
} else if (newday.day.getValue() < date.day.getValue()) {
left = mid + 1;
mid = (right + left) / 2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
} else {
break;
}
}
return mid;
}
}
这里对于getNextDays()和getPreviousDays()两个函数的算法都是,判断n是否大于该月最大天数,
若是则减去该月的最大天数,直到n<该月最大天数则此时用day加上或减去n而对于函数getDaysOfDates()
则调用了函数getNextDays()函数去找到一个N满足使更小的日期加上N天等于更大的日期。这里我采用了
折半查找,但是提前要设置好right的初始值,使其保证初始值right使得小的日期加上最大值right天数可
以大过最大日期,既保证N一定会在[left,right]的范围内,这样才能通过折半查找找出满足条件的N
public class Year {
private int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {//闰年判断
if(this.value%400 == 0 ||(this.value%4 == 0 &&this.value%100 != 0))
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {//合法性判断
if(this.value>=1900&&this.value<=2050) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement() {//年份自增
this.value++;
}
public void yearReduction() {//月份递增
this.value--;
}
}
public class Month {
private int value;
private Year year;
public Month() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Month(int yearValue, int monthValue) {
this.value = monthValue;
this.year = new Year(yearValue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {//重置最小月份
this.value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {//重置最大月份
this.value = 12;
}
public boolean validate() {//合法性判断
if(this.value >= 1 && this.value <=12) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement() {//月份自增
this.value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {//月份自减
this.value--;
}
}
public class Day {
private int value;
private Month month;
private int []mom_maxmum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public Day() {
}
public Day(int yearValue , int monthValue,int dayValue) {
this.value = dayValue;
month = new Month(yearValue , monthValue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void resetMin() {\\最小日设置
this.value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {\\当月最大天数设置
Year year = month.getYear();
if(year.isLeapYear()) {
mom_maxmum[1]=29;
}else {
mom_maxmum[1]=28;
}
this.value = mom_maxmum[month.getValue()-1];
}
public boolean validate() {\\合法性检测
Year year = month.getYear();
if(year.isLeapYear()) {
mom_maxmum[1]=29;
}else {
mom_maxmum[1]=28;
}
if(this.value>=1&&this.value<=mom_maxmum[month.getValue()-1]) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void dayIncrement() {\\日自增
this.value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {\\日自减
this.value--;
}
}
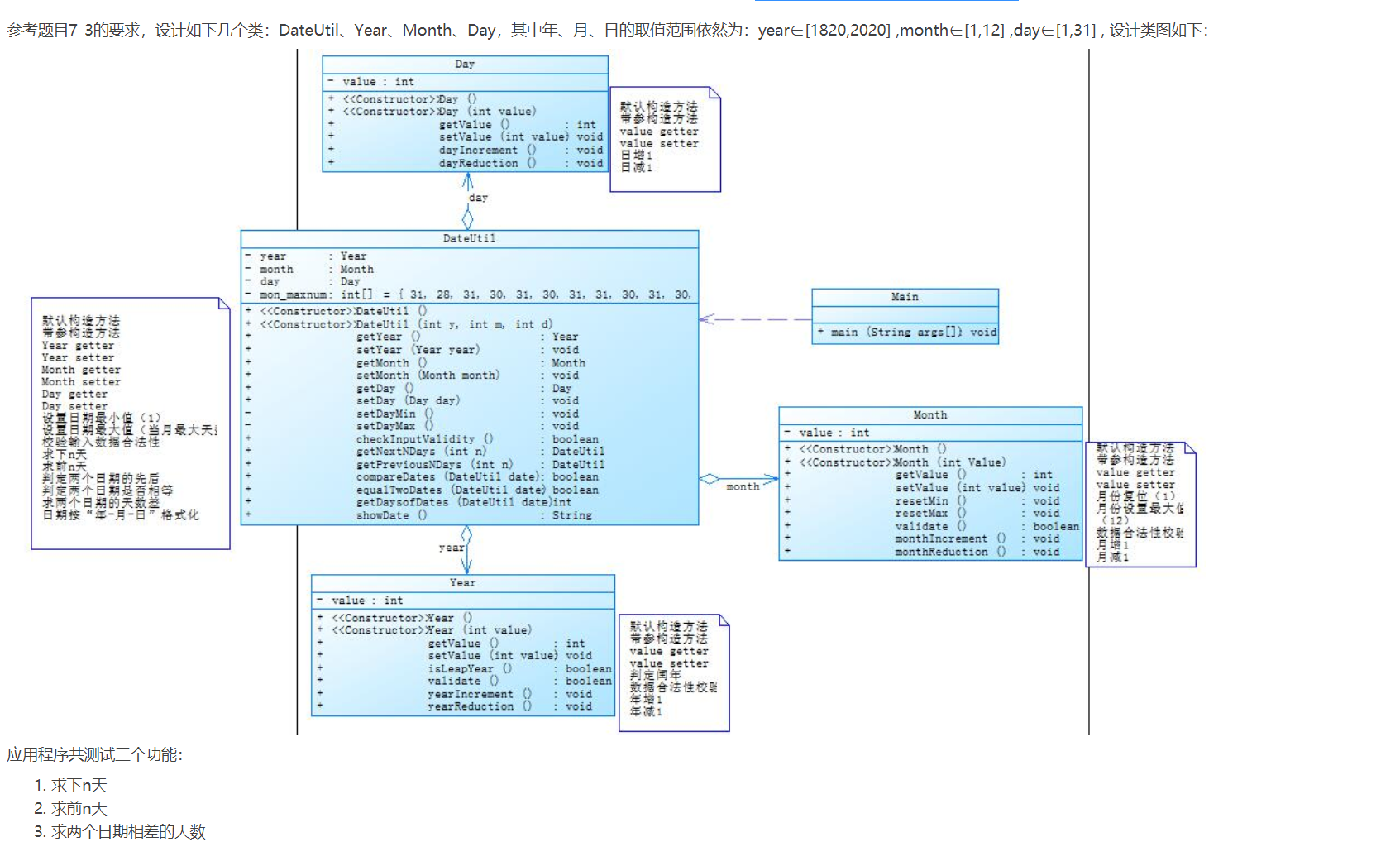
Day、Month、Year三个类是嵌套的,Year嵌套在Month里,而Month嵌套在Year里,他们之间为组合关系同时Day与DateUtil也是组合关系。
类图如下:
负责度分析:
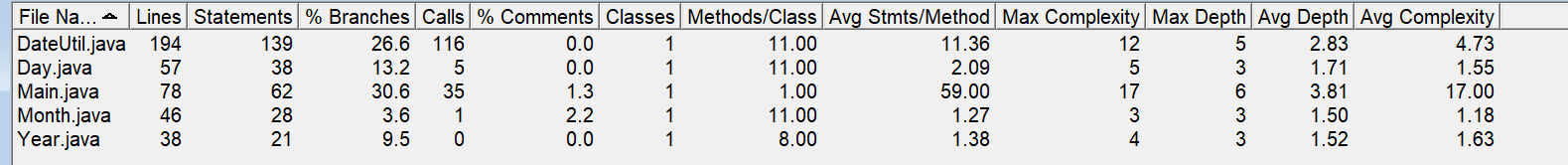
其中DateUtil类的复杂度过高,进而导致main类的负责度也过高。
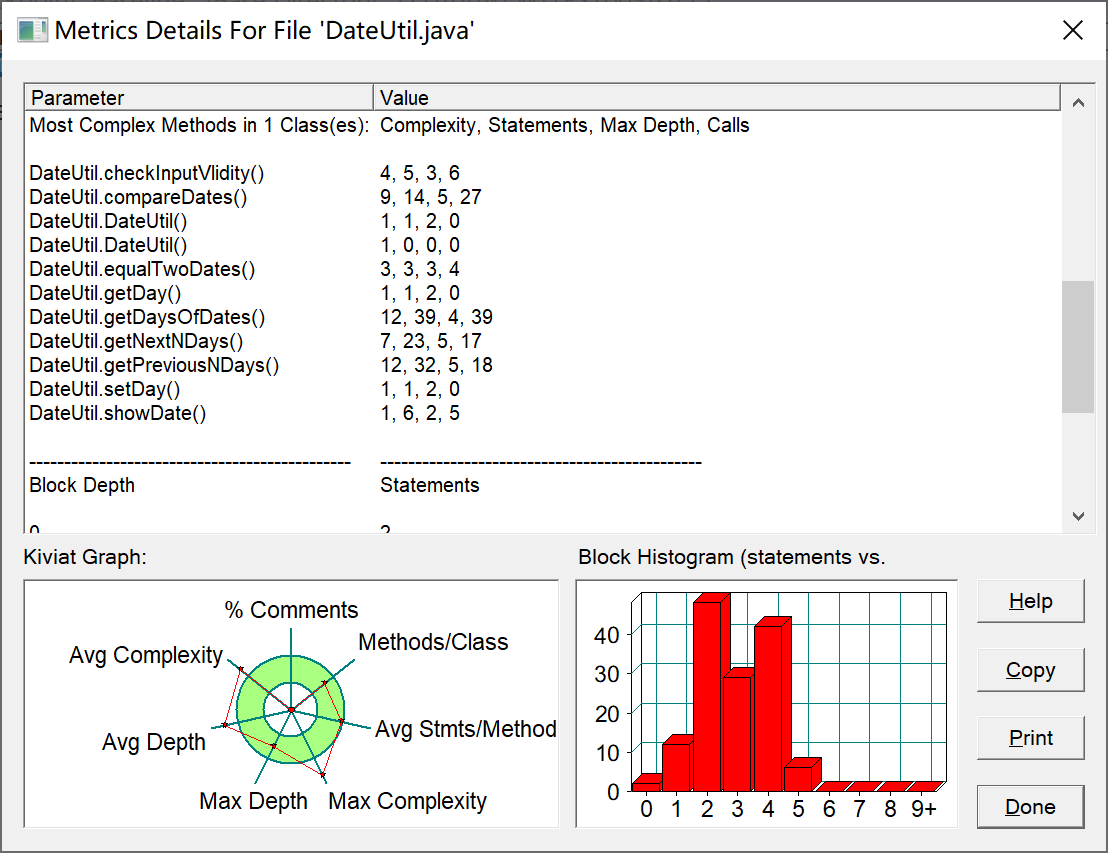
其中getDaysOfDates()函数复杂度过高,原因当时认为折半查找和采用getNextDays()函数会比暴力循环
查找更优越,虽然是更为优越一点但是其复杂度依旧是比较高。
对比第五次题集5.日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = input.nextInt();
int year ;
int month ;
int day ;
int year2 ;
int month2 ;
int day2 ;
int n ;
switch(option) {//选择操作
case 1://获取N天后的日期
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
n = input.nextInt();
DateUtil dateUtil = new DateUtil(year,month,day);
if(dateUtil.checkInputValidity()) {//合法性检测
DateUtil newDateUtil = dateUtil.getNextNDays(n);
System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day+" next "+n+" days is:"+newDateUtil.showDate());
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
break;
case 2://获取前N天日期
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
n = input.nextInt();
DateUtil dateUtil2 = new DateUtil(year,month,day);
if(dateUtil2.checkInputValidity()) {//合法性检验
DateUtil newDateUtil2 = dateUtil2.getPreviousNDays(n);
