second
前言:
- 第四次
(1) 第一题sdut-String-2 识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志(II)(正则表达式)
“蛟龙号”载人深潜器是我国首台自主设计、自主集成研制的作业型深海载人潜水器,设计最大下潜深度为7000米级,也是目前世界上下潜能力最强的作业型载人潜水器。“蛟龙号”可在占世界海洋面积99.8%的广阔海域中使用,对于我国开发利用深海的资源有着重要的意义。
中国是继美、法、俄、日之后世界上第五个掌握大深度载人深潜技术的国家。在全球载人潜水器中,“蛟龙号”属于第一梯队。目前全世界投入使用的各类载人潜水器约90艘,其中下潜深度超过1000米的仅有12艘,更深的潜水器数量更少,目前拥有6000米以上深度载人潜水器的国家包括中国、美国、日本、法国和俄罗斯。除中国外,其他4国的作业型载人潜水器最大工作深度为日本深潜器的6527米,因此“蛟龙号”载人潜水器在西太平洋的马里亚纳海沟海试成功到达7020米海底,创造了作业类载人潜水器新的世界纪录。
从2009年至2012年,蛟龙号接连取得1000米级、3000米级、5000米级和7000米级海试成功。下潜至7000米,说明蛟龙号载人潜水器集成技术的成熟,标志着我国深海潜水器成为海洋科学考察的前沿与制高点之一。
2012年6月27日11时47分,中国“蛟龙”再次刷新“中国深度”——下潜7062米。6月3日,“蛟龙”出征以来,已经连续书写了5个“中国深度”新纪录:6月15日,6671米;6月19日,6965米;6月22日,6963米;6月24日,7020米;6月27日,7062米。下潜至7000米,标志着我国具备了载人到达全球99%以上海洋深处进行作业的能力,标志着“蛟龙”载人潜水器集成技术的成熟,标志着我国深海潜水器成为海洋科学考察的前沿与制高点之一,标志着中国海底载人科学研究和资源勘探能力达到国际领先水平。
‘蛟龙’号是我国载人深潜发展历程中的一个重要里程碑。它不只是一个深海装备,更代表了一种精神,一种不畏艰险、赶超世界的精神,它是中华民族进军深海的号角。
了解蛟龙号”载人深潜器“的骄人业绩,为我国海底载人科学研究和资源勘探能力达到国际领先水平而自豪,小伙伴们与祖国同呼吸、共命运,一定要学好科学文化知识、提高个人能力,增强创新意识,做事精益求精,立科技报国之志!
请编写程序,实现如下功能:读入关于蛟龙号载人潜水器探测数据的多行字符串,从给定的信息找出数字字符,输出每行的数字之和。
提示 若输入为“2012年2月”,则该行的输出为:2014。若干个连续的数字字符作为一个整体,以十进制形式相加。
本题目主要考验我们Java语言最基本的输入、输出、按照不同的数据类型定义不同的数据以及数据的运算,还有就是if语句的使用以及十进制和字符串中某一段内容的提取。相对来说本题难度不大;
(2) 第二题点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
本题难度相对来说非常大,基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升,结合了点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离、点线形系列2-线的计算、点线形系列3-三角形的计算。
(3) 第三题,设计一个银行业务类
编写一个银行业务类BankBusiness,具有以下属性和方法:
(1)公有、静态的属性:银行名称bankName,初始值为“中国银行”。
(2)私有属性:账户名name、密码password、账户余额balance。
(3)银行对用户到来的欢迎(welcome)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“中国银行欢迎您的到来!”,其中“中国银行”自动使用bankName的值。
(4)银行对用户离开的提醒(welcomeNext)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!”
