CRUD工程师---Spring使用完结篇
注解本身没有功能的,就和 xml 一样。注解和 xml 都是一种元数据,元数据即解释数据的数据,这就是所谓配置。
本文主要罗列 Spring|Spring MVC相关注解的简介。
Spring部分
1、声明bean的注解
@Component 组件,没有明确的角色
@Service 在业务逻辑层使用(service层)
@Repository 在数据访问层使用(dao层)
@Controller 在展现层使用,控制器的声明(C)
2、注入bean的注解
@Autowired:由Spring提供
@Inject:由JSR-330提供
@Resource:由JSR-250提供
都可以注解在set方法和属性上,推荐注解在属性上(一目了然,少写代码)。
3、java配置类相关注解
@Configuration 声明当前类为配置类,相当于xml形式的Spring配置(类上)
@Bean 注解在方法上,声明当前方法的返回值为一个bean,替代xml中的方式(方法上)
@Configuration 声明当前类为配置类,其中内部组合了@Component注解,表明这个类是一个bean(类上)
@ComponentScan 用于对Component进行扫描,相当于xml中的(类上)
@WishlyConfiguration 为@Configuration与@ComponentScan的组合注解,可以替代这两个注解
4、切面(AOP)相关注解
Spring支持AspectJ的注解式切面编程。
@Aspect 声明一个切面(类上)
使用@After、@Before、@Around定义建言(advice),可直接将拦截规则(切点)作为参数。
@After 在方法执行之后执行(方法上)
@Before 在方法执行之前执行(方法上)
@Around 在方法执行之前与之后执行(方法上)
@PointCut 声明切点
在java配置类中使用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启Spring对AspectJ代理的支持(类上)
5、@Bean的属性支持
@Scope 设置Spring容器如何新建Bean实例(方法上,得有@Bean)
其设置类型包括:
Singleton (单例,一个Spring容器中只有一个bean实例,默认模式),
Protetype (每次调用新建一个bean),
Request (web项目中,给每个http request新建一个bean),
Session (web项目中,给每个http session新建一个bean),
GlobalSession(给每一个 global http session新建一个Bean实例)
@StepScope 在Spring Batch中还有涉及
@PostConstruct 由JSR-250提供,在构造函数执行完之后执行,等价于xml配置文件中bean的initMethod
@PreDestory 由JSR-250提供,在Bean销毁之前执行,等价于xml配置文件中bean的destroyMethod
6、@Value注解
@Value 为属性注入值(属性上)
支持如下方式的注入:
》注入普通字符
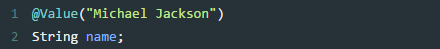
》注入操作系统属性

》注入表达式结果
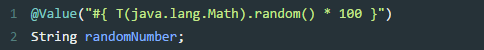
》注入其它bean属性
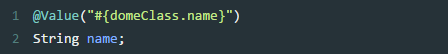
》注入文件资源
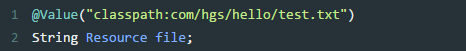
》注入配置文件
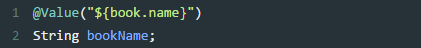
注入配置使用方法:
① 编写配置文件(test.properties)
book.name=《三体》
② @PropertySource 加载配置文件(类上)

③ 还需配置一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的bean。
7、环境切换
@Profile 通过设定Environment的ActiveProfiles来设定当前context需要使用的配置环境。(类或方法上)
@Conditional Spring4中可以使用此注解定义条件话的bean,通过实现Condition接口,并重写matches方法,从而决定该bean是否被实例化。(方法上)
8、异步相关
@EnableAsync 配置类中,通过此注解开启对异步任务的支持,叙事性AsyncConfigurer接口(类上)
@Async 在实际执行的bean方法使用该注解来申明其是一个异步任务(方法上或类上所有的方法都将异步,需要@EnableAsync开启异步任务)
9、定时任务相关
@EnableScheduling 在配置类上使用,开启计划任务的支持(类上)
@Scheduled 来申明这是一个任务,包括cron,fixDelay,fixRate等类型(方法上,需先开启计划任务的支持)
10、@Enable*注解说明
这些注解主要用来开启对xxx的支持。
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启对AspectJ自动代理的支持
@EnableAsync 开启异步方法的支持
@EnableScheduling 开启计划任务的支持
@EnableWebMvc 开启Web MVC的配置支持
@EnableConfigurationProperties 开启对@ConfigurationProperties注解配置Bean的支持
@EnableJpaRepositories 开启对SpringData JPA Repository的支持
@EnableTransactionManagement 开启注解式事务的支持
@EnableTransactionManagement 开启注解式事务的支持
@EnableCaching 开启注解式的缓存支持
11、测试相关注解
@RunWith 运行器,Spring中通常用于对JUnit的支持

