C++大一课设解析记录
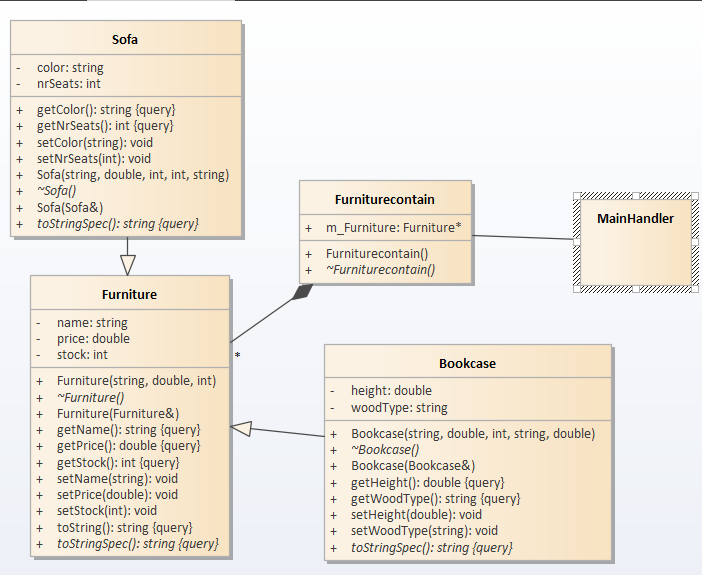
首先,我们运用EA画出一个大概需求:

运用EA自动生成代码后,我们发现每种有.h 与.cpp两种文件
.h用来声明里面所包含的功能函数类,.cpp用来编写声明的函数或者类的编写
各个类的用途:
在main函数中,我们只需要编写最外层的交互界面,实现输入相关指令,就可以从Furniturecontainer中获取到要输出的结果(实现显示
在Furniturecontainer中,我们将他作为一个数据库,编写相应的动态内存代码,以及各种指令返回的字符串流(实现储蓄以及调用
在剩下的Furniture以及sofa、bookcase中,Furniture是一个主的类,sofa、bookcase为他的继承子类,在Furniture中我们完成两个子类共通的要储蓄的信息创建,在子类中完成各自特殊的信息创建(告知要储存的数据格式类型)
注:过于基础的知识这里不再提及(像是类的构造函数等知识),如果有疑问可以将相关名词带上C++去菜鸟教程、博客园、CSDN这几个网站上进行搜索
Furniture类
包含:规定需要传入的数值、类的析构、复制构造函数用于传入、转为字符串流的函数
//首先,定义声明的.h
#ifndef FURNITURE_H
#define FURNITURE_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Furniture {
public:
//沙发和书柜都包含名字价格库存,我们要先对他们进行声明(其中的变量要现在类当中声明)
Furniture(string name = "?", double price = 0, int stock = -1);
virtual ~Furniture();//析构函数,因为有两个继承类,所以我们用虚函数来实现多态
Furniture(const Furniture& furniture);//复制构造函数
void setName(string name);
string getName() const;
void setPrice(double price);//其他的set get 省略,格式都一样
string toString() const;//将一样的数据转为字串流
virtual string toStringSpec() const = 0;//将不一样的数据转为字串流
private:
string name;
double price;
int stock;
};
#endif
= Furniture.cpp=//申明函数的实现
#include "Furniture.h"
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
//将一开始申明的数据进行初始化
Furniture::Furniture(string name /* = "?" */, double price /* = 0 */, int stock /* = -1 */){
this->name = name;
this->price = price;
this->stock = stock;
}
//析构函数
Furniture::~Furniture(){}
//此处将包含名字、库存、价格的Furniture变量通过引用的方式传入
Furniture::Furniture(const Furniture& furniture){
this->name = furniture.name;
this->price = furniture.price;
this->stock = furniture.stock;
}
//仅仅展示name 的get set其他同理
void Furniture::setName(string name){
this->name = name;
}
string Furniture::getName() const{
return this->name;
}
string Furniture::toString() const{//将数据转为字串流方便之后的输出(convertor为自己取得名字)
stringstream convertor;
convertor << "The name is: " << this->name
<< ", the price is: " << this->price
<< ", and the stock is: " << this->stock
<< toStringSpec();
return convertor.str();
}
上段代码中涉及到的知识点:
析构函数:
用于函数的销毁,用' ~ '符号加函数名构成
虚函数:
虚函数可以有多种实现方法,运用虚函数我们可以实现多态:程序运行后才能知道要运行哪一个虚函数。比如定义上述虚构函数为虚函数,那么只有在实际执行的时候才知道程序要析构的是sofa还是bookcase
详细可参考此链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Node-Sans-Blog/p/14249366.html
const:
表示变量的限定,放在函数的定义中意味着这个函数不能对任何数值进行改变,放在变量前面表示在这个函数中不能对这个变量经行改变
复制构造函数:
一般我们在程序中会用Furniture方法去定义一个变量A,其中A就包含A.name,A.price,A.stock.这里的复制构造函数运用(const Furniture& furniture)的方法直接通过传引用而不用复制就把整个A的数据传入函数当中,避免了内存泄漏
另:
&为取地址符号 this->表示这个变量是在这个类当中的变量 Furniture::(函数名)表示这个函数是从属于Furniture类当中的
SOFA类
包含:继承申明、sofa类的变量申明、析构、特殊变量转为字符串
#ifndef SOFA_H
#define SOFA_H
#include "Furniture.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Sofa :public Furniture { //表示从Furniture中继承
public:
Sofa(string name = "?", double price = 0, int stock = -1,int nrSeats = 0, string color = "?");
virtual ~Sofa();
Sofa(const Sofa& sofa);
//只要申明Furniture类中没有的就好
void setNrSeats(int nrSeats);
int getNrSeats()const;
void setColor(string color);
string getColor() const;
virtual string toStringSpec() const;//声明虚函数
private:
int nrSeats;
string color;
};
#endif
=sofa.cpp=
#include "Sofa.h"
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
