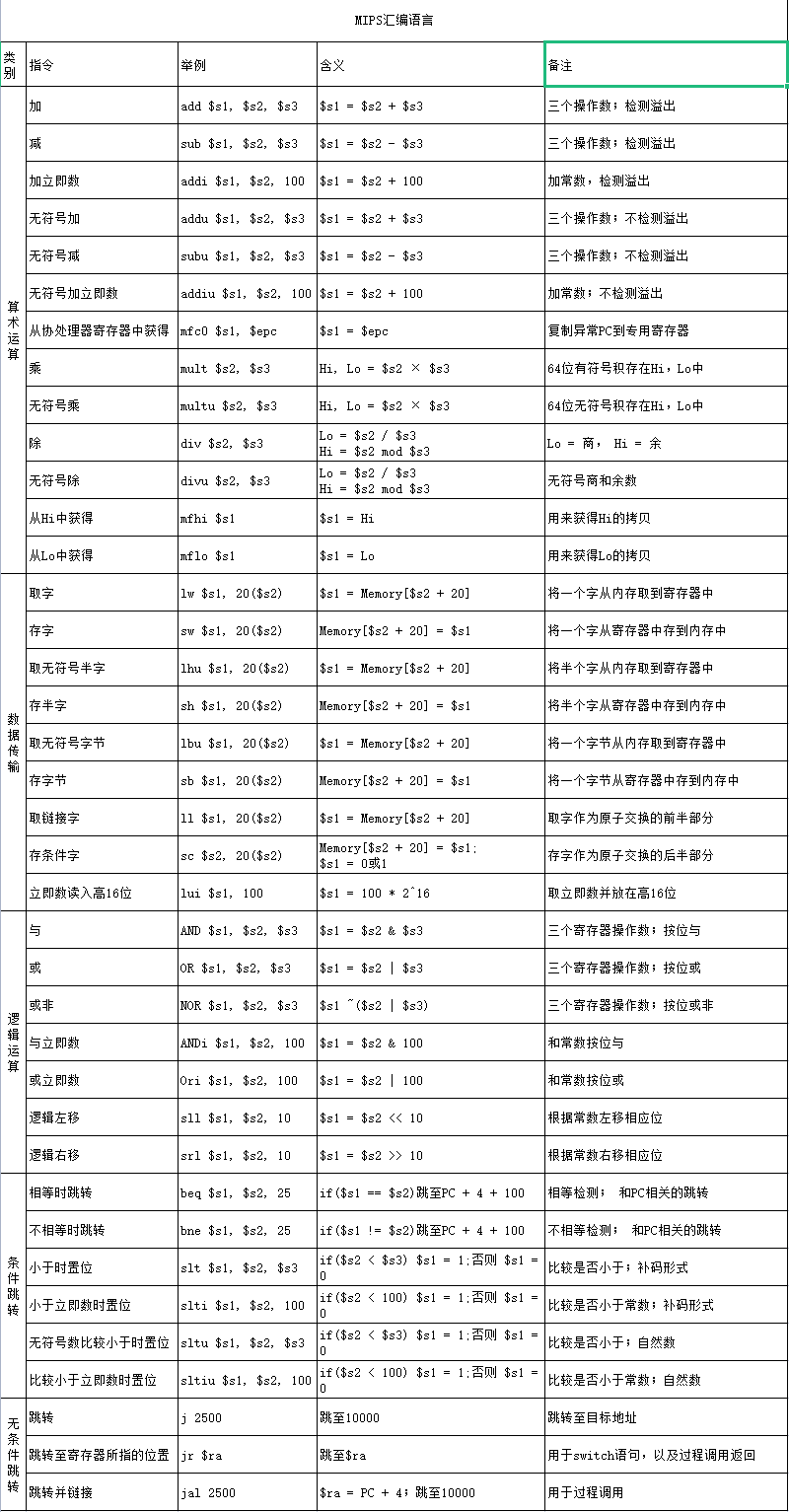
MIPS汇编语言和相关调试环境
1. 安装使用MARS
MARS是MIPS汇编语言的模拟机,由密苏里州立大学开发。
下载地址:https://courses.missouristate.edu/KenVollmar/MARS/download.htm
将MAR4_5.jar存放在XXX文件夹中。
启动MARS
- win+R+cmd,使用
java -version看java版本
![]()
java -jar打开MARS
![]()
![]()
打开的是桌面上的mars.jar,其他盘的mars.jar不知道为什么无法打开
打开示例文件mips-ex1.asm
点击菜单file->open,选中asm文件并打开。
打开后如图所示: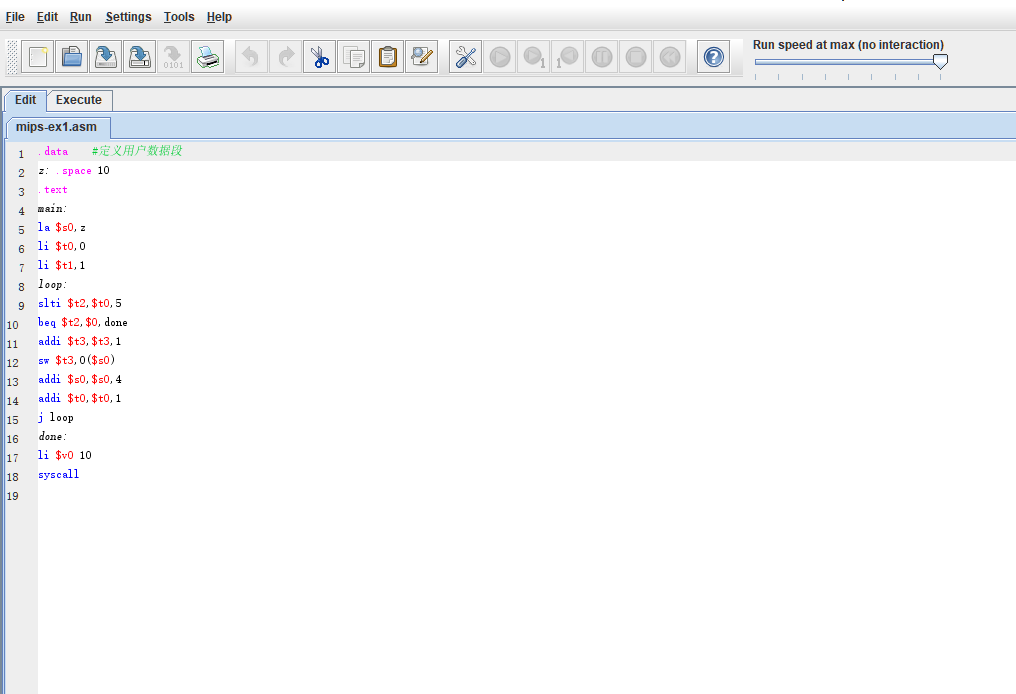
.data #定义用户数据段
z: .space 10
.text
main:
la $s0,z
li $t0,0
li $t1,1
loop:
slti $t2,$t0,5
beq $t2,$0,done
addi $t3,$t3,1
sw $t3,0($s0)
addi $s0,$s0,4
addi $t0,$t0,1
j loop
done:
li $v0 10
syscall
汇编
双击工具栏按钮  ,汇编该程序
,汇编该程序
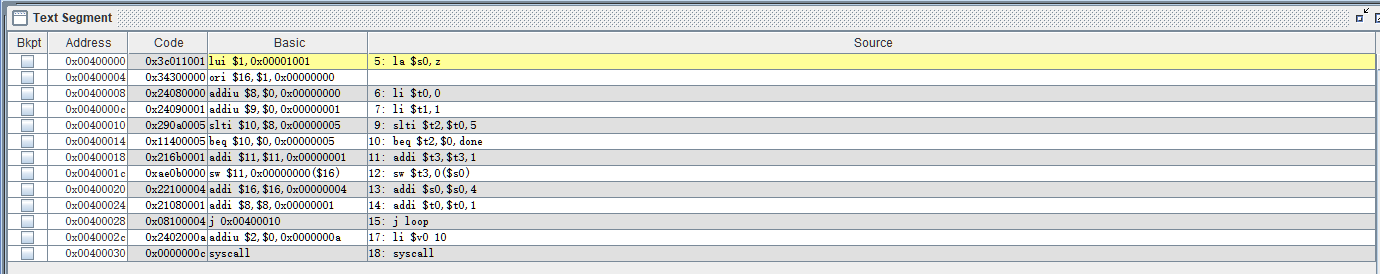
程序初始数据在内存中的位置和具体的数值,单击复选框 ,在“10进制显示”和“16进制显示”之间进行切换。
,在“10进制显示”和“16进制显示”之间进行切换。
