MD5 Algorithm
MD5 is a cryptographic hash function algorithm that takes the message as input of any length and changes it into a fixed-length message of 16 bytes. MD5 algorithm stands for the message-digest algorithm. MD5 was developed as an improvement of MD4, with advanced security purposes. The output of MD5 (Digest size) is always 128 bits. MD5 was developed in 1991 by Ronald Rivest.
Use Of MD5 Algorithm:
- It is used for file authentication.
- In a web application, it is used for security purposes. e.g. Secure password of users etc.
- Using this algorithm, We can store our password in 128 bits format.

MD5 Algorithm
Working of the MD5 Algorithm:
MD5 algorithm follows the following steps
1. Append Padding Bits: In the first step, we add padding bits in the original message in such a way that the total length of the message is 64 bits less than the exact multiple of 512.
Suppose we are given a message of 1000 bits. Now we have to add padding bits to the original message. Here we will add 472 padding bits to the original message. After adding the padding bits the size of the original message/output of the first step will be 1472 i.e. 64 bits less than an exact multiple of 512 (i.e. 512*3 = 1536).
Length(original message + padding bits) = 512 * i – 64 where i = 1,2,3 . . .
2. Append Length Bits: In this step, we add the length bit in the output of the first step in such a way that the total number of the bits is the perfect multiple of 512. Simply, here we add the 64-bit as a length bit in the output of the first step.
i.e. output of first step = 512 * n – 64
length bits = 64.
After adding both we will get 512 * n i.e. the exact multiple of 512.
3. Initialize MD buffer: Here, we use the 4 buffers i.e. J, K, L, and M. The size of each buffer is 32 bits.
- J = 0x67425301
- K = 0xEDFCBA45
- L = 0x98CBADFE
- M = 0x13DCE476
4. Process Each 512-bit Block: This is the most important step of the MD5 algorithm. Here, a total of 64 operations are performed in 4 rounds. In the 1st round, 16 operations will be performed, 2nd round 16 operations will be performed, 3rd round 16 operations will be performed, and in the 4th round, 16 operations will be performed. We apply a different function on each round i.e. for the 1st round we apply the F function, for the 2nd G function, 3rd for the H function, and 4th for the I function.
We perform OR, AND, XOR, and NOT (basically these are logic gates) for calculating functions. We use 3 buffers for each function i.e. K, L, M.
- F(K,L,M) = (K AND L) OR (NOT K AND M)
- G(K,L,M) = (K AND L) OR (L AND NOT M)
- H(K,L,M) = K XOR L XOR M
- I(K,L,M) = L XOR (K OR NOT M)
After applying the function now we perform an operation on each block. For performing operations we need
- add modulo 232
- M[i] – 32 bit message.
- K[i] – 32-bit constant.
- <<<n – Left shift by n bits.
Now take input as initialize MD buffer i.e. J, K, L, M. Output of K will be fed in L, L will be fed into M, and M will be fed into J. After doing this now we perform some operations to find the output for J.
- In the first step, Outputs of K, L, and M are taken and then the function F is applied to them. We will add modulo 232 bits for the output of this with J.
- In the second step, we add the M[i] bit message with the output of the first step.
- Then add 32 bits constant i.e. K[i] to the output of the second step.
- At last, we do left shift operation by n (can be any value of n) and addition modulo by 232.
After all steps, the result of J will be fed into K. Now same steps will be used for all functions G, H, and I. After performing all 64 operations we will get our message digest.
Output:
After all, rounds have been performed, the buffer J, K, L, and M contains the MD5 output starting with the lower bit J and ending with Higher bits M.
Code:
# importing the required libraries
import hashlib
# making a message
inputstring = "This is a message sent by a computer user."
# encoding the message using the library function
output = hashlib.md5(inputstring.encode())
# printing the hash function
print("Hash of the input string:")
print(output.hexdigest())
Hash of the input string: 922547e866c89b8f677312df0ccec8ee
Application Of MD5 Algorithm:
- We use message digest to verify the integrity of files/ authenticates files.
- MD5 was used for data security and encryption.
- It is used to Digest the message of any size and also used for Password verification.
- For Game Boards and Graphics.
Advantages of MD5 Algorithm:
- MD5 is faster and simple to understand.
- MD5 algorithm generates a strong password in 16 bytes format. All developers like web developers etc use the MD5 algorithm to secure the password of users.
- To integrate the MD5 algorithm, relatively low memory is necessary.
- It is very easy and faster to generate a digest message of the original message.
Disadvantages of MD5 Algorithm:
- MD5 generates the same hash function for different inputs.
- MD5 provides poor security over SHA1.
