树链剖分
这个专题做的还算比较顺利吧。
主要就是通过轻重链把树上问题变成序列上的问题,可以让我们用数据结构来优化。
挺好理解的,随便粘一个学习\(blog\)
所以这个东西还是看之前的基础,看如何处理序列上的问题
染色
这个东西如果在序列上还是挺好处理的,类似山海经的一个区间信息合并。
只要用一个结构体来记录这个区间内的颜色种类,左端点颜色,右端点颜色。
合并的时候直接看左区间的右端点和右区间的左端点颜色是否相同就行了。
看错题面以为让求颜色种类废了半天劲还是不会
直接返回一个结构体是真的香
code
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#define mp make_pair
#define R register int
#define int long
#define printf Ruusupuu = printf
int Ruusupuu ;
using namespace std ;
typedef long long L ;
typedef long double D ;
typedef unsigned long long G ;
typedef pair< int , int > PI ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
inline int read(){
int w = 0 ; bool fg = 0 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while( ch < '0' || ch > '9' ) fg |= ( ch == '-' ) , ch = getchar() ;
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) w = ( w << 1 ) + ( w << 3 ) + ( ch ^ '0' ) , ch = getchar() ;
return fg ? -w : w ;
}
int n , m , cor [N] , knt ; char ch ;
int head [N] , fr [N << 1] , to [N << 1] , net [N << 1] , fg [N << 1] , cnt = 1 ;
#define add( f , t ) fr [++ cnt] = f , to [cnt] = t , net [cnt] = head [f] , head [f] = cnt
int sz [N] , dep [N] , fa [N] , bs [N] ;
int top [N] , lz [N] , fl [N] , gnt , lec , ric , ans ;
int l [N << 2] , r [N << 2] , lc [N << 2] , rc [N << 2] , lazy [N << 2] ;
struct T{ int lc , rc , num ; T(){ lc = rc = num = 0 ; } } data [N << 2] ;
int lx , rx , x , y , z ;
void dfs1( int x ){
R i = head [x] ; while( ~i && fg [i] ) i = net [i] ;
for( ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
if( fg [i] ) continue ;
fg [i] = fg [i ^ 1] = 1 ;
int y = to [i] ; dep [y] = dep [x] + 1 , fa [y] = x ;
dfs1( y ) , sz [x] += sz [y] ;
if( sz [y] > sz [bs [x]] ) bs [x] = y ;
} sz [x] ++ ;
}
void dfs2( int x , int tops ){
top [x] = tops , lz [x] = ++ gnt , fl [gnt] = x ;
if( !bs [x] ) return ;
dfs2( bs [x] , tops ) ;
for( R i = head [x] ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
int y = to [i] ;
if( y == bs [x] || y == fa [x] ) continue ;
dfs2( y , y ) ;
}
}
void sc(){
n = read() , m = read() ; memset( head , -1 , sizeof( head ) ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) cor [i] = read() ;
for( R i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ ) x = read() , y = read() , add( x , y ) , add( y , x ) ;
}
inline T ud( T a , T b ){
if( a.num == 0 ) return b ;
if( b.num == 0 ) return a ;
T ans ; ans.lc = a.lc , ans.rc = b.rc ;
ans.num = a.num + b.num - ( a.rc == b.lc ) ;
return ans ;
}
inline void sp( int x ){
if( !lazy [x] ) return ;
int k = lazy [x] ; lazy [x] = 0 ;
data [x << 1].lc = data [x << 1].rc = k ;
data [x << 1 | 1].lc = data [x << 1 | 1].rc = k ;
data [x << 1].num = data [x << 1 | 1].num = 1 ;
lazy [x << 1] = lazy [x << 1 | 1] = k ;
}
void build( int x , int ll , int rr ){
l [x] = ll , r [x] = rr ;
if( ll == rr ){ data [x].lc = data [x].rc = cor [fl [ll]] , data [x].num = 1 ; return ; }
int mid = ( ll + rr ) >> 1 ;
