Splay 平衡树
前置知识
平衡树,顾名思义是一种数据结构。
我们一般讨论的是二叉平衡树。
对于每一个子树来说:左子树的所有数比根小,右子树我的所有数比根大。
Splay
rotate
先介绍 zig,zag.
可以发现 zig 和 zag 是不改变树的中序遍历的。
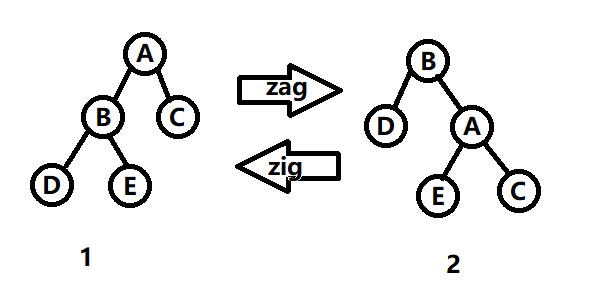
这两个操作构成了 rotate 函数,即把一个元素向上转。
code
bool get(int x) {return ch[fa[x]][1]==x;}
void pushup(int x) {
if(x) {
sz[x]=cnt[x];
if(ch[x][0]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][0]];
if(ch[x][1]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][1]];
}
}
void rotate(int x) {
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y],k=get(x);
ch[y][k]=ch[x][k^1]; fa[ch[x][k^1]]=y;
ch[x][k^1]=y; fa[y]=x;
fa[x]=z;
if(z) ch[z][ch[z][1]==y]=x;
pushup(y); pushup(x);
}
splay
继续,多次 rotate 构成了 splay, 即把一个元素旋转到根节点(伸展)
考虑子节点,父亲节点,和爷爷节点。
若共线,则先转父节点,再转子节点。若不共线,则转两次子节点。
这是为了维护树的平衡。
此外,记得在每次更新信息后要 splay 一下。
code
void splay(int x,int goal=0) {
for(; fa[x]!=goal; ) {
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y];
if(z!=goal) rotate(get(x)==get(y)?y:x);
rotate(x);
}
if(goal==0) rt=x;
}
find
即找到一个数所在位置。
根据平衡树的特性,我们可以在每个节点二分。(类似线段树)
注意找到后要把 splay 一下。
若平衡树里不存在这个数,可能返回它的后继或者前驱。
code
void find(int x) {
int u=rt;
if(!u) return ;
for(; ch[u][x>val[u]]&&x!=val[u]; )
u=ch[u][x>val[u]];
splay(u,0);
}
insert
插入一个数。
先找到它所应插入的位置,然后插入,并 pushup,最后 splay.
code
void insert(int x) {
int u=rt,f=0;
for(; u&&val[u]!=x; ) {
f=u;
u=ch[u][x>val[u]];
}
if(u) {cnt[u]++; pushup(u); pushup(f);}
else {
u=++tot;
val[u]=x; sz[u]=cnt[u]=1;
fa[u]=f; ch[u][0]=ch[u][1]=0;
if(f) {ch[f][x>val[f]]=u; pushup(f);}
else rt=u;
}
splay(u,0);
}
queryrank
先 find,旋转到根节点。
然后讨论一下 find 找到的是什么。
然后得出答案是 根节点左孩子的 siz +1 / 或加上根节点的 cnt
code
int query_rank(int x) {
find(x);
if(val[rt]>=x) return sz[ch[rt][0]]+1;
else return sz[ch[rt][0]]+cnt[rt]+1;
}
querykth
二分(类似线段树).