- MD5 has been considered an insecure algorithm. So now we are using SHA256 instead of MD5
- MD5 is neither a symmetric nor asymmetric algorithm.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MD5消息摘要算法,属Hash算法一类。MD5算法对输入任意长度的消息进行运行,产生一个128位的消息摘要。
以下所描述的消息长度、填充数据都以位(Bit)为单位,字节序为小端字节。
算法原理
1、数据填充
对消息进行数据填充,使消息的长度对512取模得448,设消息长度为X,即满足X mod 512=448。根据此公式得出需要填充的数据长度。
填充方法:在消息后面进行填充,填充第一位为1,其余为0。
2、添加消息长度
在第一步结果之后再填充上原消息的长度,可用来进行的存储长度为64位。如果消息长度大于264,则只使用其低64位的值,即(消息长度 对 264取模)。
在此步骤进行完毕后,最终消息长度就是512的整数倍。
3、数据处理
准备需要用到的数据:
- 4个常数: A = 0x67452301, B = 0x0EFCDAB89, C = 0x98BADCFE, D = 0x10325476;
- 4个函数:F(X,Y,Z)=(X & Y) | ((~X) & Z); G(X,Y,Z)=(X & Z) | (Y & (~Z)); H(X,Y,Z)=X ^ Y ^ Z; I(X,Y,Z)=Y ^ (X | (~Z));
把消息分以512位为一分组进行处理,每一个分组进行4轮变换,以上面所说4个常数为起始变量进行计算,重新输出4个变量,以这4个变量再进行下一分组的运算,如果已经是最后一个分组,则这4个变量为最后的结果,即MD5值。
具体计算的实现较为复杂,建议查阅相关书籍,下面给出在C++上的实现代码。
代码实现
#MD5.h
1 #ifndef MD5H 2 #define MD5H 3 #include <math.h> 4 #include <Windows.h> 5 6 void ROL(unsigned int &s, unsigned short cx); //32位数循环左移实现函数 7 void ltob(unsigned int &i); //B\L互转,接受UINT类型 8 unsigned int* MD5(const char* mStr); //接口函数,并执行数据填充,计算MD5时调用此函数 9 10 #endif
#MD5.cpp
1 #include "MD5.h"
2
3 /*4组计算函数*/
4 inline unsigned int F(unsigned int X, unsigned int Y, unsigned int Z)
5 {
6 return (X & Y) | ((~X) & Z);
7 }
8 inline unsigned int G(unsigned int X, unsigned int Y, unsigned int Z)
9 {
10 return (X & Z) | (Y & (~Z));
11 }
12 inline unsigned int H(unsigned int X, unsigned int Y, unsigned int Z)
13 {
14 return X ^ Y ^ Z;
15 }
16 inline unsigned int I(unsigned int X, unsigned int Y, unsigned int Z)
17 {
18 return Y ^ (X | (~Z));
19 }
20 /*4组计算函数结束*/
21
22 /*32位数循环左移实现函数*/
23 void ROL(unsigned int &s, unsigned short cx)
24 {
25 if (cx > 32)cx %= 32;
26 s = (s << cx) | (s >> (32 - cx));
27 return;
28 }
29
30 /*B\L互转,接收UINT类型*/
31 void ltob(unsigned int &i)
32 {
33 unsigned int tmp = i;//保存副本
34 byte *psour = (byte*)&tmp, *pdes = (byte*)&i;
35 pdes += 3;//调整指针,准备左右调转
36 for (short i = 3; i >= 0; --i)
37 {
38 CopyMemory(pdes - i, psour + i, 1);
39 }
40 return;
41 }
42
43 /*
44 MD5循环计算函数,label=第几轮循环(1<=label<=4),lGroup数组=4个种子副本,M=数据(16组32位数指针)
45 种子数组排列方式: --A--D--C--B--,即 lGroup[0]=A; lGroup[1]=D; lGroup[2]=C; lGroup[3]=B;
46 */
47 void AccLoop(unsigned short label, unsigned int *lGroup, void *M)
48 {
49 unsigned int *i1, *i2, *i3, *i4, TAcc, tmpi = 0; //定义:4个指针; T表累加器; 局部变量
50 typedef unsigned int(*clac)(unsigned int X, unsigned int Y, unsigned int Z); //定义函数类型
51 const unsigned int rolarray[4][4] = {
52 { 7, 12, 17, 22 },
53 { 5, 9, 14, 20 },
54 { 4, 11, 16, 23 },
55 { 6, 10, 15, 21 }
56 };//循环左移-位数表
57 const unsigned short mN[4][16] = {
58 { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 },
59 { 1, 6, 11, 0, 5, 10, 15, 4, 9, 14, 3, 8, 13, 2, 7, 12 },
60 { 5, 8, 11, 14, 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 2 },
61 { 0, 7, 14, 5, 12, 3, 10, 1, 8, 15, 6, 13, 4, 11, 2, 9 }
62 };//数据坐标表
63 const unsigned int *pM = static_cast<unsigned int*>(M);//转换类型为32位的Uint
64 TAcc = ((label - 1) * 16) + 1; //根据第几轮循环初始化T表累加器
65 clac clacArr[4] = { F, G, H, I }; //定义并初始化计算函数指针数组
66
67 /*一轮循环开始(16组->16次)*/
68 for (short i = 0; i < 16; ++i)
69 {
70 /*进行指针自变换*/
71 i1 = lGroup + ((0 + i) % 4);
72 i2 = lGroup + ((3 + i) % 4);
73 i3 = lGroup + ((2 + i) % 4);
74 i4 = lGroup + ((1 + i) % 4);
75
76 /*第一步计算开始: A+F(B,C,D)+M[i]+T[i+1] 注:第一步中直接计算T表*/
77 tmpi = (*i1 + clacArr[label - 1](*i2, *i3, *i4) + pM[(mN[label - 1][i])] + (unsigned int)(0x100000000UL * abs(sin((double)(TAcc + i)))));
78 ROL(tmpi, rolarray[label - 1][i % 4]);//第二步:循环左移
79 *i1 = *i2 + tmpi;//第三步:相加并赋值到种子
80 }
81 return;
82 }
83
84 /*接口函数,并执行数据填充*/
85 unsigned int* MD5(const char* mStr)
86 {
87 unsigned int mLen = strlen(mStr); //计算字符串长度
88 if (mLen < 0) return 0;
89 unsigned int FillSize = 448 - ((mLen * 8) % 512); //计算需填充的bit数
90 unsigned int FSbyte = FillSize / 8; //以字节表示的填充数
91 unsigned int BuffLen = mLen + 8 + FSbyte; //缓冲区长度或者说填充后的长度
92 unsigned char *md5Buff = new unsigned char[BuffLen]; //分配缓冲区
93 CopyMemory(md5Buff, mStr, mLen); //复制字符串到缓冲区
94
95 /*数据填充开始*/
96 md5Buff[mLen] = 0x80; //第一个bit填充1
