Servlet中涉及到的对象
本文将对Servlet中涉及到的一些对象
----水至清则无鱼
- HttpServletRequest
作用:HttpServletRequest 对象代表客户端浏览器的请求,当客户端浏览器通过 HTTP 协议访问服务器时,HTTP 请求中的所有信息都会被 Tomcat 所解析并封装在这个对象中,通过这个对象提供的方法,可以获得客户端请求的所有信息。
生命周期:当有请求到达 Tomcat 时,Tomcat 会创建 HttpServletRequest 对象,并将该对象通过参数 的方式传递到我们Servlet 的方法中,当处理请求处理完毕并产生响应后该对象生命周期结 束。
练习:
获取请求信息
/** * 测试servlet获取请求信息 * @author wujunhong */ public class DemoServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //获得完整的urL StringBuffer requestURL = req.getRequestURL(); //获得除了协议主机端口之后的地址 String requestURI = req.getRequestURI(); //获得远程访问着的ip String remoteAddr = req.getRemoteAddr(); System.out.println(requestURL); System.out.println(requestURI); System.out.println(remoteAddr); } }
获取请求数据
/** * @author wujunhong * 获取请求数据 * (key和value是一对一的时候,用getParameter,如果是一对多,比如复选框就用getParameterValues) * 获取请求信息中的所有的key: req.getParameterNames() */ public class GetRequestDataServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //获取单个文本框,单选框的数据 String username = req.getParameter("username"); //获取复选框,checkbox数据 String[] userlikes = req.getParameterValues("userlike"); //获取请求信息中所有的key Enumeration<String> parameterNames = req.getParameterNames(); List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = req.getParameterMap(); while (parameterNames.hasMoreElements()){ list1.add(parameterNames.nextElement()); } List<String> list = Arrays.asList(userlikes); System.out.println(username); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list1); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String[]>> iterator = parameterMap.entrySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<String, String[]> next = iterator.next(); System.out.println("key:"+next.getKey()); System.out.println("value"+Arrays.asList(next.getValue())); } } }
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form action="demo02.do" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> 用户爱好:<input type="checkbox" name="userlike" value="体育"> 体育 <input type="checkbox" name="userlike" value="英语"> 英语 <input type="submit" value="ok"> </form> </body> </html>
设置请求编码
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8")
当浏览器向服务器发送请求之后,tomcat最先拿到请求数据包,他根据自己默认的 ISO-8859-1规范将字节数据包转换成字符数据包,如果请求信息中有中文,就会产生乱码,就需要设置请求编码。
获取请求头信息
获取请求头信息
/** * @author wujunhong */ public class GetRequestHeaderServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //通过指定key获取value String host = req.getHeader("Host"); //获取请求头中所有的key和value Enumeration<String> headerNames = req.getHeaderNames(); while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()){ //得到key String key = headerNames.nextElement(); //根据指定key获取value String value = req.getHeader(key); System.out.println("key:"+key+" value:"+value); } } }
- HttpServletResponse
作用:HttpServletResponse 对象代表服务器的响应。这个对象中封装了响应客户端浏览器的流对象,以及向客户端浏览器响应的响应头、响应数据、响应状态码等信息。
设置响应类型
浏览器会根据响应类型来决定如何处理相应的内容,分别问字节型响应和字符型响应
字符型响应
响应内容中含有文本需要设置字符型响应
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 使用Resp对象设置字符型响应类型 * @date: 2021/12/11 15:04 */ public class RespCharacterServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //设置字符型相应 //响应类型为文本型,内容含有html字符串,默认的响应类型,浏览器可以解析HTML resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8"); //响应类型为文本型,内容是普通文本 resp.setContentType("text/plain"); } }
字节型响应
需要响应图片视频就需要设置字节型响应
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 使用Resp对象设置字节型相应,将一个图片响应回浏览器 * @date: 2021/12/11 15:19 */ public class RespByteServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 读取文件图片 File file=new File("C:/Users/wujunhong/Desktop/Java图片/Java全系列.jpg"); // 将图片内容读取到数组中 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file); byte[] buff=new byte[fis.available()]; fis.read(buff); // 设置响应类型 resp.setContentType("image/jpeg"); // 将内容响应到网页 ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write(buff); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); } }
设置响应编码
一行代码,全部搞定,将响应编码设置到响应类型中,能够保证tomcat和浏览器使用同一种编码解析方式
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
在响应中添加附加信息