build( x << 1 , ll , mid ) , build( x << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , rr ) ;
data [x] = ud( data [x << 1] , data [x << 1 | 1] ) ;
}
void cge( int x ){
if( l [x] >= lx && r [x] <= rx ){ data [x].lc = data [x].rc = z , data [x].num = 1 , lazy [x] = z ; return ; }
sp ( x ) ; int mid = ( l [x] + r [x] ) >> 1 ;
if( lx <= mid ) cge( x << 1 ) ;
if( rx > mid ) cge( x << 1 | 1 ) ;
data [x] = ud( data [x << 1] , data [x << 1 | 1] ) ;
}
T ask( int x ){
// printf( "asking%ld %ld %ld\n" , x , lx , rx ) ;
if( l [x] >= lx && r [x] <= rx ) return data [x] ;
sp( x ) ; int mid = ( l [x] + r [x] ) >> 1 ;
T ans ;
if( lx <= mid ) ans = ud( ans , ask ( x << 1 ) ) ;
if( rx > mid ) ans = ud( ans , ask( x << 1 | 1 ) ) ;
// printf( "backing %ld %ld %ld %ld \n" , x , ans.lc , ans.rc , ans.num ) ;
return ans ;
}
inline int askmax(){
T ansx , ansy ;
while( top [x] != top [y] ){
if( dep [top [x]] < dep [top [y]] ) swap( x , y ) , swap( ansx , ansy ) ;
lx = lz [top [x]] , rx = lz [x] ;
ansx = ud( ask( 1 ) , ansx ) ;
x = fa [top [x]] ;
}
if( dep [x] < dep [y] ) swap( x , y ) , swap( ansx , ansy ) ;
lx = lz [y] , rx = lz [x] ;
ansx = ud( ask( 1 ) , ansx ) ;
return ansx.num + ansy.num - ( ansx.lc == ansy.lc ) ;
}
inline void cgeroad(){
while( top [x] != top [y] ){
if( dep [top [x]] < dep [top [y]] ) swap( x , y ) ;
lx = lz [top [x]] , rx = lz [x] ;
cge( 1 ) , x = fa [top [x]] ;
} if( dep [x] < dep [y] ) swap( x , y ) ;
lx = lz [y] , rx = lz [x] , cge( 1 ) ;
}
void work(){
dfs1( 1 ) , dfs2( 1 , 1 ) ;
build( 1 , 1 , n ) ;
while( m -- ){
ch = getchar() ;
if( ch == 'Q' ) x = read() , y = read() , printf( "%ld\n" , askmax() ) ;
else x = read() , y = read() , z = read() , cgeroad() ;
}
}
signed main(){
sc() ;
work() ;
return 0 ;
}
难存的情缘
这道题挺板的,主要来一下我特殊的边权压成点权的方法。
因为在树中,每个节点,他的父亲是唯一的,所以和父亲相连的边只有一条。
我们就把这条边压到他的点上。
但是有一个问题,就是\(Lca\)的点会被记录一次,然而我们并不希望记录\(Lca\)(因为是\(Lca\)与\(fa[Lca]\)的连边)
我们这里粘贴一个\(OI-wiki\)上用树剖求\(Lca\)的图片
可以发现,\(top\)相同时,深度小的就是\(Lca\)
所以我们直接在最后一步对深度小的进行\(ask\)的时候把左端点设为\(Lca\)的\(dfs\)序加一就行了。
code
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#define mp make_pair
#define R register int
#define int long
#define printf Ruusupuu = printf
int Ruusupuu ;
using namespace std ;
typedef long long L ;
typedef long double D ;
typedef unsigned long long G ;
typedef pair< int , int > PI ;
const int N = 1e4 + 10 ;
inline int read(){
int w = 0 ; bool fg = 0 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while( ch < '0' || ch > '9' ) fg |= ( ch == '-' ) , ch = getchar() ;
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) w = ( w << 1 ) + ( w << 3 ) + ( ch ^ '0' ) , ch = getchar() ;
return fg ? -w : w ;
}
int n , w [N] , x , y , ww , rtp [N << 1] ; string kk ;
int head [N] , fr [N << 1] , to [N << 1] , net [N << 1] , wr [N << 1] , fg [N << 1] , cnt = 1 ;
#define add( f , t , w ) fr [++ cnt] = f , to [cnt] = t , net [cnt] = head [f] , head [f] = cnt , wr [cnt] = w
int sz [N] , fa [N] , bs [N] , dep [N] ;
int top [N] , lz [N] , fl [N] , gnt ;