System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day+" previous "+n+" days is:"+newDateUtil2.showDate());
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
break;
case 3://获取两个日期之间相差天数
year = input.nextInt();
month = input.nextInt();
day = input.nextInt();
year2 = input.nextInt();
month2 = input.nextInt();
day2 = input.nextInt();
DateUtil dateUtil3 = new DateUtil(year,month,day);
DateUtil dateUtil4 = new DateUtil(year2,month2,day2);
if(dateUtil3.compareDates(dateUtil4)) {//判断两个日期哪个更小
if(dateUtil4.checkInputValidity()&&dateUtil3.checkInputValidity()) {
int sum = dateUtil4.getDaysOfDates(dateUtil3);
System.out.println("The days between "+dateUtil3.showDate()+" and "+dateUtil4.showDate()+" are:"+sum);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}else {
if(dateUtil3.checkInputValidity()&&dateUtil4.checkInputValidity()) {
int sum = dateUtil3.getDaysOfDates(dateUtil4);
System.out.println("The days between "+dateUtil3.showDate()+" and "+dateUtil4.showDate()+" are:"+sum);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
break;
default :
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
main类里与之前一直,没有改动
public class DateUtil {
private Year year;//将三个类作为属性
private Month month;
private Day day;
private int x =0;
private int []mom_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public DateUtil(int y , int m ,int d) {
this.year = new Year(y);
this.month = new Month(m);
this.day = new Day(d);
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void setDayMin() {//设置最小日数
day.setValue(1);
}
public void setDayMax() {//设置该月份最大日数
if(this.year.isLeapYear()) {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
this.day.setValue(this.mom_maxnum[this.month.getValue()-1]);
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {//合法性检测
if(this.month.validate() == false) {
return false;
}
if(this.year.validate() == false) {
return false;
}
if(this.year.isLeapYear()) {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
if(this.day.getValue() < 1||this.day.getValue()>this.mom_maxnum[this.month.getValue()-1]) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(this.year.getValue(),this.month.getValue(),this.day.getValue());
while(true) {
if(newDate.year.isLeapYear()) {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
if(n >this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1] ) {//是否大于当月最大天数
n -= this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1];
newDate.month.monthIncrement();
if(newDate.month.getValue()>12) {//判断月份是否要重置
newDate.year.yearIncrement();
newDate.month.resetMin();
}
}else {
int tmp =newDate.day.getValue()+n;
if(tmp>this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1])//判断是否号数大于当月最大天数
{
tmp -= this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1];
newDate.day.setValue(tmp);
newDate.month.monthIncrement();
if(newDate.month.getValue()>12) {
newDate.year.yearIncrement();
newDate.month.resetMin();
}
}else {
newDate.day.setValue(tmp);
}
break;
}
}
return newDate;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {
DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(this.year.getValue(),this.month.getValue(),this.day.getValue());
n = n - this.day.getValue();
if(newDate.year.isLeapYear()) {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
newDate.month.monthReduction();
if(this.month.getValue()<1) {
newDate.month.resetMax();
newDate.year.yearDeduction();
}
newDate.day.setValue(this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1]);
while(true) {
if(newDate.year.isLeapYear()) {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
