【学校训练记录】十月个人训练赛1题解
A
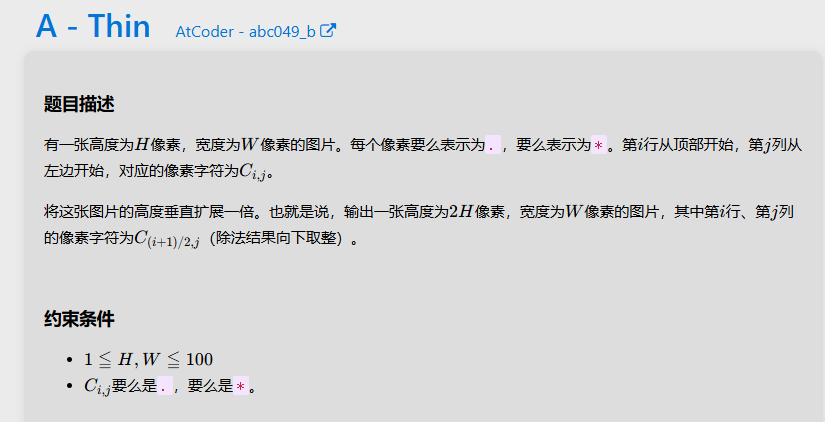
只需按照题目意思扩展h倍即可,先记录初始字符,打印时扩展为2*h根据题目公式打印
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
int n;
int a[MAXN];
char mp[105][105];
signed main(){
int h, w;
cin >> h >> w;
for(int i = 1; i <= h; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= w; j++)
cin >> mp[i][j];
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * h; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= w; j++)
cout << mp[(i+1) / 2][j];
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B
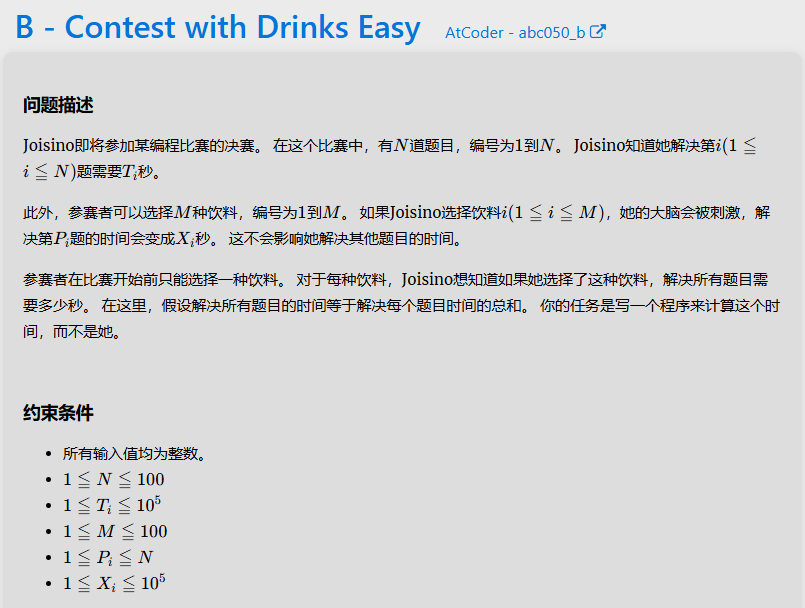
因为饮料只会改变一道题的解题时间,可以先用sum预处理记录未喝饮料的初始总时间(数据量小,不预处理直接暴力求也可),再根据每喝的一瓶饮料改变的时间进行增减即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
int n, m;
int a[MAXN];
signed main(){
cin >> n;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
sum += a[i];
}
cin >> m;
while(m--){
int i, t;
cin >> i >> t;
cout << sum - a[i] + t << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C
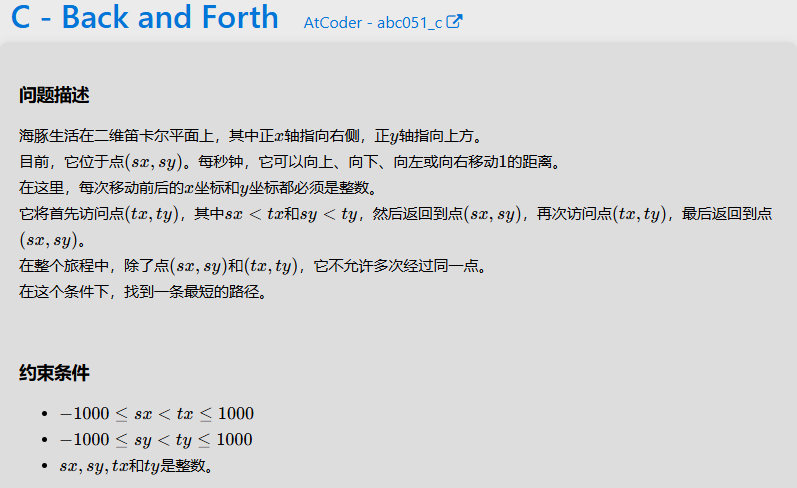
观察到目标点始终位于起始点右上角,所以就是简单的绕圈(可以画个图思考一下),纯模拟。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
int sx, sy, tx, ty;
signed main(){
cin >> sx >> sy >> tx >> ty;
int x = tx - sx;
int y = ty - sy;
for(int i = 1; i <= y; i++) cout << "U";
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++) cout << "R";
for(int i = 1; i <= y; i++) cout << "D";
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++) cout << "L";
cout << "L";
for(int i = 1; i <= y + 1; i++) cout << "U";
for(int i = 1; i <= x + 1; i++) cout << "R";
cout << "D";
cout << "R";
for(int i = 1; i <= y + 1; i++) cout << "D";
for(int i = 1; i <= x + 1; i++) cout << "L";
cout << "U";
return 0;
}
D
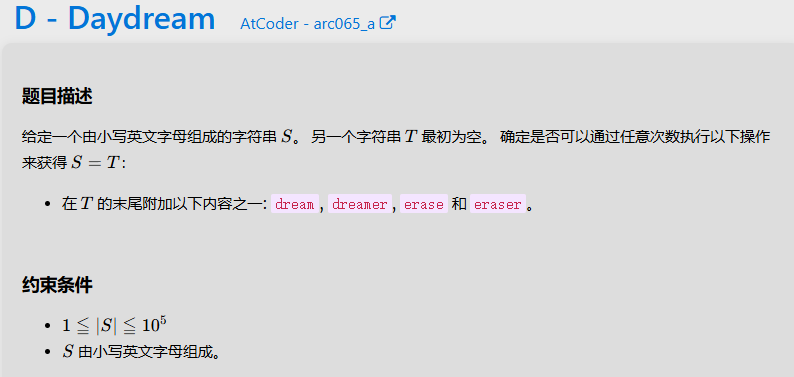
字符串模拟,考虑从左到右遍历字符串S,如果中间有不满足构成题目要求的四个单词时,即为T不能构成S。每次循环考虑一个单词,
如果不是以d或者e为头的单词必定不能构成。另外要注意一个细节,dream后的er不单是能构成dreamer,也有可能后面的字母补上凑成dreamerase,
因此需要特判dream后的er,如果能构成erase就构成,不能就构成dreamer再进行判断。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
signed main(){
string s;
string s1 = "dream", s2 = "dreamer", s3 = "erase", s4 = "eraser";
cin >> s;
int f = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
if(s[i] != 'd' && s[i] != 'e'){
f = 1;
break;
}//如果接下来单词不是d和e开头即错误,直接break就好
if(s[i] == 'd'){
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++, i++)//判断是否是dream
if(s[i] != s1[j]){
f = 1;
break;
}
if(s[i] == 'e' && s[i+1] == 'r'){//特判dream后的er能否构成erase,不能的话就将er给dream
