PTA第三次BLOG
一、前言
-
PTA题目集6:刚开始见到这个题目集的时候,发现这个题目集实质上并不是难度高,因为它不像之前的四边形,五边形一样要求你去构造正确的算法,求得一个正确的结果,对于电信计费的情况,其计算十分的简单,无非就是计算每条通话记录的通话时间,然后根据收费规则求得其费用,然后求和即可。但我认为其难度也不小,主要难点在于这是一个系统,也就意味着会有许多的类,如何构建安排处理好各个类成为了首要的难题。即便老师一开始就给了类图,但当拿到类图的时候也看了好一段时间才逐渐理解类图中各个类的构建及其关系。更不用说如果要自己从零开始构建类的关系的话,会有多难于起步了。
-
PTA题目集7:其同样是电信计费的题目,如果说之前的题目集合6是让我们初步构建起来电信计费系列的框架,并且理解各个类之间的关系和联系的话。那么这次题目集应该算是自己在初步了解了这个系统之后,考验自己对于这个系统的拓展能力。包括如何添加手机,构建新的收费类别,怎么处理与之前的关系等等。这里并没有像第一次那样给出明明白白的类图,而是要自己根据自己的理解,练习出一定的拓展能力。
-
PTA题目集8:题目集8其实就比较的简单了,经过了题目集7后,其实对于整个系统的构造已经有了比较完整的理解,而在题目集7中也完成了对于系统拓展,所以题目集8其实已经算是小case了,同样是拓展,那么构造类以及处理关系已经有了一定的经验,主要步骤也是构建新的收费方式,改正则,由于没有那么多的种类,因此我认为在电信系列中,这个题目集算是最简单的了。
二、设计与分析
PTA题目集6-电信计费系列1-座机计费
-
题目内容
实现一个简单的电信计费程序:
假设南昌市电信分公司针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式:
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
南昌市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码除区号外由是7-8位数字组成。
本题只考虑计费类型0-座机计费,电信系列2、3题会逐步增加计费类型。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。 -
题目设计
显然,对于输入的数据,有数据属于开户,有的数据属于添加通话记录。对于输入的数据属于开户:
①首先肯定是要通过正则表达式来判断是否手机号符合规则
②对于正确的数据,那么将其提取创建为一个用户,添加到用户列表中对于输入的数据属于通话记录:
①首先也还是要通过正则表达式来判断通话双方,时间等是否规范
②提取通话的双方,包括其地区码,通话时间,然后根据这些创建一个新的通话记录
③搜索用户列表,根据通话的双发,将该通话记录插入到对应用户的拨打/接听的记录中去对于座机的三个收费模式:
可以构建分别构建三个类,标明为座机在室内,在省内,在国内的通话收费标准
并将其添加到收费规则列表中去 -
完整代码
import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<String> inputList=Input.getAllInput(); inputList=Input.deleteCoincide(inputList); Format.trueInputFormat(inputList); Handle.userRecords(inputList); } } class Handle{ public static void userRecords(ArrayList<String> inputList){ ArrayList<User> users=Input.initUser(inputList); Collections.sort(users); for(User user:users){ System.out.println(user.number+" "+Format.Format_Str(user.calCost(),2)+" "+Format.Format_Str(user.calBalance(),2)); } } } class Input{ public static ArrayList<String> getAllInput(){ ArrayList<String> inputList=new ArrayList<String>(); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String info=input.nextLine(); while (!info.equals("end")) { inputList.add(info); info=input.nextLine(); } return inputList; } public static ArrayList<String> deleteCoincide(ArrayList<String> inputList){ ArrayList<String> newList=new ArrayList<String>(); for(String s:inputList){ if(!Input.isExist(s,newList)) newList.add(s); } return newList; } public static boolean isExist(String s,ArrayList<String> sList){ for(String input:sList){ if(input.equals(s)) return true; } return false; } public static ArrayList<User> initUser(ArrayList<String> inputList){ ArrayList<User> users=new ArrayList<User>(); for(String s:inputList){ if(s.charAt(0)=='u'){ User newUser=new User(s); users.add(newUser); } else if(s.charAt(0)=='t'){ CallRecord callRecord=new CallRecord(s); Input.addRecord(users,callRecord); } } return users; } private static void addRecord(ArrayList<User> users, CallRecord callRecord) { for (User user:users){ if(user.number.equals(callRecord.callingNumber)){ if(callRecord.callingAddressAreaCode.equals(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode)) user.userRecords.addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); else if(Input.areaCodeInProvince(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode)) user.userRecords.addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord); else user.userRecords.addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord); } if(user.number.equals(callRecord.answerNumber)){ if(callRecord.callingAddressAreaCode.equals(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode)) user.userRecords.addAnswerInCityRecords(callRecord); else if(Input.areaCodeInProvince(callRecord.callingAddressAreaCode)) user.userRecords.addAnswerInProvinceRecords(callRecord); else user.userRecords.addAnswerInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } public static boolean areaCodeInProvince(String areaCode){ //0790~0799以及0701 String[] AreaCode=new String[]{"0790","0791","0792","0793","0794","0795","0796","0797","0798","0799","0701"}; for(int i=0;i<AreaCode.length;i++){ if(areaCode.equals(AreaCode[i])) return true; } return false; } } class Format { public static double Format_Str(double s,int num) { String s1=String.format("%."+num+"f",s); s=Double.parseDouble(s1); return s; } public static void trueInputFormat(ArrayList<String> inputList){ for(int i=0;i<inputList.size();){ String s=inputList.get(i); if(!s.matches("[u]-[0][7]([9][0-9]|[0][1])[0-9]{7,8} [0-3]")==true&&!s.matches("^t\\-0\\d{9,11}\\s0\\d{9,11}((\\s\\d{4}\\.