if(n >this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1] ) {
n -= this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1];
newDate.month.monthReduction();
if(newDate.month.getValue()<1) {
newDate.year.yearDeduction();
newDate.month.resetMax();
}
newDate.day.setValue(this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1]);
}else {
newDate.day.setValue(newDate.day.getValue() - n);
break;
}
}
if(newDate.year.isLeapYear()) {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 29;
}else {
this.mom_maxnum[1] = 28;
}
if(newDate.day.getValue()>this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1])
{
int tmp =newDate.day.getValue() ;
int tmp2 =this.mom_maxnum[newDate.month.getValue()-1];
newDate.day.setValue(tmp - tmp2);
newDate.month.monthIncrement();
if(this.month.getValue()>12) {
newDate.month.resetMin();
newDate.year.yearIncrement();
}
}
return newDate;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue() && this.month.getValue() == date.month.getValue() && this.year.getValue() == date.year.getValue()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.year.getValue() > date.year.getValue()) {
return true;
}else if (this.year.getValue() < date.year.getValue()) {
return false;
}else if(this.month.getValue() > date.month.getValue()) {
return true;
}else if(this.month.getValue() < date.month.getValue()) {
return false;
}else if(this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int getDaysOfDates(DateUtil date) {//同样的还是依靠折半查找确定N值
int left = 0;
int right = 1000;
int mid = (left+right)/2;
DateUtil newday = this.getNextNDays(right);
while (true) {//保证N值在[left,right]范围内
if(newday.year.getValue() < date.year.getValue()) {
left = right;
right = right*2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(right);
}else {
break;
}
}
mid =(left+right)/2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
while (right>left){//折半查找
if(newday.year.getValue()> date.year.getValue()) {
right = mid -1;
mid = (int)((right+left)/2);
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
}else if(newday.year.getValue() < date.year.getValue()) {
left = mid + 1;
mid = (right+left)/2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
}else if (newday.month.getValue()>date.month.getValue()) {
right = mid -1;
mid = (right+left)/2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
}else if(newday.month.getValue()<date.month.getValue()) {
left = mid + 1;
mid = (right+left)/2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
}else if (newday.day.getValue()>date.day.getValue()) {
right = mid -1;
mid = (right+left)/2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
}else if(newday.day.getValue()<date.day.getValue()) {
left = mid + 1;
mid = (right+left)/2;
newday = this.getNextNDays(mid);
}else{
break;
}
}
return mid;
}
public String showDate() {//格式化日期
String temp;
Integer x = this.year.getValue();
Integer z = this.month.getValue();
Integer c = this.day.getValue();
temp = x.toString() + "-" + z.toString() + "-" + c.toString();
return temp;
}
}
这里对于getNextDays()和getPreviousDays()两个函数的算法都是,判断n是否大于该月最大天数,
若是则减去该月的最大天数,直到n<该月最大天数则此时用day加上或减去n,但是由于这次题目集有整数
型最大值的边界,所以对于像原来的先把day的值先加给n然后设置day为0进而使得最后day+n时不
用再次判断是否越界当月份最大天数的方法不再适用,因为n一旦为最大边界,则不能整数型n=n+day会超
过整数型最大范围从而导致错误。而对于函数 getDaysOfDates() 则调用了函数getNextDays()函数去
找到一个N满足使更小的日期加上N天等于更大的日期。这里我采用了折半查找,但是提前要设置好right的初
始值,使其保证初始值right使得小的日期加上最大值right天数可以大过最大日期,既保证N一定会在[left,right]
的范围内,这样才能通过折半查找找出满足条件的N。
public class Day {
private int value;
public Day() {
}
public Day(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void dayIncrement() {//自增
