[AGC047F] Rooks 题解
Description
有 \(N\) 个车在一张无限大的棋盘上,第 \(i\) 个在 \((X_i,Y_i)\)。每行每列最多一个车。
有一个卒,会替换第 \(s\) 个车,可以走八连通,但是不能走到被车攻击的地方。吃车的时候可以走对角,否则只能走上下左右。
对于 \(s=1\ldots N\),求出吃掉最多的车时的最小步数。
\(2\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5,1\leq X_i,Y_i\leq 10^6,X_i\neq X_j,Y_i\neq Y_j\)。
Solution
先对 \(x,y\) 分别离散化并按照 \(x\) 坐标从小到大排序,那么 \(s\) 任何时刻吃的车一定构成一个区间 \([l,r]\),满足 \(l\leq s\leq r\)。
显然可以进行 dp。
设 \(f_{l,r,0/1}\) 表示当前吃掉的车为 \([l,r]\),且当前的位置是 \(l/r\),到最终状态的最小步数。
容易发现任意时刻吃掉车的 \(y\) 坐标也构成一个区间 \([l_y,r_y]\),所以下一步走的车坐标一定为 \((l-1,l_y-1),(l-1,r_y+1),(r+1,l_y-1),(r+1,r_y+1)\)。具体的,如果 \(y_{l-1}=l_y-1\),可以得到转移方程:\(f_{l,r,0}\leftarrow f_{l-1,r,0}+\text{dis}(l-1,l)-1\),剩下的同理。
这个做法的时间复杂度是 \(O(n^2)\),过不了。
注意到这个做法的转移是 \(O(1)\) 的,而状态很多,所以考虑优化状态。
首先对于 \(y_i=i\) 的问题,一定是先从 \(s\) 走到 \(1\) 再走到 \(n\),或者先到 \(n\) 再一路到 \(1\)。
这里也是一样的,如果先走到 \(l-1\) 且 \(|y_{l-2}-y_{l-1}|=1\),那么一路向左走直到差不是 \(1\) 了一定更优。
考虑把这些相邻差为 \(1\) 的段缩起来,容易发现到达段内的任何一个点后段里的其它点也可以走过去。并且如果第一次到了这个段的左右端点,则之后一路把整段走完一定最优。
所以每次拓展时按照整段拓展即可,可以发现现在状态数减少了不少,实际状态上变成 \(O(n)\) 的了。
证明就考虑有用的状态一定满足区间内 \(y\) 构成一段区间且不能拓展,形如下面的图(图源:link):

然后对于每个 \(y\) 相差 \(1\) 的极长连续段 \([l,r]\),计算有多少个状态满足最后一次是从它拓展的。
由于 \([l,r]\) 极长,所以只有两种包含它的方案:
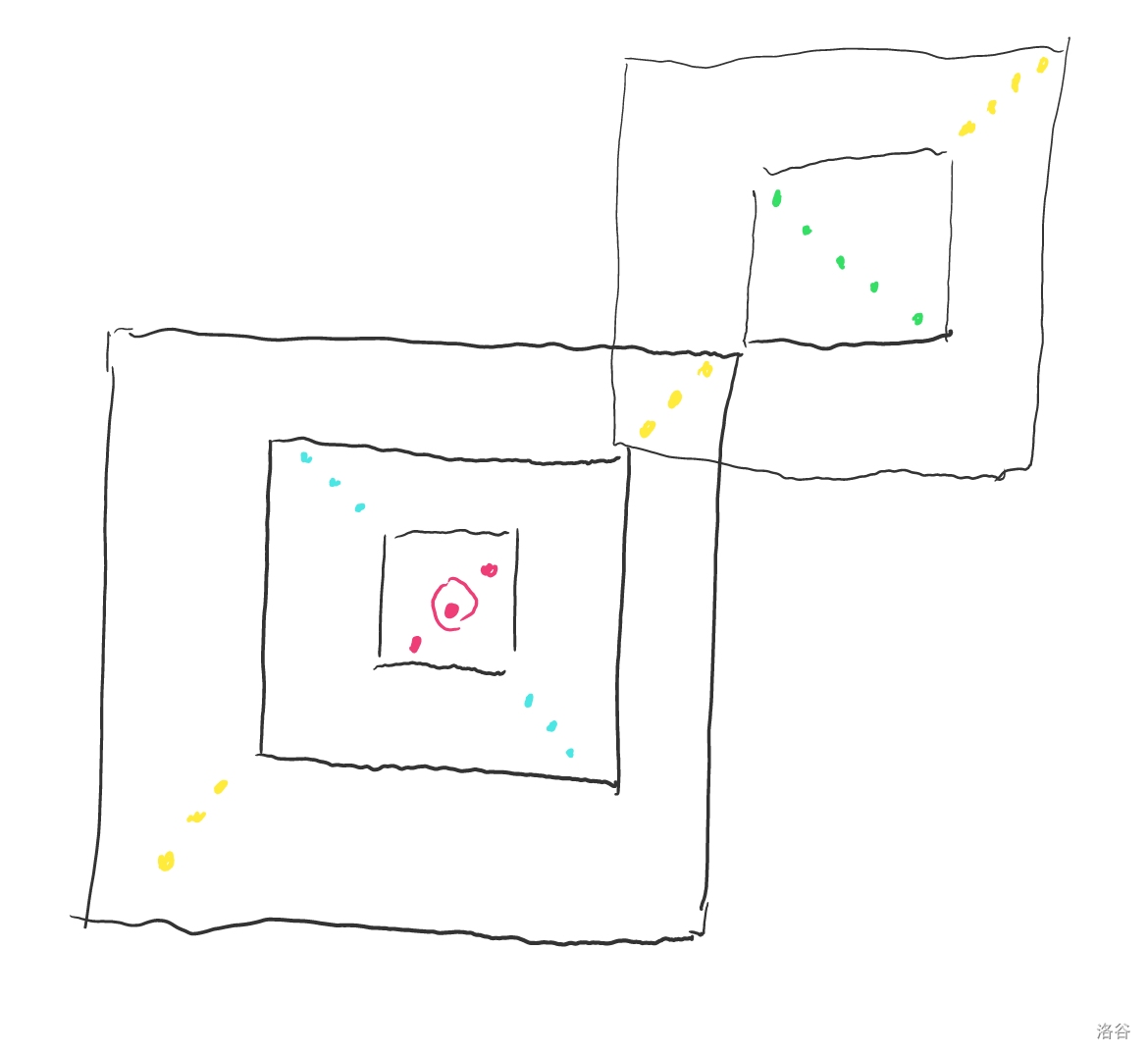
所以总状态数是 \(O(n)\) 的。
用一个哈希表存下这些状态即可。
时间复杂度:\(O(n\log n)\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int int64_t
const int kMaxN = 2e5 + 5;
struct custom_hash {
static uint64_t splitmix64(uint64_t x) {
x += 0x9e3779b97f4a7c15;
x = (x ^ (x >> 30)) * 0xbf58476d1ce4e5b9;
x = (x ^ (x >> 27)) * 0x94d049bb133111eb;
return x ^ (x >> 31);
}
size_t operator()(uint64_t x) const {
static const uint64_t FIXED_RANDOM = std::chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
return splitmix64(x + FIXED_RANDOM);
}
size_t operator()(std::tuple<uint64_t, uint64_t, uint64_t> x) const {
static const uint64_t FIXED_RANDOM = std::chrono::steady_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
return splitmix64(std::get<0>(x) + FIXED_RANDOM) ^
(splitmix64(std::get<1>(x) + FIXED_RANDOM) >> 1) ^
(splitmix64(std::get<2>(x) + FIXED_RANDOM) >> 2);
}
};
int n;
int x[kMaxN], y[kMaxN], unqx[kMaxN], unqy[kMaxN], ans[kMaxN];
int L[kMaxN], R[kMaxN];