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 重定向响应(浏览器会发送两次请求) * 实现用百度引擎搜索东西 * @date: 2021/12/11 16:20 */ public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); String search = req.getParameter("search"); resp.sendRedirect("https://www.baidu.com/s?wd="+ URLEncoder.encode(search,"utf-8")); } }
在响应头中添加附加信息,实现文件的下载
/**
* @author: Mr.Wu
* @description 通过resp对象在响应头中添加附加信息,实现文件下载
* @date: 2021/12/11 18:09
*/
public class DownFileServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 读取文件
File file=new File("C:/Users/wujunhong/Desktop/Java图片/Java全系列.jpg");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 将文件放在数组中
byte[] buff=new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(buff);
// 添加响应信息
resp.addHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+file.getName());
ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(buff);
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
}
- ServletContext
解释:ServletContext对象,又成文Servlet上下文对象,服务器会为每一个web应用创建一个ServletContext对象,这个对象全局唯一,web中的所有Servlet都共享这个对象
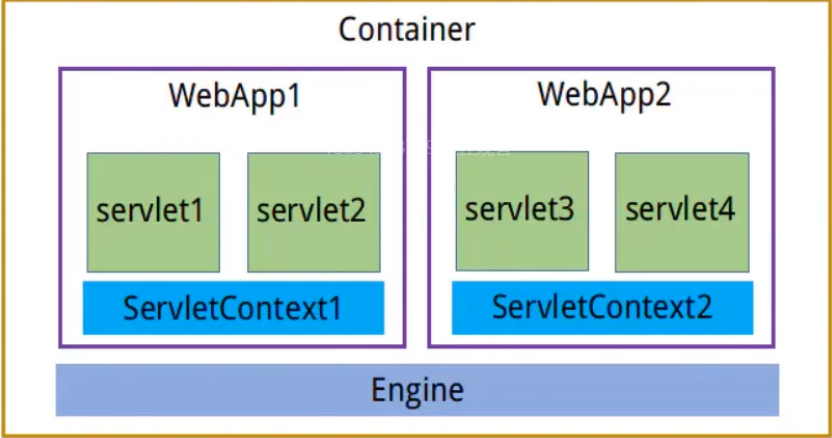
作用:相对路径转绝对路径、 获取容器的附加信息、读取配置信息、全局容器
生命周期:当容器启动时会创建 ServletContext 对象并一直缓存该对象,直到容器关闭后该对象生 命周期结束。ServletContext 对象的生命周期非常长,所以在使用全局容器时不建议存放业务数据。
相对路径转化绝对路径
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 使用ServletContext对象实现绝对路径转化为相对路径 * @date: 2021/12/11 18:46 */ public class DemoServletContext extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //拿到ServletContext对象 ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext(); String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("image/Java全系列.jpg"); System.out.println(realPath); // 读取文件 File file=new File(realPath); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); // 将文件放在数组中 byte[] buff=new byte[fis.available()]; fis.read(buff); // 添加响应信息 resp.addHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+file.getName()); ServletOutputStream outputStream = resp.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write(buff); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); } }
通过ServletContext获取容器的基本信息
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 通过ServletContext对象获得容器的一些基本信息 * @date: 2021/12/11 19:42 */ public class GetBaseInfoSerlvet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext(); String serverInfo = servletContext.getServerInfo(); int majorVersion = servletContext.getMajorVersion(); int minorVersion = servletContext.getMinorVersion(); System.out.println(serverInfo); System.out.println(majorVersion); System.out.println(minorVersion); } }
通过ServletContext对象来获取web.xml文件中的内容
//在web.xml文件中添加下面信息 <context-param> <param-name>name1</param-name> <param-value>23</param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>name2</param-name> <param-value>34</param-value> </context-param>
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 使用ServletContext对象来获取web.xml文件中的信息 * @date: 2021/12/11 19:55 */ public class ContextReadInfoServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext(); Enumeration<String> initParameterNames = servletContext.getInitParameterNames(); while (initParameterNames.hasMoreElements()){ String key=initParameterNames.nextElement(); System.out.println("key:"+key+" value"+servletContext.getInitParameter(key)); } } }
ServletContext作为全局容器存放数据
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description ServletContext对象作为全局容器存放数据 * @date: 2021/12/11 20:11 */ public class GlobalContainerServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext(); servletContext.setAttribute("key1", "张三"); servletContext.setAttribute("key2","李四"); // 设置相应编码格式 resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); String key1 = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("key1"); String key2 = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("key2"); System.out.println(key1); System.out.println(key2); } }
- ServletConfig
概念:ServletConfig 对象对应 web.xml 文件中的<servlet>节点。当 Tomcat 初始化一个 Servlet 时,会将该 Servlet 的配置信息,封装到一个 ServletConfig 对象中。我们可以通过该对象读 取<servlet>节点中的配置信息。