使用“Settings”菜单配置MARS的显示内容。
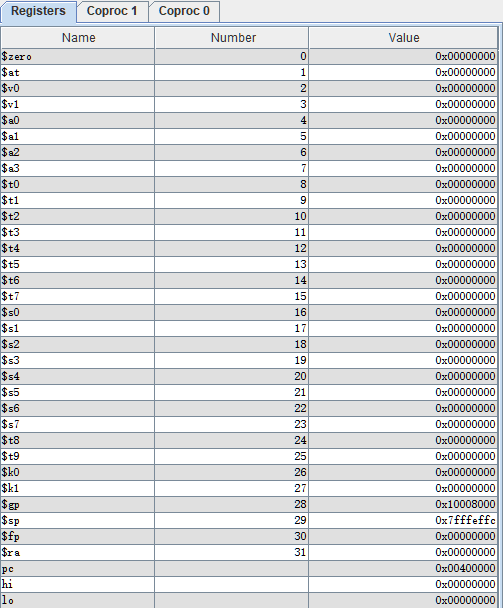
观察寄存器显示窗口,这里显示了32个通用MIPS寄存器的内容。寄存器显示窗口里的另外两个标签页显示了浮点运算寄存器(Coproc 1)和(Coproc 0)

使用滑动条来改变运行速度,便于观察汇编程序的执行过程
选择程序运行方式
![]() 直接运行程序:通过黄色高亮部分来观察程序的运行,并在数据段显示窗口Data Segment display中观察数值的变化。可以用滑动条改变运行速度如下图中黄色和蓝色部分。
直接运行程序:通过黄色高亮部分来观察程序的运行,并在数据段显示窗口Data Segment display中观察数值的变化。可以用滑动条改变运行速度如下图中黄色和蓝色部分。
![]()
![]() 重置程序为初始值
重置程序为初始值![]() 单步执行程序,与
单步执行程序,与![]() (单步回退程序)功能相反。
(单步回退程序)功能相反。
在输入输出窗口中观察程序的输出
修改某个内存地址中的内容。(修改寄存器的内容类似)
- 在输出结果子程序的第一条指令前添加断点,即勾中该指令的复选框。
![]()
- 单击
![]() 和
和![]() ,重新运行程序后,程序将在断点处停止运行。
,重新运行程序后,程序将在断点处停止运行。 - 双击某个内存位置,该单元将高亮显示,并接受键盘输入。输入一个数值,按回车键结束输入
- 单击
![]() ,从断点处继续执行程序。程序的输出将会包含刚才输入的数值
,从断点处继续执行程序。程序的输出将会包含刚才输入的数值
单击![]()