(5)带参数的构造方法,完成开户操作。需要账户名name、密码password信息,同时让账户余额为0。
(6)用户的存款(deposit)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息),密码不对时无法存款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确、完成用户存款操作后,要提示用户的账户余额,例如“您的余额有1000.0元。”。
(7)用户的取款(withdraw)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息)。密码不对时无法取款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确但余额不足时提示“您的余额不足!”;密码正确且余额充足时扣除交易额并提示用户的账户余额,例如“请取走钞票,您的余额还有500.0元。”。
编写一个测试类Main,在main方法中,先后执行以下操作:
(1)调用BankBusiness类的welcome()方法。
(2)接收键盘输入的用户名、密码信息作为参数,调用BankBusiness类带参数的构造方法,从而创建一个BankBusiness类的对象account。
(3)调用account的存款方法,输入正确的密码,存入若干元。密码及存款金额从键盘输入。
(4)调用account的取款方法,输入错误的密码,试图取款若干元。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(5)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额大于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(6)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额小于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(7)调用BankBusiness类的welcomeNext()方法。
- 第五次作业,
(1) 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
本题难度相对来说非常大,基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升,结合了点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离、点线形系列2-线的计算、点线形系列3-三角形的计算、点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算。
(2)点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
本题难度相对来说非常大,基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升,结合了点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离、点线形系列2-线的计算、点线形系列3-三角形的计算、点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算。
注意:这两个题实际上为一个题的不同选项,在主体内容上可以不作更改。
- 期中作业
(1)点与线(类设计)
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
The line's color is:颜色值
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(x1,y1)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(x2,y2)
The line's length is:长度值
其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用String.format("%.2f", data)方法。
设计类图如下图所示。
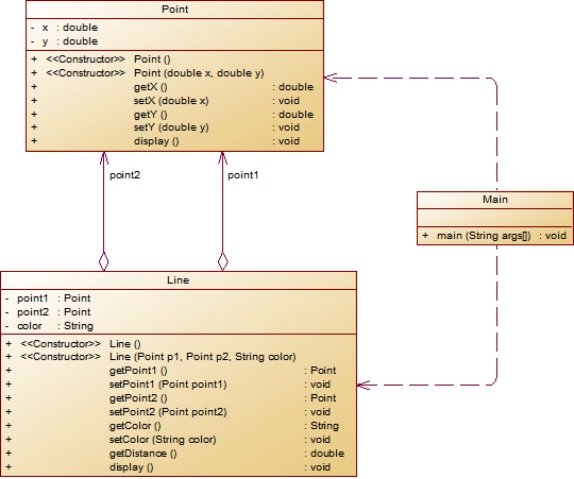
** 题目要求:在主方法中定义一条线段对象,从键盘输入该线段的起点坐标与终点坐标以及颜色,然后调用该线段的display()方法进行输出。**
以下情况为无效作业
无法运行
设计不符合所给类图要求
未通过任何测试点测试
判定为抄袭
本题难度相对来说非常大,基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升,结合了点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离、点线形系列2-线的计算、点线形系列3-三角形的计算、点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算、点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1、点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
(2)点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:The Plane's color is:颜色
在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
element = p1;//起点Point
element.display();
element = p2;//终点Point
element.display();
element = line;//线段
element.display();
element = plane;//面
element.display();
类结构如下图所示:
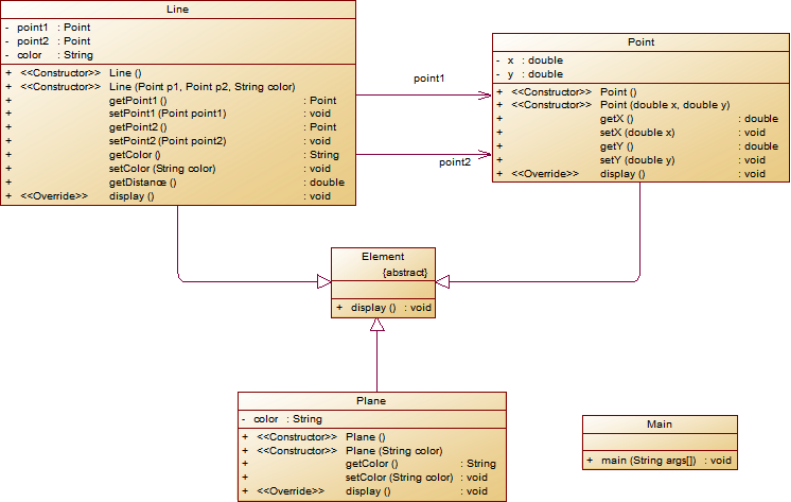
其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用String.format("%.2f", data)方法。
以下情况为无效作业
无法运行
设计不符合所给类图要求
未通过任何测试点测试
判定为抄袭
本题难度相对来说非常大,基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升,结合了点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离、点线形系列2-线的计算、点线形系列3-三角形的计算、点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算、点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1、点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
(3)点线面问题再重构(容器类)
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>)
增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象
在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
1:向容器中增加Point对象
2:向容器中增加Line对象
3:向容器中增加Plane对象
4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
0:输入结束
示例代码如下:
choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1://insert Point object into list
break;
case 2://insert Line object into list
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
int index = input.nextInt();
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
输入结束后,按容器中的对象顺序分别调用每个对象的display()方法进行输出。
类图如下所示:
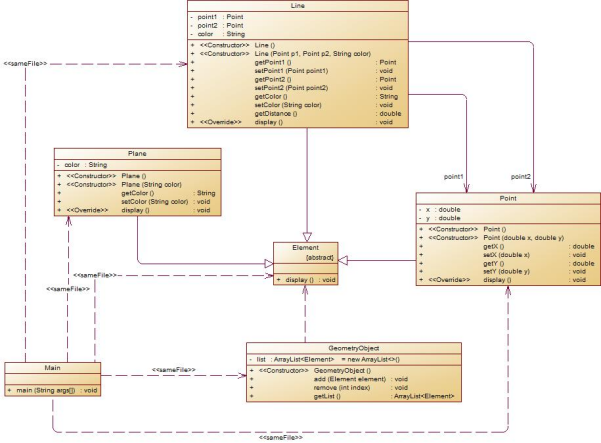