this.value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {//自减
this.value--;
}
}
public class Month {
private int value;
public Month() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Month(int value) {
super();
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void resetMin() {
this.value = 1;
}
public void resetMax() {
this.value = 12;
}
public boolean validate() {//合法性判断
if(this.value<1 || this.value>12) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void monthIncrement() {//自增
this.value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {//自减
this.value--;
}
}
public class Year {
private int value;
public Year() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Year(int value) {
super();
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {//合法性判断
if(this.value%400 == 0 ||(this.value%4 == 0 && this.value%100 != 0)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(this.value<1820||this.value>2020) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void yearIncrement() {//自增
this.value++;
}
public void yearDeduction() {//自减
this.value--;
}
}
类图如下:
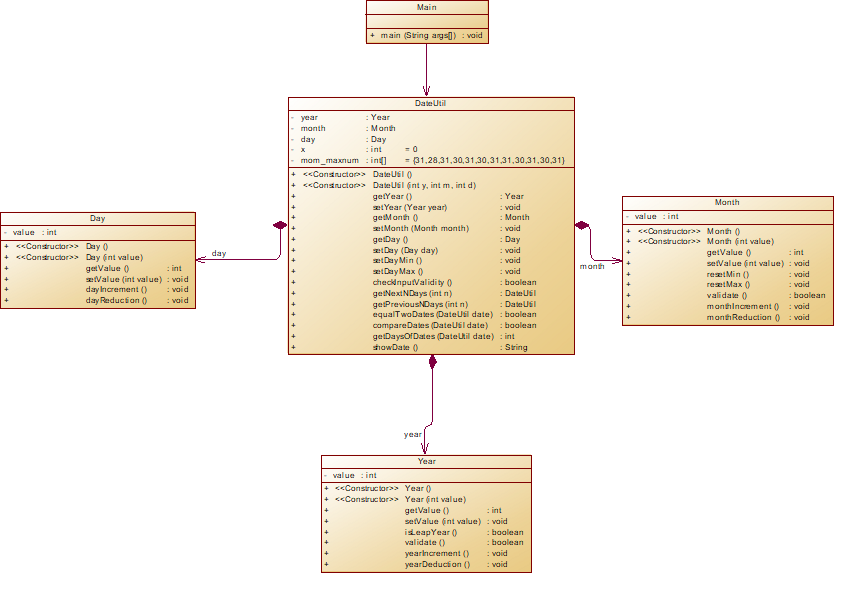
很明显Day、Month、Year三个类平行且各种相对独立的,他们之间为没有类的关系
但是Day、Month、Year三个类都是与DateUtil为组合关系。
复杂度:

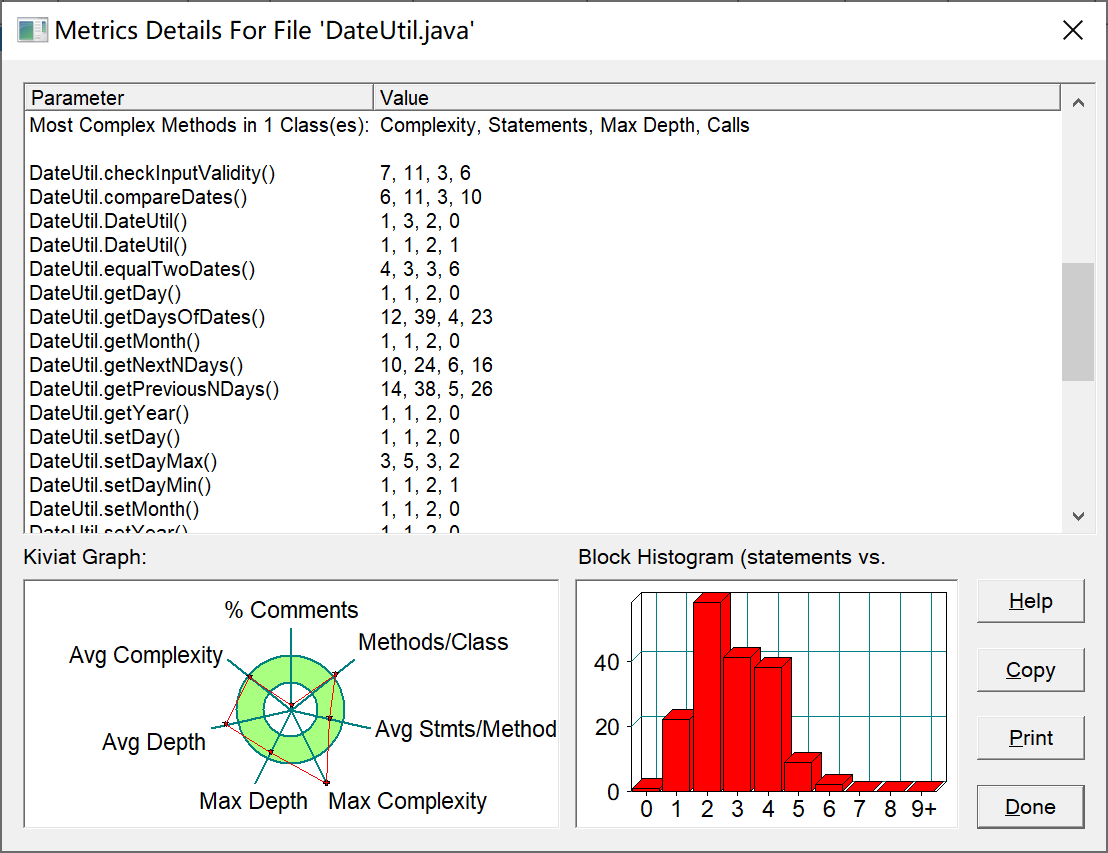
其中getDaysOfDates()函数复杂度过高,原因当时认为折半查找和采用getNextDays()函数会比暴力循环
查找更优越,虽然是更为优越一点但是其复杂度依旧是比较高。
题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
相同点:对于两次作业其一些关键的计算天数和日期的算法类似,没有大的改动,唯一不同之处就是由于
给定测试范围问题,之前一次的一些小技巧无法使用,会造成越界,同时对于计算N天前和后的算法一致
没有以n是否大于每年的天数来判断进而加一年或者减一年,原因是这时候要添加不少判断,判断是否闰年,
是否初始日期超过了二月份进而是应该有n-365或者n-366,这样会使得代码更为复杂,故没有选择此方法。
不同点:主要是对类关系的处理:
在题目集4的7-2中采用了Day、Month、Year三个类平行且各种相对独立的,他们之间为没有类的关系三个类是嵌套组合的,Year嵌套在Month里组合,
而Month嵌套在Day里组合,他们之间为组合关系同时Day与DateUtil也是组合关系
但是在题目集5的7-4则是采用Day、Month、Year三个类平行且各种相对独立的,他们之间没有关系
虽然在DateUtil是组合关系但是对于Day、Month、Year来说在后者的设计中能够其三者数独立的没
有关系,所以后者更具有优越性,他们的耦合度更低,其复用的可能性更大
分析进而可能改进的可能:
对于在题目集5的7-4来说,为什么我将Day、Month、Year依旧设计成与DateUtil类是组合关系,
因为DateUtil本来就是对时间进行处理的控制类,虽然用聚合关系可以降低他的耦合性,但完全没必要,
而时间的三个实体类都已经是独立的的类,已经是可以单独复用的类。
题目集4 7-3图形继承
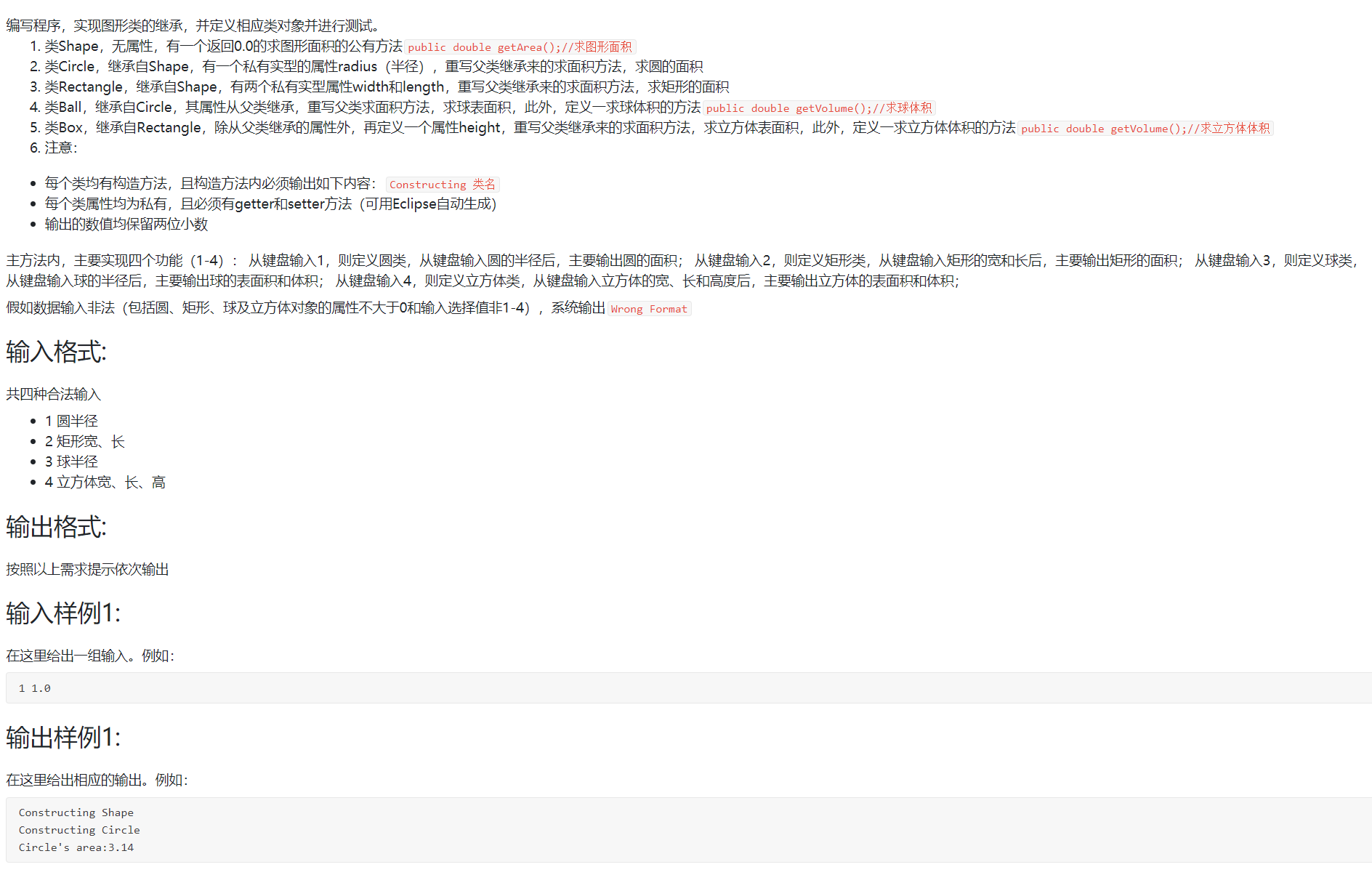
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String [] agrs) {
Agent agent = new Agent();//一个控制类对象
agent.setOption();
}
}
abstract class Shape {//图形的抽象类
public abstract double getArea();//计算面积的抽象函数
}
class Circle extends Shape {//继承类抽象类Shape
protected double radlius = 0;
public Circle() {
super();
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Circle(double radlius) {
this.radlius = radlius;
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
}
public double getRadlius() {
return radlius;
}
public void setRadlius(double radlius) {
this.radlius = radlius;
}
public double getArea() {//实例化抽象函数
return (double)(Math.pow(radlius, 2)*Math.PI);
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {//继承抽象类Shape
protected double width = 0;
protected double length = 0;
public Rectangle() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
public Rectangle(double width, double length) {
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getArea() {//实例化函数
return (double)(width*length);
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{//继承抽象类Shape
public Ball() {
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Ball(double radlius) {
this.radlius = radlius;
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
}
public double getRadlius() {
return radlius;
}
public void setRadlius(double radlius) {
this.radlius = radlius ;
}
public double getArea() {//实例化函数,计算面积
return (double)(4*Math.PI*Math.pow(radlius, 2));