@ContextConfiguration 用来加载配置ApplicationContext,其中classes属性用来加载配置类

SpringMVC部分
@EnableWebMvc 在配置类中开启Web MVC的配置支持,如一些ViewResolver或者MessageConverter等,若无此句,重写WebMvcConfigurerAdapter方法(用于对SpringMVC的配置)。
@Controller 声明该类为SpringMVC中的Controller
@RequestMapping 用于映射Web请求,包括访问路径和参数(类或方法上)
@ResponseBody 支持将返回值放在response内,而不是一个页面,通常用户返回json数据(返回值旁或方法上)
@RequestBody 允许request的参数在request体中,而不是在直接连接在地址后面。(放在参数前)
@PathVariable 用于接收路径参数,比如@RequestMapping(“/hello/{name}”)申明的路径,将注解放在参数中前,即可获取该值,通常作为Restful的接口实现方法。
@RestController 该注解为一个组合注解,相当于@Controller和@ResponseBody的组合,注解在类上,意味着,该Controller的所有方法都默认加上了@ResponseBody。
@ControllerAdvice 通过该注解,我们可以将对于控制器的全局配置放置在同一个位置,注解了@Controller的类的方法可使用@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder、@ModelAttribute注解到方法上,
这对所有注解了 @RequestMapping的控制器内的方法有效。
@ExceptionHandler 用于全局处理控制器里的异常
@InitBinder 用来设置WebDataBinder,WebDataBinder用来自动绑定前台请求参数到Model中。
@ModelAttribute 本来的作用是绑定键值对到Model里,在@ControllerAdvice中是让全局的@RequestMapping都能获得在此处设置的键值对。
Spring全局异常处理★★★★
- 使用Spring MVC提供的SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
- 实现Spring的异常处理接口HandlerExceptionResolver 自定义自己的异常处理器
- 使用@ExceptionHandler注解实现异常处理
(一) SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
使用这种方式具有集成简单、有良好的扩展性、对已有代码没有入侵性等优点,但该方法仅能获取到异常信息,若在出现异常时,对需要获取除异常以外的数据的情况不适用。
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.balbala.mvc.web"})
public class WebMVCConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
@Bean
public SimpleMappingExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver()
{
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver b = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
Properties mappings = new Properties();
mappings.put("org.springframework.web.servlet.PageNotFound", "page-404");
mappings.put("org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException", "data-access");
mappings.put("org.springframework.transaction.TransactionException", "transaction-Failure");
b.setExceptionMappings(mappings);
return b;
}
}(basePackages = {"com.balbala.mvc.web"})
public class WebMVCConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
public SimpleMappingExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver()
{
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver b = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
Properties mappings = new Properties();
mappings.put("org.springframework.web.servlet.PageNotFound", "page-404");
mappings.put("org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException", "data-access");
mappings.put("org.springframework.transaction.TransactionException", "transaction-Failure");
b.setExceptionMappings(mappings);
return b;
}
}
(二) HandlerExceptionResolver
public class GlobalHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalHandlerExceptionResolver.class);
/**
* 在这里处理所有得异常信息
*/
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp, Object o, Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
if (ex instanceof AthenaException) {
//AthenaException为一个自定义异常
ex.printStackTrace();
printWrite(ex.toString(), resp);
return new ModelAndView();
}
//RspMsg为一个自定义处理异常信息的类
//ResponseCode为一个自定义错误码的接口
RspMsg unknownException = null;
if (ex instanceof NullPointerException) {
unknownException = new RspMsg(ResponseCode.CODE_UNKNOWN, "业务判空异常", null);
} else {
unknownException = new RspMsg(ResponseCode.CODE_UNKNOWN, ex.getMessage(), null); }
printWrite(unknownException.toString(), resp);
return new ModelAndView();
}
/**
* 将错误信息添加到response中
*
* @param msg
* @param response
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void printWrite(String msg, HttpServletResponse response) {
try {
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.write(msg);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class GlobalHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalHandlerExceptionResolver.class);
/**
* 在这里处理所有得异常信息
*/
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp, Object o, Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
if (ex instanceof AthenaException) {
//AthenaException为一个自定义异常
ex.printStackTrace();
printWrite(ex.toString(), resp);
return new ModelAndView();
}
//RspMsg为一个自定义处理异常信息的类
//ResponseCode为一个自定义错误码的接口
RspMsg unknownException = null;
if (ex instanceof NullPointerException) {
unknownException = new RspMsg(ResponseCode.CODE_UNKNOWN, "业务判空异常", null);
} else {
unknownException = new RspMsg(ResponseCode.CODE_UNKNOWN, ex.getMessage(), null); }
printWrite(unknownException.toString(), resp);
return new ModelAndView();
}
/**
* 将错误信息添加到response中
*
* @param msg
* @param response
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void printWrite(String msg, HttpServletResponse response) {
try {
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.write(msg);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class BaseGlobalExceptionHandler {
protected static final Logger logger = null;
protected static final String DEFAULT_ERROR_MESSAGE = "系统忙,请稍后再试";
protected ModelAndView handleError(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Exception e, String viewName, HttpStatus status) throws Exception {
if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(e.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class) != null)
throw e;
String errorMsg = e instanceof MessageException ? e.getMessage() : DEFAULT_ERROR_MESSAGE;
String errorStack = Throwables.getStackTraceAsString(e);
getLogger().error("Request: {} raised {}", req.getRequestURI(), errorStack);