查看帮助文件,熟悉MIPS指令、伪指令、directives和syscalls。
2. MIPS 体系结构和汇编语言
基本知识
数据类型和文法
- 数据类型:字节,1 byte 占用( 8bit ), halfword 占 (2 byte= 16bit), word 占用(4byte = 32bit)
- 一个字符需要一个 Byte 的空间;
- 一个整数需要 1 个 Word(4 Byte)的空间;
- MIPS 结构的每条指令长度都是 32bit
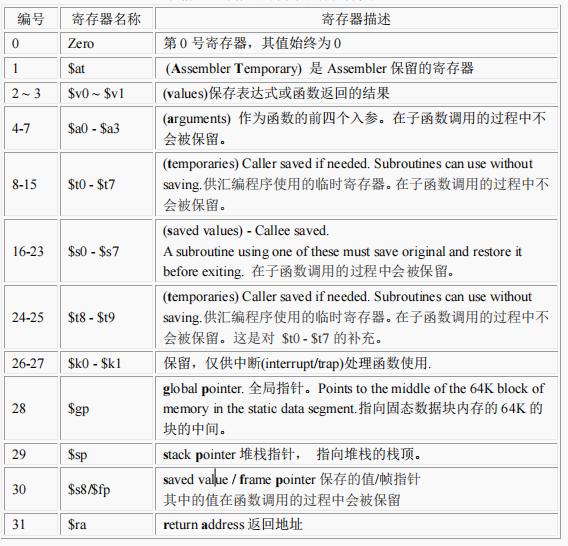
寄存器
- MIPS体系架构有32个通用寄存器,在汇编程序中,可以用编号
$0到$31来表示,或者使用寄存器的名字表示,如$sp,$t1,$ra... - 有两个特殊的寄存器,名为Lo,Hi,用来保存乘法/除法的运算结果。这两个寄存器不能直接寻址,只能使用特殊的指令:
mfhi和mflo来 access其中的内容
(mfhi : move from Hi ; mflo : Move from low) - 堆栈(stack)的增长方向:从内存的高地址方向向低地址方向增长
![]()
** MIPS寄存器编号及其分类 **
汇编程序结构框架
汇编源程序代码本质上是文本文件。由数据声明、代码段两部分组成。汇编程序文件以.s为后缀,在Spim或ASM中进行模拟。
- 数据声明
以.data开始,声明代码中使用的变量名,同事在主存RAM中创建了对应空间。 - 程序代码
以.text开始,包含了以指令构成的程序功能代码。代码以main:开始,结束点调用exit system call。 - 注释
使用#符号注释
汇编程序框架如下:
