浅谈随机化算法
随机函数
应该很简单,介绍三个最常用的。
-
rand(),会返回一个在 \([0,r]\) 内的随机整数。\(r\) 为RAND_MAX,标准库中的宏,在 Windows 下取 \(2^{15}-1\),在 Linux 下取 \(2^{31}-1\)。rand()效率较低。可使用
srand(seed)做种。配合time(0)。 -
mt19937,可用于快速生成高质量的在 \(\left[0,2^{32}-1\right]\) 范围内的随机整数,返回值为unsigned int。定义方式:
#include<random> mt19937 Rand(time(0));之后直接调用
Rand()生成整数即可,定义时填入的time(0)是为了做种。关于
mt19937_64mt19937_64是 $64$ 位的mt19937的实现,可生成 $\left[0,2^{64}-1\right]$ 范围内的整数,返回unsigned long long。 -
shuffle,用于随机打乱序列,时间复杂度 \(\mathcal O(n)\)。shuffle(a+1,a+n+1,Rand);其中
Rand为随机数生成函数,推荐mt19937。
爬山算法
也称「梯度下降」。
考虑当前状态 \(x\),\(x\) 可以转移到一个新的状态 \(y\),如果说 \(y\) 的答案优于 \(x\),则保留 \(y\),否则保持 \(x\) 不变。其实爬山算法就是贪心算法,最终会找到一个局部最优解。
因此当且仅当原问题单峰时,爬山算法可以保证得到正解。而你使用爬山算法,往往是因为你不会利用单峰的性质。
爬山算法引入温度参数,用于确定单次状态偏移量的大小。温度参数逐渐下降,偏移量也逐渐变小,最终趋近于最优解。降温参数接近于 \(1\)。具体而言,设温度参数 \(t\)、降温参数 \(d\),则每次更新状态后令 \(t\leftarrow dt\)。同时,根据 \(t\) 的大小来确定偏移量的大小。
luogu P1337 [JSOI2004] 平衡点 / 吊打XXX
即求 \(n\) 个点的带权类费马点。
几何题,或者物理题。可以使用力的分解、正交分解或势能分析来解决。
计算合力方向,运用爬山算法向该方向偏移即可。
调参与卡时
爬山算法在降温参数过大时,可能会因为运行次数过多而超时。这时就需要修改降温参数以使得程序能够在限定时间内完成,即调参。
但是在有些时候,你可以通过在快要超时时输出当前最优解,称之为卡时。
注意:降温参数过低可能导致爬山算法答案错误。
参考代码
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
constexpr const int N=1000;
constexpr const double eps=1e-6;
struct node{
int x,y,w;
}a[N+1];
int n;
double dist(pair<double,double>a,pair<double,double>b){
return sqrt((a.first-b.first)*(a.first-b.first)+(a.second-b.second)*(a.second-b.second));
}
void move(double &x0,double &y0,double op){
double deltaX=0,deltaY=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
double d=dist({x0,y0},{a[i].x,a[i].y});
if(d==0){
continue;
}
deltaX+=a[i].w*(a[i].x-x0)/d;
deltaY+=a[i].w*(a[i].y-y0)/d;
}
double d=sqrt(deltaX*deltaX+deltaY*deltaY);
if(d==0){
return;
}
x0+=op*deltaX/d;
y0+=op*deltaY/d;
}
int main(){
/*freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
freopen("test.out","w",stdout);*/
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y>>a[i].w;
}
double x0=0,y0=0,op=10000*sqrt(2);
while(op>eps){
move(x0,y0,op);
op*=0.9;
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<<x0<<' '<<y0<<'\n';
cout.flush();
/*fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);*/
return 0;
}
模拟退火
Simulated Annealing,也称 SA 算法。
考虑爬山算法可能会陷入某个局部最优解中无法跳出,因此便有了模拟退火。模拟退火会以一定概率跳出局部最优解,从而寻找可能的全局最优解。
关于退火