以下情况为无效作业
无法运行
设计不符合所给类图要求
未通过任何测试点测试
判定为抄袭
本题难度相对来说非常大,基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升,结合了点线形系列1-计算两点之间的距离、点线形系列2-线的计算、点线形系列3-三角形的计算、点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算、点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1、点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
同样,也只有三个题,但是会使用到一些比较深入的代码,很多比较深入的语句,需要很多次重复对格式的判断,导致在刚开始写的时候无从下手,前期在查资料,后期在调试,导致时间不够用,测试的点又非常多,写完的代码甚至不如直接输入报错得到的分多,相对来说工作量比较大。题目难度相对于第四五次作业简单了很多,但是由于类图的限制,还是要更改更多的代码。
设计与分析:
- 第四次作业
(1) sdut-String-2 识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志(II)(正则表达式):
①
public static void main(String[] args){
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
String line=sc.nextLine();//读入字符串
②
if(line.equals("end"))
break;
String[] split=line.split("\\D+");
//数组split接收分割的字符串,正则判断连续的整数用于split分割
③
int i;
long sum=0;
for(i=0;i<split.length;i++){
if(!split[i].equals(""))
//如果每个数组元素split[i].equals("")为假,则if语句执行
④
int digit=Integer.parseInt(split[i]);
//字符串强制转换成int
sum+=digit;
⑤
System.out.println(sum);
(2) 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
① 切割选项
switch (choice) {
case 1:
handle1(ps);
break;
case 2:
handle2(ps);
break;
case 3:
handle3(ps);
break;
case 4:
handle4(ps);
break;
case 5:
handle5(ps);
break;
}
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-5]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
②
public static double getPerimeter(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
sum += Point.gDistance(ps.get(i), ps.get((i + 1) % 4));
}
return sum;
}
③ 定义点类
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if (this.x == p.getX() && this.y == p.getY()) {
b = true;
}
return b;
}
public double getDistance(Point p2) {
return Math.sqrt((x - p2.x) * (x - p2.x) + (y - p2.y) * (y - p2.y));
}
public static double gDistance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return Math.sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
}
}
⑥ 点输入错误类
class PointInputError {
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
⑦ 格式错误类
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) { if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } }
⑧ 输入格式限制
class ParseInput { public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) { PointInputError.wrongChoice(s); d.setChoice(getChoice(s)); s = s.substring(2); pasePoints(s, d); } public static int getChoice(String s) { char c = s.charAt(0); return c - 48; } public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) { String[] ss = s.split(" "); if (ss.length == 0) return; for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) { d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i])); } } public static Point readPoint(String s) { PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s); String[] ss = s.split(","); double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]); double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]); return new Point(x, y); } }
⑨ 线类定义
class Line { private Point p1; private Point p2; public Line(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } public Line(Point p1, Point p2) { LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } public Double getSlope() { return (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) / (p2.getX() - p1.getX()); } public boolean isOnline(Point x) { if ((x.getX() == p1.getX() && x.getY() == p1.getY()) || (x.getX() == p2.getX() && x.getY() == p2.getY())) { return true; } Line l = new Line(p1, x); if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() && this.getSlope().isInfinite()) { return true; } double b1 = l.getSlope(), b2 = this.getSlope(); return Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001; } public double getDistance(Point x) { double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY(); double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX(); return