第八章 多态性
第八章 多态性
一、多态性的各种概念
- 多态的定义:同样的消息被不同类型的对象接收时导致不同的行为
- 多态的类型:重载多态、强制多态、包含多态和参数多态。前两种为专用多态,后两种为通用多态。
- [强制多态]:将一个变元的类型加以变化,以符合一个函数或者操作的要求。(例如:加法运算符在进行浮点数与整型数相加时,首先进行强制转换,把整型数先变为浮点型数再相加的情况)
- [多态的实现]:编译时的多态性(在编译过程中确定了同名操作的具体操作对象)和运行时的多态(在程序运行过程中才动态的确定操作所针对的具体对象)
- [绑定]:指计算机程序自身彼此关联的过程,就是把一个标识符名和一个地址绑定的过程
- [静态绑定]:绑定工作在编译阶段完成的情况。
- [动态绑定]:绑定在程序运行阶段完成的情况。
- [运算符重载]:对已有的运算符赋予多重含义,使同一个运算符作用于不同类型的数据时导致的不同行为。
二、运算符的重载实验
1.成员函数形式的重载
【复数的加减法】
/*例题8-1*//*复数的加减法*/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class complex {
private:
double real; //负数实部
double imag; //实数虚部
public:
complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0) :real(r), imag(i) {}
complex operator +(const complex& c2) const;
complex operator -(const complex& c2) const;
void display() const {
cout << "(" << real << "," << imag << ")" << endl;
}
};
complex complex ::operator +(const complex& c2) const {
return complex(real + c2.real, imag + c2.imag);
}
complex complex ::operator -(const complex& c2) const {
return complex(real - c2.real, imag - c2.imag);
}
int main() {
complex c1(5, 4), c2(2, 10), c3;
cout << "c1="; c1.display();
cout << "c2="; c2.display();
c3 = c2 - c1;
cout << "c3=c2-c1="; c3.display();
c3 = c2 + c1;
cout << "c3=c2+c1="; c3.display();
}
运行截图:
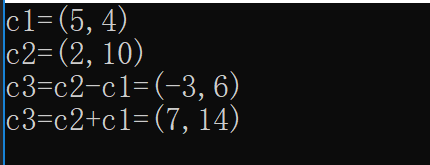
2.非成员函数形式的重载(借助friend)
【前置++和后置++的重载】
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
private:
float x, y;
public:
Point(float x, float y) {
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void show() {
cout << "point=(" << x << "," << y << ")" << endl;
}
friend Point operator ++(Point p); //前置++
friend Point operator ++(Point &p,int); //后置++
};
Point operator++(Point p) {
p.x++;
p.y++;
return p;
}
Point operator++(Point &p,int) {
Point old = p;
p.x++;
p.y++;
return old;
}
int main() {
Point p(2, 1.5);
Point* pt = &p;
p.show();
cout << "run p++: ";
(p++).show();
cout << "run ++p: ";
(++p).show();
return 0;
}
运行截图:
【将==重载为判断两个字符串相等】
/*附加题*//*重载 ==,判断两个字符串是否相等*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
class My_string{
public:
char* ch;
My_string(char *ch):ch(ch){} //构造函数
int operator ==(My_string s2)const; //重载 ==
};
int My_string::operator==(My_string s2)const {
if (strcmp(ch, s2.ch) == 0)return 1;
else return 0;
}
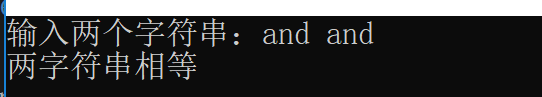
int main() {
char *op1=new char[100], *op2=new char[100];
cout << "输入两个字符串:";
cin >>op1>>op2;
assert(strlen(op1) <= 100 && strlen(op2) <= 100); //防止字符数组越界
My_string a(op1);
My_string b(op2);
if (a.operator==(b)) {
cout << "两字符串相等" << endl;
}
else cout << "两字符串不等" << endl;
delete[] op1; //删除字符串
delete[] op2;
return 0;
}
运行截图:

三、虚函数的各种概念及实验验证
1.相关概念
- [一般虚函数的声明语法]:
vitual 函数类型 函数名 (形参表);- 虚函数声明只能出现在类定义中的函数原型声明中,而不能在成员函数实现的时候。
- [运行过程中多态需要满足的条件]:
①满足赋值兼容原则
②声明虚函数
③由成员函数来调用或者是通过指针、引用来访问虚函数 - ②该函数是否与基类的虚函数有相同的参数个数及相同的对应参数类型
③该函数是否与基类的虚函数有相同的返回值或者满足赋值兼容性规则的指针、引用类型的返回值 - 只有通过基类的指针或者引用调用虚函数时,才会发生动态绑定
- 在重写继承来的虚函数时,如果函数有默认形参值,不要重新定义不同的值。原因是:虽然虚函数是动态绑定的,但默认形参值是静态绑定的。通过一个指向派生类的基类指针,可以访问到派生类的虚函数,但默认形参值只能来自基类的定义
- [虚析构函数]:析构函数设置为虚函数后,在使用指针引用时会实现动态绑定,实现运行时的多态,保证使用基类类型的指针就可以调用适当的析构函数针对不同的对象进行清理工作
- [纯虚函数的形式]:
vitual 函数类型 函数名 (参数表) = 0;- 声明为纯虚函数之后,基类中就可以不再给出函数的实现部分,纯虚函数的函数体由派生类给出。
- [抽象类]:带有纯虚函数的类是抽象类。/抽象类不能实例化。
2.纯虚函数的应用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define pi 3.14
class Shape {
public:
virtual float getArea() = 0; //纯虚函数
virtual float getPerim() = 0; //纯虚函数
};
class Circle :public Shape {
private:
float r;
public:
Circle(float r) { this->r = r; }
float getArea() {
return (float)pi * r * r;
}
float getPerim() {
return (float)pi * 2 * r;
}
void show() {
cout << "Circle:" << endl;
cout << "r=" << r << endl;
}
};
class Rectangle :public Shape {
private:
float width, height;
public:
Rectangle(float w, float h) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
float getArea() {
return width * height;
}
