11.Java Spring框架源码分析-事务-Spring事务源码分析
目录
1. 开启事务管理注解
- @EnableTransactionManagement
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)//导入了TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
这个注解向spring容器中导入了TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector,我们继续研究
2. TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector向容器导入AutoProxyRegistrar和ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
- TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.selectImports
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
//EnableTransactionManagement的mode参数,默认是PROXY
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
//导入AutoProxyRegistrar,ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {
TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
default:
return null;
}
}
2.1. ImportSelector的selectImports是什么时候被调用的
我们在TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector#selectImports打个断点,调试调用栈如下:
selectImports:45, TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector (org.springframework.transaction.annotation)
selectImports:74, AdviceModeImportSelector (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processImports:591, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
doProcessConfigurationClass:304, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigurationClass:247, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:200, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:169, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigBeanDefinitions:308, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry:228, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors:272, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:92, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:687, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:524, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
<init>:84, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.annotation)
main:48, DbConfig (com.zsk.transaction)
跟1.给容器中注入AspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreator组件.md.跟踪ConfigurationClassProprocessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法一样,也是在ConfigurationClassProprocessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法中进行处理
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//...
do {
//这里会调用ImportSelector的selectImports方法
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<ConfigurationClass>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
//这里会调用ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的registerBeanDefinitions方法
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
//...
}
3. 先研究AutoProxyRegistrar
3.1. 向容器中注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator:用于创建代理对象
3.1.1. 类图
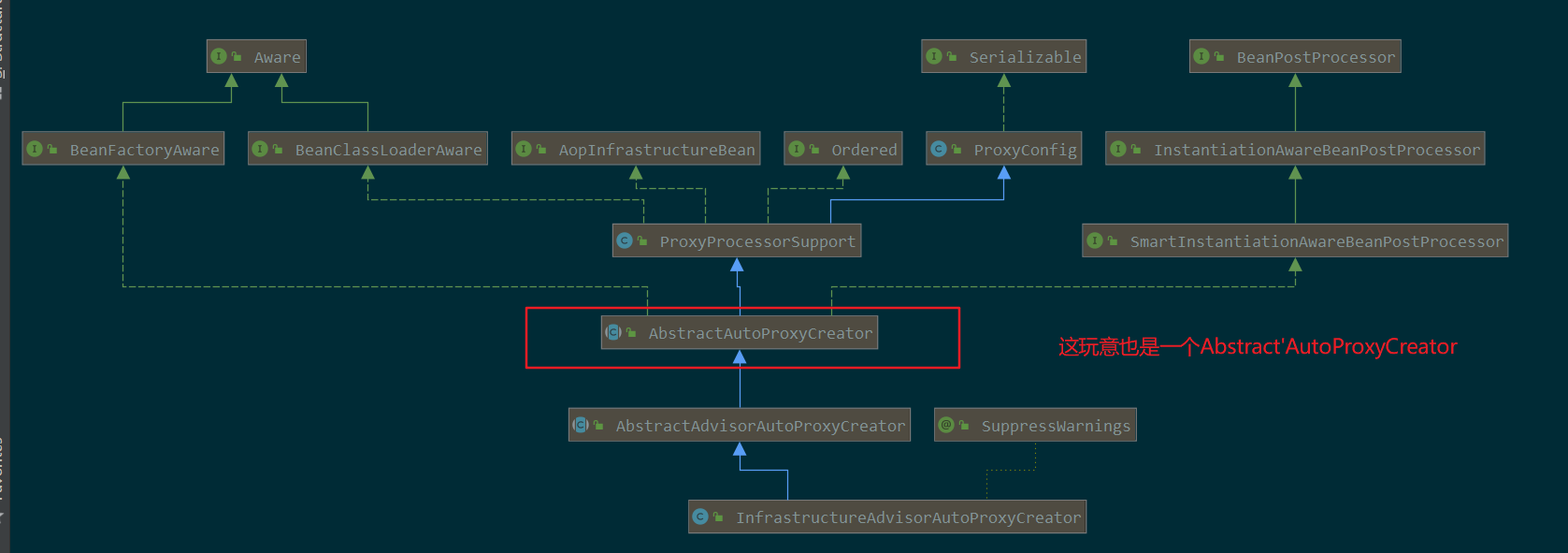
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator是spring aop 的核心,参考1.给容器中注入AspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreator组件.md
- registerBeanDefinitions
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean candidateFound = false;
Set<String> annTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes();
for (String annType : annTypes) {
AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annType);
if (candidate == null) {
continue;
}
//获取EnableTransactionManagement中的mode和proxyTartgetClass属性
Object mode = candidate.get("mode");
Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass");
if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() &&
Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) {
candidateFound = true;
//mode属性是PROXY
if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) {
//调用
AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
//如果proxyTargetClass属性是true
if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) {
//转调这个
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
return;
}
}
}
}
if (!candidateFound && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
String name = getClass().getSimpleName();
logger.warn(String.format("%s was imported but no annotations were found " +
"having both 'mode' and 'proxyTargetClass' attributes of type " +
"AdviceMode and boolean respectively. This means that auto proxy " +
"creator registration and configuration may not have occurred as " +
"intended, and components may not be proxied as expected. Check to " +
"ensure that %s has been @Import'ed on the same class where these " +
"annotations are declared; otherwise remove the import of %s " +
"altogether.", name, name, name));
}
}
- registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
return registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry, null);
}
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
