Java: Wrapper Classes
Wrapper classes provide a way to use primitive data types (int, boolean, etc..) as objects.
| Primitive Data Type | Wrapper Class |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
| char | Character |
Sometimes you must use wrapper classes, for example when working with Collection objects, such as ArrayList, where primitive types cannot be used:
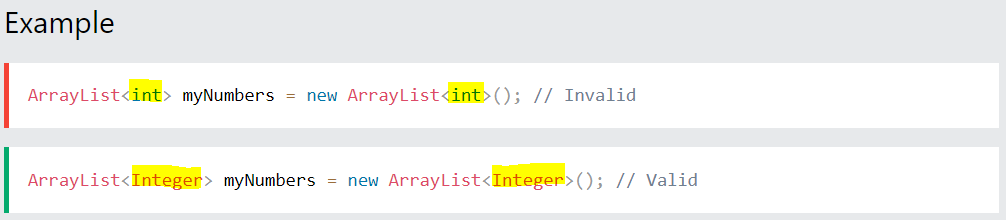
For example, the following methods are used to get the value associated with the corresponding wrapper object: intValue(), byteValue(), shortValue(), longValue(), floatValue(), doubleValue(), charValue(), booleanValue().
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer myInt = 5; -> Integer Double myDouble = 5.99; -> Double Character myChar = 'A'; -> Character System.out.println(myInt.intValue()); -> int System.out.println(myDouble.doubleValue()); -> double System.out.println(myChar.charValue()); -> char } }
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer myInt = 100; String myString = myInt.toString(); System.out.println(myString.length()); } }
// Outputs: 3




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号