code
int query_kth(int x) {
int u=rt;
for(; u; ) {
if(ch[u][0]&&x<=sz[ch[u][0]])
u=ch[u][0];
else {
int tmp=sz[ch[u][0]]+cnt[u];
if(x<=tmp) {splay(u,0); return val[u];}
x-=tmp; u=ch[u][1];
}
}
}
pre/succ
先 find ,转到根节点。
答案是根节点左子树的最大值或右子树的最小值。
code
int pre(int x) {
find(x);
if(val[rt]<x) return rt;
int u=ch[rt][0];
for(; ch[u][1]; ) u=ch[u][1];
splay(u,0);
return u;
}
int succ(int x) {
find(x);
if(val[rt]>x) return rt;
int u=ch[rt][1];
for(; ch[u][0]; ) u=ch[u][0];
splay(u,0);
return u;
}
del
先 find,旋转到根节点。
讨论一下根节点的左右子树情况,最难的是左右子树都有。
那么需要先找原来根节点的前驱,再把前驱旋转到根节点。
放个图: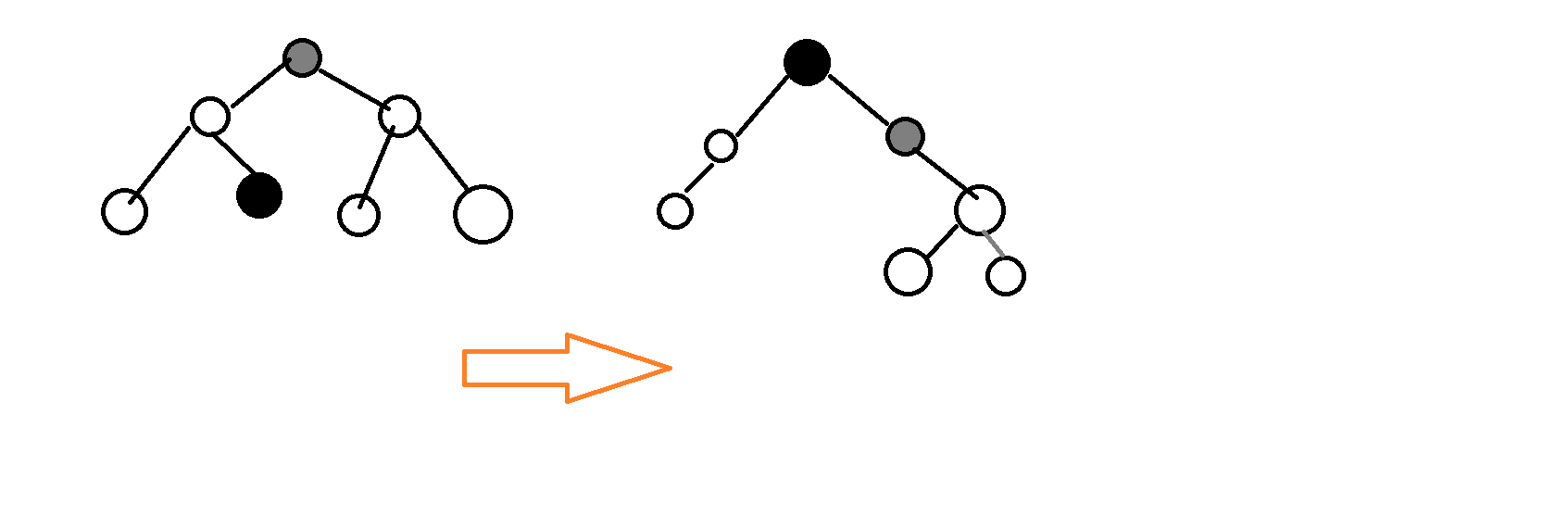
发现前驱,原来的根,原来的根的右儿子共线,且原来的根没有左儿子。
直接删去原来的根即可。
记得操作完一定要 pushup.
code
void del(int x) {
find(x);
if(cnt[rt]>1) {cnt[rt]--; pushup(rt); return ;}
if(!ch[rt][0]&&!ch[rt][1]) {rt=0; return ;}
if(!ch[rt][0]||!ch[rt][1]) {
rt=ch[rt][0]?ch[rt][0]:ch[rt][1];
fa[rt]=0;
return ;
}
int ort=rt,p=pre(x);
splay(p,0);
ch[rt][1]=ch[ort][1]; fa[ch[ort][1]]=rt;
pushup(rt);
}
应用
P6136 【模板】普通平衡树(数据加强版)
模板。
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=11e5+10;
int n,m,last,ans;
int rt,tot;
int fa[N],ch[N][2],val[N],cnt[N],sz[N];
bool get(int x) {return ch[fa[x]][1]==x;}
void pushup(int x) {
if(x) {
sz[x]=cnt[x];
if(ch[x][0]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][0]];
if(ch[x][1]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][1]];
}
}
void rotate(int x) {
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y],k=get(x);
ch[y][k]=ch[x][k^1]; fa[ch[x][k^1]]=y;
ch[x][k^1]=y; fa[y]=x;
fa[x]=z;
if(z) ch[z][ch[z][1]==y]=x;
pushup(y); pushup(x);
}
void splay(int x,int goal=0) {
for(; fa[x]!=goal; ) {
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y];
if(z!=goal) rotate(get(x)==get(y)?y:x);
rotate(x);
}
if(goal==0) rt=x;
}
void find(int x) {
int u=rt;
if(!u) return ;
for(; ch[u][x>val[u]]&&x!=val[u]; )
u=ch[u][x>val[u]];
splay(u,0);
}
void insert(int x) {
int u=rt,f=0;
for(; u&&val[u]!=x; ) {
f=u;
u=ch[u][x>val[u]];
}
if(u) {cnt[u]++; pushup(u); pushup(f);}
else {
u=++tot;
val[u]=x; sz[u]=cnt[u]=1;
fa[u]=f; ch[u][0]=ch[u][1]=0;
if(f) {ch[f][x>val[f]]=u; pushup(f);}
else rt=u;
}
splay(u,0);
}
int query_rank(int x) {
find(x);
if(val[rt]>=x) return sz[ch[rt][0]]+1;
else return sz[ch[rt][0]]+cnt[rt]+1;
}
int query_kth(int x) {
int u=rt;
for(; u; ) {
if(ch[u][0]&&x<=sz[ch[u][0]])
u=ch[u][0];
else {
int tmp=sz[ch[u][0]]+cnt[u];
if(x<=tmp) {splay(u,0); return val[u];}
x-=tmp; u=ch[u][1];
}
}
}
int pre(int x) {
find(x);
if(val[rt]<x) return rt;
int u=ch[rt][0];
for(; ch[u][1]; ) u=ch[u][1];
splay(u,0);
return u;
}
int succ(int x) {
find(x);
if(val[rt]>x) return rt;
int u=ch[rt][1];
for(; ch[u][0]; ) u=ch[u][0];
splay(u,0);
return u;
}
void del(int x) {
find(x);
if(cnt[rt]>1) {cnt[rt]--; pushup(rt); return ;}