if(s[i+2] != 'a') i = i + 1; //不能构成,指针回溯到‘r’(即当作dreamer)
else i--;//能构成则指针回溯到‘m’,在下一轮循环中判断是否构成erase
} else i--;//在判断是否是dream时指针指向‘m’下个字符,记得回溯
}
if(s[i] == 'e'){
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++, i++)//判断是否是erase
if(s[i] != s3[j]){
f = 1;
break;
}
if(s[i] != 'r') i--;//不能构成eraser,将指针回溯到‘e’
}
if(f) break;
}
if(f) cout << "NO" << endl;
else cout << "YES" << endl;
return 0;
}
E
根据排队的对称性,在左右两边位置相同的人得到的数字必然是相同的,即1-n/2与n/2+1-n求出的绝对值差相同,
判断报数毛不矛盾:报数一定是俩俩相对的,并且不同数字的总数为n/2,如果n是奇数,则最中间那个人数字一定为0,并且报数的奇偶性不能与n一致(不然绝对值之差得不到这个位数)。
利用哈希表set算不同数的数量判断是否等于n/2.剩下排序总数自然就是排列组合问题了,每个位置有两种情况,只需考虑1~n/2,另一半会固定。所以是2的n/2幂次,数值较大需要用快速幂求模。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
unordered_set<int> st;
int qPOW(int a, int b){
int res = 1, base = a;
while(b){
if(b & 1)
res = (res * base) % MOD;
b >>= 1;
base = base * base % MOD;
}
return res;
}
signed main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
int f = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x;
cin >> x;
if(n % 2 == x % 2) f = 1;
if(n % 2 == 1 && x == 0 && st.count(0) == 1) f = 1; //奇数排队中不可能有两个0
st.insert(x);
}
if(n % 2 == 1 && st.count(0) == 0) f = 1; //奇数排队中如果没0则矛盾
if(f || st.size() != (n + 1) / 2){
cout << "0" << endl;
return 0;
}
if(n % 2) cout << qPOW(2, st.size() - 1) << endl;
else cout << qPOW(2, st.size()) << endl;
return 0;
}
F

开两个并查集记录哪些城市是道路连通,哪些城市是铁路连通。如果两个城市的道路父节点与铁路父节点一致,那么城市数量就+1,
并且这两个城市的答案一致(因为第三个城市能到达第二个城市也就能到达第一个城市),利用map的特性记录这两个父节点相通的个数即为最后的答案。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 200005;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
int n, k, l, a, b;
map<pair<int, int>, int> mp;
int f1[MAXN], f2[MAXN];
int find(int x, int *fa){
if(fa[x] == x) return x;
return fa[x] = find(fa[x], fa);
}
void Union(int a, int b, int *fa){
a = find(a, fa);
b = find(b, fa);
if(a != b) fa[a] = b;
}
signed main(){
cin >> n >> k >> l;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
f1[i] = i;
f2[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
cin >> a >> b;
Union(a, b, f1);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= l; i++){
cin >> a >> b;
Union(a, b, f2);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
mp[make_pair(find(i, f1), find(i, f2))]++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cout << mp[make_pair(find(i, f1), find(i, f2))];
if(i != n) cout << " ";
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号