([1-9]|([1]{1}[0-2]{1}))\\.([1-9]|([1-2]{1}[0-9]{1})|3[0-1])\\s(([0-1][0-9])|(2[0-3]))\\:([0-5][0-9])\\:([0-5][0-9])){2})")==true){ inputList.remove(i); } else i++; } } } //用户类 class User implements Comparable<User>{ String number; double balance; UserRecords userRecords=new UserRecords();//存储通话记录 ChargeMode chargeMode; public User(String user){ String[] s=user.split("[-\\s]"); this.number=s[1]; this.chargeMode=new LandlinePhoneCharging(); this.balance=100; } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public double calBalance(){ this.balance=this.balance-this.calCost()-this.chargeMode.getMonthlyRent(); return this.balance; } public double calCost(){ return this.chargeMode.calCost(this.userRecords); } @Override public int compareTo(User user) { long a=Long.parseLong(this.number); long b=Long.parseLong(user.number); if(a-b<0) return -1; else return 1; } } //通话记录类 class UserRecords{ ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>();//在市内拨打 ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>();//在省内拨打 ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>();//在国内拨打 ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>();//在市内接听 ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>();//在省内接听 ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>();//在国内接听 public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } } abstract class communicationRecord{ String callingNumber; String answerNumber; public communicationRecord(String Record){ String[] s=Record.split("[-\\s]"); this.callingNumber=s[1]; this.answerNumber=s[2]; } public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumber() { return answerNumber; } public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber) { this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } } class CallRecord extends communicationRecord{ Date startTime; Date endTime; public CallRecord(String callRecord){ super(callRecord); DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); String[] s=callRecord.split("[-\\s]"); try { this.startTime=df.parse(s[3]+" "+s[4]); this.endTime=df.parse(s[5]+" "+s[6]); } catch (ParseException e){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } this.callingAddressAreaCode=s[1].substring(0,4); this.answerAddressAreaCode=s[2].substring(0,4); } String callingAddressAreaCode; String answerAddressAreaCode; } abstract class ChargeMode{ ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules=new ArrayList<ChargeRule>(); public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getChargeRules() { return chargeRules; } public void setChargeRules(ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules) { this.chargeRules = chargeRules; } public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); public abstract double getMonthlyRent(); } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double mothlyRent=20; public LandlinePhoneCharging(){ this.chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); this.chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); this.chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double cost=0; cost+=this.chargeRules.get(0).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()); cost+=this.chargeRules.get(1).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()); cost+=this.chargeRules.get(2).calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()); return cost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return this.mothlyRent; } } abstract class ChargeRule{ public abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords); } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule{ } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ long sec=(callRecord.endTime.getTime()-callRecord.startTime.getTime())/1000; min=sec/60; if(sec%60!=0) min+=1; cost+=0.1*min; } return cost; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ long sec=(callRecord.endTime.getTime()-callRecord.startTime.getTime())/1000; min=sec/60; if(sec%60!=0) min+=1; cost+=0.3*min; } return cost; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ long sec=(callRecord.endTime.getTime()-callRecord.startTime.getTime())/1000; min=sec/60; if(sec%60!=0) min+=1; cost+=0.6*min; } return cost; } } -
SourceMonitor分析
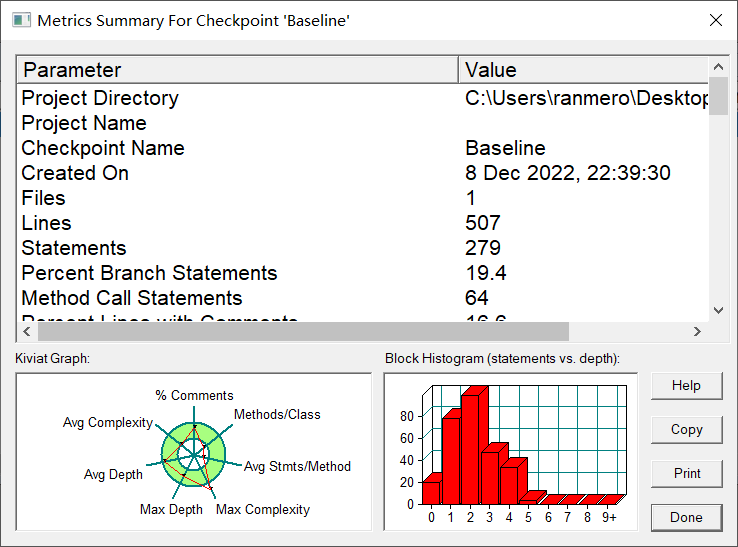
Kiviat Graph分析
①注释分析:由于依照类图构建的代码,写了部分注释帮助记忆
②每个类中方法数分析:每个类里面的方法比较的少,因为题目只需要实现计费,不像多边形这样的,并不需要太多其他的方法。