97 ZeroMemory(&md5Buff[mLen + 1], FSbyte - 1); //其它bit填充0,另一可用函数为FillMemory
98 unsigned long long lenBit = mLen * 8ULL; //计算字符串长度,准备填充
99 CopyMemory(&md5Buff[mLen + FSbyte], &lenBit, 8); //填充长度
100 /*数据填充结束*/
101
102 /*运算开始*/
103 unsigned int LoopNumber = BuffLen / 64; //以16个字为一分组,计算分组数量
104 unsigned int A = 0x67452301, B = 0x0EFCDAB89, C = 0x98BADCFE, D = 0x10325476;//初始4个种子,小端类型
105 unsigned int *lGroup = new unsigned int[4]{ A, D, C, B}; //种子副本数组,并作为返回值返回
106 for (unsigned int Bcount = 0; Bcount < LoopNumber; ++Bcount) //分组大循环开始
107 {
108 /*进入4次计算的小循环*/
109 for (unsigned short Lcount = 0; Lcount < 4;)
110 {
111 AccLoop(++Lcount, lGroup, &md5Buff[Bcount * 64]);
112 }
113 /*数据相加作为下一轮的种子或者最终输出*/
114 A = (lGroup[0] += A);
115 B = (lGroup[3] += B);
116 C = (lGroup[2] += C);
117 D = (lGroup[1] += D);
118 }
119 /*转换内存中的布局后才能正常显示*/
120 ltob(lGroup[0]);
121 ltob(lGroup[1]);
122 ltob(lGroup[2]);
123 ltob(lGroup[3]);
124 delete[] md5Buff; //清除内存并返回
125 return lGroup;
126 }
再给出调用实例(以win32控制台应用程序为例):
#main.cpp
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 #include <stdlib.h>
4 #include "MD5.h"
5
6 int main(int argc, char **argv)
7 {
8 char tmpstr[256], buf[4][10];
9 std::cout << "请输入要加密的字符串:";
10 std::cin >> tmpstr;
11 unsigned int* tmpGroup = MD5(tmpstr);
12 sprintf_s(buf[0], "%8X", tmpGroup[0]);
13 sprintf_s(buf[1], "%8X", tmpGroup[3]);
14 sprintf_s(buf[2], "%8X", tmpGroup[2]);
15 sprintf_s(buf[3], "%8X", tmpGroup[1]);
16 std::cout <<"MD5:"<< buf[0] << buf[1] << buf[2] << buf[3] << std::endl;
17
18 delete[] tmpGroup;
19 return 0; //在此下断点才能看到输出的值
20 }
注:以上代码在VS2013上编译通过
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
前面一篇,带大家对加密算法进行了鸟瞰,本篇主要谈md5算法的实现。
MD5:Message-Digest Algorithm 5(信息摘要5),确保信息的完整性。其算法是1992年公开的,那时我才几岁,鉴于大家对md5都很熟悉,且程序中经常应用,我就不再介绍了。我简单的介绍下设计者。其人是罗纳德·李维斯特,美国密码学家,后来发明了非对称秘钥RSA算法,因这个算法的在信息安全中的突破与重要性而获得了2002年的图灵奖。
好了,接下来一起看算法步骤以及源代码:
1、填充
在MD5算法中,首先需要对信息进行填充,使其位长对512求余的结果等于448,并且填充必须进行,使其位长对512求余的结果等于448。因此,信息的位长(Bits Length)将被扩展至N*512+448,N为一个非负整数,N可以是零。
理解:位长,就是位数。比如一个“wbq”,字符串是三个字节存储,一个字节8bit,所以位长就是24。
用数学语言可能更简洁:设M为位长,当且仅当 M%512==448时,才可以处理。换另一种表示方式,M=N*512+448 ,N>=0
填充的方法如下:
1) 在信息的后面填充一个1和无数个0,直到满足上面的条件时才停止用0对信息的填充。
2) 在这个结果后面附加一个以64位二进制表示的填充前信息长度(单位为Bit),如果二进制表示的填充前信息长度超过64位,则取低64位。
经过这两步的处理,M=N*512+448+64=(N+1)*512,即长度恰好是512的整数倍。这样做的原因是为满足后面处理中对信息长度的要求。
经过两步处理后,信息变成了这样,如下图所示:

64位,8个字节,用来表示原始信息的位长。
1 private static UInt32[] MD5_Append(byte[] input)
2 {
3 int zeros = 0;
4 int ones = 1;
5 int size = 0;
6 int n = input.Length;
7 int m = n % 64;
8 if (m < 56)
9 {
10 zeros = 55 - m;
11 size = n - m + 64;
12 }
13 else if (m == 56)
14 {
15 zeros = 0;
16 ones = 0;
17 size = n + 8;
18 }
19 else
20 {
21 zeros = 63 - m + 56;
22 size = n + 64 - m + 64;
23 }
24
25 ArrayList bs = new ArrayList(input);
26 if (ones == 1)
27 {
28 bs.Add((byte)0x80); // 0x80 = $10000000
29 }
30 for (int i = 0; i < zeros; i++)
31 {
32 bs.Add((byte)0);
33 }
34
35 UInt64 N = (UInt64)n * 8;
36 byte h1 = (byte)(N & 0xFF);
37 byte h2 = (byte)((N >> 8) & 0xFF);
38
39 byte h3 = (byte)((N >> 16) & 0xFF);
40 byte h4 = (byte)((N >> 24) & 0xFF);
41 byte h5 = (byte)((N >> 32) & 0xFF);
42 byte h6 = (byte)((N >> 40) & 0xFF);
43 byte h7 = (byte)((N >> 48) & 0xFF);
44 byte h8 = (byte)(N >> 56);
45 bs.Add(h1);
46 bs.Add(h2);
47 bs.Add(h3);
48 bs.Add(h4);
49 bs.Add(h5);
50 bs.Add(h6);
51 bs.Add(h7);
52 bs.Add(h8);
53 byte[] ts = (byte[])bs.ToArray(typeof(byte));
54
55 /* Decodes input (byte[]) into output (UInt32[]). Assumes len is
56 * a multiple of 4.
57 */
58 UInt32[] output = new UInt32[size / 4];
59 for (Int64 i = 0, j = 0; i < size; j++, i += 4)
60 {
61 output[j] = (UInt32)(ts[i] | ts[i + 1] << 8 | ts[i + 2] << 16 | ts[i + 3] << 24);
62 }
63 return output;
64 }
说明,补多少0,如何补?第7行,求余。第10行,为什么是55-m,而不是56-m?此时m<56,56-m表示,还需要补多少。因为需要补1个1,所以补0,就是56-m-1=55-m。那么变更后的长度size如何计算?应该是新长度=原始长度+补1的长度+补0的长度+最后64位的长度,第11行 size = n - m + 64,推导如下:
size=n+1+55-m+8=n-m+64
注意:这里的计算都是字节数的计算
其余两个分支,可以以此类推。从35-44行,把原始信息的位长转为字节,追加到数组后面。58行以后,是把信息划分了4组。分组是UInt32,无符号32位,即4个字节。61行的操作,就是把四个字节转为一个UInt32。
2、初始化变量
private static void MD5_Init()