Math.abs(x.getX() * distY - x.getY() * distX - p1.getX() * distY + p1.getY() * distX) / p1.getDistance(p2); } public boolean isBetween(Point x) { if (!this.isOnline(x)) { return false; } if (x.equals(p1) || x.equals(p2)) { return false; } double d = p2.getDistance(p1); boolean b = x.getDistance(p2) < d && x.getDistance(p1) < d; return b; } public boolean isSameSide(Point x) { return isOnline(x) && !isBetween(x); } public Point getMiddlePoint() { Point p = new Point(); p.setX((p1.getX() + p2.getX()) / 2); p.setY((p1.getY() + p2.getY()) / 2); return p; } public Point getPointA() { return p1; } public Point getPointB() { return p2; } public double getAngle(Line l) { double k2 = getSlope(); double k1 = l.getSlope(); return (double) (Math.atan(Math.abs((k2 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k2))) * 180.0 / Math.PI); } public boolean isParallel(Line l) { Double b1 = this.getSlope(); Double b2 = l.getSlope(); if ((b1.isInfinite()) && (b2.isInfinite())) { return true; } else { return (this.getSlope().doubleValue() == l.getSlope().doubleValue()); } } public boolean isCoincide(Line l) { if (!this.isParallel(l)) { return false; } if (this.isOnline(l.p1)) { return true; } return false; } public Point getIntersection(Line l) { if (this.isParallel(l)) { return null; } if (p1.equals(l.p1) || p1.equals(l.p2)) { return p1; } if (p2.equals(l.p1) || p2.equals(l.p2)) { return p2; } Point p3 = l.p1, p4 = l.p2; double x_member, x_denominator, y_member, y_denominator; Point cross_point = new Point(); x_denominator = p4.x * p2.y - p4.x * p1.y - p3.x * p2.y + p3.x * p1.y - p2.x * p4.y + p2.x * p3.y + p1.x * p4.y - p1.x * p3.y; x_member = p3.y * p4.x * p2.x - p4.y * p3.x * p2.x - p3.y * p4.x * p1.x + p4.y * p3.x * p1.x - p1.y * p2.x * p4.x + p2.y * p1.x * p4.x + p1.y * p2.x * p3.x - p2.y * p1.x * p3.x; if (x_denominator == 0) cross_point.x = 0; else cross_point.x = x_member / x_denominator; y_denominator = p4.y * p2.x - p4.y * p1.x - p3.y * p2.x + p1.x * p3.y - p2.y * p4.x + p2.y * p3.x + p1.y * p4.x - p1.y * p3.x; y_member = -p3.y * p4.x * p2.y + p4.y * p3.x * p2.y + p3.y * p4.x * p1.y - p4.y * p3.x * p1.y + p1.y * p2.x * p4.y - p1.y * p2.x * p3.y - p2.y * p1.x * p4.y + p2.y * p1.x * p3.y; if (y_denominator == 0) cross_point.y = 0; else cross_point.y = y_member / y_denominator; return cross_point; } }
⑩ 两点重合判定
class LineInputError { public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) { if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) { System.out.println("points coincide"); System.exit(0); } } }
(3)设计一个银行业务类
①第一句
System.out.println("中国银行欢迎您的到来!");
②if语句-
if (password1 == password) { System.out.println("您的余额有" + balance + "元。"); } else { System.out.println("您的密码错误!"); }
① -判断密码是否正确。
②
while (true) { if (password1 == password && balance1 <= balance) { balance = balance - balance1; System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有" + balance + "元。"); System.out.println("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!"); break; } else { if (password1 != password) { System.out.println("您的密码错误!"); } else { System.out.println("您的余额不足!"); } password1 = in.nextInt(); balance1 = in.nextDouble(); }
③ 输出
- 第五次作业
(1) 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1
① 切割选项
switch (choice) { case 1: handle1(ps); break; case 2: handle2(ps); break; case 3: handle3(ps); break; } public static void wrongChoice(String s) { if (!s.matches("[1-3]:.+")) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } }
②
public static double getPerimeter(ArrayList<Point> ps) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { sum += Point.gDistance(ps.get(i), ps.get((i + 1) % 4)); } return sum; }
③ 定义点类