退火是一种金属热处理工艺,指的是将金属缓慢加热到一定温度,保持足够时间,然后以适宜速度冷却。目的是降低硬度,改善切削加工性;消除残余应力,稳定尺寸,减少变形与裂纹倾向;细化晶粒,调整组织,消除组织缺陷。准确的说,退火是一种对材料的热处理工艺,包括金属材料、非金属材料。而且新材料的退火目的也与传统金属退火存在异同。
显然这一段都没什么用。
模拟退火引入温度参数,模拟金属退火的过程。虽然我并不觉得有什么联系。
-
对于当前状态 \(s\) 的新状态 \(s'\),\(s'\) 更优显然 \(s'\) 更优,应当被接受为可能的全局最优解,转移到 \(s'\)。
-
否则设温度参数 \(t\),答案的差为 \(\Delta\geq0\),则转移到 \(s'\) 的概率为:
\[\mathrm{e}^{-\frac{\Delta}t} \]
具体而言,设温度参数 \(t\) 初始为极大值,降温参数 \(d\) 接近于 \(1\)。每次更新状态后令 \(t\leftarrow dt\),\(t\) 足够小时结束模拟退火。显然,\(\Delta\) 一定,\(t\) 减小时,\(\mathrm e^{-\frac\Delta t}\) 会减小。
因此初期模拟退火偏移程度较大,后期较平缓、稳定。
但是,模拟退火的新状态寻找是随机的,新状态偏移量与 \(t\) 无关,这与爬山算法不同。
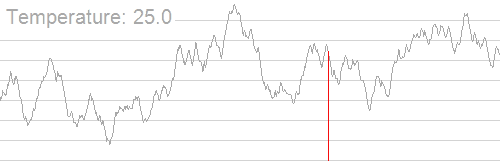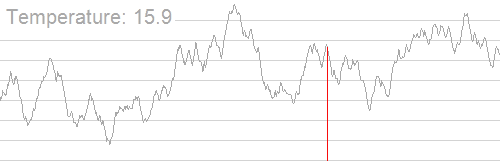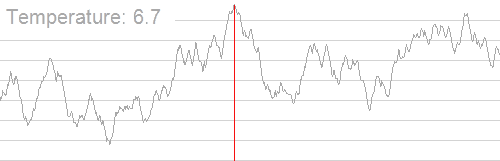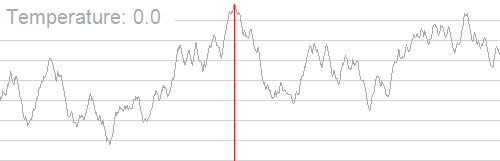
一张著名的图,展示模拟退火的过程:
luogu P2210 [USACO13OPEN] Haywire B
给定 \(a_{i,1},a_{i,2},a_{i,3}(1\leq i\leq n,n\leq12)\),将 \(a\) 进行全排列,设 \(p_i\) 为 \(a_i\) 的位置,求下式的最小值:
\[\dfrac12\sum_{i=1}^n\left(\vert p_i-p_{a_{i,1}}\vert+\vert p_i-p_{a_{i,2}}\vert+\vert p_i-p_{a_{i,3}}\vert\right) \]
显然 \(n\leq11\) 时都可以 \(\mathcal O(n\cdot n!)\) 完成,但 \(n=12\) 时就需要跑约 \(\text{14s}\)。考虑一些乱搞做法,考虑模拟退火。
那么每次就随机选择两个点交换,计算答案即可。
同时,模拟退火的退火次数越多,正确率越高。因此常配合卡时来尽可能高的提升正确率。(同样需要调参)
参考代码
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<random>
using namespace std;
constexpr const int N=12;
constexpr const double eps=1e-6;
mt19937 Rand(time(0));
int n,a[N+1][4],p[N+1];
int calc(){
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans+=abs(p[i]-p[a[i][1]])+abs(p[i]-p[a[i][2]])+abs(p[i]-p[a[i][3]]);
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
/*freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
freopen("test.out","w",stdout);*/
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i][1]>>a[i][2]>>a[i][3];
p[i]=i;
}
int ans=calc();
while(clock()<=0.95*CLOCKS_PER_SEC){
int t=1000,d=0.985;
while(t>=eps){
t*=d;
int x=Rand()%n+1,y=Rand()%n+1;
swap(p[x],p[y]);
int pl=calc();
if(pl<=ans){
ans=pl;
}else{
if(Rand()/((1ll<<32)-1.0)<=exp(-1.0*(pl-ans)/t)){
continue;
}else{
swap(p[x],p[y]);
}
}
}
}
ans>>=1;
cout<<ans<<'\n';
cout.flush();
/*fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);*/
return 0;
}
luogu P3959 [NOIP 2017 提高组] 宝藏
当然可以写 \(\mathcal O\left(n3^n\right),\mathcal O\left(n^23^n\right)\) 的状压 DP,但是模拟退火显然更为简单。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号