# Comment giving name of program and description of function
# Template.s
# Bare-bones outline of MIPS assembly language program
.data # variable declarations follow this line
# ...
.text # instructions follow this line
main: # indicates start of code (first instruction to execute)
# ...
# End of program, leave a blank line afterwards to make SPIM happy
编写MIPS汇编程序
1.数据的声明
格式:[name为变量名,values为初始值,storage_type为存储类型]
var1: .word 3 # create a single integer:
#variable with initial value 3
array1: .byte 'a','b' # create a 2-element character
# array with elements initialized:
# to a and b
array2: .space 40 # allocate 40 consecutive bytes,
# with storage uninitialized
# could be used as a 40-element
# character array, or a
# 10-element integer array;
# a comment should indicate it.
string1 .asciiz "Print this.\n" #declare a string
2.数据的装载和保存(Load/Store指令)
- 主存(RAM)的存取access只能用
load/store指令来完成 - 其他指令都使用寄存器为操作数
i. load指令
lw register_destination, RAM_source
# copy word (4 bytes) at
# source_RAM location
# to destination register.
# load word -> lw
lb register_destination, RAM_source
# copy byte at source RAM
# location to low-order byte of
# destination register,
# and sign -e.g. tend to
# higher-order bytes
# load byte -> lb
li register_destination, value
#load immediate value into
#destination register
#load immediate --> li
ii. store 指令
sw register_source, RAM_destination
#store word in source register
# into RAM destination
sb register_source, RAM_destination
#store byte (low-order) in
#source register into RAM
#destination
举例:
.data
var1: .word 23 # declare storage for var1;
#initial value is 23
.text
__start:
lw $t0, var1 # load contents of RAM location
# into register $t0:
# $t0 = var1
li $t1, 5 # $t1 = 5 ("load immediate")
sw $t1, var1 # store contents of register $t1
# into RAM: var1 = $t1 done
done
3.寻址
MIPS系统结构只能用load/store相关指令来实现寻址操作,包含三种寻址方式:
- 直接寻址/装载地址
load address把数据地址直接载入寄存器
la $t0,var1
把var1在主存(RAM)中的地址拷贝到寄存器t0中。var1也可以是程序中定义的一个子程序标签的地址 - 间接寻址
indirect addressing把寄存器内容作为地址
lw $t2,($t0)
主存中有一个字的地址存在t0中,按这个地址找到那个字,把字拷贝到寄存器t2中
sw $t2,($t0)
把t2中的字存入t0中的地址指向的内存位置 - 基线寻址/索引寻址
based or indexed addressing
lw $r2,4($t0)
把 t0 中地址+4 所得的地址所对应的主存中的字载入寄存器 t2 中,4 为包含在 t0 中的地址的偏移量
sw $t2,-12($t0)
把t2中的内容存入t0中的地址-12所得的地址所对应的主存中,存入一个字,占用四字节,消耗四个内存号。地址偏移量可以是负值。
注意:基线寻址在以下场合特别有用:
1、数组:从基址出发,通过使用偏移量,存取数组元素。
2、堆栈:利用从堆栈指针或者框架指针的偏移量来存取元素。
举例:
#example
.data
array1: .space 12 # declare 12 bytes of storage
# to hold array of 3 integers
.text
__start:
la $t0, array1 # load base address of array
# into register $t0
li $t1, 5 # $t1 = 5 ("load immediate")
sw $t1, ($t0) # first array element set to 5; # indirect addressing
li $t1, 13 # $t1 = 13
sw $t1, 4($t0) # second array element set to 13
li $t1, -7 # $t1 = -7
sw $t1, 8($t0) # third array element set to -7
done