{
A = 0x67452301; //in memory, this is 0x01234567
B = 0xefcdab89; //in memory, this is 0x89abcdef
C = 0x98badcfe; //in memory, this is 0xfedcba98
D = 0x10325476; //in memory, this is 0x76543210
}
注意:这里用的是小端模式,什么是大端和小端模式?
举一个例子,比如数字0x12 34 56 78在内存中的表示形式。
1)大端模式:Big-Endian就是高位字节排放在内存的低地址端,低位字节排放在内存的高地址端。(其实大端模式比较直观)
低地址 --------------------> 高地址
0x12 | 0x34 | 0x56 | 0x78
2)小端模式:Little-Endian就是低位字节排放在内存的低地址端,高位字节排放在内存的高地址端。
低地址 --------------------> 高地址
0x78 | 0x56 | 0x34 | 0x12
3. 处理分组数据
private static UInt32[] MD5_Trasform(UInt32[] x)
{
UInt32 a, b, c, d;
for (int k = 0; k < x.Length; k += 16)
{
a = A;
b = B;
c = C;
d = D;
/* Round 1 */
FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 0], S11, 0xd76aa478); /* 1 */
FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 1], S12, 0xe8c7b756); /* 2 */
FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 2], S13, 0x242070db); /* 3 */
FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 3], S14, 0xc1bdceee); /* 4 */
FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 4], S11, 0xf57c0faf); /* 5 */
FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 5], S12, 0x4787c62a); /* 6 */
FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 6], S13, 0xa8304613); /* 7 */
FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 7], S14, 0xfd469501); /* 8 */
FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 8], S11, 0x698098d8); /* 9 */
FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 9], S12, 0x8b44f7af); /* 10 */
FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 10], S13, 0xffff5bb1); /* 11 */
FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 11], S14, 0x895cd7be); /* 12 */
FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 12], S11, 0x6b901122); /* 13 */
FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 13], S12, 0xfd987193); /* 14 */
FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 14], S13, 0xa679438e); /* 15 */
FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 15], S14, 0x49b40821); /* 16 */
/* Round 2 */
GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 1], S21, 0xf61e2562); /* 17 */
GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 6], S22, 0xc040b340); /* 18 */
GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 11], S23, 0x265e5a51); /* 19 */
GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aa); /* 20 */
GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 5], S21, 0xd62f105d); /* 21 */
GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 10], S22, 0x2441453); /* 22 */
GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 15], S23, 0xd8a1e681); /* 23 */
GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8); /* 24 */
GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 9], S21, 0x21e1cde6); /* 25 */
GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 14], S22, 0xc33707d6); /* 26 */
GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 3], S23, 0xf4d50d87); /* 27 */
GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 8], S24, 0x455a14ed); /* 28 */
GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 13], S21, 0xa9e3e905); /* 29 */
GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8); /* 30 */
GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 7], S23, 0x676f02d9); /* 31 */
GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8a); /* 32 */
/* Round 3 */
HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 5], S31, 0xfffa3942); /* 33 */
HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 8], S32, 0x8771f681); /* 34 */
HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 11], S33, 0x6d9d6122); /* 35 */
HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 14], S34, 0xfde5380c); /* 36 */
HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 1], S31, 0xa4beea44); /* 37 */
HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9); /* 38 */
HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60); /* 39 */
HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 10], S34, 0xbebfbc70); /* 40 */
HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 13], S31, 0x289b7ec6); /* 41 */
HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 0], S32, 0xeaa127fa); /* 42 */
HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 3], S33, 0xd4ef3085); /* 43 */
HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 6], S34, 0x4881d05); /* 44 */
HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 9], S31, 0xd9d4d039); /* 45 */
HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 12], S32, 0xe6db99e5); /* 46 */
HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8); /* 47 */
HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 2], S34, 0xc4ac5665); /* 48 */
/* Round 4 */
II(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 0], S41, 0xf4292244); /* 49 */
II(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 7], S42, 0x432aff97); /* 50 */
II(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 14], S43, 0xab9423a7); /* 51 */
II(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 5], S44, 0xfc93a039); /* 52 */
II(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 12], S41, 0x655b59c3); /* 53 */
II(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92); /* 54 */
II(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 10], S43, 0xffeff47d); /* 55 */
II(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 1], S44, 0x85845dd1); /* 56 */
II(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 8], S41, 0x6fa87e4f); /* 57 */
II(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0); /* 58 */
II(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 6], S43, 0xa3014314); /* 59 */
II(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 13], S44, 0x4e0811a1); /* 60 */
II(ref a, b, c, d, x[k + 4], S41, 0xf7537e82); /* 61 */
II(ref d, a, b, c, x[k + 11], S42, 0xbd3af235); /* 62 */
II(ref c, d, a, b, x[k + 2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bb); /* 63 */
II(ref b, c, d, a, x[k + 9], S44, 0xeb86d391); /* 64 */
A += a;
B += b;
C += c;
D += d;
}
return new UInt32[] { A, B, C, D };
}
每一个分组经过64轮处理,FF、GG、HH、II为处理函数。从上面程序,可以看出,每16个数字为一组。以上是算法的核心处理方法,下面是程序主方法:
public static byte[] MD5Array(byte[] input)
{
MD5_Init();
UInt32[] block = MD5_Append(input);
UInt32[] bits = MD5_Trasform(block);
/* Encodes bits (UInt32[]) into output (byte[]). Assumes len is
* a multiple of 4.
*/
byte[] output = new byte[bits.Length * 4];
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < bits.Length; i++, j += 4)
{
output[j] = (byte)(bits[i] & 0xff);
output[j + 1] = (byte)((bits[i] >> 8) & 0xff);
output[j + 2] = (byte)((bits[i] >> 16) & 0xff);
output[j + 3] = (byte)((bits[i] >> 24) & 0xff);
}
return output;
}
把output连接起来,就是md5值,output传入到下面方法:
public static string ArrayToHexString(byte[] array, bool uppercase)
{
string hexString = "";
string format = "x2";
if (uppercase)
{
format = "X2";
}
foreach (byte b in array)
{
hexString += b.ToString(format);
}
return hexString;
}
附录:常量和基础函数:
//static state variables
private static UInt32 A;
private static UInt32 B;
private static UInt32 C;
private static UInt32 D;
#region 常量
//number of bits to rotate in tranforming
private const int S11 = 7;
private const int S12 = 12;
private const int S13 = 17;
private const int S14 = 22;
private const int S21 = 5;
private const int S22 = 9;
private const int S23 = 14;
private const int S24 = 20;
private const int S31 = 4;
private const int S32 = 11;
private const int S33 = 16;
private const int S34 = 23;
private const int S41 = 6;
private const int S42 = 10;
private const int S43 = 15;
private const int S44 = 21;
#endregion
#region 基础函数
/* F, G, H and I are basic MD5 functions.
* 四个非线性函数:
*
* F(X,Y,Z) =(X&Y)|((~X)&Z)
* G(X,Y,Z) =(X&Z)|(Y&(~Z))
* H(X,Y,Z) =X^Y^Z
* I(X,Y,Z)=Y^(X|(~Z))
*
* (&与,|或,~非,^异或)
*/
private static uint F(UInt32 x, UInt32 y, UInt32 z)
{
return (x & y) | ((~x) & z);
}
private static uint G(UInt32 x, UInt32 y, UInt32 z)
{
return (x & z) | (y & (~z));
}
private static uint H(UInt32 x, UInt32 y, UInt32 z)
{
return x ^ y ^ z;
}
private static uint I(UInt32 x, UInt32 y, UInt32 z)
{
return y ^ (x | (~z));
}
/* FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4.
