2021.6.29:新旧API转换、java.sql.Date
新旧API转换
Java提供了新旧两套时间日期API,除非涉及到遗留代码,否则我们应该坚持使用新API。
Date、Calendar→ZonedDateTime
把旧的Date、Calendar对象转换为新API对象ZonedDateTime,可以通过toInstant()方法转换为Instant对象,再用ins.atZone(ZoneId)继续转换为ZonedDateTime:
//Date → Instant Instant ins1 = new Date().toInstant(); //Calendar → Instant Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); Instant ins2 = calendar.toInstant(); //Instant → ZonedDateTime ZoneId zoneid = calendar.getTimeZone().toZoneId(); ZonedDateTime zdt = ins2.atZone(zoneid);
ZonedDateTime→Date、Calendar
需要借助long型时间戳
// ZonedDateTime -> long: ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.now(); long ts = zdt.toEpochSecond() * 1000; // long -> Date: Date date = new Date(ts); // long -> Calendar: Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.clear(); calendar.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone(zdt.getZone().getId())); calendar.setTimeInMillis(zdt.toEpochSecond() * 1000);
此外,新的ZoneId转换为旧的TimeZone,需要借助ZoneId.getId()返回的String完成。
java.sql.Date
说明
数据库中存储Date、Time。
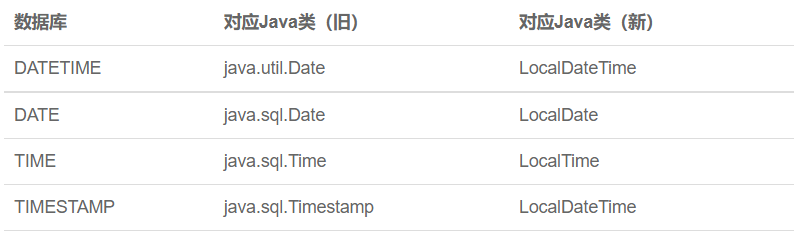
数据库中的时间类型
- DATETIME
- DATE
- TIME
- TIMESTAMP:和DATETIME类似,但是数据库会在创建或者更新记录 时同时修改TIMESTAMP
与Java新旧API的对应关系
不过在数据库中最常用的是时刻(Instant),有了时刻信息,加上时区,就可以还原出正确的本地时间。因此最好的方法是用长整数long表示,在数据库中存储为BIGINT类型。
通过存储一个long型时间戳,我们可以编写一个timestampToString()方法,可以简单地为不同用户用不同偏好显示不同的本地时间:
import java.time.*; import java.time.format.*; import java.util.Locale; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { long ts = 1574208900000L; System.out.println(timestampToString(ts,Locale.CHINA,"Asia/Shanghai")); System.out.println(timestampToString(ts,Locale.US,"America/New_York")); } static String timestampToString(long epochMilli,Locale lo,String zoneId){ Instant ins = Instant.ofEpochMilli(epochMilli); DateTimeFormatter f = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM,FormatStyle.SHORT); return f.withLocale(lo).format(ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(ins,ZoneId.of(zoneId))); } }
2019年11月20日 上午8:15
Nov 19, 2019, 7:15 PM


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号