Tarjan
- 有向图G中,以顶点v为起点的弧的数目称为v的出度,记做deg+(v);以顶点v为终点的弧的数目称为v的入度,记做deg-(v)。
- 如果在有向图G中,有一条<u,v>有向道路,则v称为u可达的,或者说,从u可达v。
- 什么是强连通?强连通其实就是指图中有两点u,v。使得能够找到有向路径从u到v并且也能够找到有向路径从v到u,则称u,v是强连通的。
- 如果有向图G的任意两个顶点都互相可达,则称图 G是强连通图,如果有向图G存在两顶点u和v使得u不能到v,或者v不能到u,则称图G是强非连通图。
- 如果有向图G不是强连通图,他的子图G2是强连通图,点v属于G2,任意包含v的强连通子图也是G2的子图,则乘G2是有向图G的极大强连通子图,也称强连通分量。
DFN【】记录遍历次序,low【】记录某环第一个被访问的点one,然后再第二次遍历到one的时候,将路径上所有的点的low【】全部更新为low【one】,也就是全部更新为第一次访问的点one;如果在回溯过程中DFN【X】 = low【X】,则说明存在一个强联通分量。
Tarjan:可以用来缩点和找环,> 将一个有向带环图变成了一个有向无环图(DAG图) <
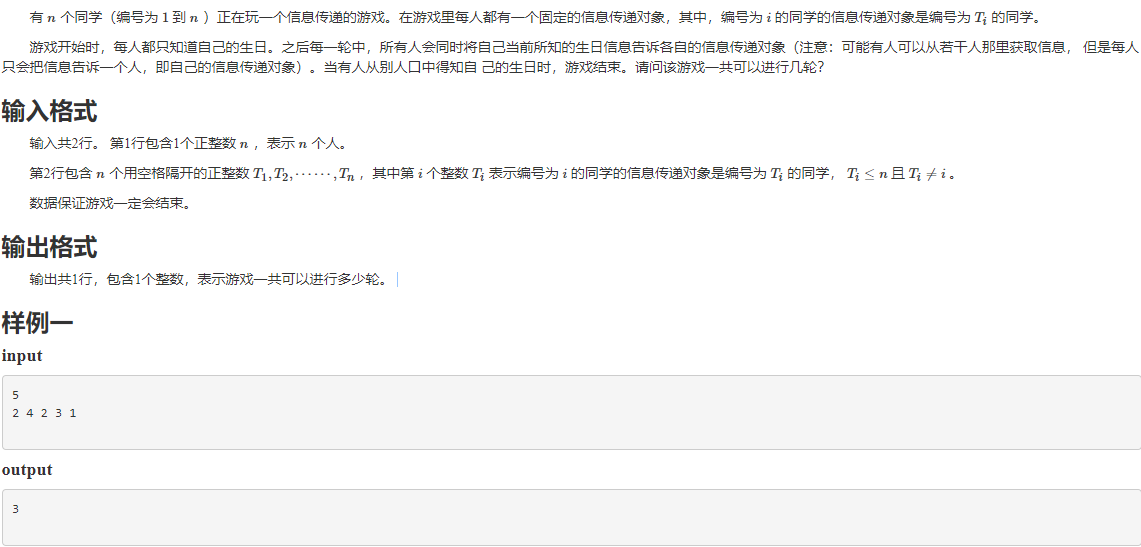
【NOIP2015】信息传递
数据规模与约定
| 测试点编号 | nn 的规模 |
|---|---|
| 1 | n≤200n≤200 |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | n≤2500n≤2500 |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | n≤200000n≤200000 |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 |
时间限制:1s
空间限制:128MB