class Point { public double x; public double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } public boolean equals(Point p) { boolean b = false; if (this.x == p.getX() && this.y == p.getY()) { b = true; } return b; } public double getDistance(Point p2) { return Math.sqrt((x - p2.x) * (x - p2.x) + (y - p2.y) * (y - p2.y)); } public static double gDistance(Point p1, Point p2) { return Math.sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y)); } }
⑪ 点输入错误类
class PointInputError { public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) { if (ps.size() != num) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0); } }
⑫ 格式错误类
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) { if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } }
⑬ 输入格式限制
class ParseInput { public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) { PointInputError.wrongChoice(s); d.setChoice(getChoice(s)); s = s.substring(2); pasePoints(s, d); } public static int getChoice(String s) { char c = s.charAt(0); return c - 48; } public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) { String[] ss = s.split(" "); if (ss.length == 0) return; for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) { d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i])); } } public static Point readPoint(String s) { PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s); String[] ss = s.split(","); double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]); double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]); return new Point(x, y); } }
⑭ 线类定义
class Line { private Point p1; private Point p2; public Line(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } public Line(Point p1, Point p2) { LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } public Double getSlope() { return (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) / (p2.getX() - p1.getX()); } public boolean isOnline(Point x) { if ((x.getX() == p1.getX() && x.getY() == p1.getY()) || (x.getX() == p2.getX() && x.getY() == p2.getY())) { return true; } Line l = new Line(p1, x); if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() && this.getSlope().isInfinite()) { return true; } double b1 = l.getSlope(), b2 = this.getSlope(); return Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001; } public double getDistance(Point x) { double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY(); double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX(); return Math.abs(x.getX() * distY - x.getY() * distX - p1.getX() * distY + p1.getY() * distX) / p1.getDistance(p2); } public boolean isBetween(Point x) { if (!this.isOnline(x)) { return false; } if (x.equals(p1) || x.equals(p2)) { return false; } double d = p2.getDistance(p1); boolean b = x.getDistance(p2) < d && x.getDistance(p1) < d; return b; } public boolean isSameSide(Point x) { return isOnline(x) && !isBetween(x); } public Point getMiddlePoint() { Point p = new Point(); p.setX((p1.getX() + p2.getX()) / 2); p.setY((p1.getY() + p2.getY()) / 2); return p; } public Point getPointA() { return p1; } public Point getPointB() { return p2; } public double getAngle(Line l) { double k2 = getSlope(); double k1 = l.getSlope(); return (double) (Math.atan(Math.abs((k2 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k2))) * 180.0 / Math.PI); } public boolean isParallel(Line l) { Double b1 = this.getSlope(); Double b2 = l.getSlope(); if ((b1.isInfinite()) && (b2.isInfinite())) { return true; } else { return (this.getSlope().doubleValue() == l.getSlope().doubleValue()); } } public boolean isCoincide(Line l) { if (!this.isParallel(l)) { return false; } if (this.isOnline(l.p1)) { return true; } return false; } public Point getIntersection(Line l) { if (this.isParallel(l)) { return null; } if (p1.equals(l.p1) || p1.equals(l.p2)) { return p1; } if (p2.equals(l.p1) || p2.equals(l.p2)) { return p2; } Point p3 = l.p1, p4 = l.p2; double x_member, x_denominator, y_member, y_denominator; Point