}
public double getVolume() {//子类里添加函数,计算体积
return (double)(4/3.0*Math.PI*Math.pow(radlius, 3));
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle {//继承抽象类Shape
private double height =0.0;
public Box() {
super();
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Box(double width, double length,double height) {
super(width, length);
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public double getArea() {//实例化抽象函数
return (width*length*2+width*height*2+height*length*2);
}
public double getVolume() {
return width*length*height;
}
}
class Agent{//控制类,进行组织各类
public Agent () {
}
public void setOption() {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = input.nextInt();
double []num = new double [3];
switch(option) {
case 1://建立一个圆
num[0] = input.nextDouble();
this.chechValid(num, 1);
Circle obj1 = new Circle(num[0]) ;
System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f\n",obj1.getArea());
break;
case 2://建立一个矩形
num[0 ] = input.nextDouble();
num[1] = input.nextDouble();
this.chechValid(num, 2);
Rectangle obj2 = new Rectangle(num[0],num[1]);
System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f\n",obj2.getArea());
break;
case 3://建立一个球体
num[0] = input.nextDouble();
this.chechValid(num, 1);
Ball obj3 = new Ball(num[0]);
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",obj3.getArea());
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f\n",obj3.getVolume());
break;
case 4://建立一个长方体
num[0] = input.nextDouble();
num[1] = input.nextDouble();
num[2] = input.nextDouble();
this.chechValid(num, 3);
Box obj4 = new Box(num[0],num[1],num[2]);
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",obj4.getArea());
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f\n",obj4.getVolume());
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
break;
}
}
public void chechValid(double num[],int n) {//检验输入数据合法性
for(int i = 0; i<n ;i++) {
if(num[i]<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
对类的设计:
首先设计了一个抽象类Shape里面有一个抽象函数getArea()用来计算图形面积
但是并没有在抽象类里设计属性和计算体积大的方法,因为这样不符合继承的原则
Circle、Rectangle、Ball、Box三个类是独立的,与Agent控制类是
聚合关系,通过Agent控制类进行组织其他四个实体类,Ball、Box两个类中
添加了GetVolume函数,进行对体积的计算。
类图如下:
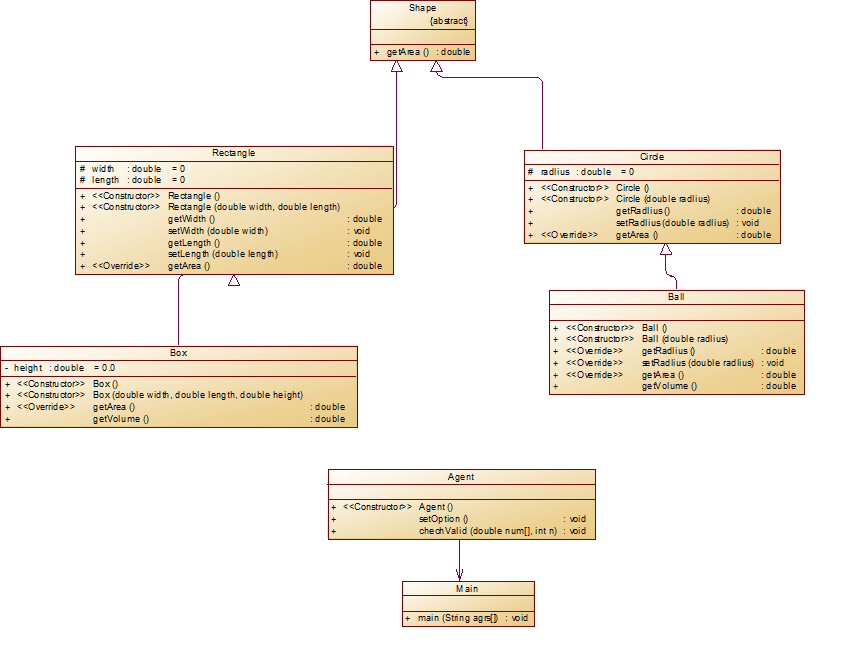
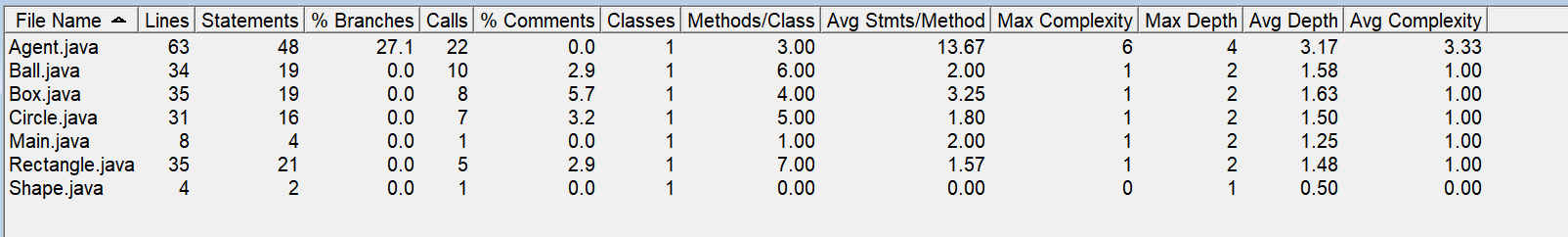
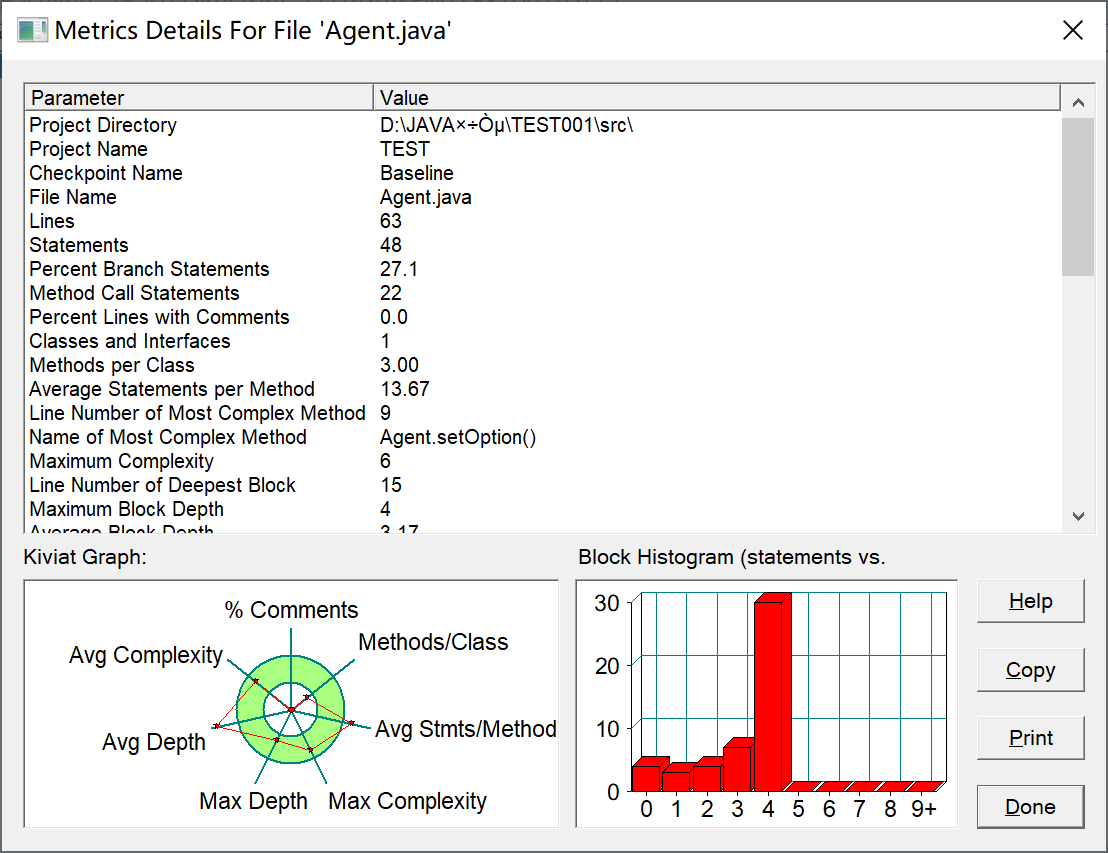
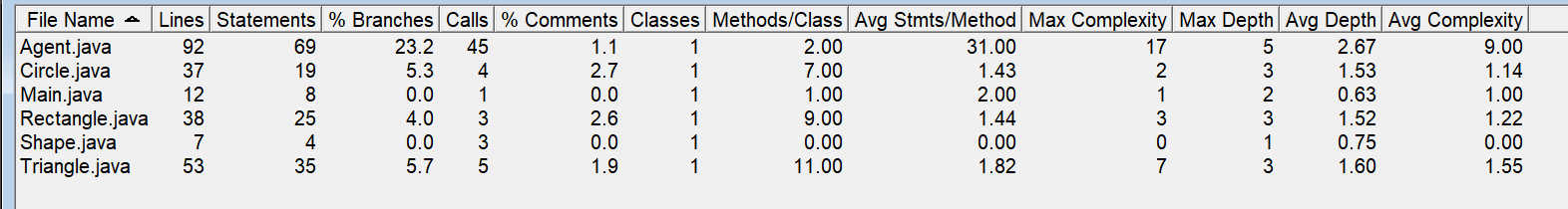
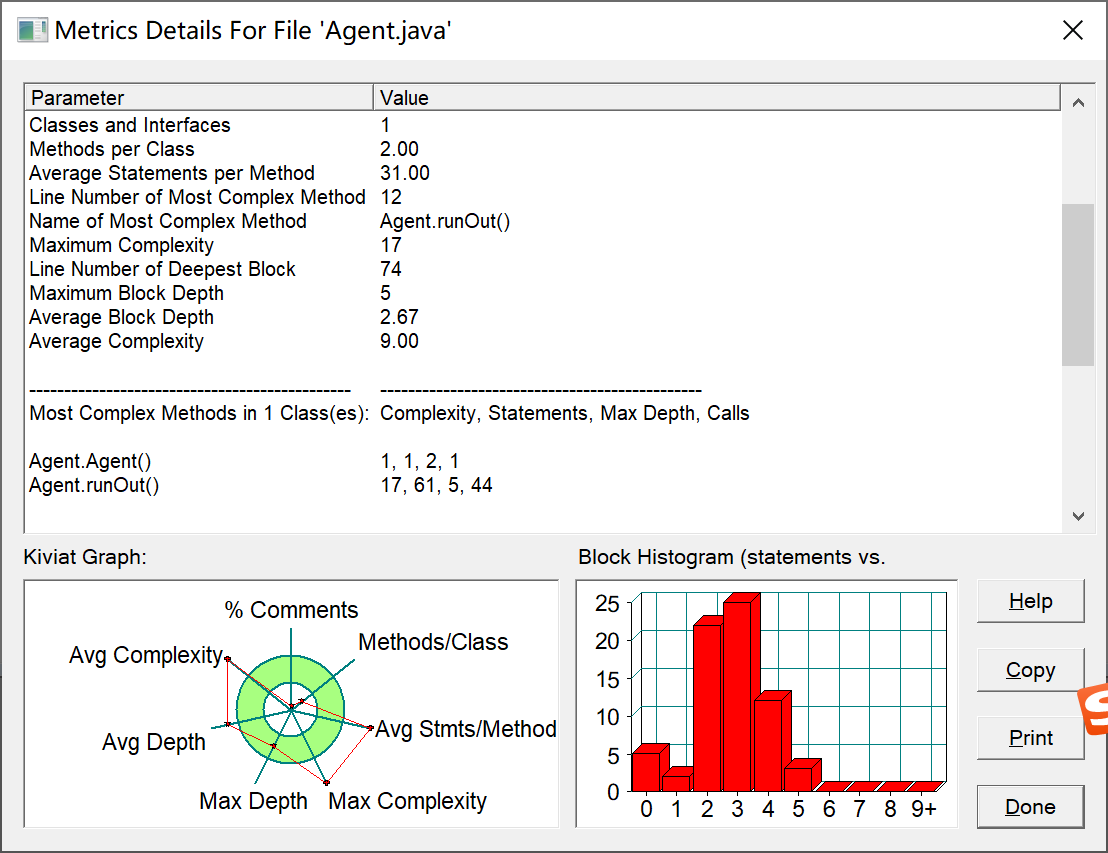
复杂度如图
题目集6 7-5 图形继承与多态
代码如下:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
Agent agent = new Agent();
agent.runOut();
}
}
public abstract class Shape {//抽象类
public abstract double getArea();//抽象函数,计算面积
public abstract boolean validate();//抽象函数,校验数据合法性
public abstract String toString();//抽象函数,格式化数据
}
public class Circle extends Shape {//继承Shape
private double radius = 0;
public Circle() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Circle(double radius) {
super();
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getArea() {//计算面积
return Math.PI*Math.pow(radius, 2);
}
public boolean validate() {//校验数据合法
if(this.radius <= 0) {//大于合法
return false;
}
return true;
}
public String toString() {//格式化,保留两位小数
return String.format("%.2f", this.getArea());
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape{//继承Shape
private double width = 0;
private double length = 0;
public Rectangle() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Rectangle(double width, double length) {
super();
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getArea() {//实例化抽象函数,计算面积
return this.width*this.length;
}
public boolean validate() {//实例化抽象函数,校验数据合法性