Sofa::Sofa(string name, double price, int stock,int nrSeats, string color) : Furniture(name,price,stock){
//位于函数变量后,函数内容大括号前的表示声明继承
this->nrSeats = nrSeats;
this->color = color;
}
Sofa::~Sofa(){}
Sofa::Sofa(const Sofa& sofa) :Furniture(sofa){
this->nrSeats = sofa.nrSeats;
this->color = sofa.color;
}
//get set 函数省略
string Sofa::toStringSpec() const{//属于sofa的虚函数所要执行的内容
stringstream convertor;
convertor << ", Number of seats is: " << this->nrSeats
<< ", and color is: " << this->color << endl;
return convertor.str();
}
bookcase类同sofa 类的关系一致,这里遍不再做详细赘述了
Furniturecontainer类
创建容量池、析构函数、数据的传入(复制构造函数)、赋值号的重载、各种对于数据库内数据进行操作的函数
#ifndef FURNITURECONTAINER_H
#define FURNITURECONTAINER_H
#include "Furniture.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
enum FurnitureType {//表示有两个继承的函数
SOFA, BOOKCASE
};
class FurnitureContainer {
public:
FurnitureContainer(int capacity = 10);
virtual ~FurnitureContainer();
FurnitureContainer(const FurnitureContainer &originalObj);
void operator=(const FurnitureContainer &originalObj);
//省略了各种对数据进行操作的函数声明
private:
Furniture **furnitureArray;
int nrOfFurniture;
int capacity;
void expand();
};
#endif
FurnitureContainer 类是几个类中最难的一个,是动态分配的核心,下面我们来一起看看他的实现:
#include "FurnitureContainer.h"
#include "Bookcase.h"
#include "Sofa.h"
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
//创建用于储蓄的数组(初始化)
FurnitureContainer::FurnitureContainer(int capacity){//传入数组容量
this->capacity = capacity;
this->nrOfFurniture = 0;//此时数组中已经有的数据数
this->furnitureArray = new Furniture*[this->capacity];//创建Furniture类型的数组furnitureArray
for (int i = 0; i < this->capacity; i++){//初始化数组
this->furnitureArray[i] = nullptr;
}
}
FurnitureContainer::~FurnitureContainer(){//析构函数时需要手动将数组中的数据以及数组本身进行删除
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {
delete this->furnitureArray[i];
}
delete[] this->furnitureArray;
}
FurnitureContainer::FurnitureContainer(const FurnitureContainer & originalObj){
this->capacity = originalObj.capacity;
this->nrOfFurniture = originalObj.nrOfFurniture;
this->furnitureArray = new Furniture*[this->capacity];
//准备好sofa类与bookcase类的指针变量(仅仅是申明,还没有创建,所以不用NEW)
Sofa * sofaPtr = nullptr;
Bookcase * bookcasePtr = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {
sofaPtr = dynamic_cast<Sofa*>(originalObj.furnitureArray[i]);//如果传入的数据不是sofa类他将返回空
if (sofaPtr != nullptr){//如果是sofa类,创建sofa类对应的数据类型的数组
this->furnitureArray[i] = new Sofa(*sofaPtr);
}
//bookcase类同理
bookcasePtr = dynamic_cast<Bookcase*>(originalObj.furnitureArray[i]);
if (bookcasePtr != nullptr){
this->furnitureArray[i] = new Bookcase(*bookcasePtr);
}
for (int i = this->nrOfFurniture; i < this->capacity; i++){
this->furnitureArray[i] = nullptr;
}
}
}
//赋值号的重载
void FurnitureContainer::operator=(const FurnitureContainer & originalObj){
if (this != &originalObj){//this表示等于前的数
//删除原本的数组
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {
delete this->furnitureArray[i];
}
delete[] this->furnitureArray;
//创建新的数组
this->capacity = originalObj.capacity;
this->nrOfFurniture = originalObj.nrOfFurniture;
this->furnitureArray = new Furniture*[this->capacity];
//判断是sofa类还是bookcase类,并动态创建对应的数组