int l [N << 2] , r [N << 2] , data [N << 2] , lx , rx , pos , dlt ;
void sc(){
n = read() ; memset( head , -1 , sizeof( head ) ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ ) x = read() , y = read() , ww = read() , add( x , y , ww ) , add( y , x , ww ) ;
}
void dfs1( int x ){
R i = head [x] ; while( ~i && fg [i] ) i = net [i] ;
for( ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
if( fg [i] ) continue ;
fg [i] = fg [i ^ 1] = 1 ;
int y = to [i] ;
dep [y] = dep [x] + 1 , fa [y] = x , w [y] = wr [i] , rtp [i / 2] = y ;
dfs1( y ) , sz [x] += sz [y] ;
if( sz [y] > sz [bs [x]] ) bs [x] = y ;
} sz [x] ++ ;
}
void dfs2( int x , int tops ){
top [x] = tops , lz [x] = ++ gnt , fl [gnt] = x ;
if( !bs [x] ) return ;
dfs2( bs [x] , tops ) ;
for( R i = head [x] ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
int y = to [i] ;
if( y == bs [x] || y == fa [x] ) continue ;
dfs2( y , y ) ;
}
}
#define ud( x ) data [x] = data [x << 1] > data [x << 1 | 1] ? data [x << 1] : data [x << 1 | 1] ;
void build( int x , int ll , int rr ){
l [x] = ll , r [x] = rr ;
if( ll == rr ){ data [x] = w [fl [ll]] ; return ; }
int mid = ( ll + rr ) >> 1 ;
build( x << 1 , ll , mid ) , build( x << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , rr ) ;
ud( x ) ;
}
int ask( int x ){
if( l [x] >= lx && r [x] <= rx ) return data [x] ;
int mid = ( l [x] + r [x] ) >> 1 , ans = 0 ;
if( lx <= mid ) ans = max( ans , ask( x << 1 ) ) ;
if( rx > mid ) ans = max( ans , ask( x << 1 | 1 ) ) ;
return ans ;
}
void cge( int x ){
if( l [x] == r [x] ) { data [x] = dlt ; return ; }
int mid = ( l [x] + r [x] ) >> 1 ;
if( pos <= mid ) cge( x << 1 ) ;
else cge( x << 1 | 1 ) ;
ud( x ) ;
}
inline int askmax(){
int ans = 0 ;
while( top [x] != top [y] ){
if( dep [top [x]] < dep [top [y]] ) swap( x , y ) ;
lx = lz [top [x]] , rx = lz [x] ;
int res = ask( 1 ) ;
ans = res > ans ? res : ans ;
x = fa [top [x]] ;
}
if( dep [x] < dep [y] ) swap( x , y ) ;
lx = lz [y] + 1 , rx = lz [x] ;
int res = ask( 1 ) ;
return res > ans ? res : ans ;
}
void work(){
dfs1( 1 ) , dfs2( 1 , 1 ) ;
build( 1 , 1 , n ) ;
while( 1 ){
cin >> kk ;
if( kk == "DONE" ) break ;
if( kk == "QUERY" ) x = read() , y = read() , printf( "%ld\n" , askmax() ) ;
if( kk == "CHANGE" ) x = read() , y = read() , pos = lz [rtp [x]] , dlt = y , cge( 1 ) ;
}
}
signed main(){
sc() ;
work() ;
return 0 ;
}
遥远的国度
这个跟之前的一道\(lca\)里面的题很像,记录一下这个换根技巧,因为这次没有一遍打对。
我们只需要记录当前的根是谁,画图观察规律可以发现:
- 如果根不在当前查询点的子树内,那么正常\(dfs\)序查询
- 如果根就是当前查询的点,输出全局最小值
- 如果根在当前子树内,那么需要好好画图还观察一下(一定要把情况考虑全)
我一开始误认为是除了\(root\)的子树之外所有节点的最小值,原因是我画的图都把\(root\)当成当前查询点的直接儿子了
后来才发现如果有这种情况
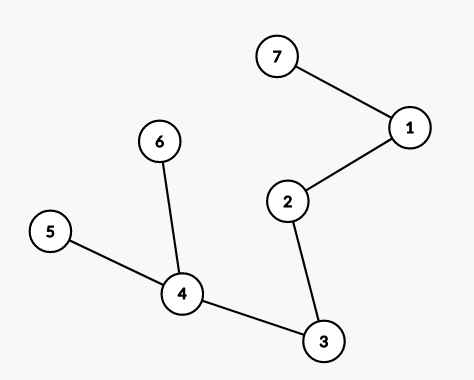
如果当前的根是\(4\),当前在查询\(2\)。
那么如果按我说的,会多查一个\(3\)。
我们设当前查询节点是\(x\),当前根是\(root\)
所以,我们应该通过跳\(lca\)跳到\(x\)和\(root\)的路径上的\(x\)的儿子(在本例子中是\(3\))
然后查询除了\(3\)的子树之外所有节点的最小值,也就是答案了。
注意一下读字符最好还是别花里胡哨\(Getchar\),稳稳当当\(cin\)或者\(scanf\)挺香的
code
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define mp make_pair