if(this.width<=0||this.length<=0) {//所有数据大于0合法
return false;
}
return true;
}
public String toString() {//实例化抽象函数,格式化数据,保留两位小数
return String.format("%.2f", this.getArea());
}
}
public class Triangle extends Shape{//继承Shape
double sides1 = 0;
double sides2 = 0;
double sides3 = 0;
public Triangle() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Triangle(double sides1, double sides2, double sides3) {
super();
this.sides1 = sides1;
this.sides2 = sides2;
this.sides3 = sides3;
}
public double getSides1() {
return sides1;
}
public void setSides1(double sides1) {
this.sides1 = sides1;
}
public double getSides2() {
return sides2;
}
public void setSides2(double sides2) {
this.sides2 = sides2;
}
public double getSides3() {
return sides3;
}
public void setSides3(double sides3) {
this.sides3 = sides3;
}
public double getArea() {//实例化抽象函数,计算面积
double s = (this.sides1+this.sides2+this.sides3)/2;
double area2C = s*(s-this.sides1)*(s-this.sides2)*(s-this.sides3);
return Math.sqrt(area2C);
}
public boolean validate() {//实例化抽象函数,校验数据合法性
if(this.sides1 <= 0||this.sides2 <= 0 || this.sides3 <= 0) {
return false;
}
if(this.sides1 + this.sides2 <= this.sides3 ||this.sides3 + this.sides2 <= this.sides1 || this.sides1 + this.sides3 <= this.sides2) {//利用三角形性质,两边之和大于第三边进行校验
return false;
}
return true;
}
public String toString() {//格式化数据
return String.format("%.2f", this.getArea());
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Agent {
public Agent() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public void runOut() {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
List<Shape> list = new ArrayList<Shape>();//利用列表存储
int count = 0;
int []num = new int [3];
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++) {//输入各图形个数
num[i] = input.nextInt();
count += num[i];
if(num[i] < 0) {//合法性校验
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<num[0];i++) {
double radius = input.nextDouble();
Circle tmp = new Circle(radius);
if(tmp.validate()) {
list.add(tmp);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<num[1];i++) {
double width = input.nextDouble();
double length =input.nextDouble();
Rectangle tmp = new Rectangle(width,length);
if(tmp.validate()) {
list.add(tmp);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<num[2];i++) {
double sides1 = input.nextDouble();
double sides2 =input.nextDouble();
double sides3 =input.nextDouble();
Triangle tmp = new Triangle(sides1,sides2,sides3);
if(tmp.validate()) {
list.add(tmp);
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
System.out.println("Original area:");
Iterator<Shape> it = list.iterator();
double sum = 0.0;
while(it.hasNext()) {
Shape tmp = it.next();
System.out.print(tmp.toString()+" ");
sum += tmp.getArea();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sum of area:"+String.format("%.2f", sum));
for( int i = 0 ;i<count-1;i++) {
for(int j = 0 ;j<count-i-1;j++) {
if(list.get(j).getArea()>list.get(j+1).getArea()) {
Shape tmp =list.get(j);
list.set(j, list.get(j+1));
list.set(j+1,tmp );
}
}
}
sum = 0;
Iterator<Shape> its = list.iterator();
System.out.println("Sorted area:");
while(its.hasNext()) {
Shape tmp = its.next();
System.out.print(tmp.toString()+" ");
sum += tmp.getArea();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sum of area:"+String.format("%.2f", sum));
}
}
思路:
Circle、Triangle、Rectangle三个实体类设计成为Shape类的子类,他们有三个共同函数,在父类将其抽象化
然后在三个子类中根据具体要求各自实例化,在通控制类Agent组织三个子类而在Agent通过泛型和多态使得将三个类产生
对象存在List中,再通过循环就算并输出。
类图:
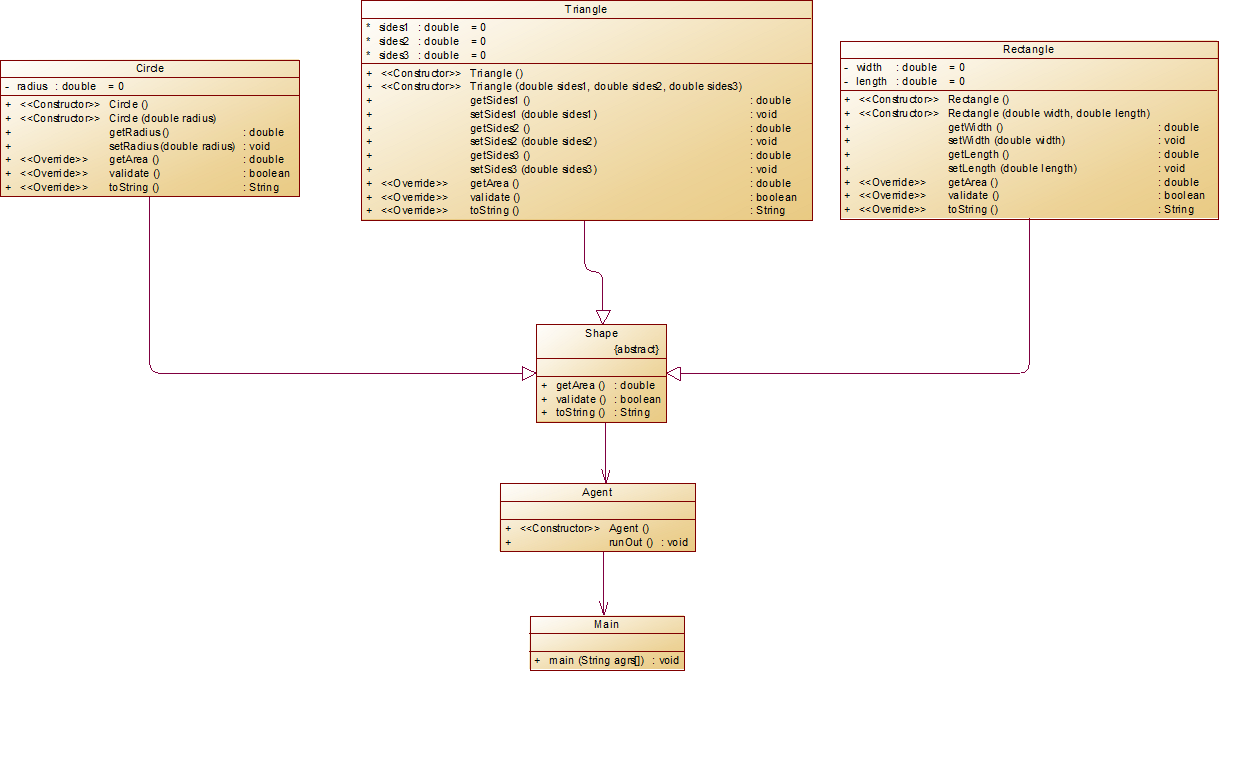
Circle、Triangle、Rectangle三个实体类为Shape类的子类,而三个类和Agent类是聚合关系
题目集5 7-6 实现图形接口及多态性