Sofa * sofaPtr = nullptr;
Bookcase * bookcasePtr = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {
sofaPtr = dynamic_cast<Sofa*>(originalObj.furnitureArray[i]);
if (sofaPtr != nullptr){
this->furnitureArray[i] = new Sofa(*sofaPtr);
}
bookcasePtr = dynamic_cast<Bookcase*>(originalObj.furnitureArray[i]);
if (bookcasePtr != nullptr){
this->furnitureArray[i] = new Bookcase(*bookcasePtr);
}
for (int i = this->nrOfFurniture; i < this->capacity; i++) {
this->furnitureArray[i] = nullptr;
}
}
}
}
//————————————————————————————————————————————以下为功能实现(仅包含部分)————————————————————————————————————//
//主要为字符串输出流的运用
string FurnitureContainer::presentAll() const{
stringstream convertor;
convertor << "All the furniture: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {
convertor << this->furnitureArray[i]->toString();//*运用->去调用函数
}
convertor << endl;
return convertor.str();
}
string FurnitureContainer::presentAllValuesByType(FurnitureType type) const{//显示sofa或者bookcase
stringstream convertor;
double valueSofa = 0;
double valueBookcase = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {
if (dynamic_cast<Sofa*>(this->furnitureArray[i]) != nullptr){
valueSofa += this->furnitureArray[i]->getPrice();
}else {
valueBookcase += this->furnitureArray[i]->getPrice();
}
}
convertor << "the total value in stock of the is: "
<< (type == SOFA ? valueSofa : valueBookcase) << endl;
return convertor.str();
}
//添加数据函数
void FurnitureContainer::addSofa(string name, double price, int stock, int nrSeats, string color){
if (this->nrOfFurniture == this->capacity){
this->expand();
}
this->furnitureArray[this->nrOfFurniture++] = new Sofa(name, price, stock, nrSeats, color);
}
//删除数据
bool FurnitureContainer::remove(string name){
int i = 0;
bool isRemove = false;
while (i < this->nrOfFurniture){
if (this->furnitureArray[i]->getName() == name){
delete this->furnitureArray[i];
this->furnitureArray[i] = this->furnitureArray[--this->nrOfFurniture];//将最后的一个数据填充上楼来
isRemove = true;
}else{
i++;
}
}
return isRemove;
}
//扩大数组容量的数据
void FurnitureContainer::expand(){
this->capacity += 10;
Furniture** temp = new Furniture*[this->capacity];//双指针;指针数组
for (int i = 0; i < this->nrOfFurniture; i++) {//将原数据暂存于双指针temp中
temp[i] = this->furnitureArray[i];
}
delete[] this->furnitureArray;//删除原来的
this->furnitureArray = temp;//将temp放在新的地址当中
}
NEW
动态分配需要用new来创建数组来划定储蓄区域
详细可了解:https://blog.csdn.net/songthin/article/details/1703966
赋值号重载:
可参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoshiwang/p/9491365.html
t2 = t1;实际的运作方式是t2.operator=t1,所以函数里面的this就是t2
重载类FurnitureContainer的=号函数,当对类FurnitureContainer的对象用=号操作的时候,就会调用这个重载后的函数
指针
详情链接:https://www.runoob.com/cplusplus/cpp-pointers.html
指针是一个变量,其值为另一个变量的地址。
数组与指针:
int var[MAX] = {10, 100, 200};
int *ptr;
ptr = var;//var作为一个指向数组开头的常量,是不能修改的,但是可以用指针运算符,如:*(var+2)=500即var[2]=500
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
cout << "var[" << i << "]的内存地址为 ";
cout << ptr << endl;
cout << "var[" << i << "] 的值为 ";
cout << *ptr << endl;
ptr++;// 移动到下一个位置
}
双指针

另:
①如果类中有函数,需要自己写复制构造函数实现深拷贝
②a[3]与*(a+3)效果相同(后者称为取间访)
③两个同类型指针相减表示中间间隔了多少
最后:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号