std::unordered_map<std::tuple<int, int, bool>, int, custom_hash> f;
struct Node {
int x, y, id;
} t[kMaxN];
int getdis(int i, int j) {
return abs(unqx[t[i].x] - unqx[t[j].x]) + abs(unqy[t[i].y] - unqy[t[j].y]);
}
int solve(int l, int r, int ly, int ry, bool isleft) {
if (f.count({l, r, isleft})) return f[{l, r, isleft}];
int ret = 1e18;
if (l > 1 && (t[l - 1].y == ly - 1 || t[l - 1].y == ry + 1))
ret = std::min(ret, solve(L[l - 1], r, std::min({ly, t[l - 1].y, t[L[l - 1]].y}), std::max({ry, t[l - 1].y, t[L[l - 1]].y}), 1) + getdis(l - 1, isleft ? l : r) + getdis(l - 1, L[l - 1]));
if (r < n && (t[r + 1].y == ly - 1 || t[r + 1].y == ry + 1))
ret = std::min(ret, solve(l, R[r + 1], std::min({ly, t[r + 1].y, t[R[r + 1]].y}), std::max({ry, t[r + 1].y, t[R[r + 1]].y}), 0) + getdis(r + 1, isleft ? l : r) + getdis(r + 1, R[r + 1]));
if (ret == 1e18) ret = -(r - l);
return f[{l, r, isleft}] = ret;
}
void dickdreamer() {
std::cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
std::cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
unqx[i] = x[i], unqy[i] = y[i];
}
std::sort(unqx + 1, unqx + 1 + n);
std::sort(unqy + 1, unqy + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
x[i] = std::lower_bound(unqx + 1, unqx + 1 + n, x[i]) - unqx;
y[i] = std::lower_bound(unqy + 1, unqy + 1 + n, y[i]) - unqy;
t[i] = {x[i], y[i], i};
}
std::sort(t + 1, t + 1 + n, [&] (auto a, auto b) { return a.x < b.x; });
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (i > 1 && abs(t[i].y - t[i - 1].y) == 1) L[i] = L[i - 1];
else L[i] = i;
}
for (int i = n; i; --i) {
if (i < n && abs(t[i].y - t[i + 1].y) == 1) R[i] = R[i + 1];
else R[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ans[t[i].id] = solve(i, i, t[i].y, t[i].y, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) std::cout << ans[i] << '\n';
}
int32_t main() {
#ifdef ORZXKR
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0), std::cin.tie(0), std::cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// std::cin >> T;
while (T--) dickdreamer();
// std::cerr << 1.0 * clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s\n";
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号