机器学习—分类3-2(朴素贝叶斯算法)
基于朴素贝叶斯预测客户是否购买汽车新车型
主要步骤流程:
- 1. 导入包
- 2. 导入数据集
- 3. 数据预处理
- 3.1 检测缺失值
- 3.2 生成自变量和因变量
- 3.3 查看样本是否均衡
- 3.4 将数据拆分成训练集和测试集
- 3.5 特征缩放
- 4. 构建朴素贝叶斯模型做预测
- 4.1 构建模型并训练
- 4.2 预测测试集
- 4.3 生成混淆矩阵
- 4.4 可视化测试集的预测结果
- 4.5 评估模型性能
1. 导入包
In [1]:
# 导入包
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2. 导入数据集
In [2]:
# 导入数据集
dataset = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv')
dataset
Out[2]:
3. 数据预处理
3.1 检测缺失值
In [3]:
# 检测缺失值
null_df = dataset.isnull().sum()
null_df
Out[3]:
3.2 生成自变量和因变量
为了可视化分类效果,仅选取 Age 和 EstimatedSalary 这2个字段作为自变量
In [4]:
# 生成自变量和因变量
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values
y = dataset.iloc[:, 4].values
In [5]:
X[:5, :]
Out[5]:
3.3 查看样本是否均衡
In [6]:
# 查看样本是否均衡
sample_0 = sum(dataset['Purchased']==0)
sample_1 = sum(dataset['Purchased']==1)
print('不买车的样本占总样本的%.2f' %(sample_0/(sample_0 + sample_1)))
3.4 将数据拆分成训练集和测试集
In [7]:
# 将数据拆分成训练集和测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
print(X_train.shape)
print(X_test.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
print(y_test.shape)
3.5 特征缩放
In [8]:
# 特征缩放
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
4. 构建朴素贝叶斯模型做预测
4.1 构建模型并训练
In [9]:
# 构建高斯朴素贝叶斯模型并训练模型
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
classifier = GaussianNB()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
Out[9]:
4.2 预测测试集
In [10]:
# 预测测试集
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
y_pred[:5]
Out[10]:
4.3 生成混淆矩阵
In [11]:
# 生成混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print(cm)
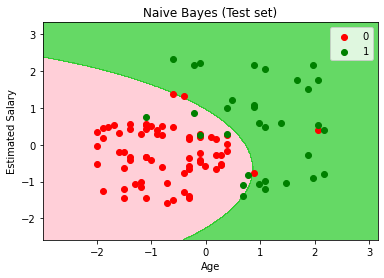
4.4 可视化测试集的预测结果
In [12]:
# 可视化测试集的预测结果
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
plt.figure()
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('pink', 'limegreen')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
color = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
plt.title('Naive Bayes (Test set)')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
4.5 评估模型性能
In [13]:
# 评估模型性能
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
In [14]:
(cm[0][0] + cm[1][1])/(cm[0][0] + cm[0][1] + cm[1][0] + cm[1][1])
Out[14]:
结论:1)由上图可见,朴素贝叶斯分类可以做非线性分类。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号