4.算数运算指令(Arithmetic Instructions)
- 算数运算指令的所有操作数都是寄存器,不能直接使用RAM地址或间接寻址
- 操作数的大小都为word[4 byte = 32 bit]
add $t0,$t1,$t2 # $t0 = $t1 + $t2; add as signed
# (2's complement) integers
sub $t2,$t3,$t4 # $t2 = $t3 Ð $t4
addi $t2,$t3, 5 # $t2 = $t3 + 5; "add immediate"
# (no sub immediate)
addu $t1,$t6,$t7 # $t1 = $t6 + $t7;
addu $t1,$t6,5 # $t1 = $t6 + 5;
# add as unsigned integers
subu $t1,$t6,$t7 # $t1 = $t6 - $t7;
subu $t1,$t6,5 # $t1 = $t6 - 5
# subtract as unsigned integers
mult $t3,$t4 # multiply 32-bit quantities in $t3
# and $t4, and store 64-bit
# result in special registers Lo
# and Hi: (Hi,Lo) = $t3 * $t4
div $t5,$t6 # Lo = $t5 / $t6 (integer quotient)
# Hi = $t5 mod $t6 (remainder)
mfhi $t0 # move quantity in special register Hi
# to $t0: $t0 = Hi
mflo $t1 # move quantity in special register Lo
# to $t1: $t1 = Lo, used to get at
# result of product or quotient
move $t2,$t3 # $t2 = $t3
5.程序控制指令(Control Instructions)
- 分支指令(branches)
条件分支的比较机制已经内建在指令中
b target # unconditional branch to program label target
beq $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 = $t1
blt $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 < $t1
ble $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 <= $t1
bgt $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 > $t1
bge $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 >= $t1
bne $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 <> $t1
beqz $t0, lab # Branch to lab if $t0 = 0.
bnez $t0, lab # Branch to lab if $t0 != 0.
bgez $t0, lab # Branch to lab if $t0 >= 0.
bgtz $t0, lab # Branch to lab if $t0 > 0.
blez $t0, lab # Branch to lab if $t0 <= 0.
bltz $t0, lab # Branch to lab if $t0 < 0.
bgezal $t0, lab #If $t0 >= 0, then put the address of the next
#instruction into $ra and branch to lab.
bgtzal $t0, lab #If $t0 > 0, then put the address of the next
#instruction into $ra and branch to lab.
bltzal $t0, lab #If $t0 < 0, then put the address of the next
#instruction into $ra and branch to lab.
- 跳转指令(Jumps)
j target # unconditional jump to program label target
jr $t3 #jump to address contained in $t3 ("jump register")
- 子程序调用指令
子程序调用指令的实质是跳转并链接(jump and link),它把当前程序计数器的值保存在$ra中,以备调回:
跳转到子程序:
jal sub_label # "jump and link",preserve pc to $ra
sub_label为子程序标签,如LOOP,SUB_ROUTINE
从子程序返回:
jr $ra #"jump register",jump as the value of $ra
返回到$ra中储存的返回地址相应的位置,$ra中的返回地址由jal指令保存
注意,返回地址存放在\(ra 寄存器中。如果子程序调用了下一级子程序,或者是递归调 用,此时需要将返回地址保存在堆栈中,因为每执行一次 jal 指令就会覆盖\)ra 中的返回
地址。
6.系统调用和I/O操作(SPIM仿真)
系统调用是指调用操作系统的特定子程序。
系统调用用来在仿真器的窗口中打印或者读入字符串 string, 并可显示程序是否结束。
用 syscall 指令进行对系统子程序的调用。
本操作首先支持$v0 and $a0-$a1 中的相对值
调用以后的返回值(如果存在)会保存在$v0 中。
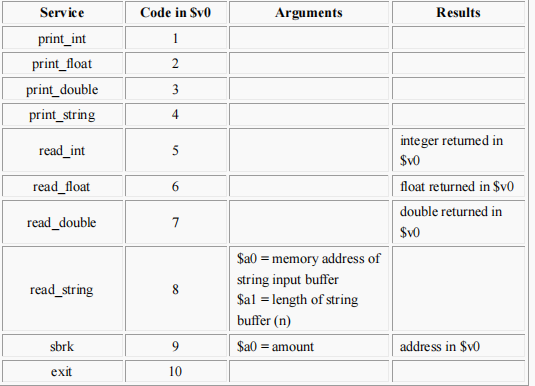
系统调用的功能
The print_string service expects the address to start a null-terminated character string. The
directive .asciiz creates a null-terminated character string.