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double []data = new double [3];
for(int i = 0 ;i<3;i++) {
data[i] = input.nextDouble();
if(data[i]<= 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
Circle circle = new Circle(data[0]);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(data[1],data[2]);
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", circle.getArea()));
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", rectangle.getArea()));
}
}
interface GetArea {//接口
public abstract double getArea();//抽象函数,计算面积
}
class Circle implements GetArea{
private double radlius = 0.0;
public Circle() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Circle(double radlius) {
super();
this.radlius = radlius;
}
public double getRadlius() {
return radlius;
}
public void setRadlius(double radlius) {
this.radlius = radlius;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI*Math.pow(radlius, 2);
}
}
public class Rectangle implements GetArea{//接口
private double width = 0.0;
private double length = 0.0;
public Rectangle() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Rectangle(double width, double length) {
super();
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getArea() {//实例抽象函数,计算面积
return length*width;
}
}
}
思路:
将Rectangle和Circle设计成两个独立类,再通过含有GetArea()抽象函数的接口完成两个类的设计
类图
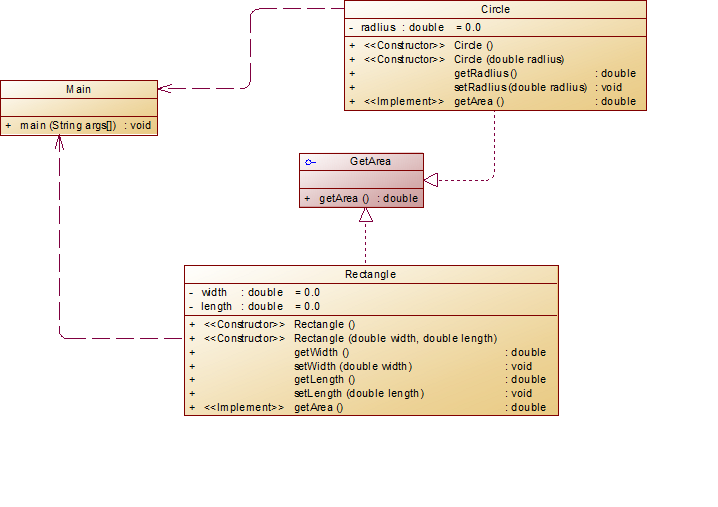
Rectangle和Circle设计成两个独立类,通过接口实现类功能的完整性
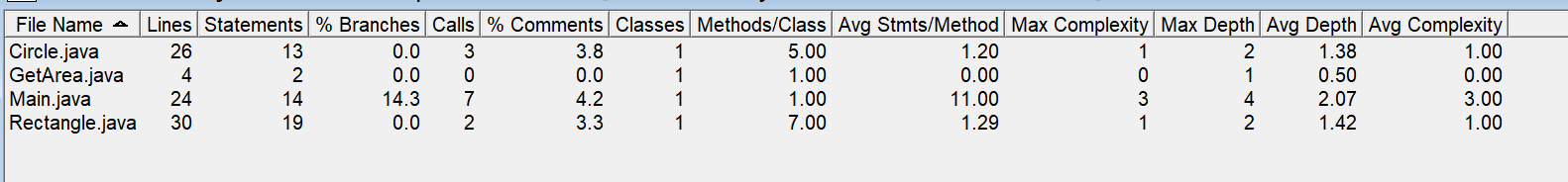
题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计对比:
第一次题目中,是将Shape设计为抽象的父类,而其他为子类,通过子类继承父类的getArea()抽象函数计算面积
但是没有在父类中设计计算体积的抽象函数,因为有部分子类不需要该方法,这里主要的技术是继承和方法对的多态
并且在部分子类中添加了子类独有的计算体积对的方法
第二次题目中,同样的设计了一个Shape的父类里面带有三个抽象类,子类通过继承父类,来校验数据的合法性
和对面积的计算,技术也是继承和方法的多态,但是对多数据的处理,采用了List将其泛型Shape利用类的
多态进行存储。
第三次题目集,利用了接口技术,让三个图形类可以使用接口的抽象函数,进行计算。
改进的可能:
对于第一次题目,其实这样设计父类与子类是违背了类的设计原则
其实对于一些子类有的方法但是父类没有的方法,可以选择采用接
口进行处理。
题目集5 7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数

import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String str;
StringBuilder tmpStr = new StringBuilder();
String[] key = { "abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const",
"continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "false", "final", "finally", "float",
"for", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new",
"null", "package", "private", "protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", "strictfp", "super",
"switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws", "transient", "true", "try", "void", "volatile",
"while"
};//首先在数组里将关键字升序进行排序
int[] count = new int[53];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; true; i++) {
str = input.nextLine();
if (str.compareTo("exit") == 0)
break;
if (str.matches("(.*)//(.*)")) {
String t[] = str.split("//");
tmpStr.append(t[0] + " ");
} else {
tmpStr.append(str + " ");
}
}
String string = tmpStr.toString();
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\"");//匹配注释符里的字符串
Matcher m = p.matcher(string);
while (m.find()) {
string = string.replace(m.group(), " ");//用空格与注释符里字符串进行替换
p = Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\"");
m = p.matcher(string);
}
string = string.replace(".", " ");//将特殊字符改为空格
string = string.replace("(", " ");
string = string.replace(")", " ");
string = string.replace("[", " ");
string = string.replace("]", " ");
string = string.replace(";", " ");
if (string.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
String tempS;
for (int i = 0; i < 53; i++) {
tempS = key[i]+" ";//保证检测出来的关键字就是一个单词,而不是某个字符串单词中的子串
count[i] = stringFind(string, tempS);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 53; i++) {
