21. Java JUC源码分析系列笔记-JDK1.7的ConcurrentHashMap
目录
1. 构造方法
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
//16,0.75f,16
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
2. put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
//value不能为空
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//计算key的hash值
int hash = hash(key);
//在用hash值计算j
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
//用j计算地址,并且cas获取segment对象
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
//初始化
s = ensureSegment(j);
//调用segment的put方法
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
2.1. hash
private int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if ((0 != h) && (k instanceof String)) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// Spread bits to regularize both segment and index locations,
// using variant of single-word Wang/Jenkins hash.
h += (h << 15) ^ 0xffffcd7d;
h ^= (h >>> 10);
h += (h << 3);
h ^= (h >>> 6);
h += (h << 2) + (h << 14);
return h ^ (h >>> 16);
}
2.2. ensureSegment
private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment(int k) {
final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this.segments;
long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offset
Segment<K,V> seg;
//segment为空,需要初始化。为什么使用cas而不是直接用下标???
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {
//原型模式,使用第一个segment作为原型
Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototype
//获取第一个segment的capacity,loadFactor,threshold,(后续用于创建entry table和segment)
int cap = proto.table.length;
float lf = proto.loadFactor;
int threshold = (int)(cap * lf);
//创建entry table(后续用于创建segment)
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap];
//重新确认为空,不为空说明已经有其他线程初始化了,直接退出,避免进入死循环+cas浪费cpu
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) { // recheck
//创建segment
Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab);
//死循环+cas设置segment
while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))
break;
}
}
}
return seg;
}
2.3. segment的put方法
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//先sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1)快速获取锁
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
//计算下标
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
//头节点
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);
//遍历链表
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
//链表不为空
if (e != null) {
K k;
//找到相等的节点
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
//替换value
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
//链表为空
else
{
//上面已经找到了这个节点
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);
//计数增加
int c = count + 1;
//此时数量超过了threshold
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
//扩容
rehash(node);
else
//cas设置头节点。
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
//解锁
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
2.3.1. scanAndLockForPut
private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
HashEntry<K,V> node = null;
int retries = -1; // negative while locating node
//死循环直到获取锁
while (!tryLock()) {
HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below
if (retries < 0) {
//链表头节点为空
if (e == null) {
if (node == null) // speculatively create node
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
retries = 0;
}
//找到了相等的节点
else if (key.equals(e.key))
retries = 0;
//链表下一个节点
else
e = e.next;
}
//循环次数太多,升级为加锁
else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
lock();
break;
}
else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed
retries = -1;
}
}
return node;
}
2.3.2. rehash
private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) {
/*
* Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we
* are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from
* each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a
* power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node
* creation by catching cases where old nodes can be
* reused because their next fields won't change.
* Statistically, at the default threshold, only about
* one-sixth of them need cloning when a table
* doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage
* collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by
* any reader thread that may be in the midst of
* concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain
* array indexing because they are followed by volatile
* table write.
*/
HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
//新的容量为旧容量*2
int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
//用新容量创建新的entry数组
HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable =
(HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity];
int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1;
//遍历原数组里的每个元素
for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) {
HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i];
if (e != null) {
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
//计算在新数组的位置
int idx = e.hash & sizeMask;
//只有一个节点
if (next == null) // Single node on list
newTable[idx] = e;
else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot
HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e;
int lastIdx = idx;
//遍历链表
for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next;
last != null;
last = last.next) {
int k = last.hash & sizeMask;
if (k != lastIdx) {
lastIdx = k;
lastRun = last;
}
}
newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun;
// Clone remaining nodes
for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
V v = p.value;
int h = p.hash;
int k = h & sizeMask;
HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k];
newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n);
}
}
}
}
int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node
node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]);
newTable[nodeIndex] = node;
table = newTable;
}
3. get
public V get(Object key) {
Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab;
//通过key计算segment地址
int h = hash(key);
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
//通过cas获取segment
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
//通过cas获取entry
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
//遍历链表找到相等的节点
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
4. containsKey方法
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
Segment<K,V> s; // same as get() except no need for volatile value read
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
//cas获取相应的segment
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
//cas获取相应的entry,并且遍历链表
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
//找到相等的节点
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
5. remove
public V remove(Object key) {
int hash = hash(key);
//先找到segment
Segment<K,V> s = segmentForHash(hash);
return s == null ? null : s.remove(key, hash, null);
}
5.1. segmentForHash
private Segment<K,V> segmentForHash(int h) {
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
//cas获取
return (Segment<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u);
}
5.2. segment的remove
final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
//尝试获取锁,失败则死循环+cas获取锁
if (!tryLock())
scanAndLock(key, hash);
V oldValue = null;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> e = enUNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, n);tryAt(tab, index);
HashEntry<K,V> pred = null;
//遍历链表
while (e != null) {
K k;
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
//找到了相等的节点
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) {
if (pred == null)
//UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(tab, ((long)i << TSHIFT) + TBASE, e);
setEntryAt(tab, index, next);
else
//UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, n);
pred.setNext(next);
++modCount;
--count;
oldValue = v;
}
break;
}
pred = e;
e = next;
}
} finally {
//解锁
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
总结
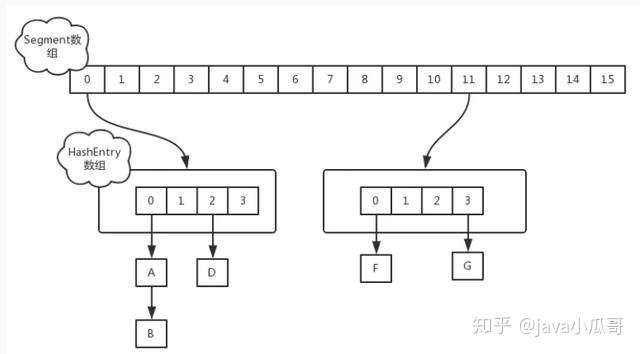
JDK 1.7 中,采用分段锁的机制,实现并发的更新操作,底层采用数组+链表的存储结构,包括两个核心静态内部类 Segment 和 HashEntry。
-
Segment 继承 ReentrantLock(重入锁) 用来充当锁的角色,每个 Segment 对象守护每个散列映射表的若干个桶;
-
HashEntry 用来封装映射表的键-值对;
-
每个桶是由若干个 HashEntry 对象链接起来的链表




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号