if(!ch[rt][0]&&!ch[rt][1]) {rt=0; return ;}
if(!ch[rt][0]||!ch[rt][1]) {
rt=ch[rt][0]?ch[rt][0]:ch[rt][1];
fa[rt]=0;
return ;
}
int ort=rt,p=pre(x);
splay(p,0);
ch[rt][1]=ch[ort][1]; fa[ch[ort][1]]=rt;
pushup(rt);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int x; n--; ) {
scanf("%d",&x);
insert(x);
}
for(int op,x; m--; ) {
scanf("%d%d",&op,&x);
x^=last;
switch(op) {
case 1: insert(x); break;
case 2: del(x); break;
case 3: last=query_rank(x); ans^=last; break;
case 4: last=query_kth(x); ans^=last; break;
case 5: last=val[pre(x)]; ans^=last; break;
case 6: last=val[succ(x)]; ans^=last; break;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
P3391 【模板】文艺平衡树
这道题维护的是区间序列顺序,所以不能用权值排序了,而要维护的是 splay 的中序遍历。
平衡树可能不满足权值的关系。
怎么翻转一个区间呢?先把其他的元素隔离开罢。
我们把 l-1,r+1 旋转上来。
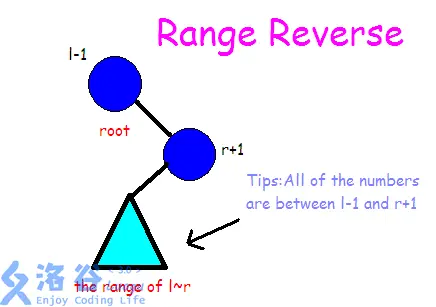
那么就把 l,r 区间打上标记,代表其子树内所有节点需要翻转。
注意:当一个打了标记的节点需要改变位置的时候:一定要标记下传。
最后输出树的中序遍历即可。
注意这里的 find 和模板的 find 不一样。
此处 find 为寻找数列排第 x 的数。
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+10,inf=1e9;
int n,m;
int rt,tot;
int fa[N],ch[N][2],val[N],cnt[N],sz[N],tag[N];
bool get(int x) {return ch[fa[x]][1]==x;}
void pushup(int x) {
if(x) {
sz[x]=cnt[x];
if(ch[x][0]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][0]];
if(ch[x][1]) sz[x]+=sz[ch[x][1]];
}
}
void pushdown(int x) {
if(x&&tag[x]) {
tag[ch[x][0]]^=1;
tag[ch[x][1]]^=1;
swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]);
tag[x]=0;
}
}
void rotate(int x) {
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y],k=get(x);
pushdown(y); pushdown(x);
ch[y][k]=ch[x][k^1]; fa[ch[x][k^1]]=y;
ch[x][k^1]=y; fa[y]=x;
fa[x]=z;
if(z) ch[z][ch[z][1]==y]=x;
pushup(y); pushup(x);
}
void splay(int x,int goal) {
for(; fa[x]!=goal; ) {
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y];
if(z!=goal) rotate(get(x)==get(y)?y:x);
rotate(x);
}
if(goal==0) rt=x;
}
int find(int x) {
int u=rt;
for(; u; ) {
pushdown(u);
if(x<=sz[ch[u][0]]) u=ch[u][0];
else {
x-=sz[ch[u][0]]+cnt[u];
if(!x) return u;
u=ch[u][1];
}
}
}
void insert(int x) {
int u=rt,f=0;
for(; u&&val[u]!=x; ) {
f=u;
u=ch[u][x>val[u]];
}
u=++tot;
val[u]=x; sz[u]=cnt[u]=1;
fa[u]=f; ch[u][0]=ch[u][1]=0;
if(f) {ch[f][x>val[f]]=u; pushup(f);}
else rt=u;
splay(u,0);
}
void reverse(int x,int y) {
int l=find(x-1),r=find(y+1);
splay(l,0); splay(r,l);
tag[ch[r][0]]^=1;
}
void dfs(int x) {
pushdown(x);
if(ch[x][0]) dfs(ch[x][0]);
if(val[x]!=-inf&&val[x]!=inf)
printf("%d ",val[x]);
if(ch[x][1]) dfs(ch[x][1]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
insert(-inf);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) insert(i);
insert(inf);
for(int i=1,l,r; i<=m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
reverse(l+1,r+1);
}
dfs(rt);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号