打印字符串的功能认为起始地址为一个空终止符串。声明字符串使用的.asciiz 指示符会
建立一个空终止符串。
The read_int, read_float and read_double services read an entire line of input up to and
including the newline character.
读入整形,读入浮点型和读入双精度的功能会读取一整行,包含换行符。
The read_string service has the same semantices as the UNIX library routine fgets.
It reads up to n-1 characters into a buffer and terminates the string with a null character.
If fewer than n-1 characters are in the current line, it reads up to and including the newline
and terminates the string with a null character.
读入字符串的功能和 UNIX 库中 fgets 函数的语法相同。他会读入 n-1 个字符到缓存,
然后以空字符结尾。如果少于 n-1 的字符,它会读到结尾并包含换行符,并以空字符结
尾。
The sbrk service returns the address to a block of memory containing n additional bytes. This
would be used for dynamic memory allocation.
sbrk 功能返回一个包含有 n 个附加字节的存储区的地址,这回被用于动态内存分配。
exit 功能用于停止程序运行。
举例:打印在$t2中的整数的值
li $v0, 1 # load appropriate system call
# code into register $v0;
#code for printing integer is 1
move $a0, $t2 # move integer to be printed
# into $a0: $a0 = $t2
syscall # call operating system to
# perform operation
#e.g. Read integer value, store in RAM location with label
# int_value (presumably declared in data section)
li $v0, 5 # load appropriate system call