③每个方法中有效代码行数分析:每个方法中的有效语句较少,比较的简短,有些可能一个方法只有一个return(点名get语句)
④最大圈复杂度分析:最大圈复杂度比较高,因为在插入通话记录时使用了较多循环。
⑤最大深度分析:最大深度比较理想
⑥平均深度分析:平均深度也比较理想,但也可以适当优化。
⑦平均圈复杂度分析:平均圈复杂度比较低,说明程序设计的还是比较合理的。Block Histogram分析
深度多数集中在1-3,这也印证了之前的最大深度以及平均深度。
PTA题目集7-电信计费系列2-手机+座机计费
-
题目内容
实现南昌市电信分公司的计费程序,假设该公司针对手机和座机用户分别采取了两种计费方案,分别如下:
1、针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式(与电信计费系列1内容相同):
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
假设本市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
2、针对手机用户采用实时计费方式:
月租15元,市内省内接电话均免费,市内拨打市内电话0.1元/分钟,市内拨打省内电话0.2元/分钟,市内拨打省外电话0.3元/分钟,省内漫游打电话0.3元/分钟,省外漫游接听0.3元/分钟,省外漫游拨打0.6元/分钟;
注:被叫电话属于市内、省内还是国内由被叫电话的接听地点区号决定,比如以下案例中,南昌市手机用户13307912264在区号为020的广州接听了电话,主叫号码应被计算为拨打了一个省外长途,同时,手机用户13307912264也要被计算省外接听漫游费:
u-13307912264 1
t-079186330022 13307912264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市用户开户的信息,每行一个用户,含手机和座机用户
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐)
例如:u-079186300001 0
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题在电信计费系列1基础上增加类型1-手机实时计费。
手机设置0或者座机设置成1,此种错误可不做判断。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的通讯信息,通讯信息格式:
座机呼叫座机:t-主叫号码 接听号码 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 058686330022 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
以上四项内容之间以一个英文空格分隔,
时间必须符合"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"格式。提示:使用SimpleDateFormat类。
输入格式增加手机接打电话以及收发短信的格式,手机接打电话的信息除了号码之外需要额外记录拨打/接听的地点的区号,比如:
座机打手机:
t-主叫号码 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-079186330022 13305862264 020 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11
手机互打:
t-主叫号码 拨号地点 接听号码 接听地点区号 起始时间 结束时间
t-18907910010 0791 13305862264 0371 2022.1.3 10:00:25 2022.1.3 10:05:11注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
-
题目设计
在前言中也说过了,这里无非就是在PTA题目集6上额外添加一些内容,因为手机的加入,导致
出现了手机拨打座机,座机拨打手机,手机拨打手机等等情况。对于用户的创建:
①在PTA6的基础上,更正正则表达式,使得能判断正确的手机号以及座机号
②其他倒不需要更改太多,创建的手机用户一样和座机用户放在同一个用户表中对于通话记录的插入:
①插入方式其实不需要太大的改动,同样是根据拨打以及接听的号码,查找到对应的用户,插入到用户类的对应的通话记录中去
②需要对数据进行额外的鉴别,因为对于座机来说,地区号为其号码前3-4位,而手机的位置会发生变化,因此通话记录中,手机
号后会有一个表示手机所在区号的信息,因此,需要更改创建新的通话记录的代码,其要适应新的通话记录格式。
③当然,主要是新增了三种记录,座机拨打手机,手机拨打座机,手机拨打手机,而原本的座机拨打座机的代码可以不用更改。对于手机计费方式:
①显然,手机的计费方式和座机的大不相同,但是,仍旧可以按照每个计费策略建立一个类的方式,来创建计费规则
②分析可得,手机对于自己在市内,省内,国内等地区的拨打和接听电话的收费可以各自创建一个类,因为部分情况下手机接听
电话也会扣费,而座机接听电话免费。
③新创建的计费规则依旧继承收费类,实现计算花费的方法,并同样将每个计费规则添加到手机用户的计费规则列表中去 -
完整源码(其中多余的部分是在之后的题目中添加的,本题中用不到)
import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<String> inputList=Input.getAllInput(); inputList=Input.deleteCoincide(inputList); Format.trueInputFormat(inputList); Handle.userRecords(inputList); } } class Handle{ public static void userRecords(ArrayList<String> inputList){ ArrayList<User> users=Input.initUser(inputList); Collections.sort(users); for(User user:users){ System.out.println(user.number+" "+Format.Format_Str(user.calCost(),2)+" "+Format.Format_Str(user.calBalance(),2)); } } } class Input{ public static ArrayList<String> getAllInput(){ ArrayList<String> inputList=new ArrayList<String>(); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String info=input.nextLine(); while (!info.equals("end")) { inputList.add(info); info=input.nextLine(); } return inputList; } public static ArrayList<String> deleteCoincide(ArrayList<String> inputList){ ArrayList<String> newList=new ArrayList<String>(); for(String s:inputList){ if(!Input.isExist(s,newList)) newList.add(s); } return newList; } public static boolean isExist(String s,ArrayList<String> sList){ for(String input:sList){ if(input.equals(s)) return true; } return false; } public static ArrayList<User> initUser(ArrayList<String> inputList){ ArrayList<User> users=new ArrayList<User>(); ArrayList<String> newInput=new ArrayList<String>(); for(String s:inputList){ if(s.charAt(0)=='u'){ User newUser=new User(s); users.add(newUser); } else if(s.charAt(0)=='t'){ CallRecord callRecord=new CallRecord(s); Input.addRecord(users,callRecord); } } return users; } private static void addRecord(ArrayList<User> users, CallRecord callRecord) { for (User user:users){ if(user.number.equals(callRecord.callingNumber)){ if(callRecord.callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) user.userRecords.addCallingInCityRecords(callRecord); else if(Input.areaCodeInProvince(callRecord.callingAddressAreaCode)) user.userRecords.addCallingInProvinceRecords(callRecord); else user.userRecords.addCallingInLandRecords(callRecord); } if(user.number.equals(callRecord.answerNumber)){ if(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) user.userRecords.addAnswerInCityRecords(callRecord); else if(Input.areaCodeInProvince(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode)) user.userRecords.addAnswerInProvinceRecords(callRecord); else user.userRecords.addAnswerInLandRecords(callRecord); } } } public static boolean areaCodeInProvince(String areaCode){ //0790~0799以及0701 String[] AreaCode=new String[]{"0790","0791","0792","0793","0794","0795","0796","0797","0798","0799","0701"}; for(int i=0;i<AreaCode.length;i++){ if(areaCode.equals(AreaCode[i])) return true; } return false; } } class Format { public static double Format_Str(double s,int num) { String s1=String.format("%."+num+"f",s); s=Double.parseDouble(s1); return s; } public static void trueInputFormat(ArrayList<String> inputList){ for(int i=0;i<inputList.size();){ String s=inputList.get(i); if (s.matches("[u]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s[0]") || s.matches("[u]-1[0-9]{10}\\s[1]")) { i++; } else if (s.matches("(([t]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s" + "0[0-9]{9,11}\\s)|" + "([t]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s)|" + "([t]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s" + "0[0-9]{9,11}\\s)|" + "([t]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s))" + "((([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})\\.(((0?[13578]|1[02])\\.(0?" + "[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)\\.([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2\\.([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8]))))|(((" + "[0-9]{2})([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))\\.2\\.29))" + "\\s([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s" + "((([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})\\.((([13578]|1[02])\\.(" + "[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)\\.([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2\\.([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8]))))|(((" + "[0-9]{2})([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))\\.2\\.29))" + "\\s([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])")) { i++; } else inputList.remove(i); } } } class User implements Comparable<User>{ String number; double balance; UserRecords userRecords=new UserRecords(); ChargeMode chargeMode; public User(String user){ String[] s=user.split("[-\\s]"); this.number=s[1]; if(s[s.length-1].equals("0")){ this.chargeMode=new LandlinePhoneCharging(); } else { this.chargeMode=new MobilePhoneCharging(); } this.balance=100; } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public double calBalance(){ this.balance=this.balance-this.calCost()-this.chargeMode.getMonthlyRent(); return this.balance; } public double calCost(){ return this.chargeMode.calCost(this.userRecords); } @Override public int compareTo(User user) { if(this.number.compareTo(user.number)<0) return -1; else return 1; } } class UserRecords{ ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); ArrayList<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords=new ArrayList<CallRecord>(); public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public ArrayList<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { this.answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } } abstract class communicationRecord{ String callingNumber; String answerNumber; public communicationRecord(String Record){ String[] s=Record.split("[-\\s]"); switch (s.length){ case 7: case 8: this.callingNumber=s[1]; this.answerNumber=s[2]; break; case 9: this.callingNumber=s[1]; this.answerNumber=s[3]; } } public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } public String getAnswerNumber() { return answerNumber; } public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber) { this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } } class CallRecord extends communicationRecord{ Date startTime; Date endTime; public CallRecord(String callRecord){ super(callRecord); DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"); String[] s=callRecord.split("[-\\s]"); //提取通话时间 try { this.startTime=df.parse(s[s.length-4]+" "+s[s.length-3]); this.endTime=df.parse(s[s.length-2]+" "+s[s.length-1]); } catch (ParseException e){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } //提取通话区号 switch (s.length){ case 7: this.callingAddressAreaCode=s[1].substring(0,4); this.answerAddressAreaCode=s[2].substring(0,4); break; case 8: if(s[2].length()==3||s[2].length()==4){ this.callingAddressAreaCode=s[2]; this.answerAddressAreaCode=s[3].substring(0,4); } else{ this.callingAddressAreaCode=s[1].substring(0,4); this.answerAddressAreaCode=s[3]; } break; case 9: this.callingAddressAreaCode=s[2]; this.answerAddressAreaCode=s[4]; } } public long getCallTime(){ long sec=(this.endTime.getTime()-this.startTime.getTime())/1000; long min=sec/60; if(sec%60!