#define R register int
#define int long long
#define printf Ruusupuu = printf
int Ruusupuu ;
using namespace std ;
typedef long long L ;
typedef long double D ;
typedef unsigned long long G ;
typedef pair< int , int > PI ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
const int Inf = 0x7ffffffff ;
inline int read(){
int w = 0 ; bool fg = 0 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while( ch < '0' || ch > '9' ) fg |= ( ch == '-' ) , ch = getchar() ;
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) w = ( w << 1 ) + ( w << 3 ) + ( ch ^ '0' ) , ch = getchar() ;
return fg ? -w : w ;
}
int n , m , x , y , z , w [N] , root , opt ;
int fr [N << 1] , to [N << 1] , net [N << 1] , head [N] , fg [N << 1] , cnt = 1 ;
#define add( f , t ) fr [++ cnt] = f , to [cnt] = t , net [cnt] = head [f] , head [f] = cnt
int bs [N] , fa [N] , dep [N] , sz [N] ;
int lz [N] , fl [N] , top [N] , gnt ;
int l [N << 2] , r [N << 2] , ly [N << 2] , data [N << 2] , lx , rx ;
int fh [N][25] ;
void sc(){
n = read() , m = read() ; memset( head , -1 , sizeof( head ) ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ ) x = read() , y = read() , add( x , y ) , add( y , x ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) w [i] = read() ; root = read() ;
}
void dfs1( int x , int far ){
for( R i = head [x] ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
int y = to [i] ;
if( y == far ) continue ;
fa [y] = x , dep [y] = dep [x] + 1 ;
dfs1( y , x ) , sz [x] += sz [y] ;
if( sz [y] > sz [bs [x]] ) bs [x] = y ;
} sz [x] ++ ;
}
void dfs2( int x , int tops ){
top [x] = tops , lz [x] = ++ gnt , fl [gnt] = x ;
if( !bs [x] ) return ; dfs2( bs [x] , tops ) ;
for( R i = head [x] ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
int y = to [i] ;
if( y == fa [x] || y == bs [x] ) continue ;
dfs2( y , y ) ;
}
}
#define ud( x ) data [x] = data [x << 1] < data [x << 1 | 1] ? data [x << 1] : data [x << 1 | 1] ;
inline void sp( int x ){
if( !ly [x] ) return ;
int k = ly [x] ; ly [x] = 0 ;
data [x << 1] = data [x << 1 | 1] = k ;
ly [x << 1] = ly [x << 1 | 1] = k ;
}
void build( int x , int ll , int rr ){
l [x] = ll , r [x] = rr ;
if( ll == rr ){ data [x] = w [fl [ll]] ; return ; }
int mid = ( ll + rr ) >> 1 ;
build( x << 1 , ll , mid ) , build( x << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , rr ) ;
ud( x ) ;
}
void cge( int x ){
if( l [x] >= lx && r [x] <= rx ) { data [x] = ly [x] = z ; return ; }
sp( x ) ;
int mid = ( l [x] + r [x] ) >> 1 ;
if( lx <= mid ) cge( x << 1 ) ;
if( rx > mid ) cge( x << 1 | 1 ) ;
ud( x ) ;
}
int ask( int x ){
if( l [x] >= lx && r [x] <= rx ) return data [x] ;
sp( x ) ;
int mid = ( l [x] + r [x] ) >> 1 , ans = Inf ;
if( lx <= mid ) ans = min( ans , ask( x << 1 ) ) ;
if( rx > mid ) ans = min( ans , ask( x << 1 | 1 ) ) ;
return ans ;
}
void cgeroad(){
while( top [x] != top [y] ){
if( dep [top [x]] < dep [top [y]] ) swap( x , y ) ;
lx = lz [top [x]] , rx = lz [x] , cge( 1 ) ;