* Rotation is separate from addition to prevent recomputation.
*/
private static void FF(ref UInt32 a, UInt32 b, UInt32 c, UInt32 d, UInt32 mj, int s, UInt32 ti)
{
a = a + F(b, c, d) + mj + ti;
a = a << s | a >> (32 - s);
a += b;
}
private static void GG(ref UInt32 a, UInt32 b, UInt32 c, UInt32 d, UInt32 mj, int s, UInt32 ti)
{
a = a + G(b, c, d) + mj + ti;
a = a << s | a >> (32 - s);
a += b;
}
private static void HH(ref UInt32 a, UInt32 b, UInt32 c, UInt32 d, UInt32 mj, int s, UInt32 ti)
{
a = a + H(b, c, d) + mj + ti;
a = a << s | a >> (32 - s);
a += b;
}
private static void II(ref UInt32 a, UInt32 b, UInt32 c, UInt32 d, UInt32 mj, int s, UInt32 ti)
{
a = a + I(b, c, d) + mj + ti;
a = a << s | a >> (32 - s);
a += b;
}
#endregion
说明:
假设Mj表示消息的第j个子分组(从0到15),常数ti是4294967296*abs( sin(i) )的整数部分,i 取值从1到64,单位是弧度。(4294967296=2的32次方)
现定义:
FF(a ,b ,c ,d ,Mj ,s ,ti ) 操作为 a = b + ( (a + F(b,c,d) + Mj + ti) << s)
GG(a ,b ,c ,d ,Mj ,s ,ti ) 操作为 a = b + ( (a + G(b,c,d) + Mj + ti) << s)
HH(a ,b ,c ,d ,Mj ,s ,ti) 操作为 a = b + ( (a + H(b,c,d) + Mj + ti) << s)
II(a ,b ,c ,d ,Mj ,s ,ti) 操作为 a = b + ( (a + I(b,c,d) + Mj + ti) << s)
注意:此处“<<”表示循环左移位,不是左移位。函数内部有循环左移位的处理,符号本身表示左移位。FF函数的第二行代码如下:
a = a << s | a >> (32 - s);
它先左移,然后右移,两者与操作。左移,右边补0。右移,左边补0。所以实现了循环左移。可以想象把一直线,首尾相连,然后移动点,最后从某处切开,变成了新的首尾。