# code into register $v0;
# code for reading integer is
#5 syscall # call operating system to
# perform operation
sw $v0, int_value # value read from keyboard
# returned in register $v0;
# store this in desired location
举例:Print out string (useful for prompts)
.data
string1 .asciiz "Print this.\n" # declaration
#for string variable,
# .asciiz directive makes
# string null terminated
.text
main: li $v0, 4 # load appropriate system call
#code into register $v0;
# code for printing string is 4
la $a0, string1 # load address of string to be
# printed into $a0
syscall # call operating system to
# perform print operation
举例:To indicate end of program, use exit system call; thus last lines of program should be:
li $v0, 10 # system call code for exit = 10
syscall # call operating sys
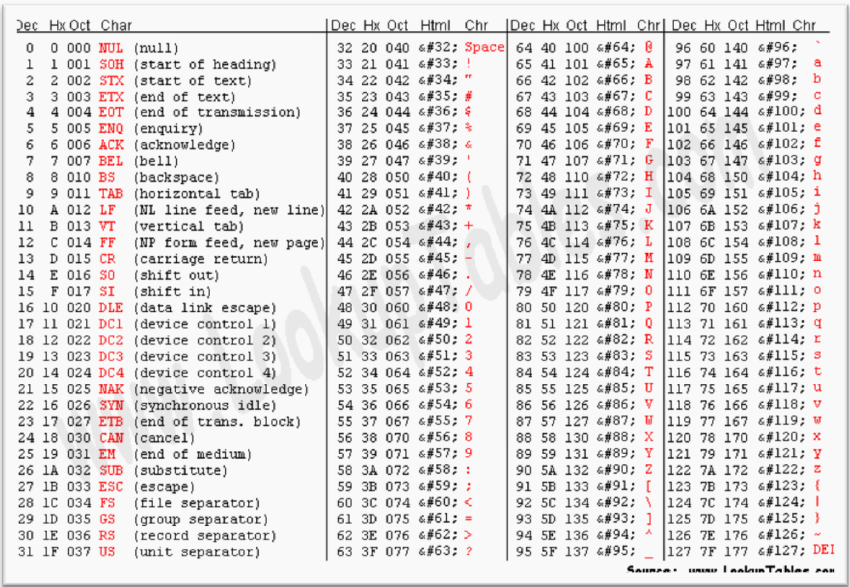
ASCII 码表
3. MIPS汇编指令





 直接运行程序:通过黄色高亮部分来观察程序的运行,并在数据段显示窗口Data Segment display中观察数值的变化。
直接运行程序:通过黄色高亮部分来观察程序的运行,并在数据段显示窗口Data Segment display中观察数值的变化。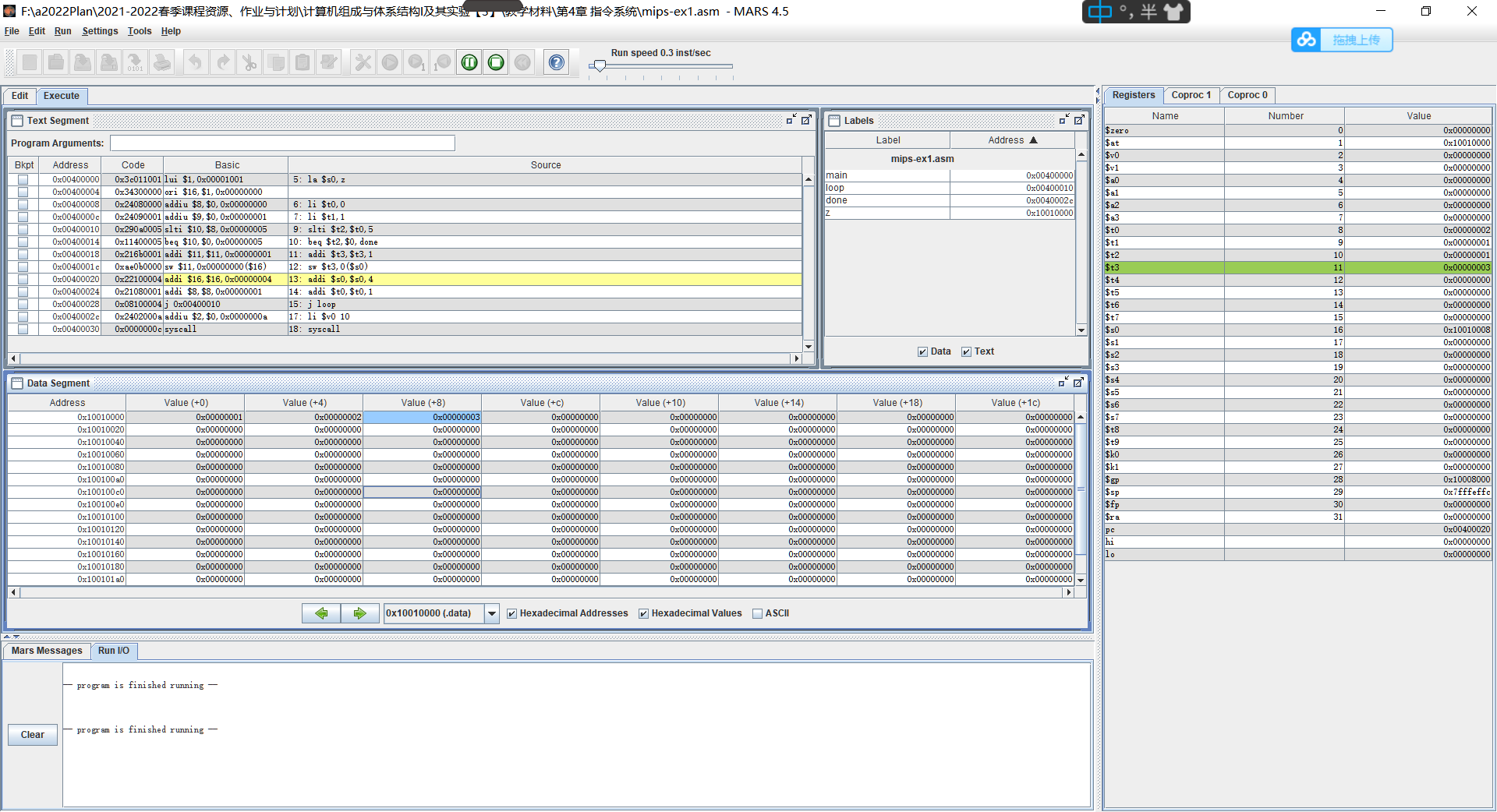
 重置程序为初始值
重置程序为初始值 单步执行程序,与
单步执行程序,与 (单步回退程序)功能相反。
(单步回退程序)功能相反。
 和
和 ,重新运行程序后,程序将在断点处停止运行。
,重新运行程序后,程序将在断点处停止运行。 ,从断点处继续执行程序。程序的输出将会包含刚才输入的数值
,从断点处继续执行程序。程序的输出将会包含刚才输入的数值

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号