x = fa [top [x]] ;
} if( dep [x] < dep [y] ) swap( x , y ) ;
lx = lz [y] , rx = lz [x] , cge( 1 ) ;
}
bool fs [N] ;
void bfs(){
queue< int > q ; q.push( 1 ) ;
while( !q.empty() ){
int x = q.front() ; fs [x] = 1 , q.pop() ;
for( R i = head [x] ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
int y = to [i] ;
if( fs [y] ) continue ;
// printf( "%lld %lld\n" , x , y ) ;
if( !fs [y] ) q.push( y ) , fs [y] = 1 ;
fh [y][0] = x ;
for( R j = 1 ; j <= 20 ; j ++ ) fh [y][j] = fh [fh [y][j - 1]][j - 1] ;
}
}
}
void work(){
dfs1( 1 , 0 ) , dfs2( 1 , 1 ) , build( 1 , 1 , n ) , bfs() ;
while( m -- ){
opt = read() ;
if( opt == 1 ) root = read() ;
else if( opt == 2 ) x = read() , y = read() , z = read() , cgeroad() ;
else{
x = read() , lx = lz [x] , rx = lz [x] + sz [x] - 1 ;
if( x == root ) lx = 1 , rx = n , printf( "%lld\n" , ask( 1 ) ) ;
else if( lz [x] < lz [root] && lz [root] <= lz [x] + sz [x] - 1 ){
int ans = Inf , y = root ;
for( R j = 20 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) if( dep [fh [y][j]] > dep [x] ) y = fh [y][j] ;
lx = 1 , rx = lz [y] - 1 , ans = min( ans , ask( 1 ) ) ;
lx = lz [y] + sz [y] , rx = n , ans = min( ans , ask( 1 ) ) ;
printf( "%lld\n" , ans ) ;
} else lx = lz [x] , rx = lz [x] + sz [x] - 1 , printf( "%lld\n" , ask( 1 ) ) ;
}
}
}
signed main(){
sc() ;
work() ;
return 0 ;
}
总结
其实树剖就是把树上的东西搞到序列上,和序列上一样,如果只有修改/查询或者一通修改之后在查询,那完全没有必要树剖。
在序列上,我们可以通过前缀和\(O(1)\)查,差分\(O(1)\)改,线段树\(O(logn)\)查,改
在树上,我们可以通过\(dfs+LCA\ O(logn)\)树上前缀和(每个点到根节点的路径长)查,
\(LCA+\)树上差分+\(dfs \ O(log n)\)改(细节:查是先\(dfs\)后\(LCA\),改是先\(LCA\)后\(dfs\)),
但是如果查和改交叉进行,我们就需要树剖\(+\)线段树\(O(log^2n)\)查改了
可见,就是序列上多了一个\(log\)而已,思想还是不变的。
货车运输
由题意不难发现选择这个图的最大生成树肯定更优。
没必要树剖,因为这道题只有询问没有修改
直接一个\(Lca\),\(fa[x][i]\)代表\(x\)节点的\(2^i\)父亲,倍增数组\(dp[x][i]\)代表到达\(fa [x][i]\)路径上的最小值。
然后在求出\(Lca\)的同时就可以就出来达到他的最小值,然后对\(x->Lca\)和\(y->Lca\)取\(min\)就是答案
code
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define mp make_pair
#define R register int
#define int long
#define printf Ruusupuu = printf
int Ruusupuu ;
using namespace std ;
typedef long long L ;
typedef long double D ;
typedef unsigned long long G ;
typedef pair< int , int > PI ;
const int N = 1e4 + 10 ;
const int M = 1e5 + 10 ;
const int Inf = 0x3f3f3f3f ;
inline int read(){
int w = 0 ; bool fg = 0 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while( ch < '0' || ch > '9' ) fg |= ( ch == '-' ) , ch = getchar() ;
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) w = ( w << 1 ) + ( w << 3 ) + ( ch ^ '0' ) , ch = getchar() ;
return fg ? -w : w ;
}
int n , m , x , y , z , fs [N] , dp [N][25] ;
int Head [N] , Cnt = 1 , res ;
struct E { int fr , to , net , w ; } a [M] ;
inline bool cmp( E a , E b ) { return a.w > b.w ; }
#define Add( f , t , z ) a [++ Cnt].fr = f , a [Cnt].to = t , a [Cnt].net = Head [f] , a [Cnt].w = z , Head [f] = Cnt
int head [N] , cnt = 1 , to [M] , w [M] , fr [M] , net [M] , fg [M] ;
#define add( f , t , z ) fr [++ cnt] = f , to [cnt] = t , net [cnt] = head [f] , head [f] = cnt , w [cnt] = z