if (Ajax.isAjax(req)) {
return handleAjaxError(rsp, errorMsg, status);
}
return handleViewError(req.getRequestURL().toString(), errorStack, errorMsg, viewName);
}
protected ModelAndView handleViewError(String url, String errorStack, String errorMessage, String viewName) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
mav.addObject("exception", errorStack);
mav.addObject("url", url);
mav.addObject("message", errorMessage);
mav.addObject("timestamp", new Date());
mav.setViewName(viewName);
return mav;
}
protected ModelAndView handleAjaxError(HttpServletResponse rsp, String errorMessage, HttpStatus status) throws IOException {
rsp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
rsp.setStatus(status.value());
PrintWriter writer = rsp.getWriter();
writer.write(errorMessage);
writer.flush();
return null;
}
public Logger getLogger() {
return LoggerFactory.getLogger(BaseGlobalExceptionHandler.class);
}
}public class BaseGlobalExceptionHandler {
protected static final Logger logger = null;
protected static final String DEFAULT_ERROR_MESSAGE = "系统忙,请稍后再试";
protected ModelAndView handleError(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Exception e, String viewName, HttpStatus status) throws Exception {
if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(e.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class) != null)
throw e;
String errorMsg = e instanceof MessageException ? e.getMessage() : DEFAULT_ERROR_MESSAGE;
String errorStack = Throwables.getStackTraceAsString(e);
getLogger().error("Request: {} raised {}", req.getRequestURI(), errorStack);
if (Ajax.isAjax(req)) {
return handleAjaxError(rsp, errorMsg, status);
}
return handleViewError(req.getRequestURL().toString(), errorStack, errorMsg, viewName);
}
protected ModelAndView handleViewError(String url, String errorStack, String errorMessage, String viewName) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
mav.addObject("exception", errorStack);
mav.addObject("url", url);
mav.addObject("message", errorMessage);
mav.addObject("timestamp", new Date());
mav.setViewName(viewName);
return mav;
}
protected ModelAndView handleAjaxError(HttpServletResponse rsp, String errorMessage, HttpStatus status) throws IOException {
rsp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
rsp.setStatus(status.value());
PrintWriter writer = rsp.getWriter();
writer.write(errorMessage);
writer.flush();
return null;
}
public Logger getLogger() {
return LoggerFactory.getLogger(BaseGlobalExceptionHandler.class);
}
}
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler extends BaseGlobalExceptionHandler {
//比如404的异常就会被这个方法捕获
@ExceptionHandler(NoHandlerFoundException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public ModelAndView handle404Error(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Exception e) throws Exception {
return handleError(req, rsp, e, "error-front", HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
//500的异常会被这个方法捕获
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public ModelAndView handleError(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Exception e) throws Exception {
return handleError(req, rsp, e, "error-front", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
//TODO 你也可以再写一个方法来捕获你的自定义异常
//TRY NOW!!!
@Override
public Logger getLogger() {
return LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
}
}public class GlobalExceptionHandler extends BaseGlobalExceptionHandler {
//比如404的异常就会被这个方法捕获
(NoHandlerFoundException.class)
(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public ModelAndView handle404Error(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Exception e) throws Exception {
return handleError(req, rsp, e, "error-front", HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
//500的异常会被这个方法捕获
(Exception.class)
(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public ModelAndView handleError(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Exception e) throws Exception {
return handleError(req, rsp, e, "error-front", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
//TODO 你也可以再写一个方法来捕获你的自定义异常
//TRY NOW!!!
public Logger getLogger() {
return LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
}
}
1.首先容器启动后,会对scope为singleton且非懒加载的bean进行实例化,
2.按照Bean定义信息配置信息,注入所有的属性,
3.如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,会回调该接口的setBeanName()方法,传入该Bean的id,此时该Bean就获得了自己在配置文件中的id,
4.如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,会回调该接口的setBeanFactory()方法,传入该Bean的BeanFactory,这样该Bean就获得了自己所在的BeanFactory,
5.如果Bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,会回调该接口的setApplicationContext()方法,传入该Bean的ApplicationContext,这样该Bean就获得了自己所在的ApplicationContext,
6.如果有Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,则会回调该接口的postProcessBeforeInitialzation()方法,
7.如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,则会回调该接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法,
8.如果Bean配置了init-method方法,则会执行init-method配置的方法,
9.如果有Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,则会回调该接口的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,
10.经过流程9之后,就可以正式使用该Bean了,对于scope为singleton的Bean,Spring的ioc容器中会缓存一份该bean的实例,而对于scope为prototype的Bean,每次被调用都会new一个新的对象,期生命周期就交给调用方管理了,不再是Spring容器进行管理了
11.容器关闭后,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,则会回调该接口的destroy()方法,
12.如果Bean配置了destroy-method方法,则会执行destroy-method配置的方法,至此,整个Bean的生命周期结束



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号