=0) min+=1; return min; } String callingAddressAreaCode; String answerAddressAreaCode; } abstract class ChargeMode{ ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules=new ArrayList<>(); public ArrayList<ChargeRule> getChargeRules() { return chargeRules; } public void setChargeRules(ArrayList<ChargeRule> chargeRules) { this.chargeRules = chargeRules; } public abstract double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); public abstract double getMonthlyRent(); } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double mothlyRent=20; public LandlinePhoneCharging(){ } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double cost=0; cost+=new LandPhoneInCityRule().calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()); return cost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return this.mothlyRent; } } class MobilePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode{ double mothlyRent=15; public MobilePhoneCharging(){ } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double cost=0; cost+=new MobilePhoneCallInCityRule().calCost(userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()); cost+=new MobilePhoneCallInProvinceRule().calCost(userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()); cost+=new MobilePhoneCallInlandRule().calCost(userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()); cost+=new MobilePhoneAnswerInlandRule().calCost(userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()); return cost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return this.mothlyRent; } } abstract class ChargeRule{ } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule{ public abstract double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords); } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ min=callRecord.getCallTime(); if(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) cost+=0.1*min; else if(Input.areaCodeInProvince(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode)) cost+=0.3*min; else cost+=0.6*min; } return cost; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ cost+=0; } return cost; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ cost+=0; } return cost; } } class MobilePhoneCallInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ min=callRecord.getCallTime(); if(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) cost+=0.1*min; else if(Input.areaCodeInProvince(callRecord.answerAddressAreaCode)) cost+=0.2*min; else cost+=0.3*min; } return cost; } } class MobilePhoneAnswerInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { return 0; } } class MobilePhoneCallInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ min=callRecord.getCallTime(); cost+=0.3*min; } return cost; } } class MobilePhoneAnswerInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { return 0; } } class MobilePhoneCallInlandRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ min=callRecord.getCallTime(); cost+=0.6*min; } return cost; } } class MobilePhoneAnswerInlandRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { double cost=0; long min; for(CallRecord callRecord:callRecords){ min=callRecord.getCallTime(); cost+=0.3*min; } return cost; } } -
SourceMonitor分析
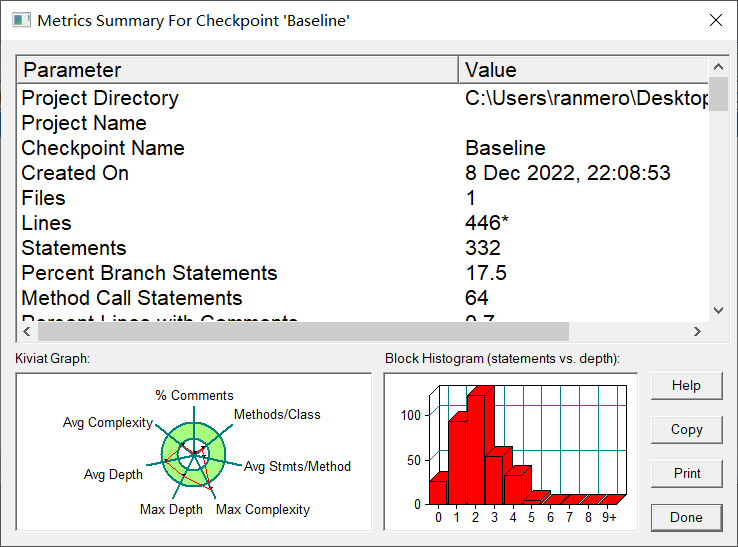
Kiviat Graph分析
①注释分析:懒得写注释点jpg(我的代码只有我能看懂hhhh)
②每个类中方法数分析:每个类中的方法也比较少
③每个方法中有效代码行数分析:每个方法中的有效语句较少,即方法分的太细
④最大圈复杂度分析:最大圈复杂度比较高,可能原因是几次for循环查找用户和插入记录
⑤最大深度分析:最大深度还比较适中
⑥平均深度分析:平均深度在合适的范围内,但可以再优化一下
⑦平均圈复杂度分析:平均圈复杂度比较的低Block Histogram分析
显然可以看出,深度的主要集中在1,2,即代码并不复杂
PTA题目集8-电信计费系列3-短信计费
-
题目内容
实现一个简单的电信计费程序,针对手机的短信采用如下计费方式:
1、接收短信免费,发送短信0.1元/条,超过3条0.2元/条,超过5条0.3元/条。
2、如果一次发送短信的字符数量超过10个,按每10个字符一条短信进行计算。输入:
输入信息包括两种类型
1、逐行输入南昌市手机用户开户的信息,每行一个用户。
格式:u-号码 计费类型 (计费类型包括:0-座机 1-手机实时计费 2-手机A套餐 3-手机短信计费)
例如:u-13305862264 3
座机号码由区号和电话号码拼接而成,电话号码包含7-8位数字,区号最高位是0。
手机号码由11位数字构成,最高位是1。
本题只针对类型3-手机短信计费。
2、逐行输入本月某些用户的短信信息,短信的格式:
m-主叫号码,接收号码,短信内容 (短信内容只能由数字、字母、空格、英文逗号、英文句号组成)
m-18907910010 13305862264 welcome to jiangxi.