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long using namespace std; const int mod = 1e9+7;/// 998244353; const int mxn = 2e5 +7; int _,m,n,t,k,ans,cnt,lg; vector<int>e[mxn]; stack<int>s; int vis[mxn] , dfn[mxn] , low[mxn] ; void tarjan(int x) { vis[x] = 1 ; s.push(x); low[x] = dfn[x] = cnt++; for(int i=0 , v ;i<e[x].size();i++){ v = e[x][i] ; if(!dfn[v]){ tarjan(v); low[x] = min( low[x] , low[v] ); } else { low[x] = min( low[x] , dfn[v] ); } } if(dfn[x]==low[x]){ int res = 0 ; while(1){ int now = s.top(); s.pop(); vis[now] = 0 ; res++; if(now==x) break; } if(res>1) ans = min(res , ans ) ; } } void solve() { while(cin>>n) { cnt = 1 ; ans = mod ; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ cin>>k; e[i].push_back(k); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!vis[i]){ tarjan(i); } } cout<< ans <<endl; } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); solve(); }
HDU - 2586 How far away ?
InputFirst line is a single integer T(T<=10), indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case,in the first line there are two numbers n(2<=n<=40000) and m (1<=m<=200),the number of houses and the number of queries. The following n-1 lines each consisting three numbers i,j,k, separated bu a single space, meaning that there is a road connecting house i and house j,with length k(0<k<=40000).The houses are labeled from 1 to n.
Next m lines each has distinct integers i and j, you areato answer the distance between house i and house j.OutputFor each test case,output m lines. Each line represents the answer of the query. Output a bland line after each test case.Sample Input
2 3 2 1 2 10 3 1 15 1 2 2 3 2 2 1 2 100 1 2 2 1
Sample Output
10 25 100 100

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long using namespace std; const int mod = 1e9+7;/// 998244353; const int mxn = 5e4 +7; int _,m,n,t,k,ans,cnt,lg; struct e{ int to,x,nx; }e[40000*2+7]; int dep[mxn] , f[mxn][30] , len[mxn] , head[mxn] ; void add(int u,int v,int w) { e[cnt].to = v; e[cnt].x = w ; e[cnt].nx = head[u]; head[u] = cnt++; } void bfs() { memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); memset(dep,0.,sizeof(dep)); queue<int>q; q.push(1); dep[1] = 1 ; while(!q.empty()) { int u = q.front() ; q.pop() ; for(int i=head[u] ; ~i ;i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].to ; if(dep[v]) continue; len[v] = len[u] + e[i].x; dep[v] = dep[u] + 1 ; f[v][0] = u ; /// 存储父节点 for(int j=1;j<=lg;j++) f[v][j] = f[ f[v][j-1] ][j-1] ; q.push(v); } } } int lca(int u,int v) { if(dep[u]>dep[v] ) swap(u,v); for(int i=lg;i>=0;i--) /// 提升 V 和 U 至相同的高度 if( dep[ f[v][i] ] >= dep[u] ) v = f[v][i] ; if(v==u) return u ; for(int i=lg;i>=0;i--) /// 找到最近的 LCA if( f[u][i] != f[v][i] ) u = f[u][i] , v = f[v][i] ; return f[u][0]; } void solve() { for(cin>>t;t;t--) { cin>>n>>m; cnt = 0 ; lg = int(log(n)/log(2))+1; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(int i=1,u,v,w;i<n;i++){ cin>>u>>v>>w; add(u,v,w); add(v,u,w); } bfs(); while(m--) { int u , v ; cin>>u>>v; cout<<len[u]+len[v] - 2*len[ lca(u,v) ]<<endl; } } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); solve(); }

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long using namespace std; const int mod = 1e9+7;/// 998244353; const int mxn = 8e4 +7; const int N = 8e4 + 7 ; int _,m,n,t,k,ans,cnt,lg; int head[N] , far[N] , len[N] , vis[N] , a[mxn] ; vector< pair<int,int> > q[N] ; struct ${ int to , nx , w ; }e[mxn*2]; int root(int x) { return x==far[x] ? x : far[x] = root(far[x]); } void add(int u,int v,int w) { e[cnt].to = v ; e[cnt].w = w ; e[cnt].nx = head[u] ; head[u] = cnt++; } void tarjan(int u) { vis[u] = 1 ; for(int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].nx){ int v = e[i].to ; if(!vis[v]){ len[v] = len[u] + e[i].w ; tarjan(v); far[v] = u ; } } for(int i=0;i<q[u].size();i++){ int v = q[u][i].first , id = q[u][i].second ; if(vis[v]==2){ int lca = root(v); a[id] = min( a[id] , len[u]+len[v] - 2*len[lca] ); } } vis[u] = 2 ; } void init() { cnt = 0 ; for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) len[i] = 0 , far[i] = i , vis[i] = 0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); } void solve() { for(cin>>t;t;t--){ cin>>n>>m; init(); for(int i=1,u,v,w;i<n;i++){ cin>>u>>v>>w; add(u,v,w); add(v,u,w); } for(int i=1,u,v;i<=m;i++){ cin>>u>>v; q[u].push_back( {v,i} ); q[v].push_back( {u,i} ); a[i] = 1<<30 ; } tarjan(1); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) cout<<a[i]<<endl; } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); solve(); }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号