if (count[i] != 0) {
System.out.println(count[i] + " " + key[i]);
}
}
}
public static int stringFind(String source, String target) {
int number = 0;
int i = 0;
while ((i = source.indexOf(target, i)) != -1) {
number++;
i++;
}
return number;
}
}
思路:
一开始本来是想用hashmap进行存储各关键字,然后通过哈希算法简化查找的量,然后再进行查找
但是发信息关键字数量也不多,而且通过数组先进行排序还可以简化算法,所以没有采用hashmap函数
而是先用数组把关键字排好序再对输入的字符串进行处理,首先先把//注释符后的字符串进行替换成空格
再把各关键字换成空格,再用通过查找字符串进行统计。但是这样的复杂度比较高。
改进的可能:
对于没有满分,没有将全部特殊字符转化为空格,并别没有讲/**/里的字符串进行去除在去除
注释符中的字符串后,对于特殊字符的转化,完全可以采用一个匹配字符串,将非字母和空格
的字符全部转化空格。然后进行匹配。
对正则表达式技术的分析:
首先要分析好并选好要怎么对字符串进行处理,再根据要处理字符串的特点进行分组的设计正则表达式
踩坑心得
两个迭代器引用要不一样,不然后面的一个迭代器初始值已近到了尾部,或者重置迭代器
to String的用法:
toString(): 返回表示 Integer 值的 String 对象。
toString(int i): 返回表示指定 int 的 String 对象。
public class Test{
public static void main(String args[]){
Integer x = 5;
System.out.println(x.toString());
System.out.println(Integer.toString(12));
}
}
public String getS() {
Integer x = this.width;
Integer y = this.length;
return "Rectangle [width="+x.toString()+", length="+y.toString()+"]";
}
存储不同的类,但是需要R和C都是Shape的子类,是多态的运用
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = Integer.parseInt(input.nextLine());
int radlius = 0;
int width = 0,length = 0;
--------> List<Shape> list = new ArrayList<Shape>();
String tmpStr ;
for(int i = 0 ;i < n ;i++) {
tmpStr = input.nextLine();
if(tmpStr.compareTo("rect") == 0) {
width =input.nextInt();
length = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
---------------->list.add (new Rectangle(width,length));
}else if(tmpStr.compareTo("cir") == 0) {
radlius = input.nextInt();
input.nextLine();
----------------------> list.add(new Circle(radlius)) ;
}
}
或者运用多态的特性。如果定义数组类型的时候定义为父类,而存进数组为父类的子类的话可以
public class test2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
father []a=new father[2];
a[0]=new son();
a[1]=new son2();
}
}
class father{
int i=0;
}
class son extends father{
int x=0;
}
class son2 extends father{
int y=0;
}
在一个类里设置 private类型的数组,但是另建立一个类,类可以直接调用数组?
好像是在相同的一个类里再次建立,所谓的private型属性仍然是visiable的
但是在别的不同的类就是invisiable的
同时对于protected是在包内的类可见,一开始误认为private修饰的属性不能被继承
实际上是可以继承的,只有'final'修饰的属性不能被继承。
总结:
三次作业中:
1.对于正则表达式有了更好的了解,但依旧是薄弱点
2.这三次对类的设计比较完善,对于对类的设计也有更好的理解
学习到了继承,多态,接口,封装等技术的使用
3.程序算法和设计较为薄弱,导致写出来的代码复杂度过高
课堂上:
1.单一职责原则:(首先保障这个原则)
一个类(或者大到模块,小到方法)承担的职责越多,它被复用的可能性越小,
而且如果一个类承担职责过多,就相当于将这些职责耦合在一起,当其中一个
职责变化时,可能会影响其他职责的运作。(保障类之间没有直接关系,迪米
特法则)也就是说,设计类的时候,都要将他们当作独立的个体
2.开闭原则
一个软件实体应当对扩展开放,对修改关闭。也就是说在设计一个模块的时候,
应当使这个模块可以在不修改的前提下被扩展,即实现在不修改源代码的情况
下改变这个模块的行为。
原则分析:
1)抽象化是开闭原则的关键
抽象
第一层:对象到类
第二层:类到抽象类
行为抽象->接口
2)
需求可能有变化就进行封装
开闭原则还还可以通过一个更具体的“对可变性封装原则”来描述,
对可变性封装原则要求找到系统的可变因素并将其封装起来。
3.里氏代换原则LSP(什么时候可以继承)
所有引用基类(父类)的地方必须能透明地使用其子类独的对象
原则分析
让鸟类飞 让麻雀飞 (则麻雀是鸟的子类)
让企鹅飞但是企鹅不能飞(所以企鹅不能是鸟的子类)即使与现实相反
4.依赖倒转原则DIP
要针对接口编程,不要针对实现编程(接口就是想象成抽象的层而不是具体层)---->针对抽象编程而不是具体
《Aglie Software Development Principles Patterns and Practice》《Clean Code》
5.接口隔离原则ISP
定义:(这里的接口可以是接口也可以是抽象类)
客户端不应该依靠那些他不需要的接口
一旦一个接口太大,则需要将它分个成一些更细小的接口,使用该接口的客户端仅需要知道与之相关的
6.合成复用原则
定义:
尽量使用对象组合,而不是继承来达到复用达到目的(继承的耦合性最强),如果需要扩展那就要继承。
7.迪米特法则(耦合性越低越低):dont talk to strangers(类与类之间都是陌生人,不要和陌生
人说话只和直接朋友发送消息。在设计类之初的时候耦合性越低越好)
example:教师——学生(在最初之间教师和学生都是独立的,不会因某个对象消失而不存在,具有独立性)
但是 在教师和学生发生了交集(让学生做作业)(发送了消息)这就出现了耦合性
一旦类之间没有关系(没继承,没组合/聚合),独立设计
比如
图书馆-借书
设计各类读者(而不是学生,因为读者范围更大也可能是老师)
读者和学生或者老师什么关系----->继承和聚合都可
但是用哪个呢?如果要扩展则用继承,如果不就聚合
书籍和读者什么关系?------>没关系(他们之间无继承/聚合/组合关系)
那他们怎么发生关?---------->找中介啊(原则7)
8.什么做出接口(把共有的行为做成接口)
经过了老师对八大原则的教学后,对于面向对象设计,以及对类的设计有了
更深刻的了解,同时也明白了这种思维的优越性。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号