m-13305862264 18907910010 thank you.注意:以上两类信息,先输入所有开户信息,再输入所有通讯信息,最后一行以“end”结束。
-
题目设计
短信计费其实和通话计费差不了太多,我认为短信计费甚至更简单一点,因为其不像通话记录一样需要分市内,省内,国内的
情况去讨论,而且其实本道题和之前的题目切合度不高,可以删除之前的通话记录的代码,保证整个流程更加的清晰同样,建立一个短信收费类,依照通话记录的模式,同样通过正则判断,然后把数据存入到相应的用户内,计算费用即可。
唯一的区别是这个收费类需要根据短信的长度来计算,而不是固定的每个字多少钱,当然,实现了类的设计,计算部分的难度都不大 -
完整源码
import java.util.*; class User { private UserRecords userRecords;//用户记录 private double balance = 100;//余额 private ChargeMode chargeMode;//计费方式 private String number;//号码 public double calBalance(){ return balance - (chargeMode.getMonthlyRent() + chargeMode.calCost(userRecords)); } public double calCost(){ return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords); } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } } abstract class ChargeMode { protected List<ChargeRule> chargeRules = new ArrayList<>(); public List<ChargeRule> getChargeRules() { return chargeRules; } public void setChargeRules(List<ChargeRule> chargeRules) { this.chargeRules = chargeRules; } abstract public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); abstract public double getMonthlyRent(); } class UserRecords { List<CallRecord> callingInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<CallRecord> callingInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<CallRecord> callingInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<CallRecord> answerInCityRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<CallRecord> answerInProvinceRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<CallRecord> answerInLandRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<MessageRecord> sendMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); List<MessageRecord> receiveMessageRecords = new ArrayList<>(); public void addCallingInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addCallingInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { callingInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInCityRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInCityRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInProvinceRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInProvinceRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addAnswerInLandRecords(CallRecord callRecord) { answerInLandRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addSendMessageRecords(MessageRecord callRecord) { sendMessageRecords.add(callRecord); } public void addReceiveMessageRecords(MessageRecord callRecord) { receiveMessageRecords.add(callRecord); } public List<CallRecord> getCallingInCityRecords() { return callingInCityRecords; } public List<CallRecord> getCallingInLandRecords() { return callingInLandRecords; } public List<CallRecord> getCallingInProvinceRecords() { return callingInProvinceRecords; } public List<CallRecord> getAnswerInCityRecords() { return answerInCityRecords; } public List<CallRecord> getAnswerInLandRecords() { return answerInLandRecords; } public List<CallRecord> getAnswerInProvinceRecords() { return answerInProvinceRecords; } public List<MessageRecord> getReceiveMessageRecords() { return receiveMessageRecords; } public List<MessageRecord> getSendMessageRecords() { return sendMessageRecords; } } class telPhoneMessageRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; int number = 0; for (MessageRecord m : userRecords.getSendMessageRecords()) { int length = m.getMessage().length(); if (length <= 10) { number++; } else { number += length / 10; if (length % 10 != 0) { number++; } } } if (number <= 3) { sumCost = number * 0.1; } else if (number <= 5) { sumCost = 0.3 + 0.2 * (number - 3); } else { sumCost = 0.7 + 0.3 * (number - 5); } return sumCost; } } class MessageRecord extends CommunicationRecord { private String message; public MessageRecord(String input) { super(); this.message = input.substring(26); } public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } } abstract class CommunicationRecord { protected String callingNumber; protected String answerNumber; public String getAnswerNumber() { return answerNumber; } public void setAnswerNumber(String answerNumber) { this.answerNumber = answerNumber; } public String getCallingNumber() { return callingNumber; } public void setCallingNumber(String callingNumber) { this.callingNumber = callingNumber; } } class CallRecord extends CommunicationRecord { private Date startTime; private Date endTime; private String callingAddressAreaCode; private String answerAddressAreaCode; public int getCallType() { int type = 0; if (callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) { type +=10; } else if (callingAddressAreaCode.matches("^079[023456789]$") || callingAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) { type +=20; } else { type +=30; } if (answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0791")) { type +=1; } else if (answerAddressAreaCode.matches("^079[023456789]$") || answerAddressAreaCode.equals("0701")) { type +=2; } else { type +=3; } //System.out.println(type/10); return type; } public Date getStartTime() { return startTime; } public void setStartTime(Date