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 通过ServletConfig对象获取Servlet中的一些配置信息 * @date: 2021/12/11 20:30 */ public class GetConfigInfoServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 同ServletContext对象一样,通过this.获取 ServletConfig servletConfig = this.getServletConfig(); Enumeration<String> initParameterNames = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames(); while (initParameterNames.hasMoreElements()){ String key = initParameterNames.nextElement(); System.out.println("key :"+key+" value:"+servletConfig.getInitParameter(key)); } } }
<servlet> <servlet-name>getConfigInfoServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.tyust.servlet.GetConfigInfoServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>key1</param-name> <param-value>张三</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>key2</param-name> <param-value>李四</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>getConfigInfoServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/demo13.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
会话对象
由于 HTTP 协议是一个无状态的协议,所以服务端并不会记录当前客户端浏览器的访问状态,但是在有些时候我们是需要服务端能够记录客户端浏览器的访问状态的,如获取当前客户端浏览器的访问服务端的次数时就需要会话状态的维持。在 Servlet 中提供了 Cookie 对象与 HttpSession 对象用于维护客户端与服务端的会话状态的维持。二者不同的是 Cookie 是通过客户端浏览器实现会话的维持,而 HttpSession 是通过服务端来实现会话状态的维持。Cookie是不安全的,而HttpSessino是安全的。
- Cookie
cookie的特点:
- Cookie 使用字符串存储数据
- Cookie 使用 Key 与 Value 结构存储数据
- 单个 Cookie 存储数据大小限制在 4097 个字节
- Cookie 存储的数据中不支持中文,Servlet4.0 中支持
- Cookie 对象保存在客户端浏览器或系统磁盘中
- Cookie 分为持久化 Cooke 与状态 Cookie
- 浏览器在保存同一域名所返回 Cookie 的数量是有限的。不同浏览器支持的数量不同
- 浏览器每次请求时都会把与当前访问的域名相关的 Cookie 在请求中提交到服务端。
创建一个cookie对象
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 创建一个Cookie对象 * @date: 2021/12/12 12:43 */ public class CreateCookieServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { Cookie cookie = new Cookie("name","张三"); //设置cookie为持久化cookie,存储到系统 的硬盘中 cookie.setMaxAge(30); resp.addCookie(cookie); } }
获取cookie对象中的数据
** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 获得Cookie中的值 * @date: 2021/12/12 12:51 */ public class GetCookieDataServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies(); for (Cookie cookie : cookies) { System.out.println("key:"+cookie.getName()+"value:"+cookie.getValue()); } } }
状态化cookie和持久化cookie
状态cookie:cookie存储在浏览器内存中,当浏览器关闭时,该cookie就消失
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("nihao", "first");
持久化cookie:cookie存储在系统指定的磁盘中,可以设置持久化cookie存在的时间
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("nihao", "first"); cookie.setMaxAge(60); //60代表60秒
- HttpSession
特点:
- HttpSession 保存在服务端
- HttpSession 可以存储任何类型的数据
- HttpSession 使用 Key 与 Value 结构存储数据
- HttpSession 存储数据大小无限制
获得session对象
HttpSession 对象的创建是通过 request.getSession()方法来创建的。客户端浏览器在请求 服务端资源时,如果在请求中没有 SessionID,getSession()方法将会为这个客户端浏览器创 建一个新的 HttpSession 对象,并为这个 HttpSession 对象生成一个 SessionID,在响应中通过 Cookie 写回给客户端浏览器,如果在请求中包含了 SessionID,getSession()方法则根据这个 ID 返回与这个客户端浏览器对应的 HttpSession 对象。
getSession()方法还有一个重载方法 getSession(true|false)。当参数为 true 时与 getSession() 方法作用相同。当参数为 false 时则只去根据 SessionID 查找是否有与这个客户端浏览器对应的 HttpSession,如果有则返回,如果没有 SessionID 则不会创建新的 HttpSession 对象。
/** * @author: Mr.Wu * @description 获得HTTP Session对象 * @date: 2021/12/12 19:06 */ public class CreateSessionServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { this.doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpSession session = req.getSession(); System.out.println(session); } }
销毁HttpSession的两种方式,如果不设置,默认销毁时间是30分钟,在tomcat中web.xml文件中有一个全局超时时间的配置
- 通过在web.xml文件中指定超时时间
<session-config> <session-timeout>1</session-timeout> </session-config> - 通过HttpSession对象中的invalidate()方法进行销毁
注意:时间的计算方式是根据最后一次请求时间作为起始时间。如果有哪个客户端浏览器 对应的 HttpSession 的失效时间已到,那么与该客户端浏览器对应的 HttpSession 对象就会被 销毁。其他客户端浏览器对应的 HttpSession 对象会继续保存不会被销毁。
HttpSession对象的生命周期
在 HttpSession 对象生命周期中没有固定的创建时间与销毁时间,何时创建取决于我们 什么时候第一次调用了 getSession()或 getSession(true)的方法。HttpSession 对象的销毁时间 取决于超时时间的到达以及调用了 invalidate()方法。如果没有超时或者没有调用 invalidate() 方法,那么 HttpSession 会一直存储。
本文来自博客园,作者:(HelloWorld!),转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Simon-s/articles/15676965.html --有志者,事竟成




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号