cross_point = new Point(); x_denominator = p4.x * p2.y - p4.x * p1.y - p3.x * p2.y + p3.x * p1.y - p2.x * p4.y + p2.x * p3.y + p1.x * p4.y - p1.x * p3.y; x_member = p3.y * p4.x * p2.x - p4.y * p3.x * p2.x - p3.y * p4.x * p1.x + p4.y * p3.x * p1.x - p1.y * p2.x * p4.x + p2.y * p1.x * p4.x + p1.y * p2.x * p3.x - p2.y * p1.x * p3.x; if (x_denominator == 0) cross_point.x = 0; else cross_point.x = x_member / x_denominator; y_denominator = p4.y * p2.x - p4.y * p1.x - p3.y * p2.x + p1.x * p3.y - p2.y * p4.x + p2.y * p3.x + p1.y * p4.x - p1.y * p3.x; y_member = -p3.y * p4.x * p2.y + p4.y * p3.x * p2.y + p3.y * p4.x * p1.y - p4.y * p3.x * p1.y + p1.y * p2.x * p4.y - p1.y * p2.x * p3.y - p2.y * p1.x * p4.y + p2.y * p1.x * p3.y; if (y_denominator == 0) cross_point.y = 0; else cross_point.y = y_member / y_denominator; return cross_point; } }
⑮ 两点重合判定
class LineInputError {
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
(2) 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
① 切割选项
switch (choice) {
case 1:
handle1(ps);
break;
case 2:
handle2(ps);
break;
case 3:
handle3(ps);
break;
}
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-3]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
②
public static double getPerimeter(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
sum += Point.gDistance(ps.get(i), ps.get((i + 1) % 4));
}
return sum;
}
③ 定义点类
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if (this.x == p.getX() && this.y == p.getY()) {
b = true;
}
return b;
}
public double getDistance(Point p2) {
return Math.sqrt((x - p2.x) * (x - p2.x) + (y - p2.y) * (y - p2.y));
}
public static double gDistance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return Math.sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
}
}
⑯ 点输入错误类
class PointInputError {
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
⑰ 格式错误类
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
⑱ 输入格式限制
class ParseInput {
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c - 48;
}
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
⑲ 线类定义
class Line {
private Point p1;
private Point p2;
public Line(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1);
Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2);
LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
public Line(Point p1, Point p2) {
LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
public Double getSlope() {
return (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) / (p2.getX() - p1.getX());
}
public boolean isOnline(Point x) {
if ((x.getX() == p1.getX() && x.getY() == p1.getY()) || (x.getX() == p2.getX() && x.getY() == p2.getY())) {
return true;
}
Line l = new Line(p1, x);
if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() && this.getSlope().isInfinite()) {
return true;
}
double b1 = l.getSlope(), b2 = this.getSlope();
return Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001;
}
public double getDistance(Point x) {
double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY();
double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX();
return Math.abs(x.getX() * distY - x.getY() * distX - p1.getX() * distY + p1.getY() * distX)
/ p1.getDistance(p2);
}
public boolean isBetween(Point x) {
if (!this.isOnline(x)) {
return false;
}
if (x.equals(p1) || x.equals(p2)) {
return false;
}
double d = p2.getDistance(p1);
boolean b = x.getDistance(p2) < d && x.getDistance(p1) < d;
return b;
}
public boolean isSameSide(Point x) {
return isOnline(x) && !isBetween(x);
}
public Point getMiddlePoint() {
Point p = new Point();
p.setX((p1.getX() + p2.getX()) / 2);
p.setY((p1.getY() + p2.getY()) / 2);
return p;
}
public Point getPointA() {
return p1;
}
public Point getPointB() {
return p2;
}
public double getAngle(Line l) {
double k2 = getSlope();
double k1 = l.getSlope();