startTime) { this.startTime = startTime; } public Date getEndTime() { return endTime; } public void setEndTime(Date endTime) { this.endTime = endTime; } public String getAnswerAddressAreaCode() { return answerAddressAreaCode; } public void setAnswerAddressAreaCode(String answerAddressAreaCode) { this.answerAddressAreaCode = answerAddressAreaCode; } public String getCallingAddressAreaCode() { return callingAddressAreaCode; } public void setCallingAddressAreaCode(String callingAddressAreaCode) { this.callingAddressAreaCode = callingAddressAreaCode; } } class telPhoneMessageCharging extends ChargeMode{ private double monthlyRent = 0; public telPhoneMessageCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new telPhoneMessageRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double sumCost = 0; for (ChargeRule rule : chargeRules) { sumCost += rule.calCost(userRecords); } return sumCost; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class telPhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 15; public telPhoneCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new telPhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new telPhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new telPhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ double Sum = 0; //System.out.println("?"); //System.out.println(chargeRules.size()); for (ChargeRule chargeRule : chargeRules) { Sum += chargeRule.calCost(userRecords); // System.out.println("sum = "+Sum); } return Sum; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } class LandlinePhoneCharging extends ChargeMode { private double monthlyRent = 20; public LandlinePhoneCharging() { super(); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInCityRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInProvinceRule()); chargeRules.add(new LandPhoneInlandRule()); } @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords){ double Sum = 0; //System.out.println("?"); //System.out.println(chargeRules.size()); for (ChargeRule chargeRule : chargeRules) { Sum += chargeRule.calCost(userRecords); //System.out.println("sum = "+Sum); } return Sum; } @Override public double getMonthlyRent() { return monthlyRent; } } abstract class CallChargeRule extends ChargeRule { //abstract public double calCost(List<CallRecord> callRecords); } abstract class ChargeRule{ abstract public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords); } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double Sum = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) { if(call.getCallType() == 11) Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.1; else if(call.getCallType() == 12) Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.3; else if(call.getCallType() == 13) Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.6; } return Sum; } } class LandPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double Sum = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) { Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.3; } return Sum; } } class LandPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double Sum = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) { Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.6; } return Sum; } } class telPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double Sum = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInCityRecords()) { if(call.getCallType() == 11) Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.1; else if(call.getCallType() == 12) Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.2; else if(call.getCallType() == 13) Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.3; } return Sum; } } class telPhoneInProvinceRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double Sum = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInProvinceRecords()) { Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.3; } return Sum; } } class telPhoneInlandRule extends CallChargeRule { @Override public double calCost(UserRecords userRecords) { double Sum = 0; for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getCallingInLandRecords()) { Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.6; } for (CallRecord call : userRecords.getAnswerInLandRecords()) { Sum += tools.getTime(call.getEndTime(),call.getStartTime())* 0.3; } return Sum; } } class tools{ public static int checkFormat(String str) { if (str.matches("[u]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s[0]") || str.matches("[u]-1[0-9]{10}\\s[1]")) return 1; else if (str.matches("(([t]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s" + "0[0-9]{9,11}\\s)|" + "([t]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s)|" + "([t]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s" + "0[0-9]{9,11}\\s)|" + "([t]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "0[0-9]{2,3}\\s))" + "((([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})\\.(((0?[13578]|1[02])\\.(0?" + "[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)\\.([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2\\.