小结:关于MD5的算法,还算是比较简单的算法,相比其它的加密算法而言。每一个算法都值得去推敲和学习。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MD5信息摘要算法(英语:MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm),一种被广泛使用的密码散列函数,可以产生出一个128位(16[字节]的散列值(hash value)),用于确保信息传输完整一致。MD5由美国密码学家[罗纳德·李维斯特](Ronald Linn Rivest)设计,于1992年公开,用以取代[MD4]算法。这套算法的程序在 RFC 1321 标准中被加以规范。1996年后该算法被证实存在弱点,可以被加以破解,对于需要高度安全性的数据,专家一般建议改用其他算法,如[SHA-2]。2004年,证实MD5算法无法防止碰撞,因此不适用于安全性认证,如[SSL]公开密钥认证或是[数字签名]等用途。
MD5的原理
MD5的“破解”
2004年,我国中科院院士王小云证实md5算法无法防止碰撞,因此,不适用于安全性认证。在2005年,王小云院士提出了md5哈希碰撞,公式如下
f(f(s, M), M') = f(f(s, N), N')
所谓的“破解”其实用“碰撞”一词语更为妥当,因为她的研究成果表明了给定消息 M1,能够计算获取 M2,使得 M2 产生的散列值与 M1 产生的散列值相同,即:
MD5(M1)=MD5(M2)
于是乎MD5不满足抗碰撞性,于是不再是安全的散列算法
但是
直到现在,给出一个MD5散列值,然后通过计算还原出原文来是不可能的的。也就是说通过一个MD5后的密文,回推明文目前还是没有方法的。
这里给出相关论文:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=7c9cd409db9bf2b5f06971928d6d7148&tn=SE_baiduxueshu_c1gjeupa&ie=utf-8
碰撞实现
这里介绍一个MD5碰撞的工具:fastcoll,fastcoll 可以用来对给定的前缀快速生成md5碰撞 (也就是说,生成两个不同的文件,每个文件都是在给定的内容后面附加一段东西生成的)
给出其主页:https://www.win.tue.nl/hashclash/
相关文章:https://homepages.cwi.nl/~stevens/papers/eprint-2006-104-S.pdf
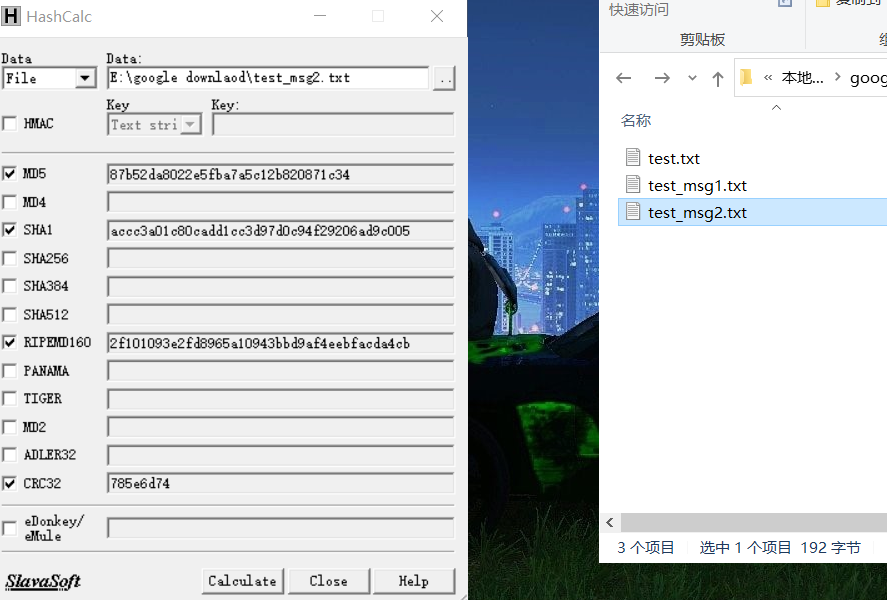
下面给出示例,我们创建一个文本文档在里面写入123456789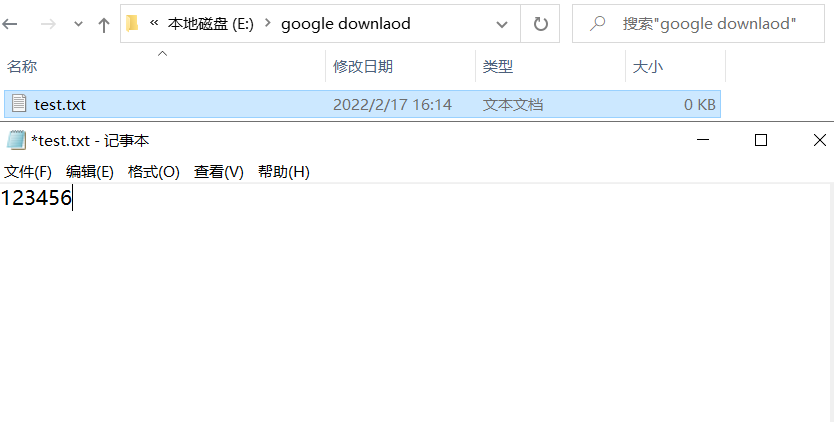
将其拖入fastcoll后得到两个文件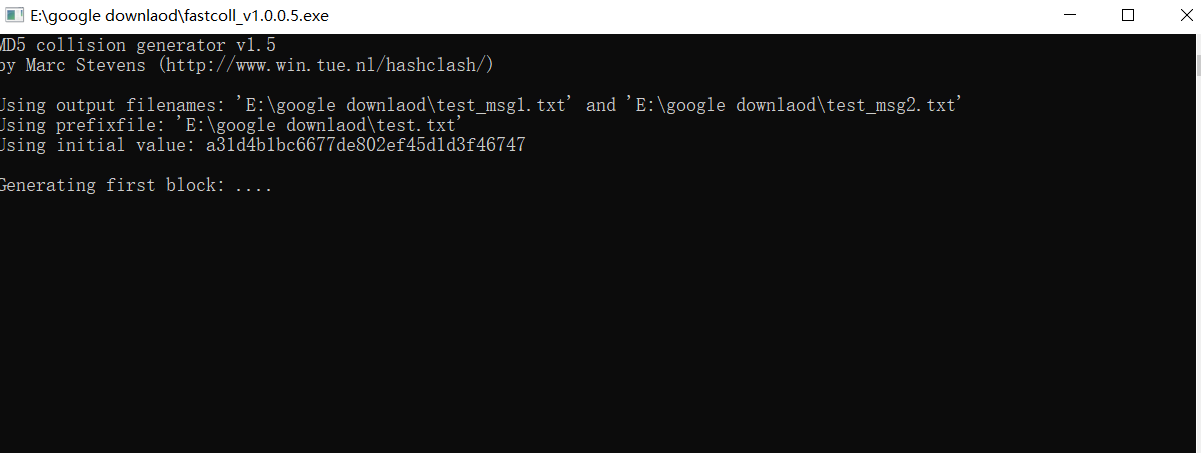
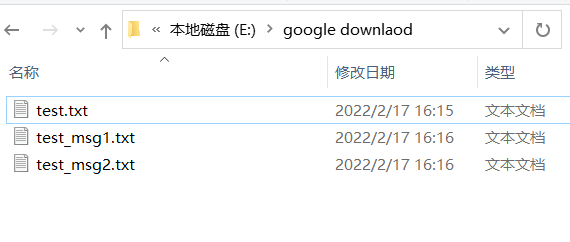
经过检验可以发现,第一个文档和第二个文档字符串不同,但最终MD5值相同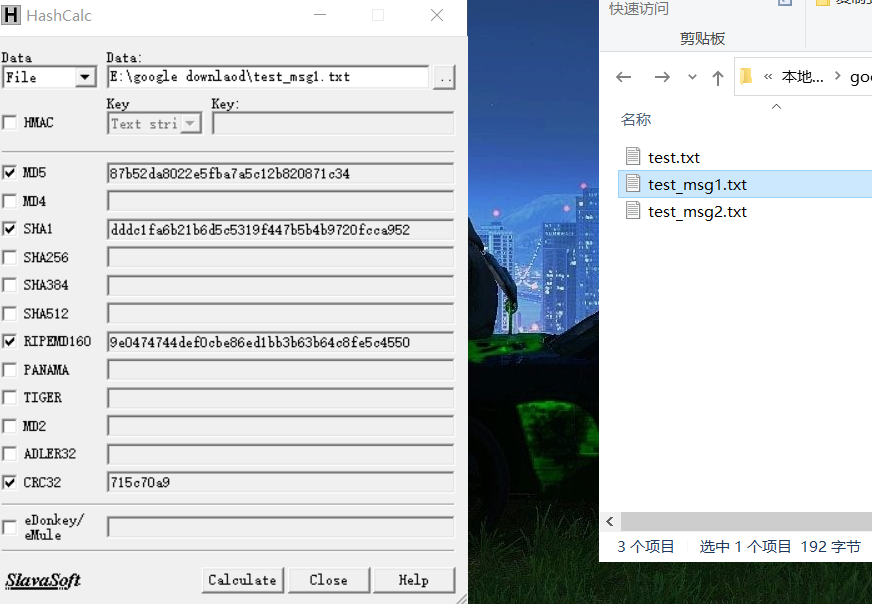
其他
之前打比赛的时候学习过一点技巧,可以通过python来爆破md5中的几位,下面给出一份示例python代码
1. import hashlib
2. for i in range(0,9999999999999999):
3. md5=hashlib.md5(str(i).encode("utf-8")).hexdigest()