float getPerim() {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
void show() {
cout << "Rectangle:" << endl;
cout << "w=" << width << " h=" << height << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Circle circle(2);
Rectangle rectangle(3, 4);
circle.show();
cout << "area = " << circle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << circle.getPerim() << endl << endl;
rectangle.show();
cout << "area = " << rectangle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << rectangle.getPerim() << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图:

3.有无虚函数的区别
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass {
public:
virtual void fun1() { cout << "BaseClass.fun1" << endl; }
void fun2() { cout << "BaseClass.fun2" << endl; }
};
class Derived :public BaseClass {
public:
void fun1() { cout << "Derived.fun1" << endl; }
void fun2() { cout << "Derived.fun2" << endl; }
};
int main() {
Derived d;
Derived* derived = &d;
BaseClass* base = &d;
cout << "通过base指针调用:" << endl;
base->fun1(); base->fun2();
cout <<endl<< "通过derived指针调用:" << endl;
derived->fun1(); derived->fun2();
return 0;
}
运行截图:

四、课后8-11题目解析
题目描述
在此前基础上,通过继承Rectangle类得到Square。在Shape中增加一个函数int getVertexCount() const用来获得当前顶点的个数,并使用以下几个方法
(1)使用dynamic_cast实现Shape::getVertexCount函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define pi 3.14
class Shape {
public:
virtual float getArea() = 0;
virtual float getPerim() = 0;
virtual int getVertexCount(Shape *s)const;
};
class Circle :public Shape {
private:
float r;
public:
int VertexCount = 0;
Circle(float r) { this->r = r; }
float getArea() {
return (float)pi * r * r;
}
float getPerim() {
return (float)pi * 2 * r;
}
void show() {
cout << "Circle:" << endl;
cout << "r=" << r << endl;
}
};
class Rectangle :public Shape {
private:
float width, height;
public:
int VertexCount = 4;
Rectangle(float w, float h) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
float getArea() {
return width * height;
}
float getPerim() {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
void show() {
cout << "Rectangle:" << endl;
cout << "w=" << width << " h=" << height << endl;
}
};
class Square :public Rectangle {
public:
int VertexCount = 4;
Square(float len) :Rectangle(len, len) { length = len; }
float getArea() {
return length * length;
}
float getPerim() {
return 4 * length;
}
void show() {
cout << "Square:" << endl;
cout << "length=" << length << endl;
}
private:
float length;
};
//使用dynamic_cast的方式实现求顶点函数
int Shape::getVertexCount(Shape *s)const {
Rectangle *r=dynamic_cast<Rectangle*>(s);
Circle* c = dynamic_cast<Circle*>(s);
Square* sq = dynamic_cast<Square*>(s);
if (r) //如果可以转换
return r->VertexCount;
if (c)
return c->VertexCount ;
if (sq)
return sq->VertexCount;
}
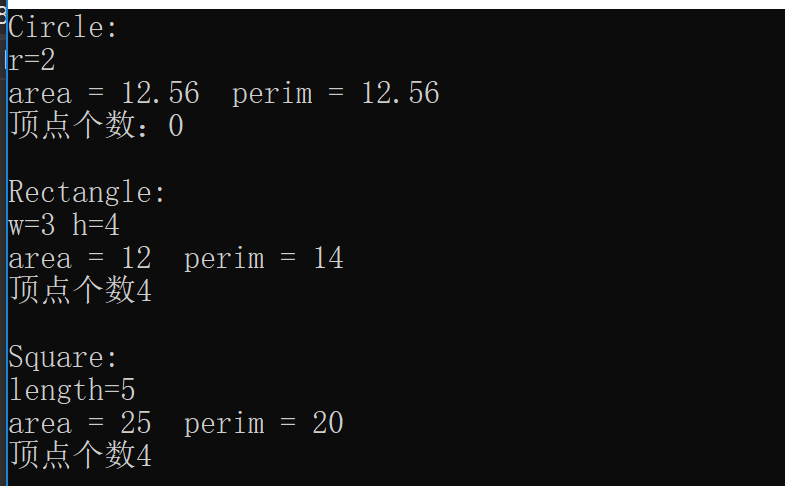
int main() {
Circle circle(2);
Rectangle rectangle(3, 4);
Square square(5);
circle.show(); //圆
cout << "area = " << circle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << circle.getPerim() << endl ;
cout<<"顶点个数:"<<circle.getVertexCount(&circle)<< endl<<endl;
rectangle.show(); //长方形
cout << "area = " << rectangle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << rectangle.getPerim() << endl;
cout <<"顶点个数"<< rectangle.getVertexCount(&rectangle) << endl<<endl;
square.show(); //正方形
cout << "area = " << square.getArea()
<< " perim = " << square.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数" << square.getVertexCount(&square) << endl;
return 0;
}
(2)使用typeid实现Shape::getVertexCount函数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<typeinfo>
using namespace std;
#define pi 3.14
class Shape {
public:
virtual float getArea() = 0;
virtual float getPerim() = 0;
int getVertexCount(Shape&s)const;
};
class Circle :public Shape {
private:
float r;
public:
Circle(float r) { this->r = r; }
float getArea() {
return (float)pi * r * r;
}