return (double) (Math.atan(Math.abs((k2 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k2))) * 180.0 / Math.PI); }
public boolean isParallel(Line l) {
Double b1 = this.getSlope();
Double b2 = l.getSlope();
if ((b1.isInfinite()) && (b2.isInfinite())) {
return true;
} else {
return (this.getSlope().doubleValue() == l.getSlope().doubleValue());
}
}
public boolean isCoincide(Line l) {
if (!this.isParallel(l)) {
return false;
}
if (this.isOnline(l.p1)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public Point getIntersection(Line l) {
if (this.isParallel(l)) {
return null;
}
if (p1.equals(l.p1) || p1.equals(l.p2)) {
return p1;
}
if (p2.equals(l.p1) || p2.equals(l.p2)) {
return p2;
}
Point p3 = l.p1, p4 = l.p2;
double x_member, x_denominator, y_member, y_denominator;
Point cross_point = new Point();
x_denominator = p4.x * p2.y - p4.x * p1.y - p3.x * p2.y + p3.x * p1.y - p2.x * p4.y + p2.x * p3.y + p1.x * p4.y
- p1.x * p3.y;
x_member = p3.y * p4.x * p2.x - p4.y * p3.x * p2.x - p3.y * p4.x * p1.x + p4.y * p3.x * p1.x
- p1.y * p2.x * p4.x + p2.y * p1.x * p4.x + p1.y * p2.x * p3.x - p2.y * p1.x * p3.x;
if (x_denominator == 0)
cross_point.x = 0;
else
cross_point.x = x_member / x_denominator;
y_denominator = p4.y * p2.x - p4.y * p1.x - p3.y * p2.x + p1.x * p3.y - p2.y * p4.x + p2.y * p3.x + p1.y * p4.x
- p1.y * p3.x;
y_member = -p3.y * p4.x * p2.y + p4.y * p3.x * p2.y + p3.y * p4.x * p1.y - p4.y * p3.x * p1.y
+ p1.y * p2.x * p4.y - p1.y * p2.x * p3.y - p2.y * p1.x * p4.y + p2.y * p1.x * p3.y;
if (y_denominator == 0)
cross_point.y = 0;
else
cross_point.y = y_member / y_denominator;
return cross_point;
}
}
⑳ 两点重合判定
class LineInputError {
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
- 期中作业
(1)点与线(类设计)
① 输入-4个double类型的实数,两个点的x,y坐标,依次是x1、y1、x2、y2,两个点的坐标之间以空格分隔,每个点的x,y坐标以英文“,”分隔。
public static class Point{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void display() {
Point p = new Point(x,y);
String s = String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)",x,y);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
① 定义线类
public static class Line{
private Point p1;
private Point p2;
private String color;
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) {
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
this.color=color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return p1;
}
public void setPoint1() {
this.p1=p1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return p2;
}
public void setPoint2() {
this.p2=p2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor() {
this.color=color;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color);
System.out.print("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
p1.display();
System.out.print("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
p2.display();
System.out.println("The line's length is:"+s);
}
public double getDistance() {
double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY();
double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX();
double s=Math.abs((p1.getX()-p2.getX())*(p1.getX()-p2.getX()) + (p1.getY()-p2.getY())*(p1.getY()-p2.getY()));
return s;
}
}
}
② 判断-输入范围是否正确
if(x1<=0||x1>200||y1<=0||y1>200||x2<=0||x2>200||y2<=0||y2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
Line L=new Line(p1,p2,color);
L.display();
System.exit(0);
}
}
输入两个点的x,y坐标,依次是x1、y1、x2、y2。
(2) 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
① 输入-4个double类型的实数,两个点的x,y坐标,依次是x1、y1、x2、y2,两个点的坐标之间以空格分隔,每个点的x,y坐标以英文“,”分隔。
public static class Point{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void display() {
Point p = new Point(x,y);
String s = String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)",x,y);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
② 定义线类
public static class Line{
private Point p1;
private Point p2;
private String color;