([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8]))))|(((" + "[0-9]{2})([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))\\.2\\.29))" + "\\s([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])\\s" + "((([0-9]{3}[1-9]|[0-9]{2}[1-9][0-9]|[0-9][1-9][0-9]{2}|[1-9][0-9]{3})\\.((([13578]|1[02])\\.(" + "[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))|(([469]|11)\\.([1-9]|[12][0-9]|30))|(2\\.([1-9]|[1][0-9]|2[0-8]))))|(((" + "[0-9]{2})([48]|[2468][048]|[13579][26])|(([48]|[2468][048]|[3579][26])00))\\.2\\.29))" + "\\s([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):([0-5][0-9]):([0-5][0-9])")) { return 2; } return -1; } public static int checkMessage(String input) { if (input.matches("[u]-0791[0-9]{7,8}\\s[0]") || input.matches("[u]-1[0-9]{10}\\s[13]")) { return 1; } else if (input.matches("[m]-1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "1[0-9]{10}\\s" + "[0-9a-zA-Z\\s\\.,]+")) { return 2; } return 0; } public static long getTime(Date endTime,Date startTime){ long t = (endTime.getTime()-startTime.getTime()) ; long time = t / 60000; if (t % 60000 != 0) { time += 1; } return time; } } class UsersLibrary { List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>(); public void addNewUser(String input){ User user = new User(); String[] inputs = input.split(" "); String tel = inputs[0].substring(2); for (User u : userList) { if (u.getNumber().equals(tel)) { return; } } user.setNumber(tel); int mode = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]); if (mode == 0) { user.setChargeMode(new LandlinePhoneCharging()); } else if (mode == 1) { user.setChargeMode(new telPhoneCharging()); } else if (mode == 3) { user.setChargeMode(new telPhoneMessageCharging()); } UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); user.setUserRecords(userRecords); userList.add(user); } public void addNewRecord(String input){ String[] inputs = input.split(" "); inputs[0] = inputs[0].substring(2); User callu = null, answeru = null; String out = inputs[0]; String in = ""; if (inputs.length == 6) { in = inputs[1]; } else if (inputs.length == 7) { in = inputs[1]; } else if (inputs.length == 8) { in = inputs[2]; } else { in = inputs[1]; } for (User u : userList) { if (u.getNumber().equals(out)) { callu = u; } if (u.getNumber().equals(in)) { answeru = u; } if (callu != null && answeru != null) { break; } } if (input.charAt(0) == 'm') { MessageRecord messageRecord = new MessageRecord(input); if (callu != null) { callu.getUserRecords().addSendMessageRecords(messageRecord); ; } if (answeru != null) { callu.getUserRecords().addReceiveMessageRecords(messageRecord); } } } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); UsersLibrary usersLibrary = new UsersLibrary(); String str = in.nextLine(); while(!str.equals("end")){ //int mode = tools.checkFormat(str); int mode = tools.checkMessage(str); if(mode == 1) usersLibrary.addNewUser(str); else if(mode == 2) usersLibrary.addNewRecord(str); str = in.nextLine(); } usersLibrary.userList.sort(new Comparator<User>() { @Override public int compare(User u1, User u2) { if (u1.getNumber().charAt(0) == '0' && u2.getNumber().charAt(0) != '0') { return -1; } else if (u1.getNumber().charAt(0) != '0' && u2.getNumber().charAt(0) == '0') { return 1; } if (Double.parseDouble(u1.getNumber()) > Double.parseDouble(u2.getNumber())) { return 1; } else { return -1; } } }); for (User u : usersLibrary.userList) { //System.out.println(" " + u.getUserRecords().callingInLandRecords.size()+" "); System.out.println(u.getNumber() +" "+ Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.1f",u.calCost())) +" " + Double.parseDouble( String.format("%.1f",u.calBalance()) ) ); } } } -
SourceMonitor分析
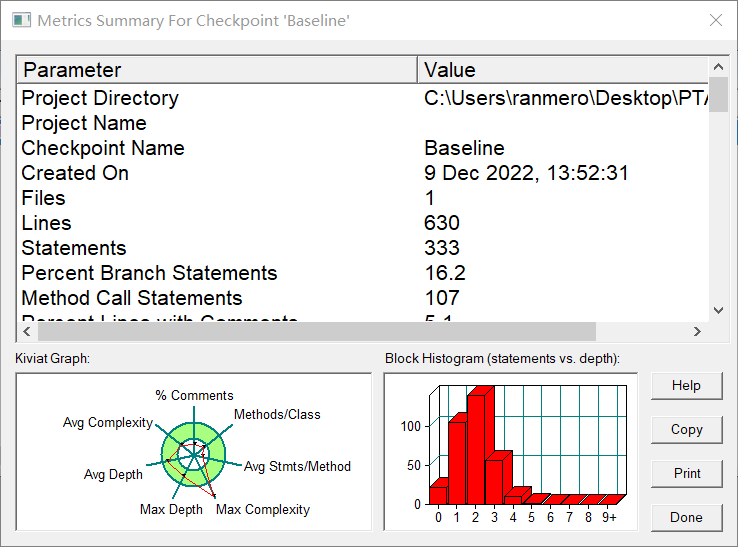
Kiviat Graph分析
①注释分析:永远都不想写注释捏(大家不要学!!)
②每个类中方法数分析:每个类中的方法数也偏少,因为这次把其他的代码都删掉了,就剩了短信的方法。
③每个方法中有效代码行数分析:每个方法中有效行数也比较少,大量的get和set方法拉低平均值。
④最大圈复杂度分析:最大圈复杂度比较的高,有些代码直接写在了main里面了,所以一般不要在main里面放实现的代码。
⑤最大深度分析:最大深度比较合适,其实这几个题目集都还比较好,我认为这也反映了类的结构其实设计的不错。
⑥平均深度分析:平均深度还可以接收,同上~~~
⑦平均圈复杂度分析:平均复杂度很低,因为就只写了一个短信的处理,比之前的手机+座机还要低。Block Histogram分析
仍旧是处在1-3的居多,比起多边形的题库,整体的深度都有下降,也侧证了我说的,计算部分比较简单,不像多边形那样调来调去。
三、踩坑心得
-
正则表达式(没错,又双叒叕是它)
正则之前一直想着是写一行总的格式进行判定,然后过不去之后,修修改改,把各种能想到的限制条件都加上去了,包括
长度啊,手机号开头的数字,时间等等,还是过不去AWA,然后开始摆烂了,把所有的情况列举出来,用好多个不同的正则
或运算,然后才过的。
-
代码卡时间
可能我的理解没有那么的深刻,照着类图上构造之后,写出来的代码居然会超时......我真的很无语,题目限制了运行时间
400ms,而我的大部分过了的测试点也在390ms左右,只能说写的可能太绕了,最最主要是,每次提交过的点还不一样,因为
有可能上一次运行超时了,这一次又在400ms内运行完成了,无语嘞......
四、改进意见
-
代码结构还可以再优化一下,包括对输入数据处理的那一段,我感觉超时大概率是因为在处理用户通话数据的时候,两重循环
导致时间过多了QWQ,不好评价好吧。至于优化方法,可以在读入每条数据的时候就将它插入到用户里去。而不是把所有数据
放在一个列表里后,再用两重循环来把列表中的所有通话记录插入到对应用户的记录中去。 -
这次倒是根据老师给出的类图构建代码,做到了属性私有化,但是get和set方法在一个类中占据了大半,剩下的处理方法就几个了,
还包括了构造函数。
五、总结
总得来说,相对于多边形的题目,还是要简单一些的,主要的问题都是在类的构建上
但之前也说过了,通过老师给的类图,还是能保证类的复杂度没有那么高,至少老师给的部分没有qwq
比如说超时问题,大概率是我后面补充的类的构造不是很合理,倒是增加了时间复杂度了。
因此,对于整个类的结构的理解还是有所欠缺,当然还是对类的构造又了新的理解。
原本我是想要将收费放在通话记录中的,这样每个通话记录之间调用cost函数,就可以得出这条通话记录的费用
但是转念一想,老师给的类图这样做确实很合理,通话记录做的应该只是记录通话的相关信息,而计费是通话后的结果
应该构建一个计费类,传参数为通话记录,然后通过计费类来计算似乎更加合理一些。
好了,不啰嗦了,Over~~


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号