float getPerim() {
return (float)pi * 2 * r;
}
void show() {
cout << "Circle:" << endl;
cout << "r=" << r << endl;
}
};
class Rectangle :public Shape {
private:
float width, height;
public:
Rectangle(float w, float h) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
float getArea() {
return width * height;
}
float getPerim() {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
void show() {
cout << "Rectangle:" << endl;
cout << "w=" << width << " h=" << height << endl;
}
};
class Square :public Rectangle {
public:
Square(float len) :Rectangle(len, len) { length = len; }
float getArea() {
return length * length;
}
float getPerim() {
return 4 * length;
}
void show() {
cout << "Square:" << endl;
cout << "length=" << length << endl;
}
private:
float length;
};
int Shape::getVertexCount(Shape& s)const {
if (!strcmp(typeid(s).name(), "class Circle"))return 0;
else if (!strcmp(typeid(s).name(), "class Rectangle") || !strcmp(typeid(s).name(), "class Square"))return 4;
else return 1;
}
int main() {
Circle circle(2);
Rectangle rectangle(3, 4);
Square square(5);
circle.show(); //圆
cout << "area = " << circle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << circle.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数:" << circle.getVertexCount(circle) << endl << endl;
rectangle.show(); //长方形
cout << "area = " << rectangle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << rectangle.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数" << rectangle.getVertexCount(rectangle) << endl << endl;
square.show(); //正方形
cout << "area = " << square.getArea()
<< " perim = " << square.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数" << square.getVertexCount(square) << endl;
return 0;
}
(3)将Shape::getVertexCount函数声明为虚函数,在派生类中给出具体实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define pi 3.14
class Shape {
public:
virtual float getArea() = 0;
virtual float getPerim() = 0;
virtual int getVertexCount(Shape* s)const = 0;
};
class Circle :public Shape {
private:
float r;
public:
int VertexCount = 0;
Circle(float r) { this->r = r; }
float getArea() {
return (float)pi * r * r;
}
float getPerim() {
return (float)pi * 2 * r;
}
void show() {
cout << "Circle:" << endl;
cout << "r=" << r << endl;
}
int getVertexCount(Shape* s)const {
return VertexCount;
}
};
class Rectangle :public Shape {
private:
float width, height;
public:
int VertexCount = 4;
Rectangle(float w, float h) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
float getArea() {
return width * height;
}
float getPerim() {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
void show() {
cout << "Rectangle:" << endl;
cout << "w=" << width << " h=" << height << endl;
}
int getVertexCount(Shape* s)const {
return VertexCount;
}
};
class Square :public Rectangle {
public:
int VertexCount = 4;
Square(float len) :Rectangle(len, len) { length = len; }
float getArea() {
return length * length;
}
float getPerim() {
return 4 * length;
}
void show() {
cout << "Square:" << endl;
cout << "length=" << length << endl;
}
int getVertexCount(Shape* s)const {
return VertexCount;
}
private:
float length;
};
int main() {
Circle circle(2);
Rectangle rectangle(3, 4);
Square square(5);
circle.show(); //圆
cout << "area = " << circle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << circle.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数:" << circle.getVertexCount(&circle) << endl << endl;
rectangle.show(); //长方形
cout << "area = " << rectangle.getArea()
<< " perim = " << rectangle.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数" << rectangle.getVertexCount(&rectangle) << endl << endl;
square.show(); //正方形
cout << "area = " << square.getArea()
<< " perim = " << square.getPerim() << endl;
cout << "顶点个数" << square.getVertexCount(&square) << endl;
return 0;
}
运行截图

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号