//给容器中注册一个InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator组件,这玩意也是个SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor。
//本质上都是利用后置处理器在对象创建之后包装对象,返回一个代理对象(增强器)。代理对象执行方法利用拦截器链进行
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
4. 然后研究ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
@Configuration//一个配置类,注入了bean
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());//设置解析@Transactional属性的类
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());//设置事务拦截器
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
//用来解析@Transactional里面的属性
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
//创建拦截器
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
//保存事务属性信息
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
//保存事务管理器信息
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
这个Configuration向容器中注册了一个@BeanBeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor ,这个Bean包含了两个bean
TransactionAttributeSource用于解析@Transactional里面的属性TransactionInterceptor事务拦截器
4.1. 创建用于解析@Transactional里面的属性的bean:AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
- AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource构造方法
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;
this.annotationParsers = new LinkedHashSet<TransactionAnnotationParser>(4);
//利用注解解析器解析SpringTransactionAnnotation、JtaTransactionAnnotation、Ejb3TransactionAnnotation
this.annotationParsers.add(new SpringTransactionAnnotationParser());
if (jta12Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new JtaTransactionAnnotationParser());
}
if (ejb3Present) {
this.annotationParsers.add(new Ejb3TransactionAnnotationParser());
}
}
4.1.1. 如何解析的
- SpringTransactionAnnotationParser parseTransactionAnnotation
protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
//解析@Transactional里面的各种属性
Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation");
rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value());
Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation");
rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value());
rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue());
rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly"));
rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value"));
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName")) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule));
}
rbta.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return rbta;
}
4.2. 创建用于拦截事务的bean:TransactionInterceptor
是一个MethodInterceptor,在目标方法执行前调用
4.2.1. 事务拦截器的调用
- invoke
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() {
@Override
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
});
}
4.2.1.1. 事务的创建、提交/回滚
- TransactionAspectSupport invokeWithinTransaction
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation)
throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
//获取事务属性
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
//获取PlatformTransactionManager
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
//创建事务
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
//执行目标方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
//如果出现了异常
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
//使用事务管理器进行回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
//没有异常,那么使用事务管理器提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr,
new TransactionCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
}
});
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
}
}
4.2.1.1.1. 判断使用事务管理器
- determineTransactionManager
protected PlatformTransactionManager determineTransactionManager(TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
// Do not attempt to lookup tx manager if no tx attributes are set
if (txAttr == null || this.beanFactory == null) {
return getTransactionManager();
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
//注解上有指定那么使用指定的TransactionManager
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(qualifier);
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.transactionManagerBeanName)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.transactionManagerBeanName);
}
//使用默认的TransactionManager
else {
PlatformTransactionManager defaultTransactionManager = getTransactionManager();
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY);
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
//其实就是从容器中获取PlatformTransactionManager bean
defaultTransactionManager = this.beanFactory.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(
DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY, defaultTransactionManager);
}
}
return defaultTransactionManager;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号