4. if md5[0:5]=="66666": #md5后前五位是66666
5. print(i)
6. print("no result")
该脚本实现了纯数字通过MD5加密后相应位数是特定字符的功能
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MD5消息摘要算法(MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm),是在计算机领域被广泛使用的一种哈希算法,用来对信息进行完整性保护。它由美国密码学家Ronald Linn Rivest设计,于1992年公开,用以取代MD4算法。它的规范为RFC 1321。
MD5将一个任意长度的数据经过编码得到一个128位(16字节)的哈希值,即为MD5值。
01
—
MD5功能
MD5算法对任意长度的消息输入,产生一个128位(16字节)的哈希结构输出。在处理过程中,以512位输入数据块为单位。
02
—
MD5用途及特征
MD5通常应用在以下场景:
1、防篡改,保障文件传输可靠性
如SVN中对文件的控制;文件下载过程中,网站提供MD5值供下载后判断文件是否被篡改;BT中对文件块进行校验的功能。
2、增强密码保存的安全性。
例如网站将用户密码的MD5值保存,而不是存储明文用户密码,当然,还会加SALT,进一步增强安全性。
3、数字签名
在部分网上赌场中,使用MD5算法来保证过程的公平性,并使用随机串进行防碰撞,增加解码难度。
MD5算法具有以下特点:
1、压缩性
任意长度的数据,算出的MD5值长度都是固定的。
2、易计算
从原数据计算出MD5值很容易。
3、抗修改性
对原数据进行任何改动,哪怕只修改1个字节,所得到的MD5值都有很大区别。
4、强抗碰撞
已知原数据和其MD5值,想找到一个具有相同MD5值的数据(即伪造数据)是非常困难的。
03
—
MD5算法过程
网络中很容易找到MD5算法的相关实现代码,这里就不列出了。我们只需要关心它的实现框架即可。
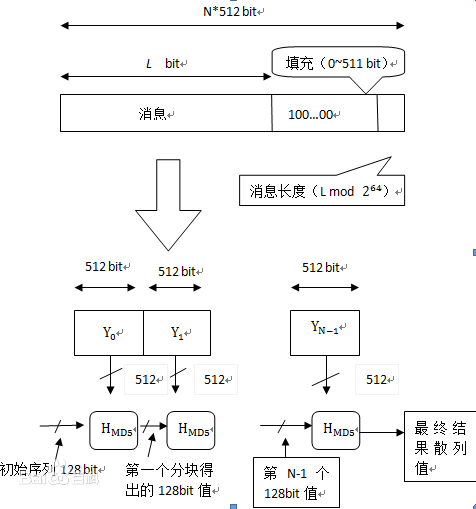
第一步:消息填充
补长到512的倍数
最后64位为消息长度(填充前的长度)的低64位
一定要补长(64+1~512),内容为100…0(如若消息长448,则填充512+64)
第二步 :分割
把结果分割为512位的块:Y0,Y1,…(每一个有16个32比特长字)
第三步 :计算
初始化MD buffer,128位常量(4个32bit字),进入循环迭代,共L次
每次:一个输入128位,另一个输入512位,结果输出128位,用于下一轮输入
第四步:结果
最后一步的输出即为散列结果128位。
04
—
MD5安全性
MD5虽然被广泛应用,但仍存在弱点,可以被加以破解,MD5算法无法防止碰撞,并已有碰撞成功案例。对于需要高度安全性的数据,专家一般建议改用其他算法,如SHA-2等。
另外,如果一个网站使用MD5进行用户名和密码的保存,请记住,一定要加SALT,不然,和明文保存差不多,基本无安全性可言。
目前互联网上已经有很多字符串与MD5的数据库,基本上可以认为没有加SALT的MD5值类似于裸奔了。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号