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) {
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
this.color=color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return p1;
}
public void setPoint1() {
this.p1=p1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return p2;
}
public void setPoint2() {
this.p2=p2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor() {
this.color=color;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color);
System.out.print("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
p1.display();
System.out.print("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
p2.display();
System.out.println("The line's length is:"+s);
}
public double getDistance() {
double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY();
double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX();
double s=Math.abs((p1.getX()-p2.getX())*(p1.getX()-p2.getX()) + (p1.getY()-p2.getY())*(p1.getY()-p2.getY()));
return s;
}
}
}
② 判断-输入范围是否正确
if(x1<=0||x1>200||y1<=0||y1>200||x2<=0||x2>200||y2<=0||y2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
Line L=new Line(p1,p2,color);
L.display();
System.exit(0);
}
}
(3) 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
① 输入-4个double类型的实数,两个点的x,y坐标,依次是x1、y1、x2、y2,两个点的坐标之间以空格分隔,每个点的x,y坐标以英文“,”分隔。
public static class Point{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void display() {
Point p = new Point(x,y);
String s = String.format("(%.2f,%.2f)",x,y);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
③ 定义线类
public static class Line{
private Point p1;
private Point p2;
private String color;
public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) {
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
this.color=color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return p1;
}
public void setPoint1() {
this.p1=p1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return p2;
}
public void setPoint2() {
this.p2=p2;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor() {
this.color=color;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color);
System.out.print("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
p1.display();
System.out.print("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
p2.display();
System.out.println("The line's length is:"+s);
}
public double getDistance() {
double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY();
double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX();
double s=Math.abs((p1.getX()-p2.getX())*(p1.getX()-p2.getX()) + (p1.getY()-p2.getY())*(p1.getY()-p2.getY()));
return s;
}
}
}
② 判断-输入范围是否正确
if(x1<=0||x1>200||y1<=0||y1>200||x2<=0||x2>200||y2<=0||y2>200)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
Line L=new Line(p1,p2,color);
L.display();
System.exit(0);
}
}
踩坑心得:
- 我在提交源码的过程中,遇到了很多不同的问题。在第一次作业中,虽然题目比较简单,但是很多琐碎的测试点和一些不存在的情况都有出现问题,要改了再改,不仅可能不能过一个测试点,甚至可能推翻别的测试点。
- 经常需要自己一遍又一遍的测试,或者是问一问已经过了测试点的同学。例如,对于一个点的定义。
- 第二次作业中,对于ascll需要引入,需要经常查资料,写完了还是很多点过不去,分数越改越少。
- 第三次做作业,整体难度偏高,需要引入正则表达式,对于我这种基础不好的同学来讲很难上手,所以我应该致力于攻克测试点。作业没过的测试点还有很多,希望有机会可以重新尝试。
- 有的题目测试点有问题,正确的代码无法通过测试。
- 有些题目内容不够详细,需要提示。
改进建议:
- 基础不好应该先进行复习,做题时与资料结合,进行知识的巩固与加强。
- 写代码的时候进行注释,方便自己的后续修改以及同学们的帮助。
- 进行简易测试点的判断,把自己尽力能得到的分得到,例如,一些输入错误的测试点相对来说最容易。
- 通过习题学习知识点,使得自己记忆更加深刻。
- 对于类的掌握不够透彻,还需要加量学习,以便自己后续程序的书写
- 输入正确错误的格式掌握不够透彻,需要进一步学习使用Java语言对格式进行判断。例如第三次作业,基本上每一次都要进行格式的判断。
- 题目结果总是出现0,0的情况,还需要进一步了解此情况出现的原因。
总结:
- 在三次作业过程中,我能看出难度跨度较大,也就说明了我们永远不会知道以后会面对多么困难的问题,必须要用尽可能多的时间提升自己。
- 在这三次作业中,我发现有很多考点是自己上课并未注意到的,所以做题的过程中,可以更加清楚的意识到自己学习的重点内容是哪一部分。
- 在三次作业过程中,我也拓宽了自己的视野,学会借助外部资料来解决自己的某一个针对性问题,合理使用手中的资源。
- 由于第三次作业写得匆忙,我更加意识到时间的宝贵,意识到作业之所以给一整周的时间是为了让我们时时刻刻可以修改自己的错误,从作业发布就要及时下手。
- 遇到问题要积极求助,虚心学习,如果问题不能自己解决就要学习,身边的同学和老师都会帮助你。
- 由于作业的需求,我们迫不得已学习了ascll语言以及正则表达式等等,但这是一件对于我们来说很有利的事情。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号