int dep [N] , fa [N][25] ;
inline int fd( int x ){
if( x == fs [x] ) return x ;
else return fs [x] = fd( fs [x] ) ;
}
void kr(){
for( R i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) fs [i] = i ;
memset( head , -1 , sizeof( head ) ) ;
sort( a + 1 , a + 1 + Cnt , cmp ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i <= Cnt ; i ++ ){
int f = a [i].fr , t = a [i].to ;
int faf = fd( f ) , fat = fd( t ) ;
if( faf == fat ) continue ;
fs [faf] = fat ;
add( f , t , a [i].w ) , add( t , f , a [i].w ) ;
// printf( "%ld %ld %ld\n" , f , t , a [i].w ) ;
}
}
void bfs(){
queue< int > q ; q.push( 1 ) ;
for( R i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) for( R j = 0 ; j <= 20 ; j ++ ) dp [i][j] = Inf ;
while( !q.empty() ){
int x = q.front() ; q.pop() ;
R i = head [x] ; while( ~i && fg [i] ) i = net [i] ;
for( ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
if( fg [i] ) continue ;
fg [i] = fg [i ^ 1] = 1 ;
int y = to [i] ;
dep [y] = dep [x] + 1 , q.push( y ) ;
fa [y][0] = x , dp [y][0] = w [i] ;
for( R j = 1 ; j <= 20 ; j ++ ){
fa [y][j] = fa [fa [y][j - 1]][j - 1] ;
dp [y][j] = min( dp [y][j - 1] , dp [fa [y][j - 1]][j - 1] ) ;
}
}
}
}
inline int Lca( int x , int y ){
res = 0x3f3f3f3f ;
if( dep [x] < dep [y] ) swap( x , y ) ;
for( R i = 20 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) if( dep [fa [x][i]] >= dep [y] ) res = min( dp [x][i] , res ) , x = fa [x][i] ;
if( x == y ) return x ;
for( R i = 20 ; i >= 0 ; i -- )
if( fa [x][i] != fa [y][i] ) res = min( res , min( dp [x][i] , dp [y][i] ) ) , x = fa [x][i] , y = fa [y][i] ;
res = min( res , min( dp [y][0] , dp [x][0] ) ) ;
return fa [x][0] ;
}
void sc(){
n = read() , m = read() ; memset( Head , -1 , sizeof( Head ) ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ ) x = read() , y = read() , z = read() , Add( x , y , z ) , Add( y , x , z ) ;
}
void work(){
kr() , dep [1] = 1 , bfs() ;
m = read() ;
while( m -- ){
x = read() , y = read() ;
int lca = Lca( x , y ) ;
// printf( "%ld %ld %ld\n" , x , y , lca ) ;
if( lca == 0 ) puts( "-1" ) ;
else printf( "%ld\n" , res ) ;
}
}
signed main(){
sc() ;
work() ;
return 0 ;
}
运输计划
让最大值最小,可以想到二分答案,也就是我们现在已知最小时间,看行不行。
我们先\(Dfs+Lca\)处理出来每个路径的长度(\(W[x]+W[y]-2*W[lca]\),\(W\)是到根节点的距离)
然后我们看哪些路径的时间比\(mid\)大,假设有\(cnt\)个,也就是我们需要找到这些路径的公共边,看去掉这条边行不行。
还是 “难存的情缘” 思想,把边权压成点权。
也就是如果我们对每一条路径经过的所有边染色,全部染色后看哪条路径被染色了\(cnt\)次。
然后我们只需要树上差分,也就是对于每条路径起点终点\(++\),\(LCA-2\)(是因为我们要经过\(lca\ 0\)次)
最后一遍\(dfs\),在回溯到一个节点后看他的值是否等于\(cnt\),去掉之后是否小于\(mid\)即可。
code
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#define mp make_pair
#define R register int
#define int long
#define printf Ruusupuu = printf
int Ruusupuu ;
using namespace std ;
typedef long long L ;
typedef long double D ;
typedef unsigned long long G ;
typedef pair< int , int > PI ;
const int N = 3e5 + 10 ;
inline void swap( int &a , int &b ){ a ^= b , b ^= a , a ^= b ; }
inline int read(){
