CSS基础 布局
1、布局的基本位置
top 距离上边的距离
right 距离右边的距离
bottom 距离下边的距离
left 距离左边的距离
去掉布局时 html 的3mm 边框
*{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
2、流式布局
float
最基本的布局方式
float: left // 向左流 float: right // 向右流 clear: both // 清掉流
在流式布局中,默认往下流动,并且占据整行位置,只有在给 float 一个方向时模块才会浮动起来
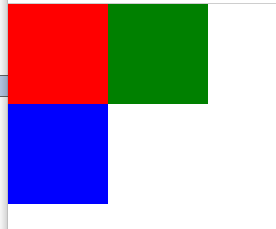
举例:
*{ padding:0px; margin:0px; } #div1{ width:100px; height:100px; background-color:red; float:lefr; } #div2{ width:100px; height:100px; background-color:green; float:left } #div3{ width:100px; height:100px; background-color:blue; } <body> <div id="div1"></div> <div id="div2"></div> <div style="clear:both;"></div> <div id="div3"></div> </body>
3、定位布局
position
(1)固定定位
position: fixed
锁定位置(相对于浏览器的位置),例如有些网站的右下角的弹出窗口。
(2)绝对位置
position: absolute
相对于父级元素(浏览器,绝对定位的上级)
absolute 是为一个浮动的模块,占不住位置,
可以随意排列位置,不会对其它任何布局位置有影响
(3)相对位置
position: relative
相对于自身应该出现的位置
是一个固定模块,能占住自己的位置
在 模块位置根据上下左右位置发生变化时,其自身应该出现的位置保留,不被其他模块占据
-- 常常用来作为 absolute 的父集使用
4、分层
z-index: 数字
值越大越靠上



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号