int w = 0 ; bool fg = 0 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while( ch < '0' || ch > '9' ) fg |= ( ch == '-' ) , ch = getchar() ;
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) w = ( w << 1 ) + ( w << 3 ) + ( ch ^ '0' ) , ch = getchar() ;
return fg ? -w : w ;
}
int n , m , x , y , z , w [N] , fs [N] , sm [N] , fa [N][25] , dep [N] , mid , zt [N] , ttt , unt ;
int fr [N << 1] , to [N << 1] , net [N << 1] , fg [N << 1] , W [N << 1] , head [N] , cnt = 1 ;
#define add() fr [++ cnt] = x , to [cnt] = y , W [cnt] = z , net [cnt] = head [x] , head [x] = cnt
struct RS{ int fr , to , w , ca ; } a [N << 1] ;
inline bool cmp( RS a , RS b ){ return a.w > b.w ; }
void sc(){
n = read() , m = read() , memset( head , -1 , sizeof( head ) ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ ) x = read() , y = read() , z = read() , add() , swap( x , y ) , add() ;
}
void dfs( int x ){
R i = head [x] ; while( ~i && fg [i] ) i = net [i] ;
for( ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
if( fg [i] ) continue ;
fg [i] = fg [i ^ 1] = 1 ;
int y = to [i] ;
w [y] = W [i] , sm [y] = sm [x] + W [i] , dfs( y ) ;
}
}
void bfs(){
queue< int > q ; q.push( 1 ) ;
while( !q.empty() ){
int x = q.front() ; q.pop() ;
for( R i = head [x] ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
int y = to [i] ;
if( fs [y] ) continue ; fs [y] = 1 , q.push( y ) ;
dep [y] = dep [x] + 1 , fa [y][0] = x ;
for( R j = 1 ; j <= 20 ; j ++ ) fa [y][j] = fa [fa [y][j - 1]][j - 1] ;
}
}
}
inline int lca( int x , int y ){
if( dep [x] < dep [y] ) swap( x , y ) ;
for( R i = 20 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) if( dep [fa [x][i]] >= dep [y] ) x = fa [x][i] ;
if( x == y ) return x ;
for( R i = 20 ; i >= 0 ; i -- )
if( fa [x][i] != fa [y][i] ) x = fa [x][i] , y = fa [y][i] ;
return fa [x][0] ;
}
void Dfs( int x ){
R i = head [x] ; while( ~i && fg [i] ) i = net [i] ;
for( ; ~i ; i = net [i] ){
if( fg [i] ) continue ;
fg [i] = fg [i ^ 1] = 1 ;
int y = to [i] ;
Dfs( y ) , zt [x] += zt [y] ;
} if( zt [x] == unt && a [1].w - w [x] <= mid ) ttt = 1 ;
}
inline bool check(){
unt = 0 ;
memset( zt , 0 , sizeof( zt ) ) , memset( fg , 0 , sizeof( fg ) ) ;
for( R i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ )
if( a [i].w <= mid ) break ;
else unt = i , zt [a [i].fr] ++ , zt [a [i].to] ++ , zt [a [i].ca] -= 2 ;
ttt = 0 , Dfs( 1 ) ;
return ttt ;
}
void work(){
dfs( 1 ) , bfs() ;
for( R i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ ){
a [i].fr = read() , a [i].to = read() ;
a [i].ca = lca( a [i].fr , a [i].to ) ;
a [i].w = sm [a [i].fr] + sm [a [i].to] - sm [a [i].ca] * 2 ;
} sort( a + 1 , a + 1 + m , cmp ) ;
int lside = 0 , rside = a [1].w , ans ;
while( lside <= rside ){
mid = ( lside + rside ) >> 1 ;
if( check() ) ans = mid , rside = mid - 1 ;
else lside = mid + 1 ;
} printf( "%ld\n" , ans ) ;
}
signed main(){
sc() ;
work() ;
return 0 ;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号